Period 2 APUSH (1607-1754)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Providence, Rhode Island
Founded by Roger Williams after being banished from Massachusetts Bay for advocating separation of church and state. It became a haven for religious dissenters and an early model of religious tolerance in the colonies.
From notes:
Anne Hutchinson: advocated women's rule, questioned authority saying they weren't truly appointed by God
Mayflower Compact
Agreement signed aboard the Mayflower establishing majority-rule self-government. It set a precedent for democratic governance in the English colonies.
John Rolfe
Jamestown settler who introduced tobacco cultivation and married Pocahontas. His crop made Virginia economically successful and dependent on plantation labor.
Starving Time (1609-1610)
A period of famine in Jamestown when settlers faced mass starvation and death. It revealed the colony's struggles and dependence on Native and outside support.
Pilgrims
English Separatists who founded Plymouth in 1620 seeking religious freedom. They established self-government through the Mayflower Compact and influenced later colonies.
Salem Witch Trials, 1692
Massachusetts trials that led to executions and imprisonments for alleged witchcraft. They reflected religious extremism and encouraged skepticism about unchecked authority.
From notes
-"crazy little girls"
-Puritan society had a specific target
-->quirky women
--> educated women
--> man jealous of woman
Jonathan Edwards
Preacher of the First Great Awakening, famous for fiery sermons like "Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God." He helped spark revivalist religious fervor and emphasized personal faith.
George Whitefield
English preacher who traveled widely during the First Great Awakening. He drew massive crowds and spread revivalist ideals that united the colonies.
From notes:
-traveled throughout colonies
-he said ministers weren't needed: it comes from you
(individuals must have their hearts transformed by God's sovereign grace to be saved)
Anne Hutchinson
Puritan woman who challenged church leaders and promoted personal revelation. Her banishment highlighted struggles over religious authority and women's roles.
Mercantilism
Economic system where colonies provided raw materials to enrich the mother country. It shaped trade policies and fueled resentment leading toward Revolution.
From notes:
-colonies provides raw materials
-enrich motherland
Puritans
Religious reformers who settled in Massachusetts Bay in the 1630s. They shaped New England society with strict religious, social, and cultural values.
Salutary Neglect
British policy of weak enforcement of colonial trade laws. It allowed colonies to develop self-government, fueling resistance when later restricted.
Virginia House of Burgesses, 1619
The first representative assembly in the English colonies. It set a foundation for American self-government and democracy.
Metacom's War (1675-1676)
Conflict between New England settlers and Native tribes under Metacom (King Philip). It devastated Native populations and secured English dominance in New England.
Pequot War, 1636
Armed conflict between New England settlers and the Pequot tribe. It resulted in near-destruction of the Pequot and set a pattern of violent expansion.
Quakers
Religious group emphasizing equality, pacifism, and tolerance, led by William Penn in Pennsylvania. They promoted fair Native relations and ideals that influenced American liberty.
Chattel Bondage
System in which enslaved Africans were treated as property for life. It became the foundation of the Southern economy and racial slavery.
Headright System
Policy granting land to settlers who paid for passage to Virginia. It encouraged migration and fueled growth of plantations and slavery.
Indentured Servitude
Labor system where workers served fixed terms for passage to America. It provided early colonial labor but later gave way to slavery.
Stono Rebellion, 1739
Major slave uprising in South Carolina by Africans seeking freedom in Florida. It led to stricter slave codes and harsher control of enslaved people.
Maryland Toleration Act, 1649
Law granting religious freedom to all Christians in Maryland. It was an early step toward broader religious liberty in America.
The Enlightenment (effect on colonies)
Intellectual movement stressing reason, science, and natural rights. It inspired colonists to challenge authority and shaped Revolutionary ideas.
Great Awakening (effect on colonies)
Religious revival emphasizing emotional faith and equality before God. It weakened church authority and encouraged resistance to established power.
Bacon's Rebellion, 1676
Revolt of Virginia frontier settlers led by Nathaniel Bacon against Governor Berkeley. It exposed class tensions and hastened the shift to African slavery.
From notes:
-(back country farmers) wanted protection from Native Americans
-burned down Jamestown
Navigation Acts (1650-1696)
British trade laws enforcing mercantilism on the colonies. They restricted colonial economies and caused resentment that fueled Revolution.
From notes
-restricted colonial trade, manufacturing & shipping to other countries
Of Plymouth Plantation (William Bradford)
Account by Plymouth governor William Bradford describing Pilgrims' experiences. It provides a key primary source on early colonial life and values.
Trial of Peter Zenger, 1736
Colonial printer tried for criticizing New York's governor, acquitted because statements were true. It set an early precedent for freedom of the press.
Beaver Wars
Conflicts between the Iroquois (backed by Europeans) and rival tribes over the fur trade. They reshaped Native power in the Northeast and showed European impact on Native wars.
John Winthrop's "City Upon a Hill" (1630)
Sermon envisioning Massachusetts Bay as a model Christian community. It became a lasting symbol of American exceptionalism and mission.
Types of Colonies
Corporate Colonies
operated by joint-stock companies (ex: Jamestown)
Royal Colonies
Direct authority from & ruled by king's government (ex. Virginia)
Proprietary Colonies
under authority of people appointed by king
Major Happenings
Slavery
reasons for increase
--> decrease of indentured servants
--> decrease in headright system
--> need for stable labor force
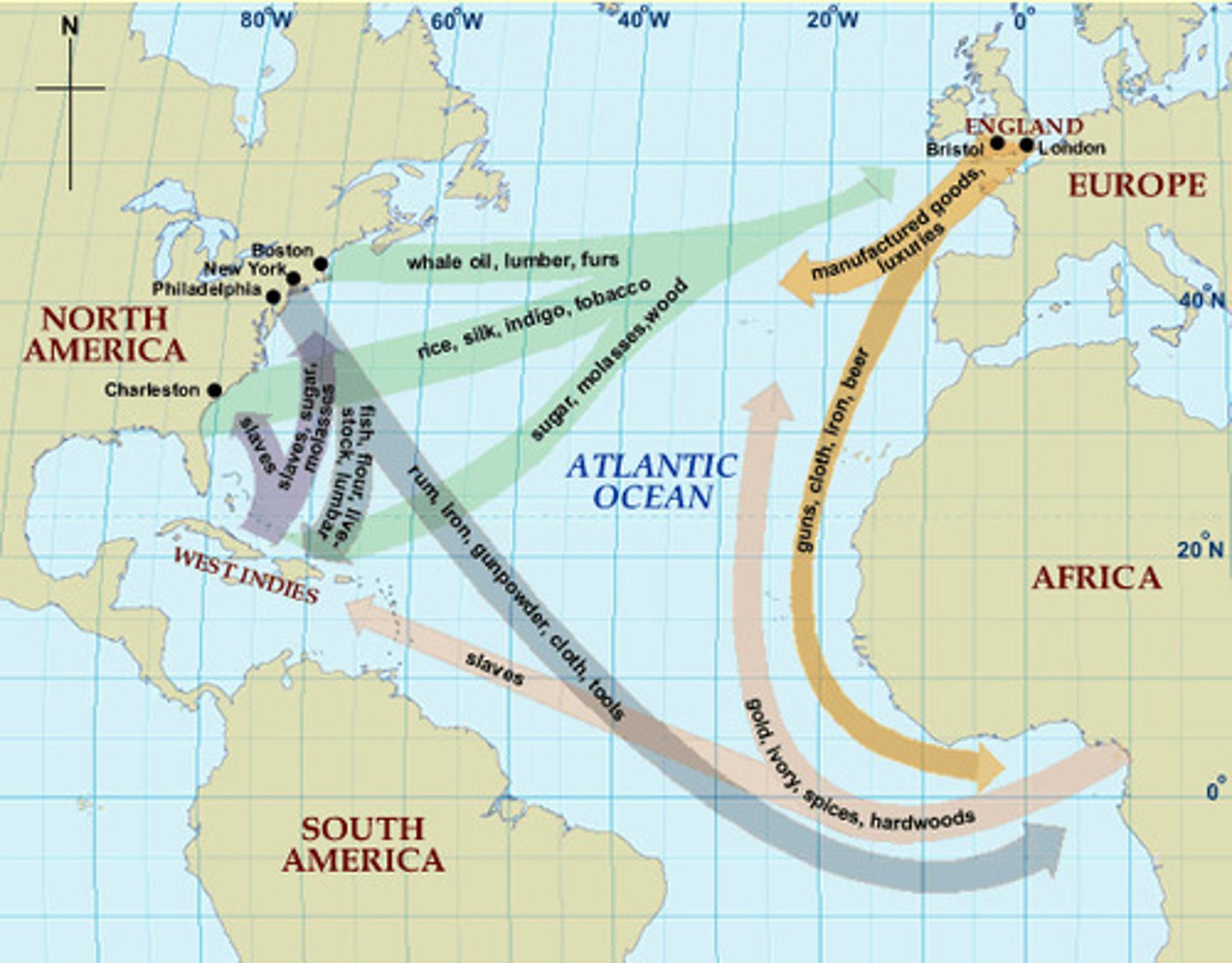
Triangular Trade
A three way system of trade during 1600-1800s Africa sent slaves to America, America sent Raw Materials to Europe, and Europe sent Guns and Rum to Africa
John Locke
-"Two Treatise of Government"
-->legitimate government arises from the consent of the governed to protect their natural rights, specifically life, liberty, and property
-Gov. must honor natural laws based on "unalienable rights" encouraged revolts if gov. failed to protect rights
*natural rights set foundation for U.S. constitution
Roanoke "Lost Colony"
-disappeared, no one knows what happened
-low on supplies, so they went back to England, when they returned no one was there
Jamestown
-first permanent British settlement
-John Rolfe introduces TOBACCO
-John Smith responsible for success of colony
Georgia (1732)
-buffer zone from Spanish Florida
-debtors sent to relieve jails
-->prisoners sent to Georgia
-governor: James Oglethorpe
James Oglethorpe
Founder and governor of the Georgia colony. He ran a tightly-disciplined, military-like colony. Slaves, alcohol, and Catholicism were forbidden in his colony. Many colonists felt that Oglethorpe was a dictator, and that (along with the colonist's dissatisfaction over not being allowed to own slaves) caused the colony to break down and Oglethorpe to lose his position as governor.
Pennsylvania
William Penn: society of friends (Quakers)
--> equality for all & nonviolence
-"Holy Experiment": religious refuge & inner light, peace
-tolerant of ppl of religious refuge, women, and Native Americans
New England Town Structure
Puritans- John Winthrop's "City on a Hill"
--> wanted the world to look at them as exemplar righteous colony
-town hall, church all at the center
Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
It has the features of a written constitution, and is considered by some as the first written Constitution. The Fundamental Orders of Connecticut is a short document, but contains some principles that were later applied in creating the United States government. Government is based in the rights of an individual, and the orders spell out some of those rights, as well as how they are ensured by the government. It provides that all free men share in electing their magistrates, and uses secret, paper ballots. It states the powers of the government, and some limits within which that power is exercised.
13 Colonies
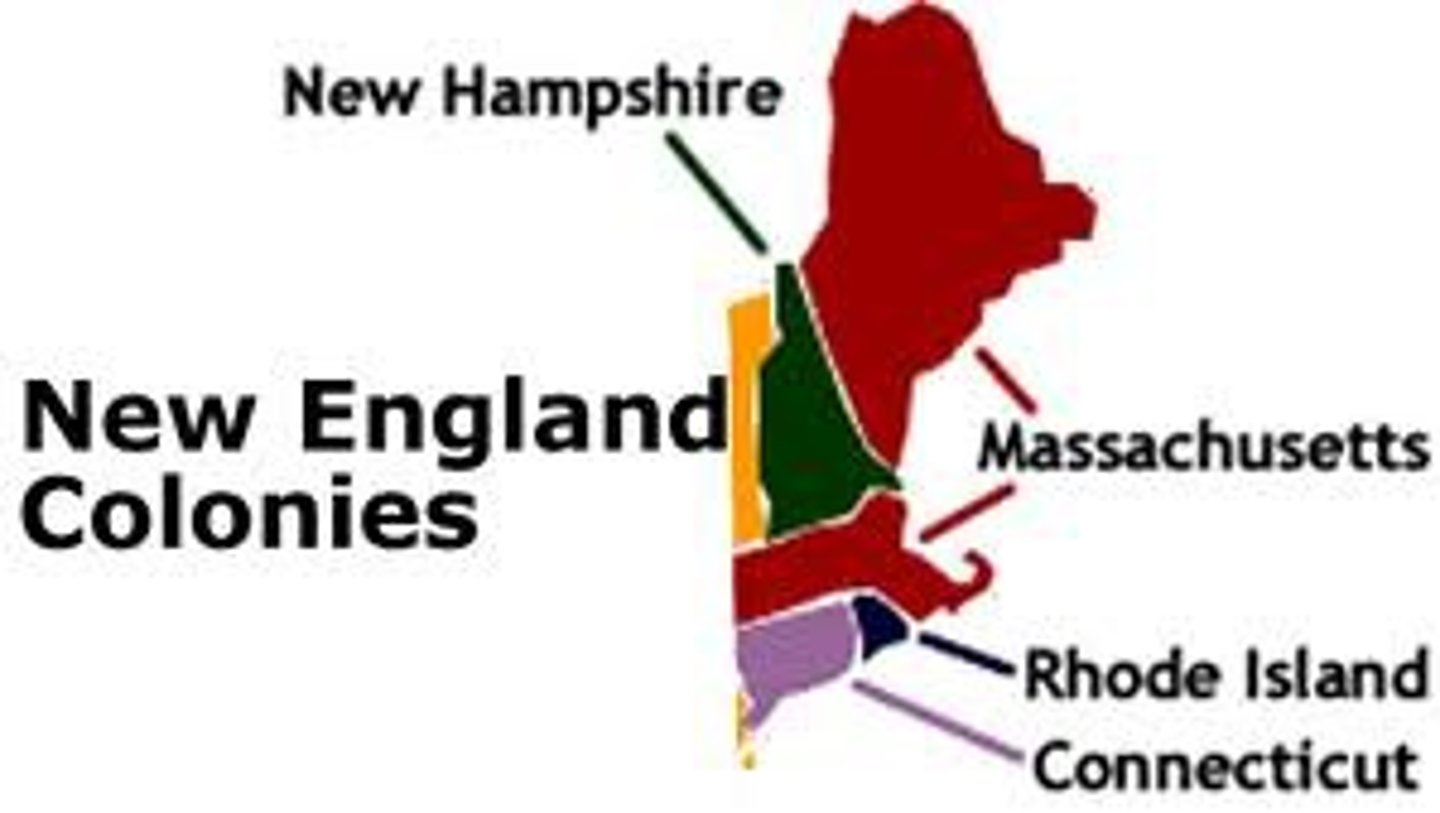
New England Colonies
New Hampshire, Rhode Island, Massachusetts, Connecticut
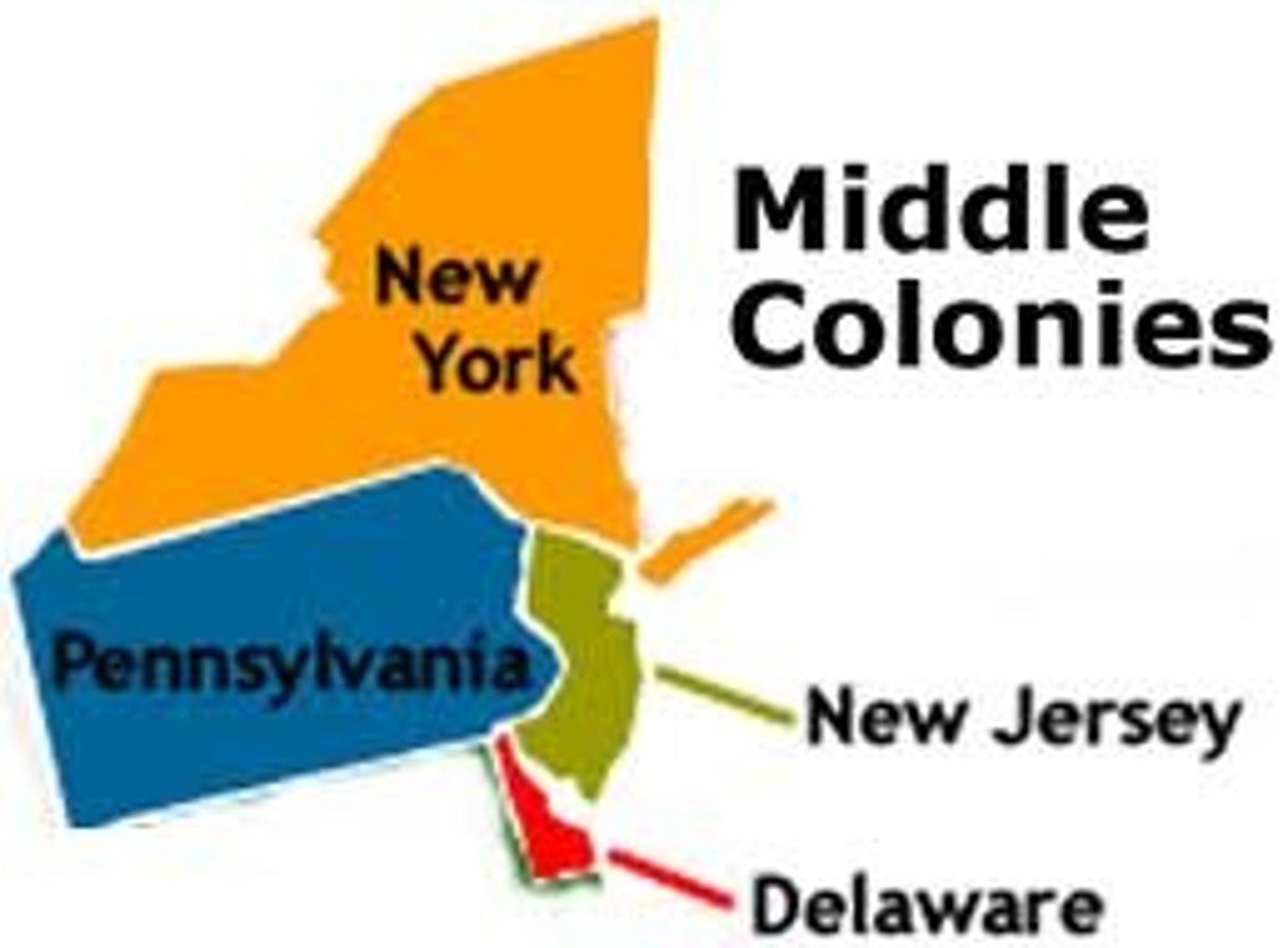
Middle Colonies
New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Delaware
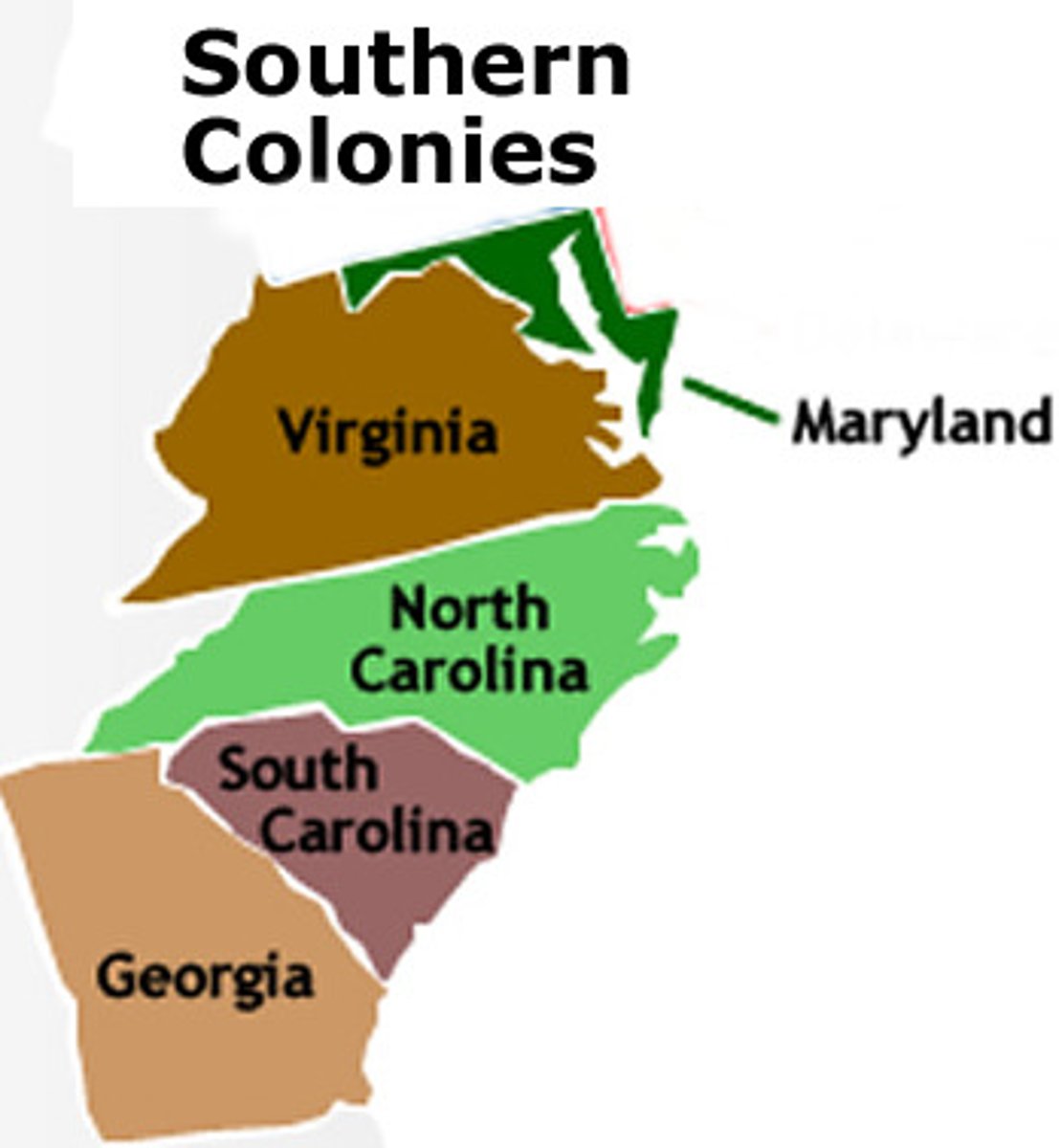
Chesapeake Colonies
Virginia and Maryland
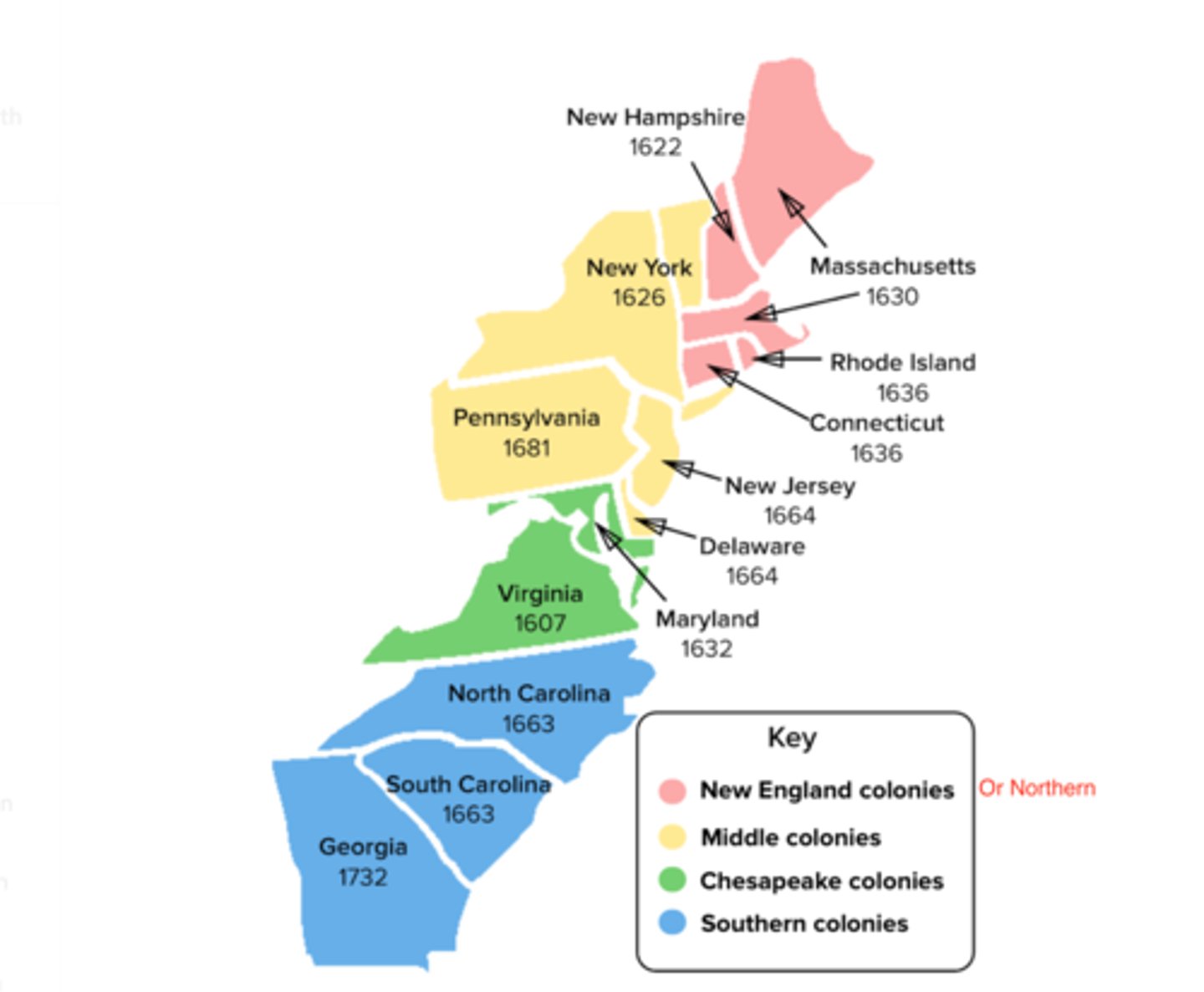
Southern Colonies
North & South Carolina, Georgia