Stage 2 Biology - Exam Revision
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Provide 3 pieces of evidence for endosymbiosis
+ Chloroplasts have a double membrane. The inner membrane was the original, prokaryotic membrane and the outer membrane is eukaryotic like, evident of the engulfing event
+ Chloroplasts replicate by binary fission, like prokaryotes
+ Chloroplasts contain their own circular DNA chromosomes like prokaryotes
+ Chloroplasts have their own ribosomes which are prokaryotic like
Explain why the cell membrane can be described as ‘fluid-mosiac’
The cell membrane consists of a semi-permeable bilayer of phospholipids, composed of a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail, embedded proteins and cholesterol. The arrangement of these components is described as a mosaic. The term fluid is used to describe the cell membrane as the components are constantly moving laterally and fluid.
Compare the internal organisation of prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Eukaryotes have a nucleus, prokaryotes do not
Eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles
Compare the shape and location of chromosomes in a prokaryote and eukaryote
Chromosomes within a prokaryote are circular and are located in the nucleoid
Chromosomes within eukaryotes are linear and are located in the nucleus
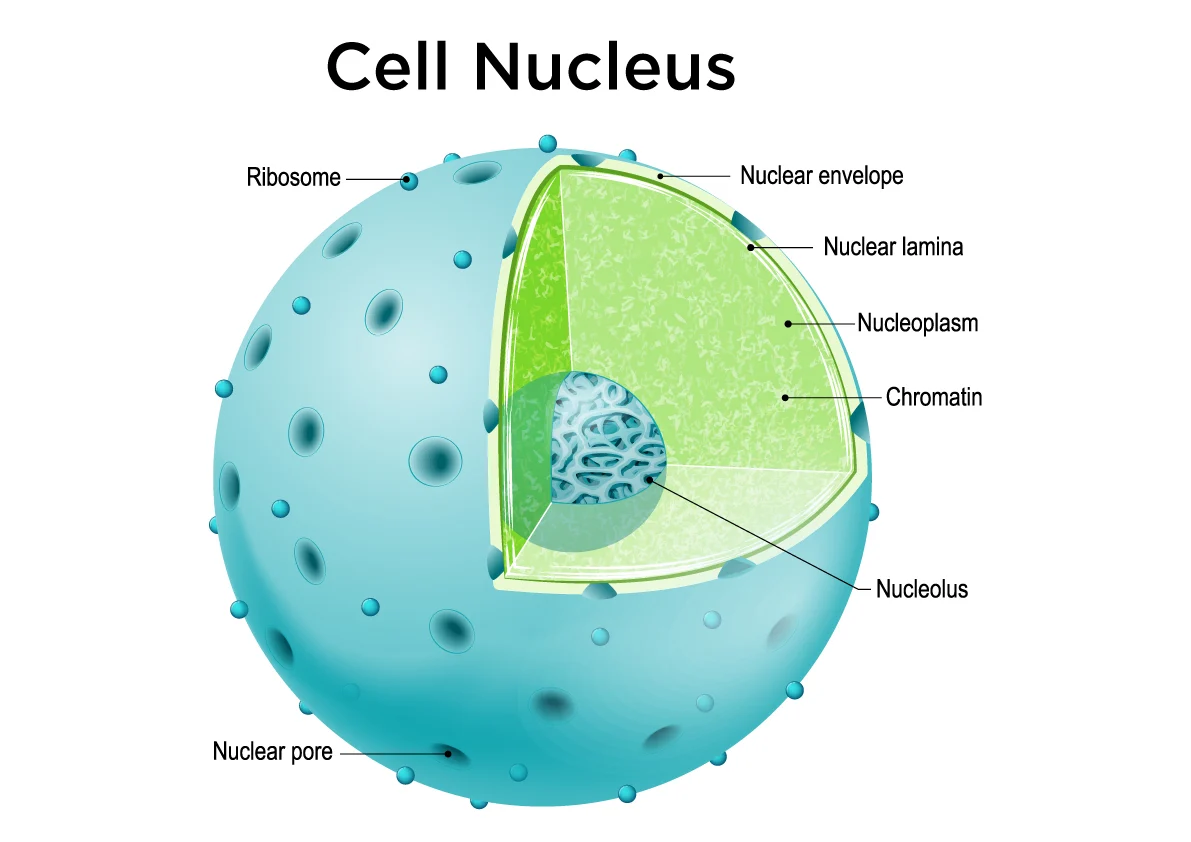
Identify and explain the function of this organelle:
The organelle is a nucleus. The nucleus regulates cell activities, stores genetic material, the site of DNA replication and translation
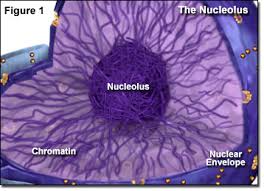
Identify and explain the function of this organelle:
This organelle is a nucleolus. The nucleolus produces and assembles the cell's ribosomes and synthesises rRNA

Identify and explain the function of this organelle:
This organelle is a mitochondrion. Mitochondria are the site of aerobic respiration

Identify and explain the function of this organelle:
This organelle is a chloroplast. Chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis
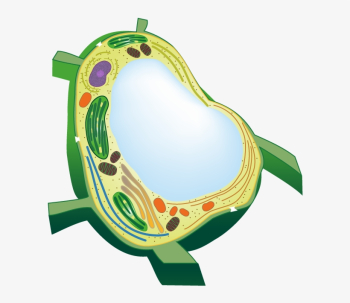
Identify and explain the function of this organelle:
This organelle is a vacuole. Plant cells have 1 large vacuole that stores water and helps maintain the structure of the cell. Animal cells have many smaller vacuoles that store nutrients

Identify and explain the function of this organelle:
This organelle is the golgi body. The golgi body packages and processes vesicles containing proteins and lipids before they're transported
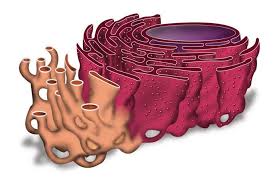
Identify and explain the function of these organelles:
These organelles are the smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum. The smooth ER synthesises lipids. The rough ER has ribosomes attached that synthesise proteins

Identify and explain the function of this organelle:
This organelle is a ribosome. Ribosomes are the site of translation and protein synthesis
Identify and explain the function of this organelle:
This organelle is a lysosome. A lysosome is a membrane bound vesicle containing digestive enzymes that breaks down materials and foreign bodies
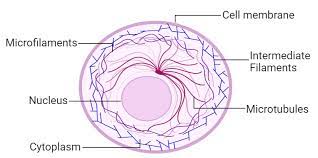
Identify and explain the function of this organelle:
This organelle is the cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton aids in the movement of organelles and cellular membrane, the assembly of spindle fibres in mitosis and, in animal cells, provides support to the cell's shape
Distinguish between autotrophs and heterotrophs
Autotrophs produce their own energy by converting light energy into chemical energy.
Heterotrophs gain energy by consuming other organisms.
What is the chemical equation of photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the chemical equation of aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
What is the chemical equation of fermentation/ anaerobic respiration in animal cells:
C6H12O6 —> 2C3H6O3
What is the chemical equation of fermentation/ anaerobic respiration in plant and yeast cells
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
What cell type does photosynthesis occur in
Plant / Autotrophs
State where photosynthesis is located
Chloroplast
Explain why the internal membrane of chloroplast facilitates photosynthesis
The internal membranes of the chloroplast facilitate photosynthesis as they are folded to produce thylakoids (stacked into geranium). This folding increases the surface area in which the chlorophyll pigments are located. Therefore, increasing the amount of trapped light which is needed for photosynthesis.
Describe the 2 parts of aerobic respiration
The glucose is broken down in the process of glycolysis in cytoplasm. This creates 2 pyruvate. Because is O2 present the 2 pyruvate is transported into the mitochondria and is further completely combusted.
State the product of anaerobic respiration/ fermentation in animal cells
Lactic acid
State the product of anaerobic respiration/ fermentation in plant and yeast cells
Ethanol and carbon dioxide
Explain why aerobic respiration produces more energy than anaerobic respiration
Aerobic in a complete combustion of glucose as the glucose is broken down into 2 pyruvate. The presence of oxygen allows the 2 pyruvate to be further broken down inside mitochondria, releasing more energy.
Anaerobic is incomplete combustion as after glycolysis O2 is not present and therefore the Kerbs cycle in the mitochondria can not occur. The pyruvate is then turned into lactic acid or ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Explain the ATP/ADP cycle
ATP is a molecule with stored energy between the second and third phosphate. If a cell requires energy the bond between the second and third phosphate in ATP is broken which releases energy and forms ADP + Pi. Energy released from aerobic and anaerobic respiration can then be used to synthesise ATP by rebinding an inorganic phosphate to ADP.
Describe the process of diffusion
Diffusion is a process of passive transport in which small and uncharged molecules, moving with the concentration gradient pass through the semi-permeable cell membrane
Describe the process fo facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is a process of passive transport in which the movement of small uncharged particles, moving with the concentration gradient pass through channel proteins embedded within the cell membrane
Describe the process of osmosis
Osmosis if the diffusion of water particles, in which water molecules are transported across the cell membrane from a hypotonic solution (low solute) to a hypertonic solution(high solute concentration) facilitated by proteins call aquaporins.
Describe active transport
A process of transport in which energy is required to move large or charged molecules or molecules moving against the concentration gradient across the cell membrane through carrier proteins.
How does the internal membrane of the mitochondria facilitates aerobic respiration
The internal membrane of mitochondria facilitate the process of aerobic respiration as the folding of the internal membrane increases the surface area, allowing for more enzymes involved in aerobic respiration to be packed into the mitochondria, resulting in a higher rate of ATP synthesis.
Explain the process of endocytosis
Endocytosis is the process in which materials are transported into a cell During exocytosis a vesicle from extracellular space attaches to the cell membrane and creates an opening within the cell membrane and expelling the contents into the cell The vesicle then fuses with the cell membrane.
Explain the process of exocytosis
Exocytosis is the process in which cells export materials out of the cell. During exocytosis a vesicle packaged via the Golgi body is moved to the cell membrane via the cytoskeleton. The vesicle then fuses with the cell membrane and expels the contents out of the cell as the vesicle attaches to the cell membrane.
Why is DNA replicated before cell division
DNA is replicated before cell division to ensure that both daughter cells have the same amount of DNA and are genetically identical.
Explain the steps of binary fission
Binary fission occurs in prokaryote cells. In binary fission DNA are first replicated. The chromosomes then attach to the cell membrane and the cell elongates, separating the chromosomes. The cell wall and cell membrane begin to form. The cell then divides into two genetically identical daughter cells.
Describe the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is when a cell requires fertilisation before reproducing. Asexual reproduction does not have fertilisation
State and explain 2 events of genetic variation in meiosis
Crossing over and independent assortment are events in round one of meiosis that result in genetic variation. Crossing over occurs when homologous chromosomes are lined up and fragments from the maternal and paternal chromosomes are broken off and exchanged. Independent assortment describes the paternal and maternal chromosomes randomly line up of either side of the equator of the cell, resulting in the random assortment of genes.
What cell type does mitosis occur in
Eukaryotic
What are the 4 phases of mitosis
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
Explain the phases of mitosis ad cytokinesis
During prophase DNA condenses around histones, the nuclear membrane breaks down and centrioles move towards opposite poles of the cell. During metaphase spindle fibres attach to the centromeres and align the chromosomes in the middle of the cell. During anaphase the spindle fibres contract and the sister chromatids are pulled apart During telophase the cell membrane begins to furrow and the nuclear membrane starts to reform. After mitosis cytokineses occurs the cell membrane is cleaved and 2 genetically identical daughter cells are produced.
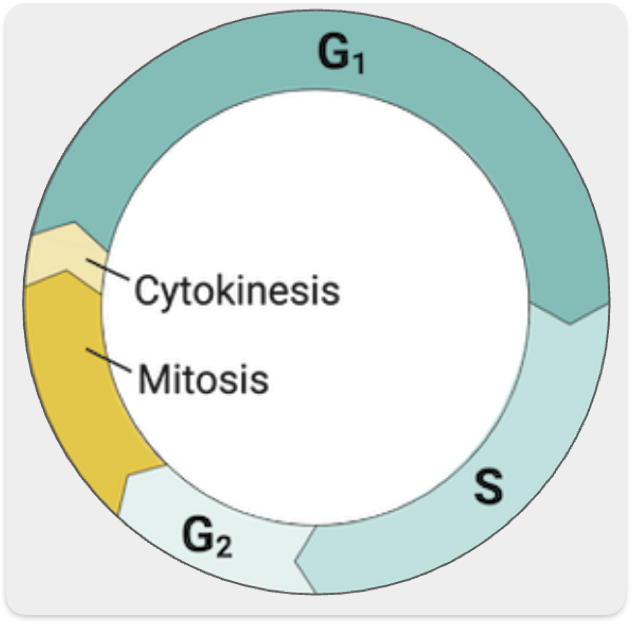
State what happens in each stage of the cell cycle
G1 - Growth; S - DNA Replication; G2 - Growth; Mitosis; Cytokinesis
Explain the process of DNA replication
The DNA is unzipped by the helicase, where it breaks the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases. DNA polymerase then binds to the separated leading and lagging strands and attaches free floating DNA nucleotides to the complementary exposed bases. DNA polymerases attached to the lagging strand attach free floating DNA nucleotides in sections called Okazaki fragments. This continues until 2 fully synthesised DNA molecules are formed. This process is described as semi-conservative as one strand on each molecule is original and one strand each is newly synthesised.
Explain the process of transcription
A promoter sequence is identified and the RNA polymerase binds to the DNA. The RNA polymerase unzips the DNA by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases. ThereRNA polymerase then attaches floating RNA nucleotides to the complementary bases on the template strand. Once the gene is fully transcribed and the mRNA is fully synthesised the immature mRNA stand detaches from the DNA and the DNA rewinds back together.
Explain the process of translation
A mature mRNA strand bind to a ribosome to begin the process of translation which is signalled by the start codon, AUG. The mRNA is read from the 5' to 3' end by the tRNA molecule which binds to the mRNA codons with it's complementary anti-codon. This then results to a specific amino acid being placed in a sequence which is bound together with peptide bonds by the ribosome to form a polypeptide chain. This continues until a stop codon is reached and then the polypeptide chain disconnects and folds into a 3D protein.
Explain the effect of pH on enzymes
Enzymes have an optimal pH level that maximises the activity of the enzyme. If the pH differs slightly to the optimal the enzyme can still tolerate the pH level, however enzyme activity is reduced. In an acidic solution Hydrogen ions (H⁺) are present. The H⁺ ions interact and bind to the enzyme which alters the charge of the active site. The charge of the active site and the substrate are then the same which therefore repulses the substrate. Extreme acidity can lead to denaturation.
Explain the effect of inhibitors on enzymes
There are two types of inhibitors the prevent enzymes from binding to a substrate. Competitive inhibitors like the substrate, are complementary to the active site and competes with the substrate for the active site. If the competitive inhibitor binds to the active site it then prevents the substrate to bind to the enzyme and inhibits a reaction from occurring.
A non-competitive inhibitor binds to the allosteric site on the back of an enzyme which alters the shape of the active site in which it is not complementary to the substrate which prevents the substrate from binding to the active site.
Explain the pathways that catalyses reactions in enzymes
Enzymes catalyses reaction through catabolic and anabolic pathways, which reduce the activation energy of a reaction. During a catabolic pathway a substrate bind to the active site of an enzyme, as they and are complementary, creating an enzyme-substrate complex which results in stress being placed on the bonds of the substrate which then allows for the substrate to breakdown with the use of less activation energy.
During an anabolic pathway the substrates binds to the active site of an enzyme as they are complementary. Once the substrates are bound it creates and enzyme-complex substrate, resulting in the correct alignment and orientation of the substrates, promoting the formation of the final product. This increases the rate of reaction as the enzyme places the substrates in the correct alignment and orientation without waiting for the chance that the reactants collide in the correct alignment and orientation.
Describe methylation
Methylation is the addition of methyl groups (CH4) to cytosine or histones. This causes for the gene to be expressed less. Therefore the mRNA strand can't be attached to the DNA and transcription doesn't occur, therefore translation doesn't occur and the protein is not synthesised.
State the four nitrogenous bases that compose DNA and the base they're complementary with
Adenine = Thymine and Cytosine = Guanine
State the four nitrogenous bases that compose RNA and the base they're complementary with
Adenine = Uracil and Cytosine = Guanine
What are the subunits of proteins?
Amino acids
State the structural properties on DNA
A double helix molecules made up of a phosphate and sugar backbone and 4 complementary nitrogenous bases, in which adenine binds to thymine and cytosine to guanine. These bases are bound together by weak hydrogen bonds.
Explain the effect of temperature on enzymes
At low temperatures, enzyme activity is low as there is not enough energy resulting in reduced collision. At a temperature just under optimal the enzyme activity increases as a result of the increase of energy. At the optimum temperature enzyme activity is maximised. At high temperatures the heat breaks the weak hydrogen bonds of the enzyme causing it to denature which prevents the enzyme from functioning and enzyme activity stopped.
What is the PCR use for?
The replication of copies of DNA
Describe histone modification, resulting in a silenced gene
Histone modification is the absence of acetyl groups on histones. Histone modification silences genes as without acetyl groups the nucleosome on the histone is tightly packed together and therefore DNA is not accessible for transcription.
Describe the primary structure of proteins
The primary structure is a linear polypeptide chain bound together with peptide bonds.
Describe the secondary structure of proteins
The linear peptide chain then folds or coils as the amino acids begin to interact with each other. The chain will shape into an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet. The amino acids are bound to one another with hydrogen bonds and seconday interactions.
Describe the tertiary structure of proteins
The polypeptide had becomes a fully formed protein with a unique 3D structure, bound together with ionic bonds. The 3D structure of the protein is essential to it's function Some proteins with only one polypeptide chain remain in a tertiary structure.
Describe the quaternary structure of proteins
A fully formed protein with a unique 3D structure consisting of 2 or more polypeptide chain
Explain why the sequence of amino acids are essential to the function of proteins
The sequence of amino acids are essential to it's function as the sequence of amino acids determine the interactions between them and how the polypeptide chain folds or coils. This then determines it's structure and the structure of the protein influences it's function.
How does the interaction between an enzyme and substrate catalyse a reaction
The enzyme-substrate complex / induced fit between the substrate and enzyme puts pressure on the bonds of the substrate
Describe histone modification, resulting in an expressed gene
Acetylation is the presence of acetyl groups on histones. Acetylation allows for increased gene expression as it results in a less tightly packed nucleosome on histones and therefore DNA is accessible for transcription.
State and describe why the product of transcription cannot be directly used in translation in eukaryotes.
The product of transcription is immature mRNA. Immature mRNA can not be directly used in translation because an immature mRNA strand contains both introns and exons. Exons are coding sections and introns are non-coding sections. Therefore immature mRNA is spliced/processed before translation to splice out all the introns, producing mature mRNA before translation.
Explain the difference between epigenetics and mutations
In epigenetics the sequence of DNA is not changed as the gene is only expressed more or less. In mutations the DNA sequence is altered.
Explain hypermethylation and hypomethylation
Hypermethylation is the addition of methyl groups (CH₄) to cytosine or histones. This causes for the gene to be expressed less. Therefore the mRNA strand can't be attached to the DNA and transcription doesn't occur, therefore translation doesn't occur and the protein is not synthesised.
Hypomethylation is the removal of methyl groups (CH₄) to cytosine or histones. This causes for the gene to be expressed more. Therefore transcription and translation occur and the protein is not synthesised.
Describe the role of primers in PCR
1) bind to the separated DNA strands and prevent them from rewinding back together
2) promotes the binding of the heat resistant (Taq) DNA polymerase
Describe the role of heating and cooling in PCR
Heating the solution in PCR separates the DNA strands by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds. The solution is then cooled to allow the attachment of the primer, heat resistant (Taq) DNA polymerase and the free floating DNA nucleotides.
Describe the role of heat resistant enzymes in PCR
Heat resistant (Taq) DNA polymerase is a thermostable enzyme, which synthesises two new complementary strands of DNA by attaching free floating DNA nucleotides to the complementary bases on the exposed DNA strands.
Describe the role of free floating DNA nucleotides in PCR
Free floating DNA nucleotides are attached to their complementary bases on the exposed DNA strands, to synthesise two fully formed DNA molecules.
Compare the different potential consequences of mutations in germ cells and somatic cells
Mutations in somatic cells only effect the individual. Mutations in germ cells cen be passed on to the offspring
Explain how inheritable mutations can lead to changes in the characteristics of the descendants
Inheritable mutations can lead to changes in the characteristics of the descendants when the mutation occurs in a germ cell.
Compare chromosomes in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
In eukaryotes, DNA is bound to histones in linear chromosomes found in the nucleus
In prokaryotes, DNA is unbound and circular in the cytoplasm
Explain why a different enzyme is needed required at each step of a metabolic pathway
A different enzyme is required at each step of a metabolic pathway as each step of a metabolic pathway has a different intermediate product. Since each enzyme has a active site that is complementary to a specific substrate, each step would need a different enzyme due to each intermediate product having a different structure.
How does a mutation of a gene lead to a change of protein function
A mutation can lead to a change of the codons in a gene sequence further impacting mRNA codon which may change the amino acid sequence. This may result in a change in the structure and therefore the function of the protein.
Explain why the 3-D shape of a protein is critical to it's function
The 3-D structure of a protein is critical to it's function as the folding determines the final structure which determines the binding/active site, and because the binding site is complementary to a specific substrate. This enables the protein to perform it's intended function. An alteration of the binding/active site the protein would be unable to bind to the specific substrate and function would be prevented
Explain how a cells have identical DNA but can have different structure and functions
Cells could have identical DNA but different structures and function due to the different gene expression, resulting from epigenetic changes. This results in different genes are either expressed or silenced in both cells and therefore different combinations of proteins are present in the cells.
Describe 2 reasons why metabolic pathways involve several regulated steps
Prevents the release of excess energy in the form of heat which would denature enzymes and other proteins.
Efficient use of energy that is released form the reactions as small bits are released at a time cells can use the energy more efficiently
State the purpose of PCR
PCR amplifies DNA copies.
DNA and proteins