Nursing Management Female Reproductive Problems
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
...
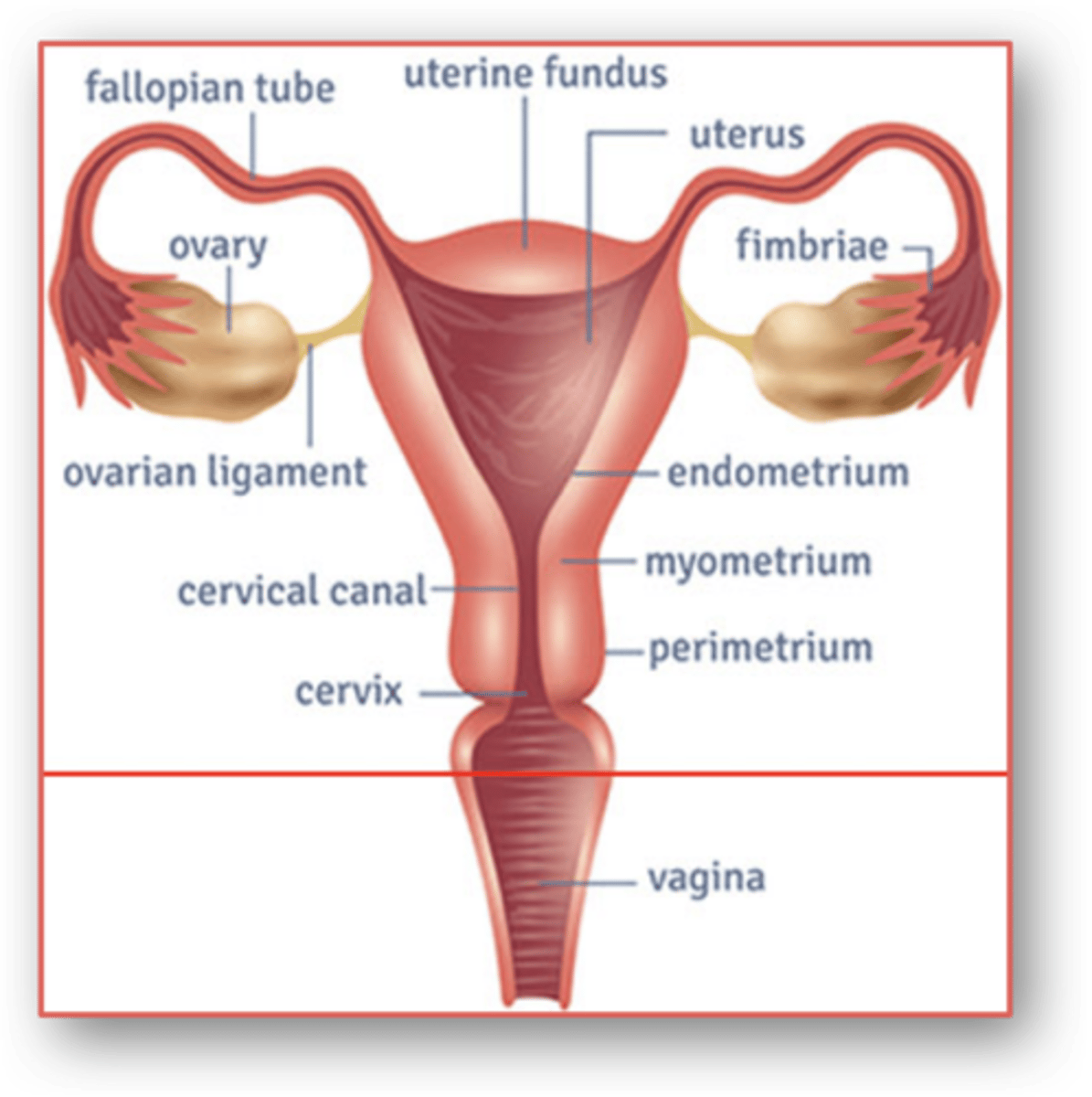
Anatomy
Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding
- common gyne concern; problem r/t menstruation
- cause varies from anovulation to more serious causes such as ectopic pregnancy or endometrial ca
- age helps identify cause (hormonal phase; prepubescent, pubescent, menopausal)
types
Problems r/t menstruation: Uterine bleeding
- Amenorrhea
- Oligomenorrhea
- Menorrhagia
- Metrorrhagia
amenorrhea
Types of Irregular Bleeding:
- the absence of menstruation
primary, secondary amenorrhea
Types of Irregular Bleeding:
- ________ _______: failure of menstrual cycles to begin by 16 yrs (or 14yrs with secondary sex characteristics of early puberty)
- _________ _______: cessation of menstrual cycle once established
amenorrhea etiology
- pregnancy *most common
- anovulation *2nd most common
anovulation
- corpus luteum that produces progesterone does not form → no shedding
- result = unopposed estrogen + excessive endometrium → increases risk of endometrial ca
- reduce risk via hormonal tx or oral contraceptives → ensure endometrium shedding 4-6x / yr
oligomenorrhea
Types of Irregular Bleeding:
- Refers to long intervals between menses
- generally >35 days
- light, irregular periods
oligomenorrhea etiology
Types of Irregular Bleeding:
- ovulation erratic for several years following menarche + before menopause
- d/t anovulation for women at beginning + end of menstruation (puberty, menopause)
menorrhagia
Excessive or Prolonged bleeding r/t
- increased duration (> 7days)
- increased amount (> 80ml)
menorrhagia etiology
Types of Irregular Bleeding:
- most common → anovulatory uterine bleeding
- young women → consider clotting dx + antifibrinolytic tx
- older women → fibroids, polyps, cancer
anovulatory bleeding
In anovulation...
- corpus luteum & progestrogen not produced → unopposed estrogen + excess endometrium buildup
- eventually becomes unstable → excess vaginal bleeding
metrorrhagia
Types of Irregular Bleeding:
- spotting, or breakthrough
- bleeding between menstrual periods
metrorrhagia etiology
Types of Irregular Bleeding:
- reproductive age: pregnancy comp (ie. spontaneous abortion, ectopic) (other: ca, polyps, infection, hormones)
- postmenopausal: endometrial/cervical ca
Interprofessional Care
- Based on underlying cause, degree of threat to pts health, desire to preserve fertility
- Amenorrhea/Oligomenorrhea
- Menorrhagia
- Surgery
amenorrhea/oligomenorrhea
Interprofessional Care: Uterine Bleeding
- If r/t anovulation
- contraceptives for normal shedding (min 4-6x yearly) + normal hormonal balance
menorrhagia
Interprofessional Care: Uterine Bleeding
- Severe → hospitalization
*most common indication for surgery*
- evaluate for secondary anemia + hypovolemia
- Treat underlying cause + minimize further blood loss
- Antifibrinolytic, Contraceptive, Ablation
contraceptives
Menorrhagia: Tx of Underlying Cause
- for pts who want to prevent pregnancy
- tx of anovulatory bleeding d/t unopposed estrogen accumulation → causes normal shedding of endometrium lining
clotting disorder
Menorrhagia: Tx of Underlying Cause
- antifibrinolytic (tranexamic acid)
- use caution w/ concurrent contraceptive use (increases risk of blood clots + stroke)
ablation
Menorrhagia: Tx of Underlying Cause
- using thermal source; endometrium destroyed; uterine lining sloughs off in 7-10 days
- contraindicated: maintain fertility, query endometrial ca, hx non–lower segment C- Section, myomectomy
surgery
Indicated for tx of underlying cause :
- Dilation and curettage (D&C)
- Ablation
- Hysterectomy
- Myomectomy (laparotomy, laparascopy, hysteroscopy)
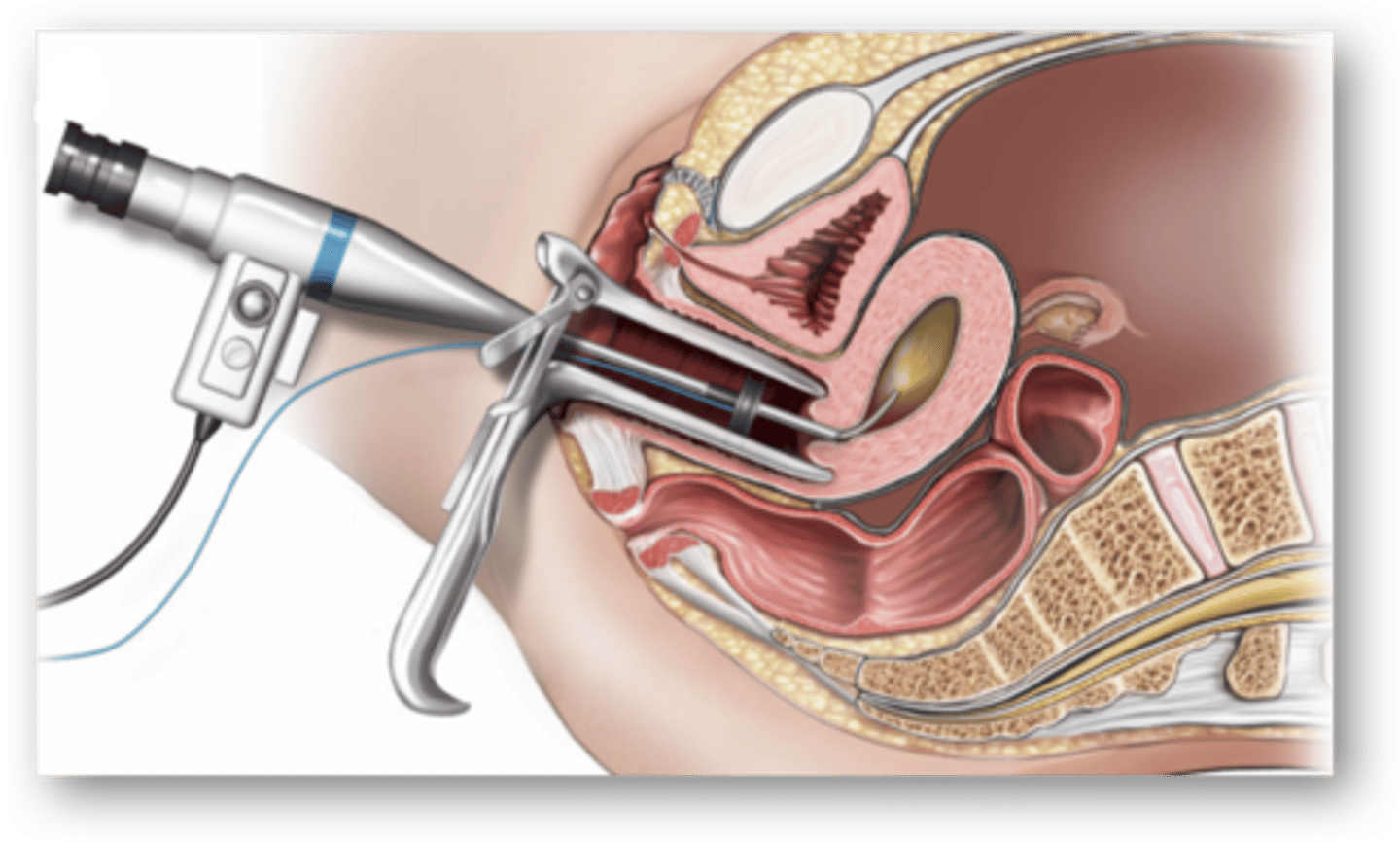
dilation and curettage (D&C)
Surgery: uterine bleeding
- in cases of acute excess bleeding
- cervix dilated + uterine lining scraped to remove any abnormal tissue
Endometrial Ablation
Surgery: uterine bleeding
- tx of acute excess bleeding (menorrhagia)
- for pts who do not want to maintain fertility
hysterectomy
Surgery: uterine bleeding
- removal of the uterus
- indications; r/t uterine fibroids or ca
myomectomy
Surgery: uterine bleeding
- removal of a fibroid without removing the uterus
- indications; r/t uterine fibroids + uterine preservation desired
- approaches: laparotomy/laparoscopy, hysteroscopy
hysteroscopy
- scope is used to look at inside of cervix
- can take biopsies, remove polyps, fibroids, tumors
Nursing Management
Uterine Bleeding:
- Health Promotion
- Acute Interventions
health promotion
Nursing Management Uterine Bleeding:
- education r/t menstrual cycle → help identify normal variations
- If abnormal variations → seek health care provider
- ↓ risk of Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
Nursing Management Uterine Bleeding: Acute Interventions
- acute condition; staphylococcus aureus
- initial, flu-like sx → high fever, N/V, diarrhea → dizziness, fainting, disorientation → sepsis
- avoid prolonged use of tampons & pads + wearing them in bodies of water
acute interventions
Nursing Management Uterine Bleeding:
- Excess vaginal bleeding assessed accurately
- Assess + Manage secondary anemia + hypovolemia
- Periop Care if surgery indicated
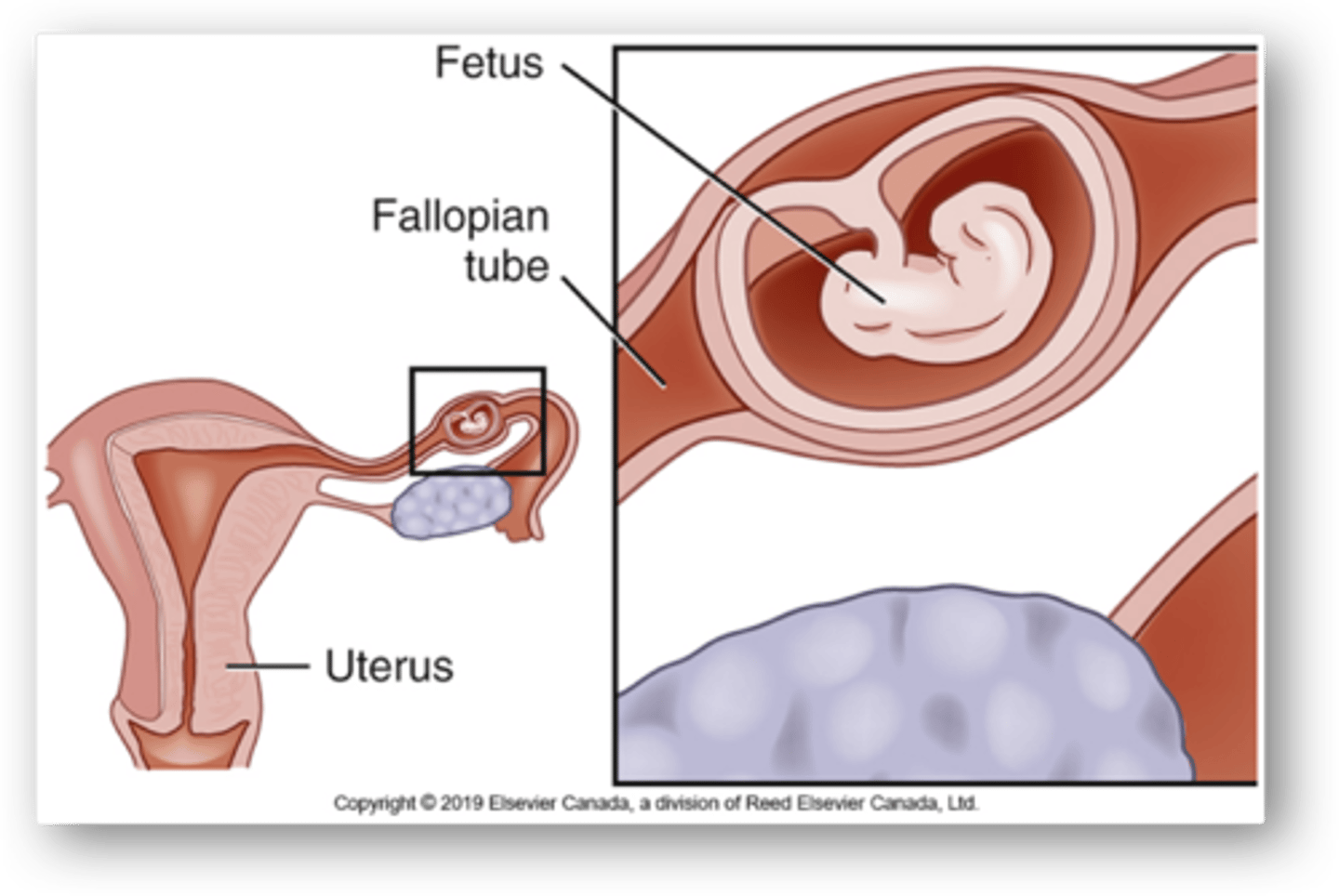
Ectopic pregnancy
- Implantation of fertilized ovum anywhere outside uterine cavity
- 3% of all pregnancies; 98% occur in fallopian tube
*remaining 2-3% may be ovarian, abdominal, cervical
etiology/patho
Ectopic pregnancy
- r/t fibrosis/damage to fallopian tube d/t infection or inflammation
- blockage/reduction of tubal peristalsis → impedes/delays zygote transport to uterus → implantation outside uterus
- growth of gestational sac expands tubal wall → eventually ruptures
...
Ectopic pregnancy in fallopian tube
tubal rupture
Ectopic pregnancy
- life-threatening condition → hemorrhage + hypovolemic shock
- suspected = emergency
- acute peritoneal symptoms (peritonitis)
risk factors
Ectopic Pregnancy:
- history of PID (pelvic inflammatory disease) (caused by STIs)
- prior ectopic pregnancy
- progestin-releasing IUD (intrauterine device)
- progestin-only birth control failure
- prior pelvic or tubal surgery
6-8
Ectopic Pregnancy:
- less acute sx: ______wks → after the last menstrual period
- weeks before gestational sac expansion → rupture
- vary depending on site of implantation
- hallmark: abdo/pelvic pain + spotting (6-8wk after last menses)
*98% = fallopian tube, 2-3% = abdominal, cervical, ovarian*
manifestations
Ectopic Pregnancy:
- Missed menses (amennorhea)
- abdominal/pelvic pain (almost always) (post-6-8wk last menses)
- Irregular bleeding (spotting/metorrhagia) (post-6-8wk last menses)
rupture
Ectopic Pregnancy:
- sudden severe pain
- shoulder tip pain when lying down
- vaginal bleeding
- pallor + sx of shock/hemorrhage
- distended/rigid abdomen
ectopic pregnancy diagnosis
Challenging d/t similarities w/ other pelvic & abdo dx (40% misdiagnosed)
- Serum (radioimmunoassay) pregnancy test
- Serum BhCG levels
- Transvaginal U/S
serum (radioimmunoassay) pregnancy test
ectopic pregnancy diagnostics:
- (+) indicative of ectopic pregnancy
- (-) likely, not ectopic pregnancy
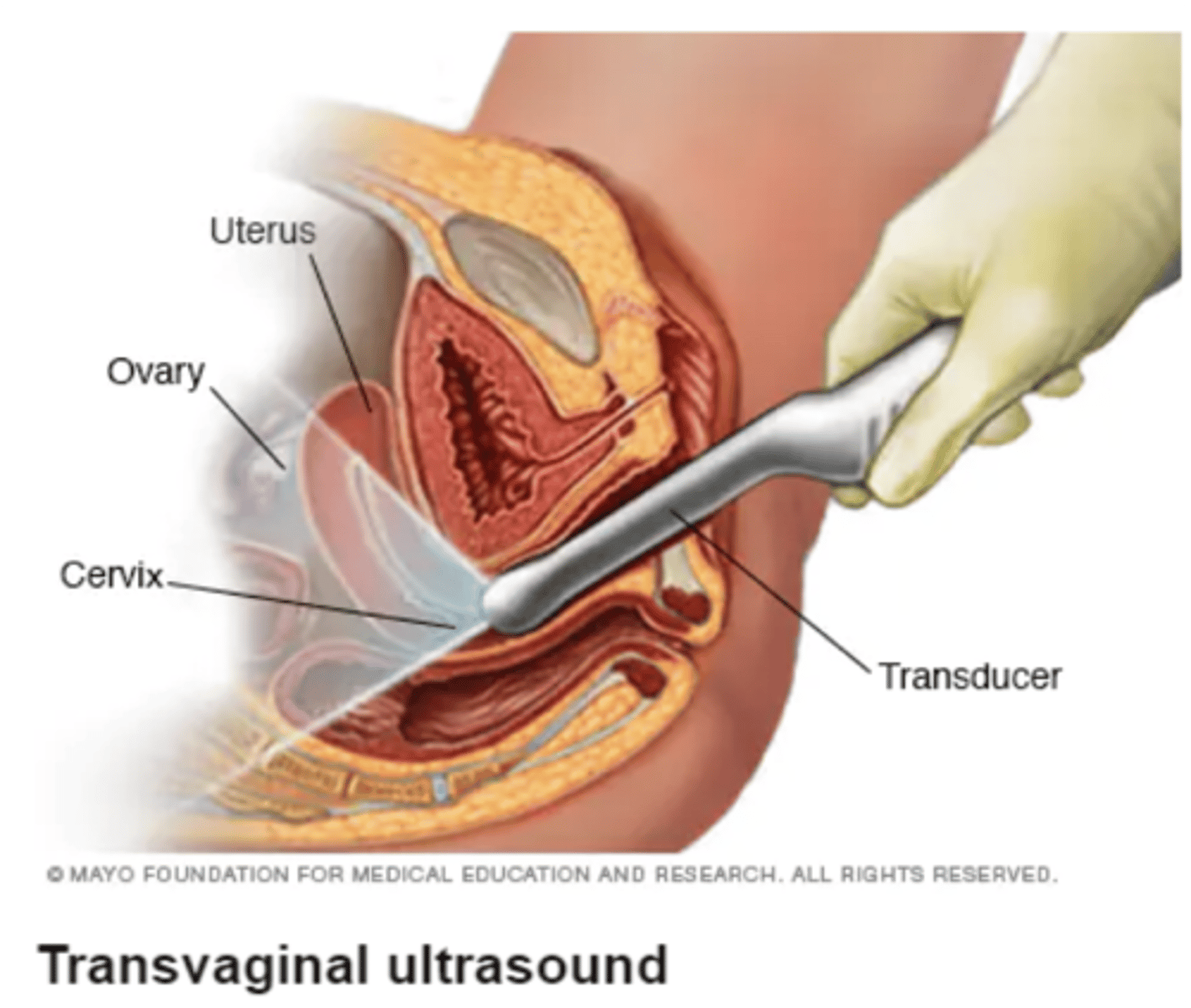
Transvaginal ultrasound
- used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy in a stable pt
- transducer inserted into vagina + visualization of uterus, cervix, ovary, fallopian tubes
- presence or absence of an intrauterine gestational sac
transvaginal u/s
ectopic pregnancy diagnostics:
- presence or absence of an intrauterine gestational sac correlated w/ BhCG levels
- suspect when no intrauterine gestational sac when the βhCG level is > 1,500 IU/L
Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin levels
ectopic pregnancy diagnostics:
- > 1,500 IU/L
- decrease in spontaneous abortion (thus measured more than once)
- measured w/ transvaginal U/S to confirm dx
ectopic pregnancy management
- Surgery
- IM methotrexate
IM methotrexate
ectopic pregnancy management:
- hemodynamically stable pt + size of gestation < 3cm
- stops cell growth + dissolves existing cells
- being used with increasing success
surgery
ectopic pregnancy management:
- primary approach → performed immediately
- fertilized egg cannot develop normally outside uterus → ectopic tissue needs to be removed
- Laparoscopy preferred over Laparotomy (↓ blood loss + LOS)
laparoscopic surgery
- preferred over laparotomy d/t ↓ blood loss + LOS
- 2 types: Salpingotomy, Salpingectomy
- choice depends on: pts age + future fertility desire + tube condition
Salpingotomy
- ectopic pregnancy removed; tube left to heal on its own (conservative)
- preferred; limits damage to reproductive system
- if pt wishes to preserve fertility
Salpingectomy
- ectopic pregnancy & tube are removed
- if tube is ruptured; bleeding profusely (conservative approach not possible)
preop
Nursing Management:
- often no time to fully prepare pt (rupture = emergency)
- 2 x Large Bore IVs
- Blood Transfusion + IV resus → tx shock + stabilize pt for safe anesthesia + operation
serum HCG levels
Nursing Management:
- checked post-op to make sure entire ectopic pregnancy removed
Endometriosis
- presence of endometrial epithelial tissue (uterus lining) in sites outside the uterine cavity
- common sites → near ovaries, broad ligament, uterosacral ligaments, bowel/bladder
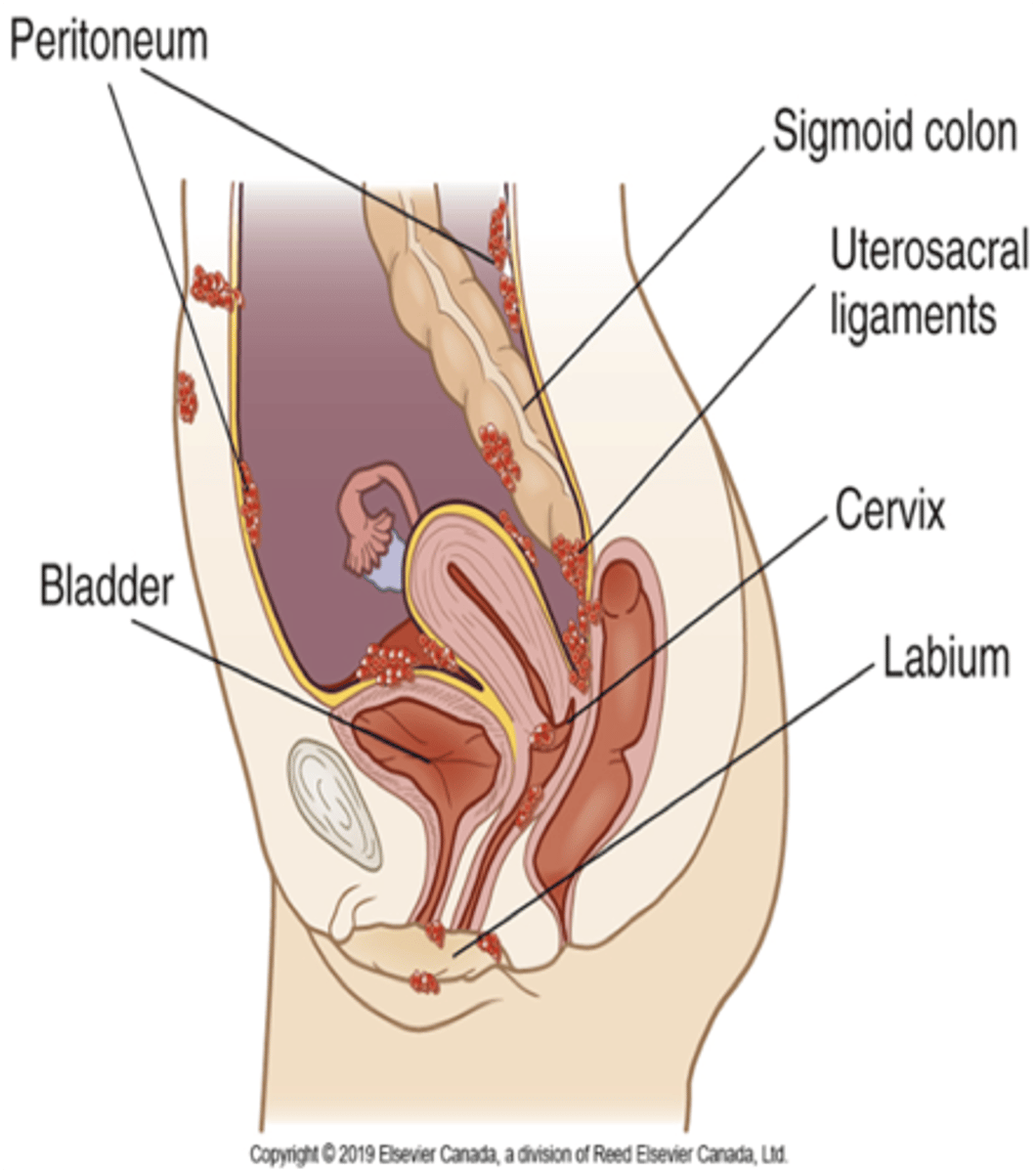
Endometriosis patho
- endometrial tissue responds to the hormones of the ovarian cycle → undergoes “mini-menstrual cycle”
- blood collects in cystlike nodules (chocolate cysts) → bluish-black + contain thick chocolate colored material
- chocolate cyst rupture (acute pain) → inflammation/irritation → endometrial adhesions
endometrial adhesions
- fix the affected area to another pelvic structure
- severe = bowel obstruction or painful micturition
endometriosis
- late 20s-30s; never had full-term pregnancy
- common cause of infertility
- ↑ risk for ovarian cancer
- causes +++ pain
etiology
Endometrosis:
- poorly understood
- common theory: retrograde menstrual flow passes through Fallopian tubes → carries viable endometrial tissues into pelvis → attaches to various sites
manifestations
Endometriosis
- vary considerably
- severity of sx does not correlate w/ extent of dx
common sx
Endometriosis
- dysmenorrhea (painful menses)
- infertility
- pelvic pain
- dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
- irregular bleeding
laparoscopy
for a definitive diagnosis of endometriosis
treatment
influenced by
- pt's age
- pregnancy desire (conserve uterus)
- sx severity
- extent + location of disease
- risk for ovarian cancer
disruptive
- when sx not _______ = "watch-and-wait" approach
- when identified as probable cause of infertility → tx proceeds more rapidly
meds
For symptomatic mngt:
- NSAIDs → Pain
- Hormonal Tx → prevent mini menstrual cycle (++ adverse effects)
cure
The only ______ is surgical removal of all the endometrial implants
endometriosis surgery
May be
- conservative
- definitive
conservative
Endometriosis surgery:
- to confirm diagnosis or to remove implants
- for women wishing to get pregnant
- removal/destruction of endometrial implants by lysing or removal of adhesion or endometrial tissue (laparoscopy or laparotomy)
- Post-op care similar to laparotomy
definitive
Endometriosis surgery:
- may be last resort
- removal of uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries and as many endometrial implants as possible hysterectomy
- post-op care similar as abdominal hysterectomy
Hysterectomy
- surgical removal of the uterus
- different types + approaches
indications
Hysterectomy:
- gyne cancer (ie. endometrial)
- fibroids
- endometriosis + chronic pelvic pain
- uterine prolapse
- abnormal vag bleeding
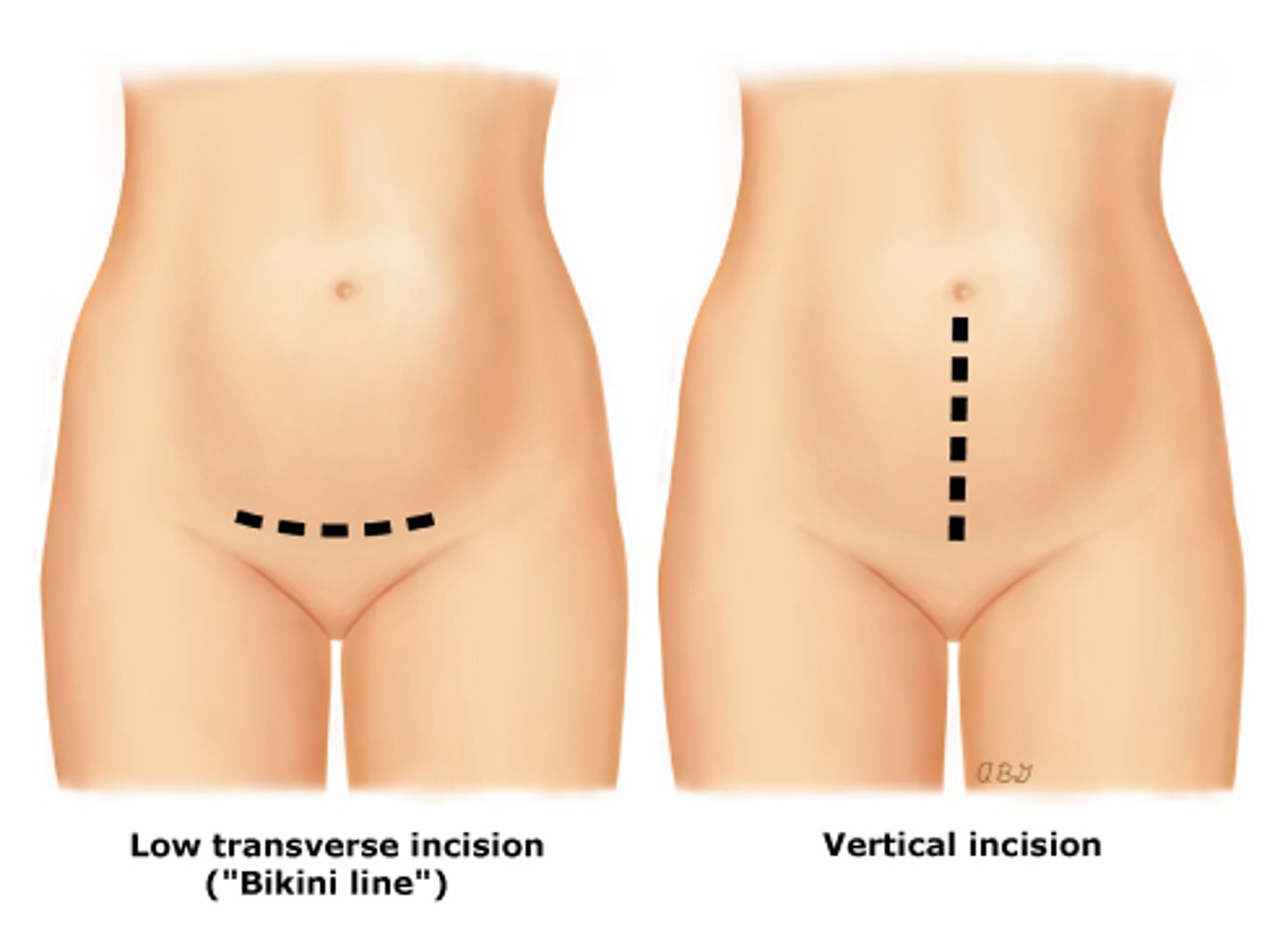
abdominal
Hysterectomy approaches:
- indications: large tumors, tube + ovary removal,exploring pelvic cavity/complex cases (need greater access + visualization)
- most invasive (last choice)
- large abdo incision
- bikini cut/horizontal or vertical (larger + longer healing)
vaginal
Hysterectomy approaches:
- cut inside vagina, at top junction of vaginal wall near cervix; suture site at vaginal cuff (no external incision)
- preferred ↓ complications + LOS + healing time
- indications: uterus prolapse, early stage cervical/uterine ca, vaginal repair w/ removal of uterus, too large for laproscopy
laparoscopic
Hysterectomy approaches:
- indications: cervix left intact (subtotal) or small uterus
- 2nd choice; not as cost effective
- may be inserted into abdomen to assist in open vaginal approach
subtotal
Hysterectomy types:
- Uterus removed + cervix left in place
- rare today
- ↓ disruption to pelvic floor + damage to urinary tract + infections
total
Hysterectomy types:
- both uterus and cervix are removed
total w/ salpingo-oophorectomy (uni/bilateral)
Hysterectomy types:
- uterus + cervix removed *and* uni/bilateral fallopian tube(s) + ovary(ies)
- bilateral removal of ovaries = sudden menopause d/t loss of ovarian hormones
- prevents recurrence of ovarian ca
wetheim's/radical
Hysterectomy types:
- removal of uterus + cervix → also bilateral ovaries + fallopian tubes AND adjacent pelvic tissue, lymph ducts, upper 1/3 of vagina
- Indications: advanced cervical/endometrial ca, tx of low
risk Stage 1 disease
preop
Hysterectomy Nursing Management:
- perineal/abdo skin prep
- vaginal douche/enema
- Empty bladder → indwelling cath
postop
Hysterectomy Nursing Management:
- ABC
- IV infusion
- Wound Care
- GI
- GU
- Analgesia
- Mobilization
- Teaching
IV infusion
Hysterectomy postop care:
- POD 1-2; 24-48 hr
- possible blood transfusion (r/t blood loss)
wound care
Hysterectomy postop care:
- Depends on approach (Abdominal/Vaginal)
- Hemovac
- prevent infection
abdominal incision
Post-Op Wound Care
- risk of dehiscence/evisceration r/t abdo incision
- splint w/ DB&C + prevent straining
- drsg; light dry x 48 hrs (unless heavy oozing)
Stitches removal
- horizontal: POD 5
- vertical: POD 7-10
vaginal incision
Post-Op Wound Care
- incision inside top of vaginal; suture site at vaginal cuff
- sterile/perineal pad
- vaginal pack (w/ ribbon gauze)
- need to be catheterized → surgical site proximity to bladder (prevent stress + infection)
vaginal pack (w/ ribbon gauze)
Vaginal Incision Care:
- inserted into vagina
- to stop bleeding from suture point
hemovac
Post-Op Wound Care
- drains blood from operation site (pelvis/abdomen) → prevent hematoma
- risk of perforation + peritonitis
abdominal
- risk of all approaches d/t anesthesia → ______ approach further increases risk
- paralytic ileus + abd distension
GI
Hysterectomy postop:
- avoid straining = surgical site stress (stool softener, hydration, mobilization, prevent nausea)
- NPO + IV fluids
- return of bowel function → PO clear fluids + SL
- monitor BM regularity
- antiemetic
GU
Hysterectomy postop:
- foley cath (hard to insert d/t swelling, infection++)
- Suprapubic cath → prevent UTI + urinary drainage + reduce strain
- strict I & O
- POD2 → ambulate to BR
- encourage bladder emptying
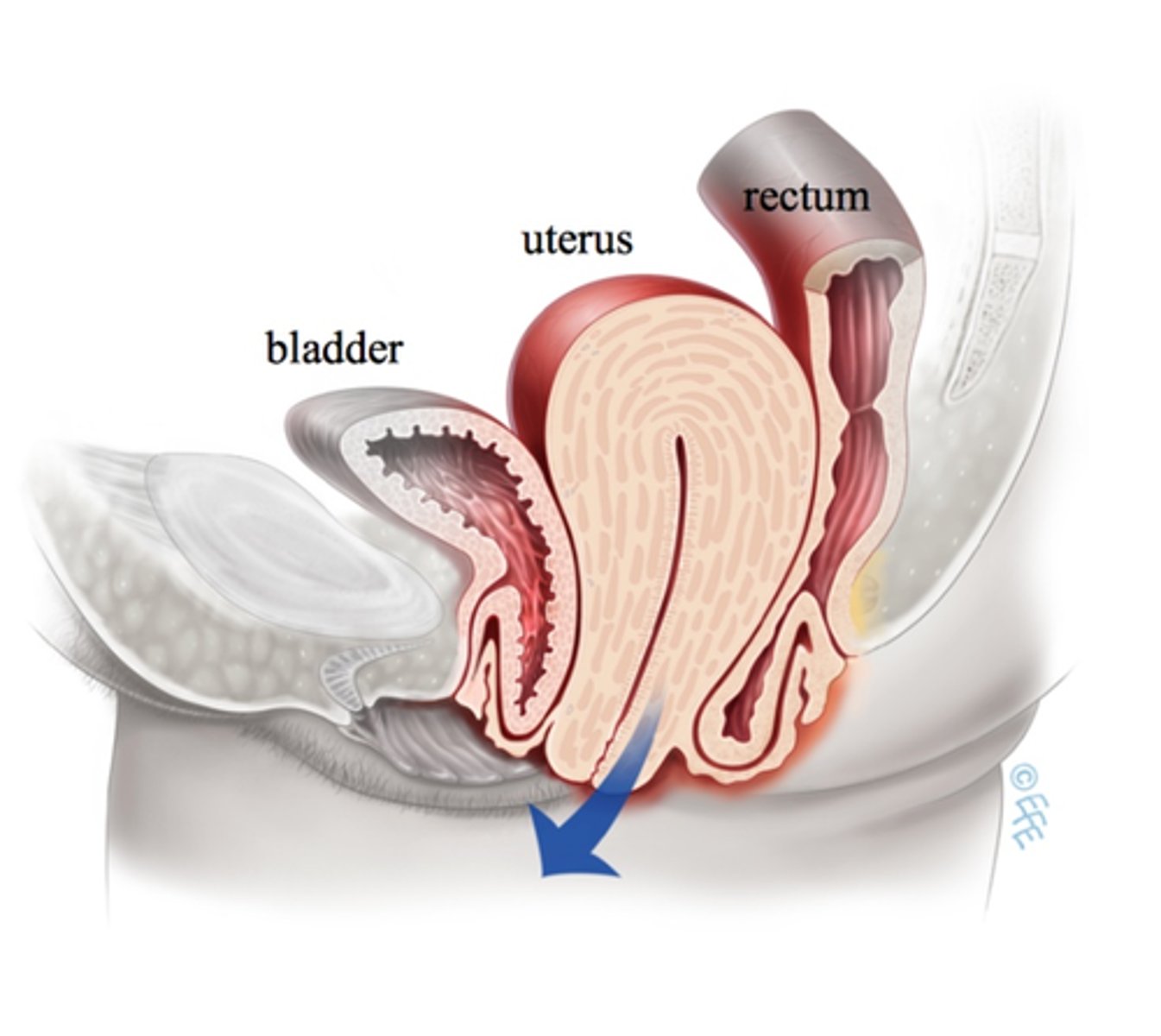
Ureter Ligation
- serious complication
- snipping of ureter during removal of uterus (ureter passes right behind site of operation)
- sx: backache, decreased UO (Report!)
analgesia
Hysterectomy postop:
- epidural or PCA
Early mobilization
Hysterectomy postop:
- sit up; bedside chair
- work w/ physio
- POD2 → should be able to ambulate to BR
- helps w/ return of BS + prevent DVT (also LMWH)
education
Hysterectomy postop:
- common to feel 'blue' on POD 3-4 → reassure pt
- may be harder for younger pts w/ loss of fertility + desire for children
DC teaching
- Bleeding
- Sufficient rest x 2 wks
- Exercise
- house work
- work
- sexual intercourse
- hormonal effects
bleeding
DC teaching:
- vaginal discharge for up to 4 wks
- change color from red to pale brown
- seek help if discharge becomes heavier, brighter in color, or offensive smell
2
DC teaching:
- common: suddenly feel tired and exhausted
- important to get sufficient rest for first ____weeks
exercise, 6
DC teaching: Hysterectomy:
- start slowly; short walks
- increase gradually in duration
- may resume swimming ___ wks post-op
housework, 2wk, 4wk, 3mo
DC teaching: Hysterectomy:
- fully restricted for __ __ postop → after light chores can done
- Do not lift heavy objects for ___ __ post-op; very heavy objects for at least __ __
work
DC teaching: Hysterectomy:
- varies in individuals
- some feel ready to return in 6-8 wks
- other take longer
sexual intercourse
DC teaching: Hysterectomy:
- approx. 6 wks to feel physically + emotionally ready
- wait until vaginal bleeding stopped → infection risk
- partner gentle + avoid undue trauma to area
hormonal effects
DC teaching:
- decreased sexual response → d/t scar tissue
- bilateral oophoerectomy*
oophorectomy
DC teaching: hormonal effects
- Bilateral = onset of surgical menopause + estrogen deficiency
- loss of menstruation, libido, vaginal atrophy, ↓vaginal lubrication
- sudden severe sx of menopause
Breast Cancer
- most common ca in women
- 2nd leading cause of death in women
- mortality is declining
- 5-year survival = 88%