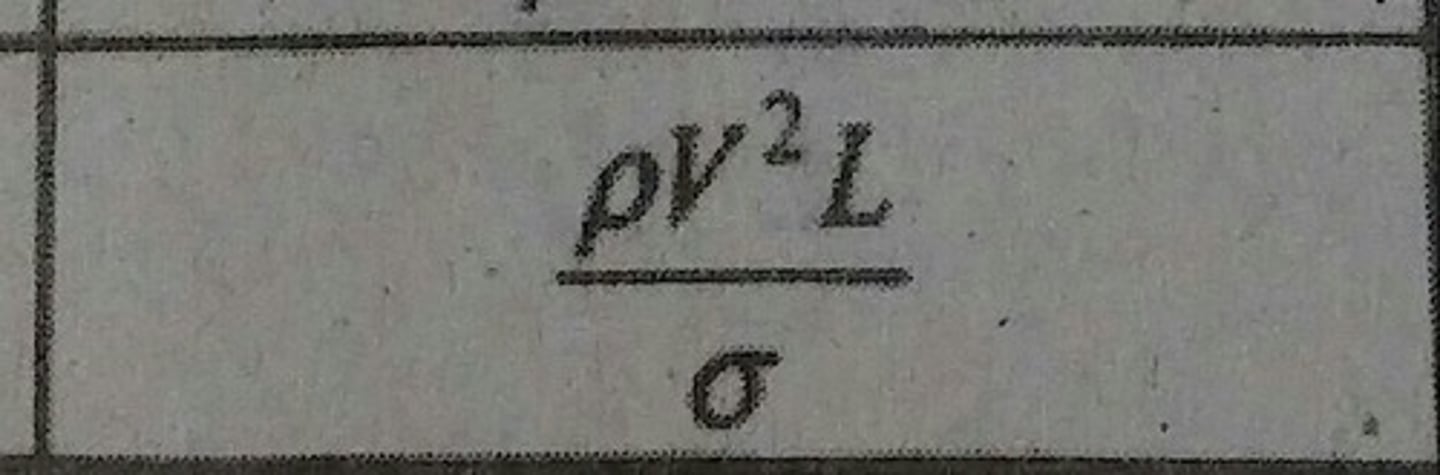Unit Operations - Dimensional Analysis
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
satisfy none of these
The repeating variables in a dimensional analysis should

inertial forces to viscous forces
Reynolds Number may be defined as the ratio of
TV^2/μK
The Brinkman Number is often used in the analysis of organic liquid flows. This dimensionless number is proportional to viscosity, μ. Derive the Brinkman Number if it depends on the viscosity, velocity of flow, V, thermal conductivity, k, and fluid temperature, T .
1/2
A pendulum bob of weight W is connected to a weightless string of length L. If the weight of the bob is doubled and the length of the string is cut to one-half, the period or time of a complete swing becomes _____ the original period
Grashof Number
It is a measure of inertial forces to gravitational forces
Peclet Number
It is essentially the ratio of buoyancy forces to viscous forces.
Mt
Which of the following is the dimensional formula for the volumetric quantity of water flowing in unit time?

1:100
The dimensionless drag coefficient on a sphere is dependent in the Reynolds Number for the fluid and is expressed as follows: (see picture)
where p is the density and μ is the viscosity. If the drag coefficient for a sphere, which has a diameter that is 1/10 the length of the diameter of the sphere of interest, is found to have the same drag coefficient as the sphere of interest, then what is the ratio of the speed of the smaller sphere to the larger sphere?
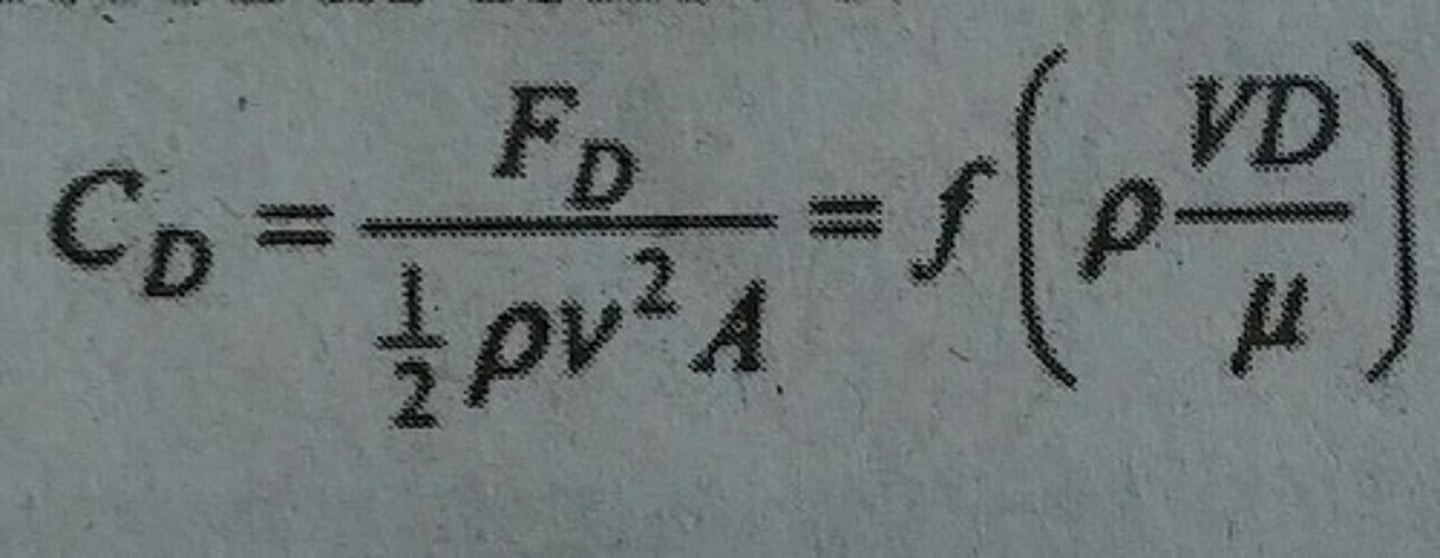
Dimensions
names given to physical quantities. Some examples of dimensions are Length(L), Time(t), Mass(M), Force(F), Volume(V), Velocity(v), and Temperature(T).
Unit
a definite standard or measure of a dimension. Examples are foot, meter, and Angstrom which are all different units of length; pound and kilogram are standard units of mass, C and kelvin(K) are units of temperature, etc.
Internation System (or SI)
meter(m), second(s), kilogram(kg), Newton(N)
English Engineering System
feet(ft), second(s), pound mass(lbm), pound force(lbf)
Absolute Engineering System
ft, s, lbf, slug
Absolute Metric System
centimeter(cm), gram(gm), second(s) dyne
Newton's Second Law of Motion
force and mass are related by
dimensional analysis
a procedure of grouping variables into meaningful dimensionless groups for the purpose of reducing the number of parameters involved in the experimental investigation of a physical phenomenon.
Arrhenius Number (a)
Ratio of activation energy to thermal energy
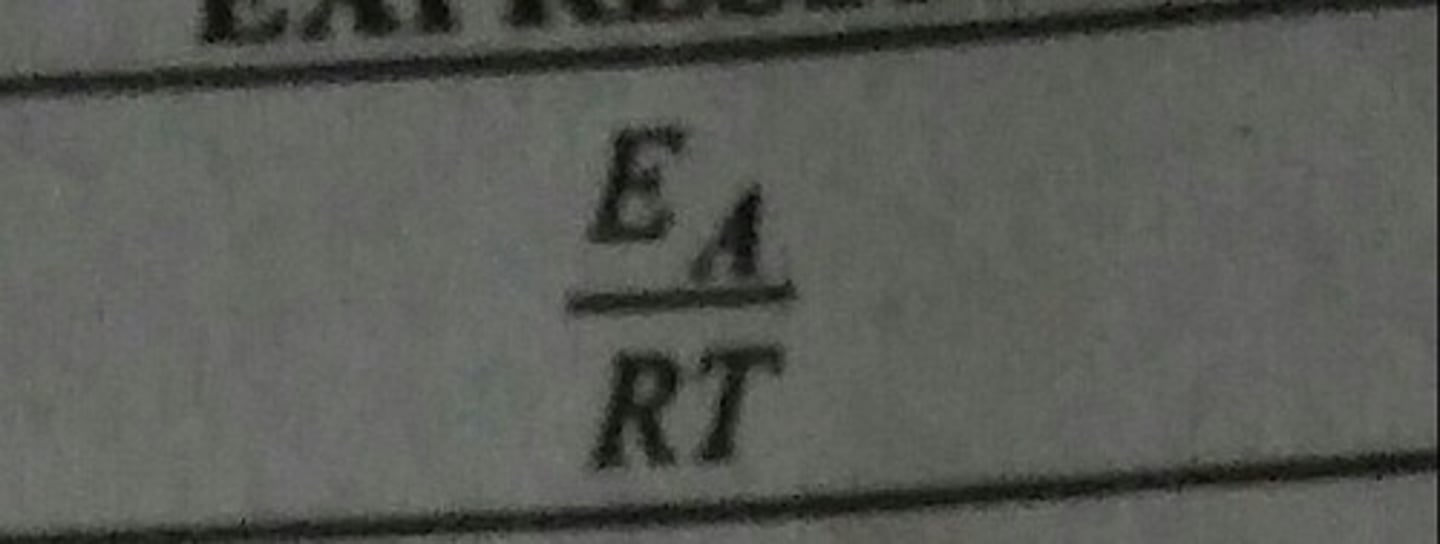
Bingham Number (Bm)
Ratio of yield stress to viscous stress
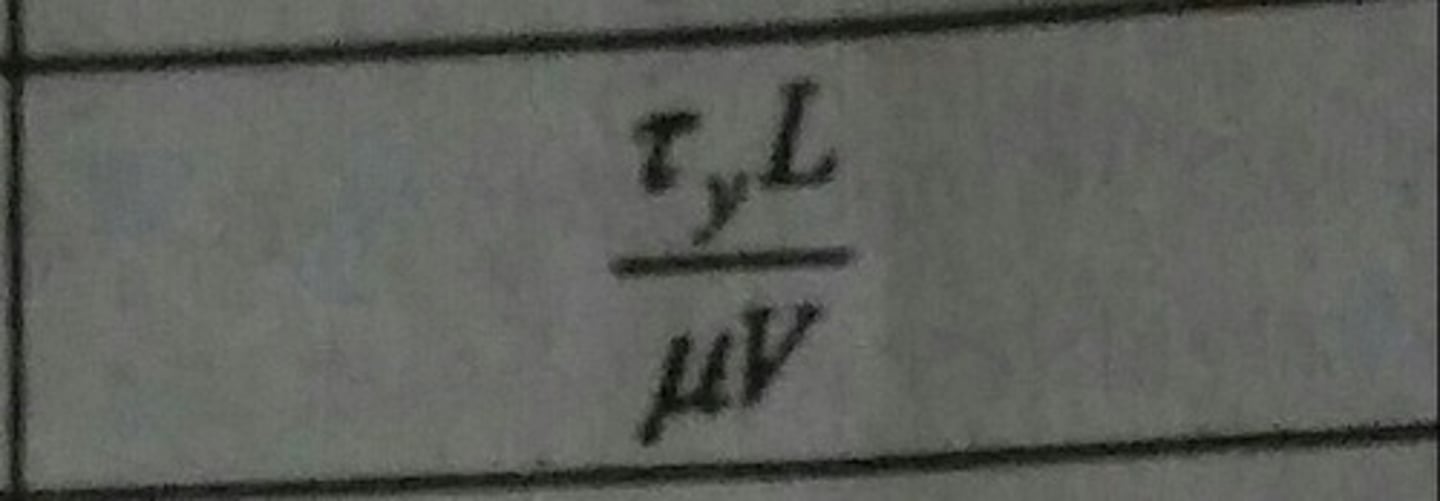
Biot Number (Bi)
Ratio of the solid's internal thermal resistance to the fluid's thermal resistance
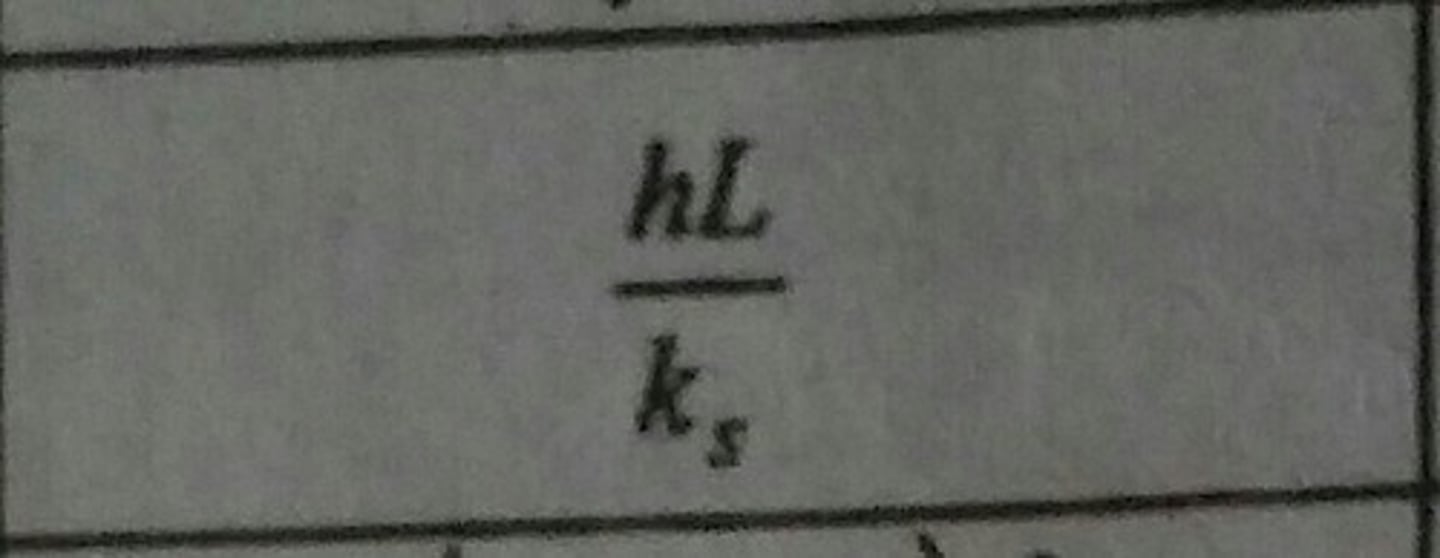
Bond Number (Bo)
Ratio of gravitational and surface tension forces
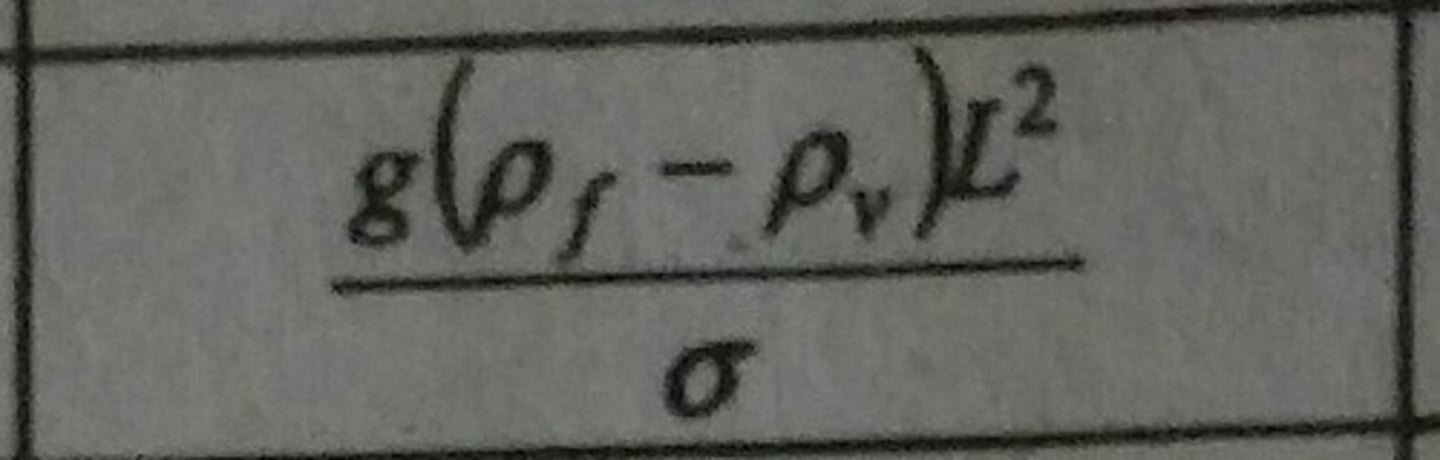
Brinkman Number (Br)
Ratio of heat generated by viscous dissipation to the heat transferred by conduction
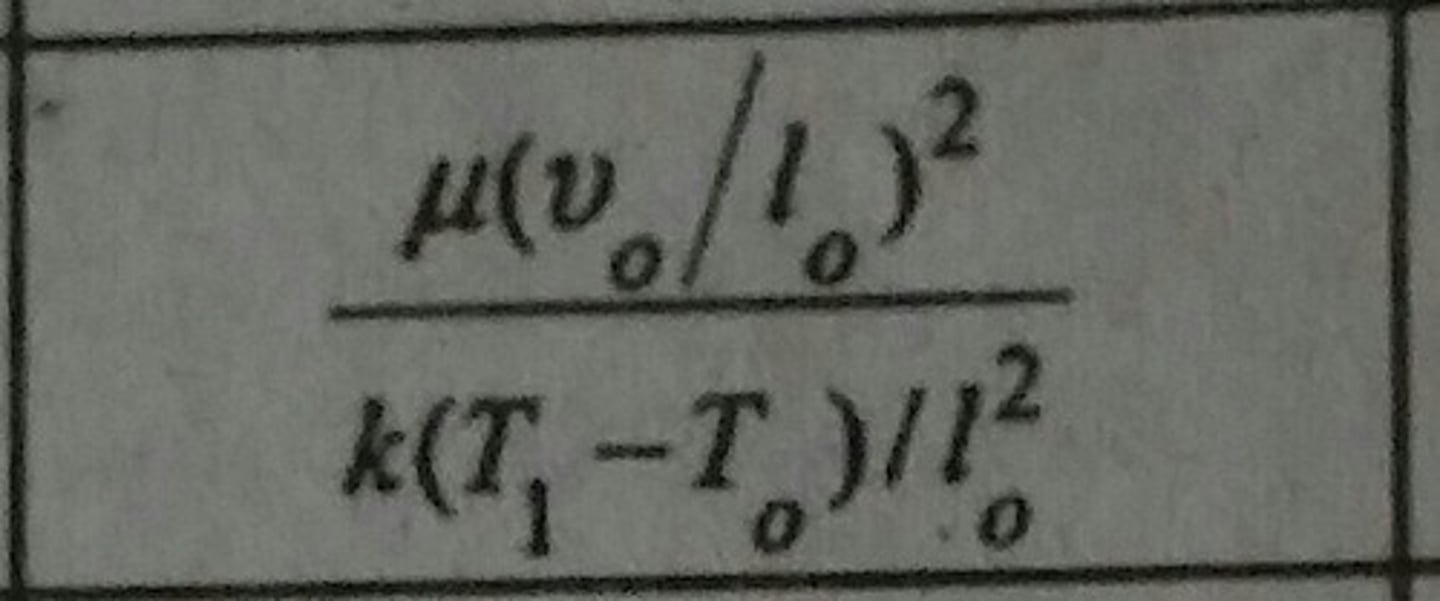
Damkohler Number (Da)
Reaction time scale versus transport phenomena properties. Definition depends on system. Eqn. given is for continuous reactors
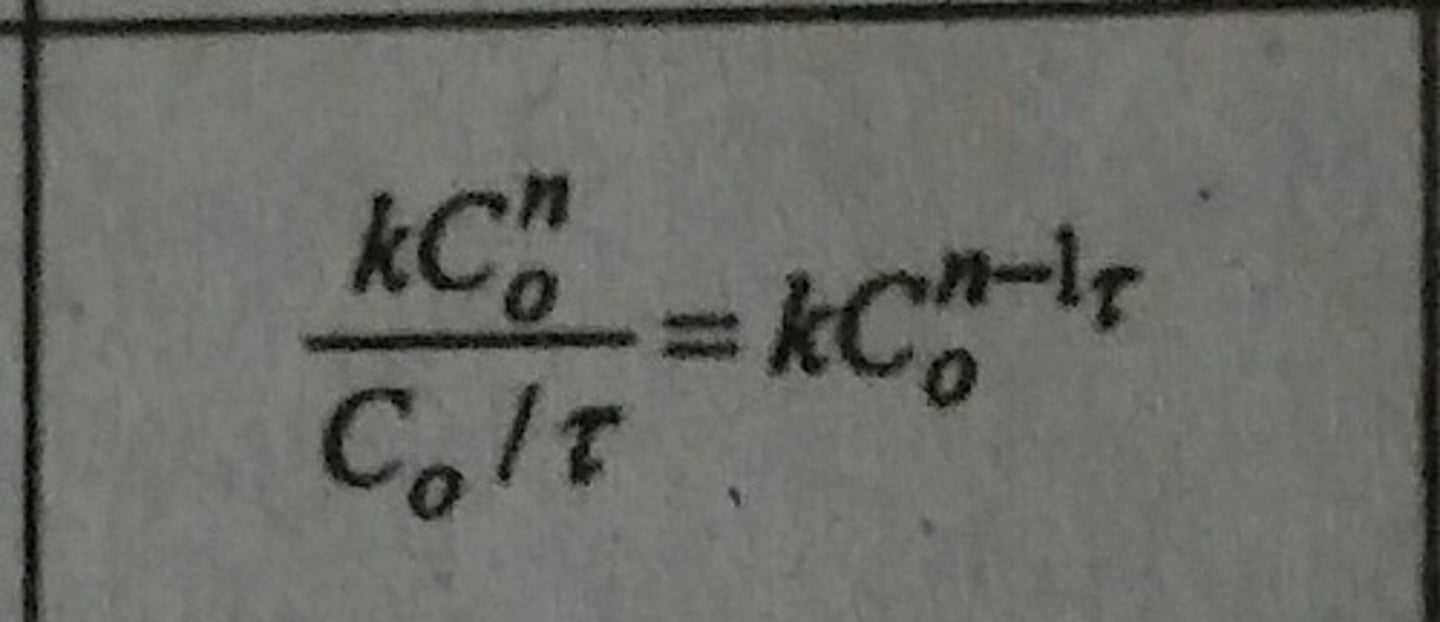
Eckert Number (Ec)
Relates kinetic energy of flow with enthalpy
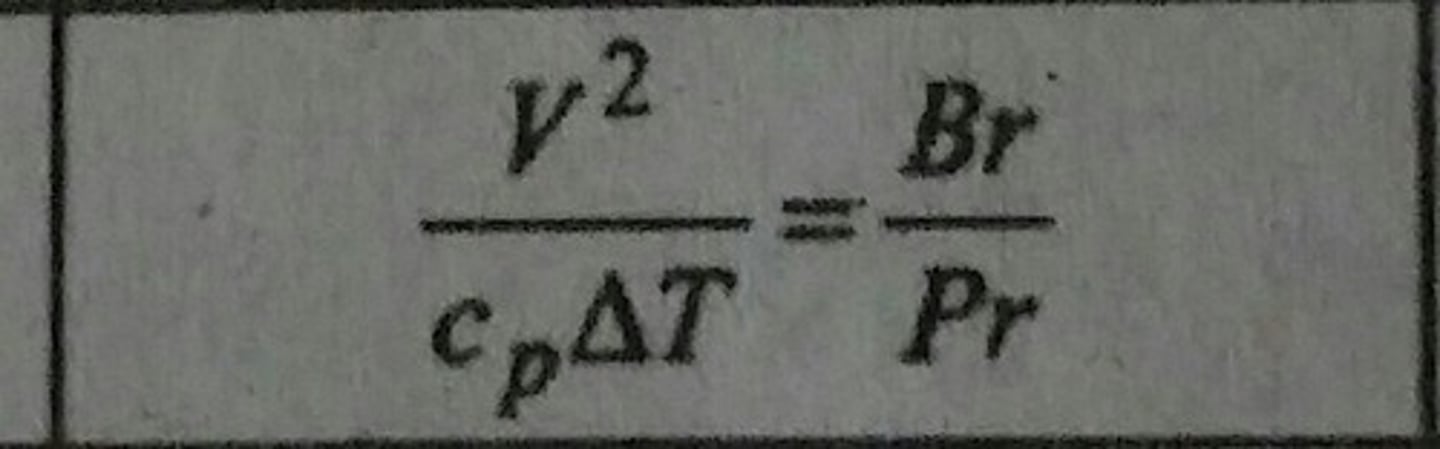
Euler Number (Eu)
Ratio of pressure force to inertia force
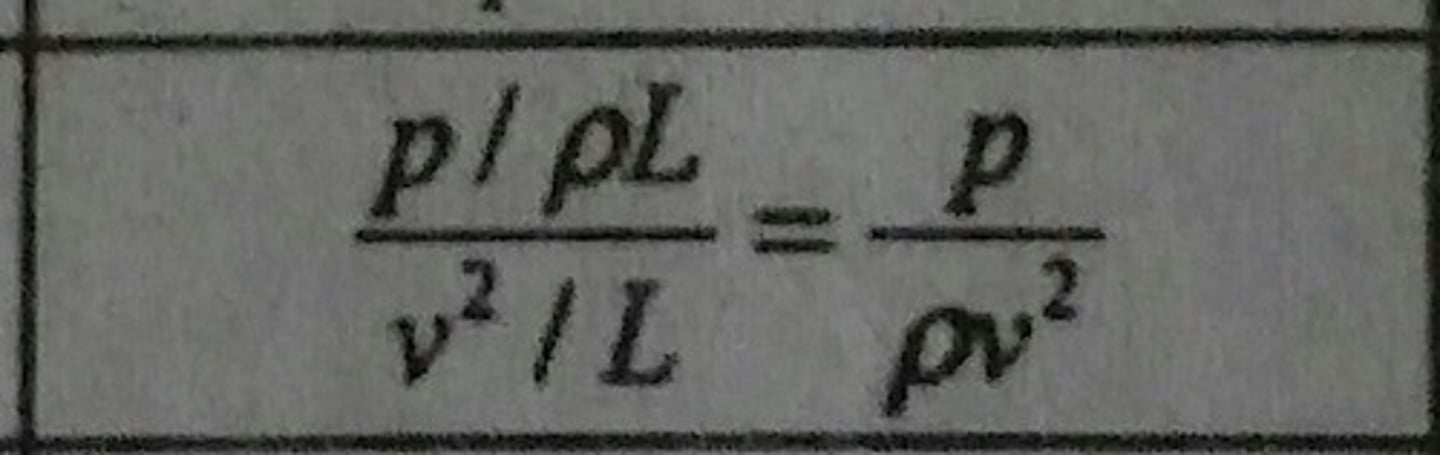
Fourier Number (Fo)
Ratio of rate by heat conduction to rate of thermal energy storage
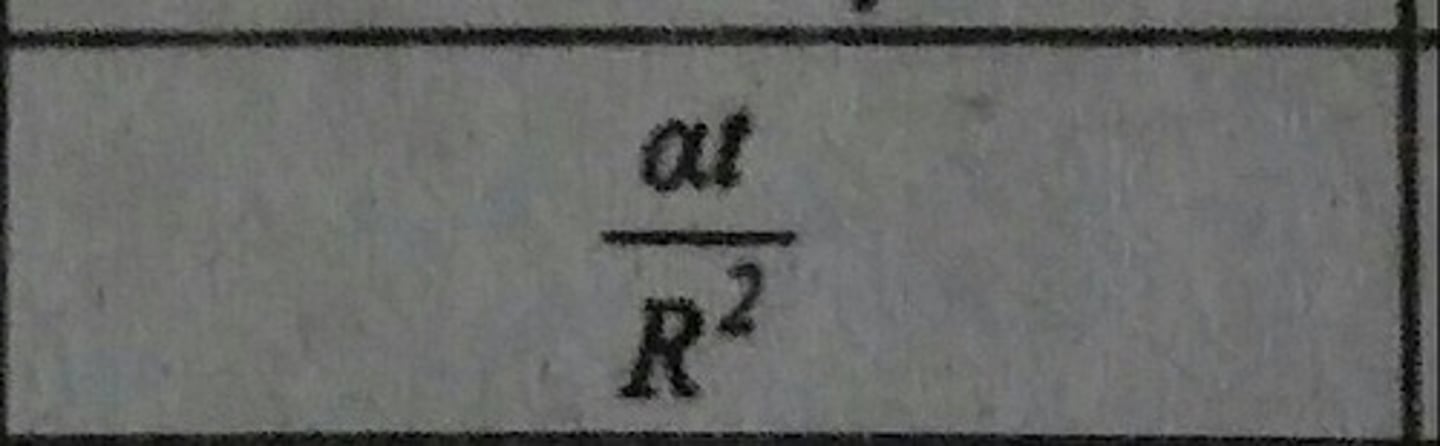
Friction Factor (f)
Dimensionless pressure drop for internal flow
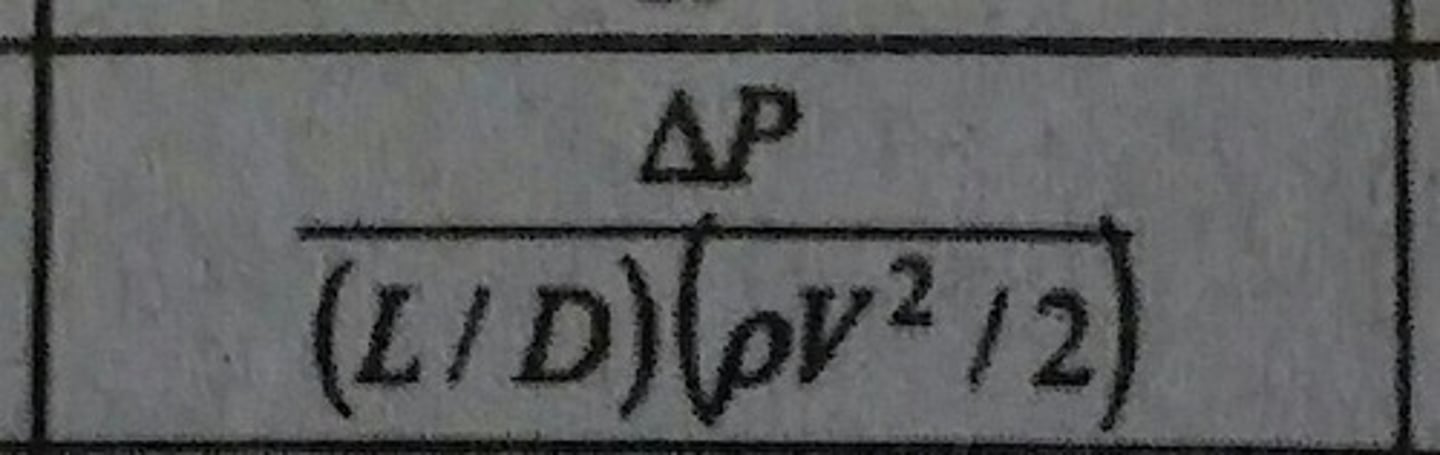
Froude Number (Fr)
Ratio of inertia force to the gravity force
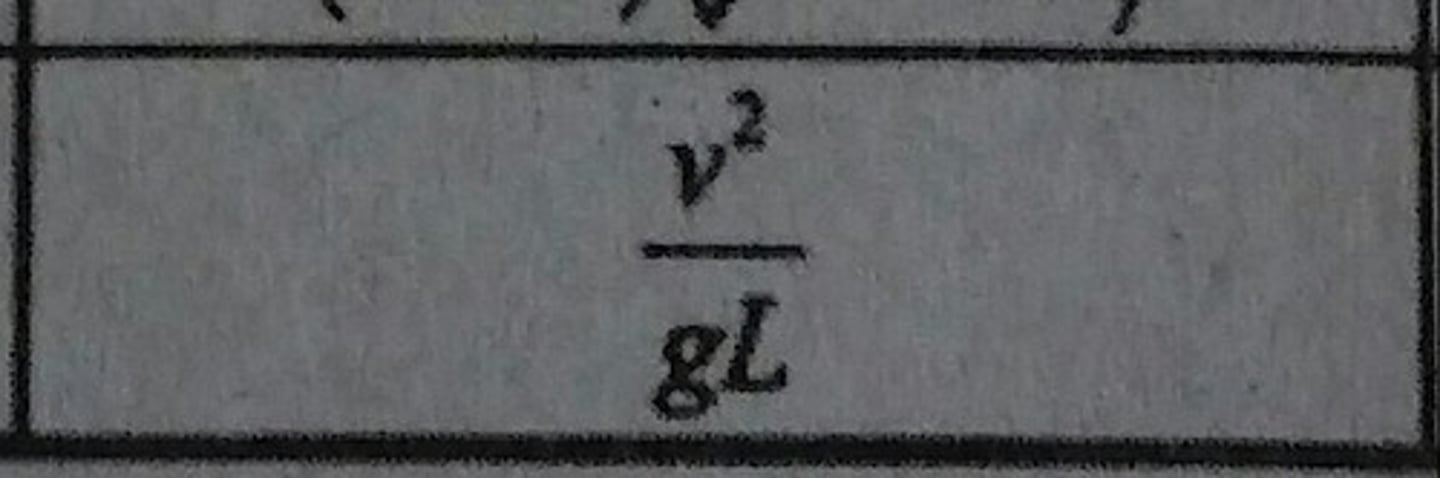
Galileo Number (Ga)
Relates viscous flow and thermal expansion
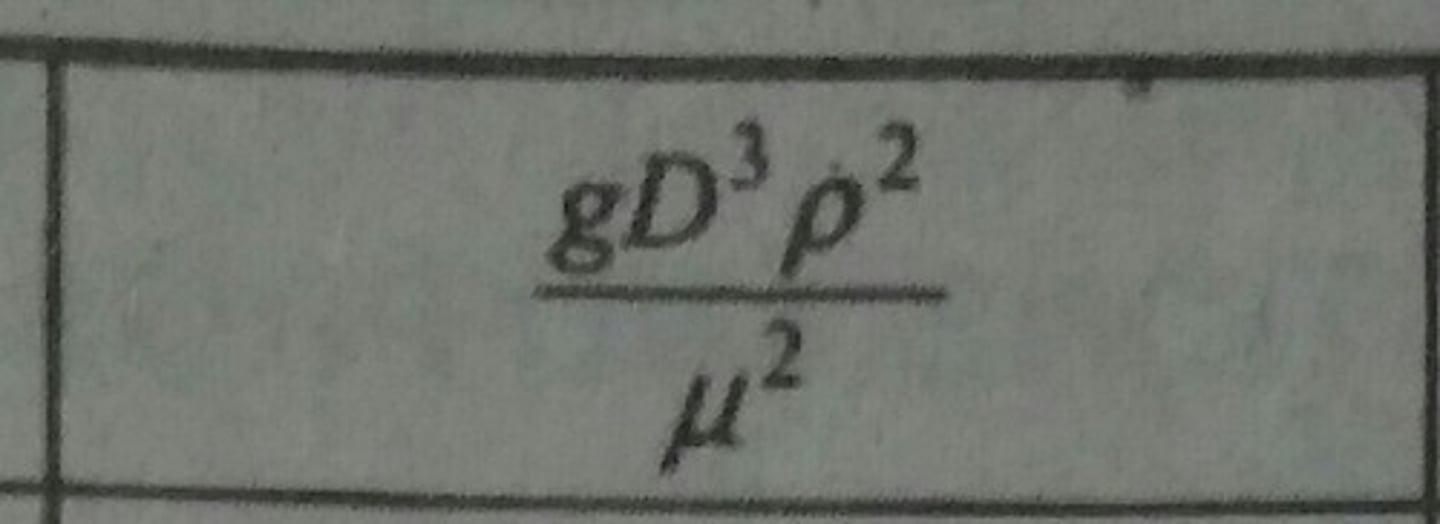
Graetz Number (Gz)
Determines the thermal or concentration development at entrance lengths or ducts.
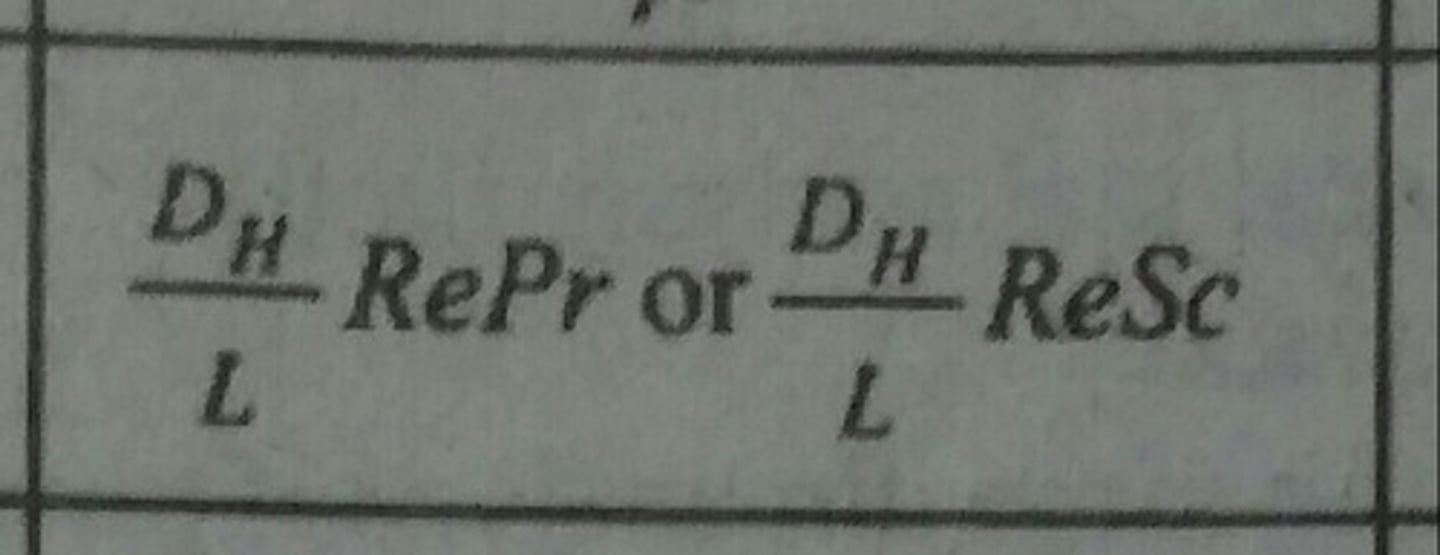
Grashof Number (Gr)
Ratio of buoyancy forces to viscous forces
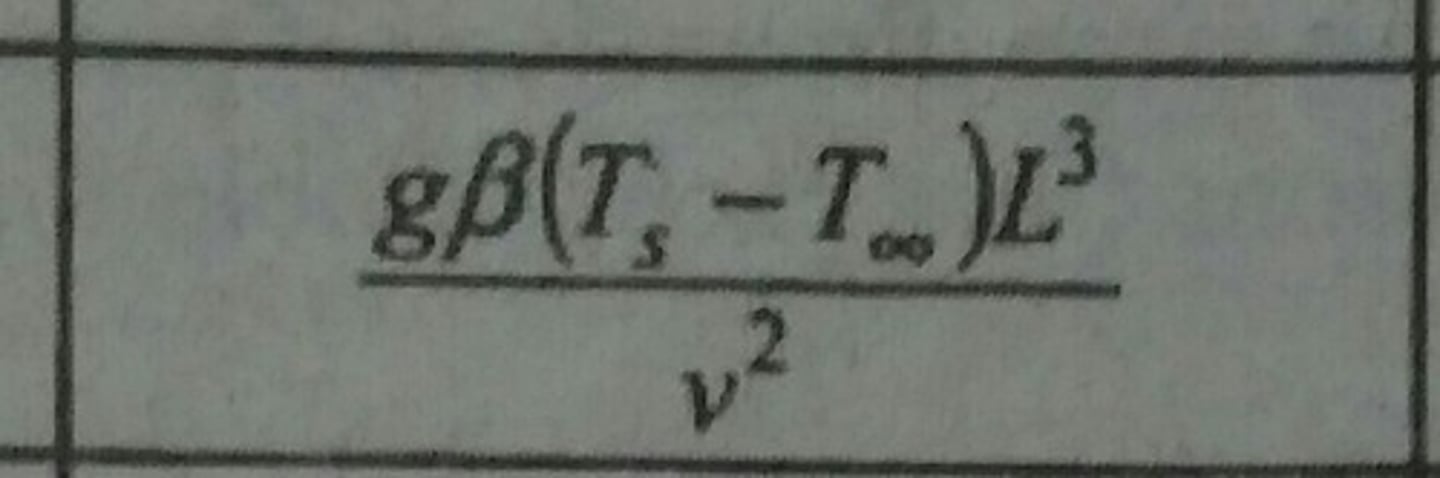
Jacob Number (Ja)
Ratio of sensible to latent heat absorbed during evaporation or condensation
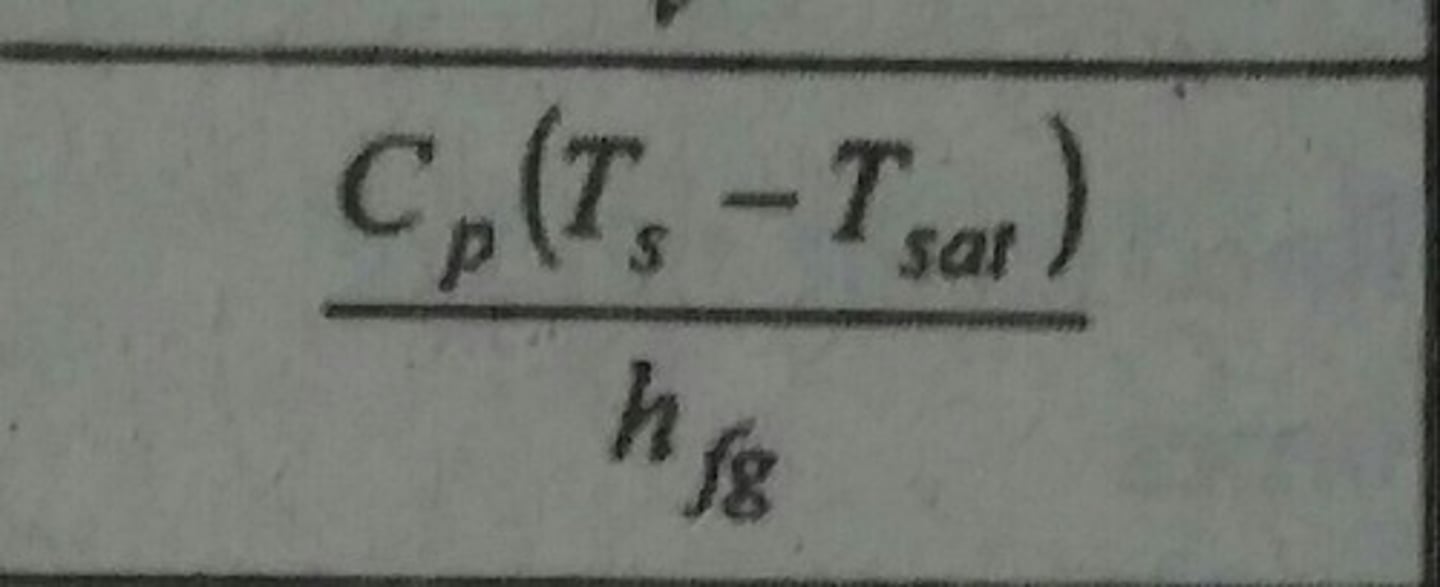
Knudsen Number (Kn)
Ratio of molecular mean free path to a physical length. Given eqn. is for ide gas.
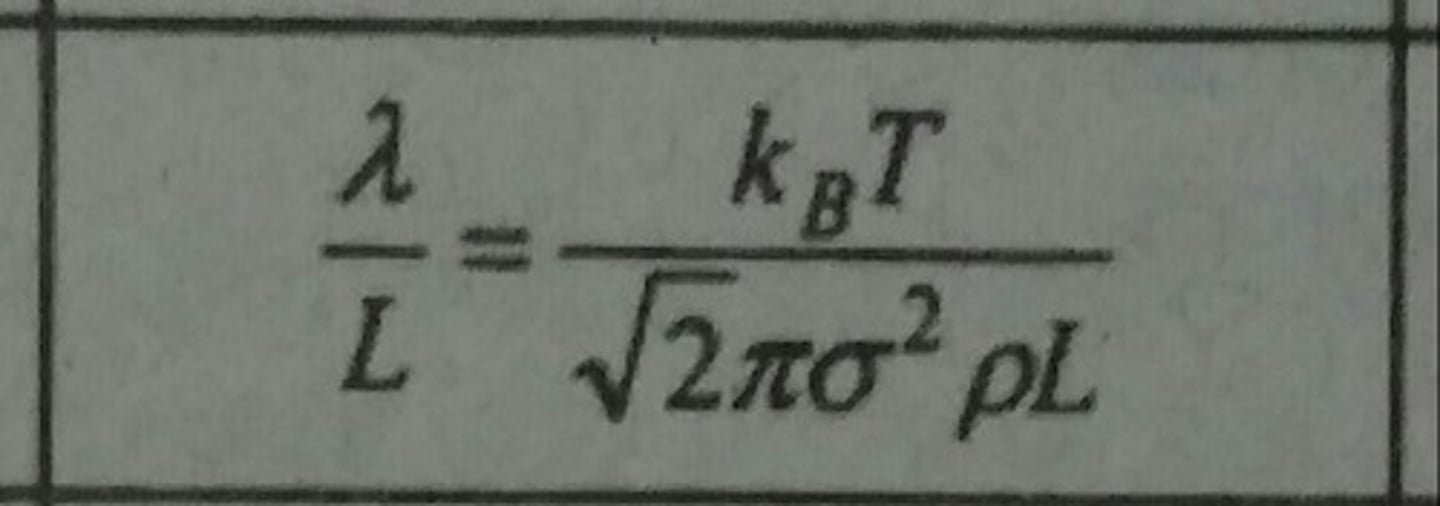
Lewis Number (Le)
Ratio of thermal and mass diffusivities.
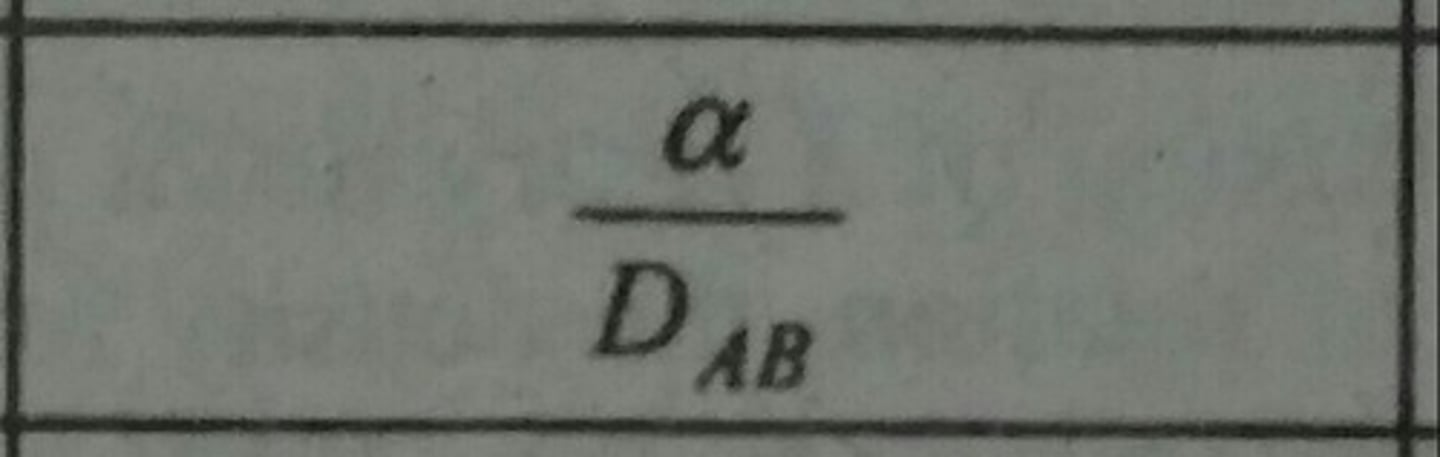
Lorentz Number (Lo)
A proportionality constant that relates the thermal conductivity, k with electrical conductivity, θ.
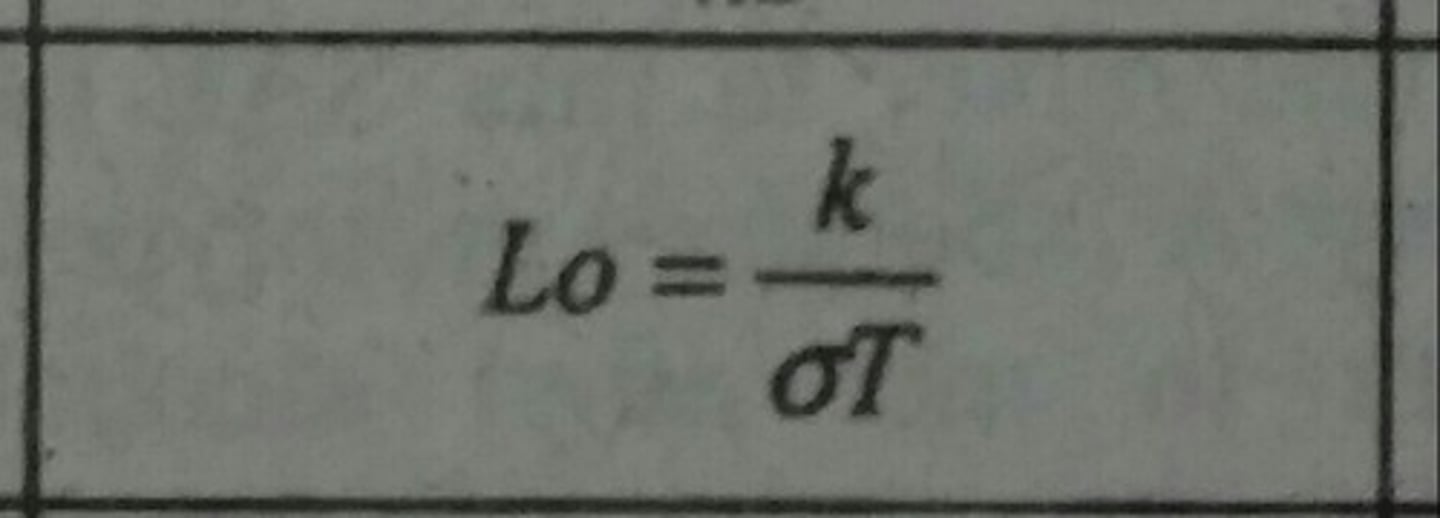
Mach Number (Ma)
Ratio of the speed of fluid flowing and that of sound measured at the same conditions
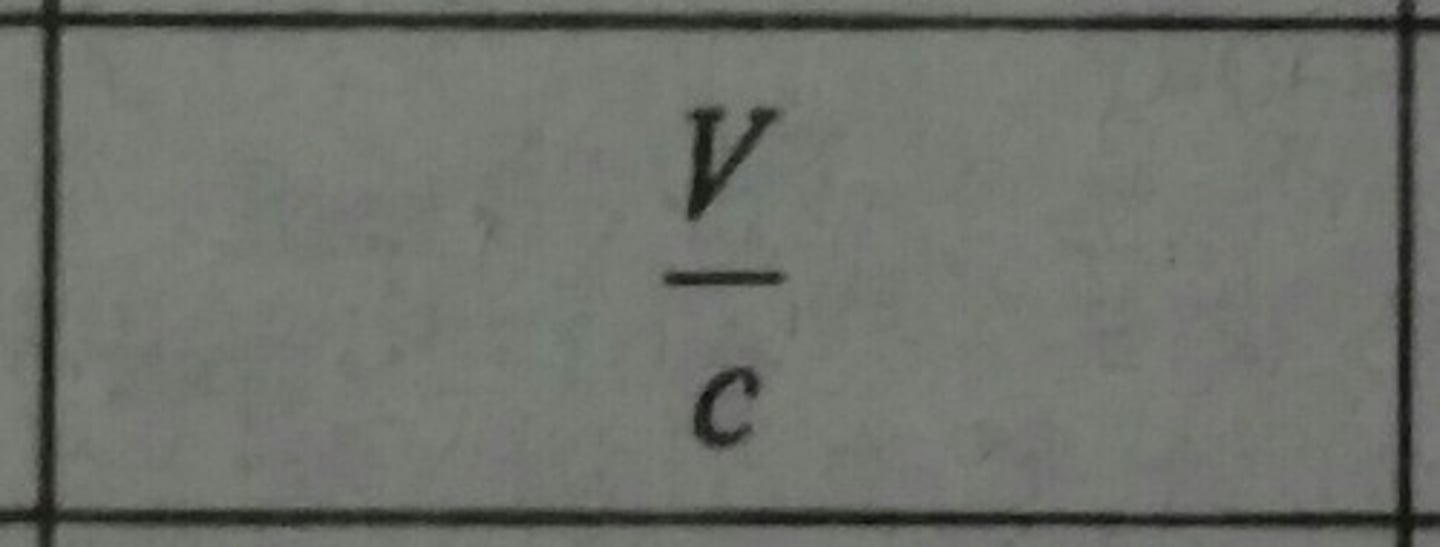
Nusselt Number (Nu)
Dimensionless temperature gradient at the surface.
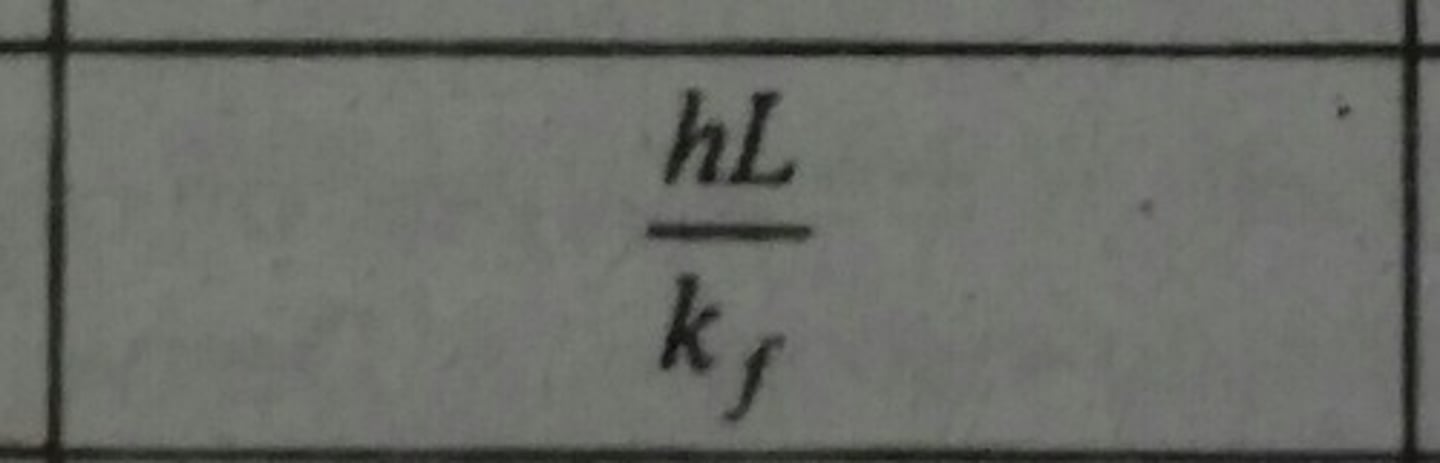
Peclet Number (Pe)
Dimensionless independent heat transfer parameter
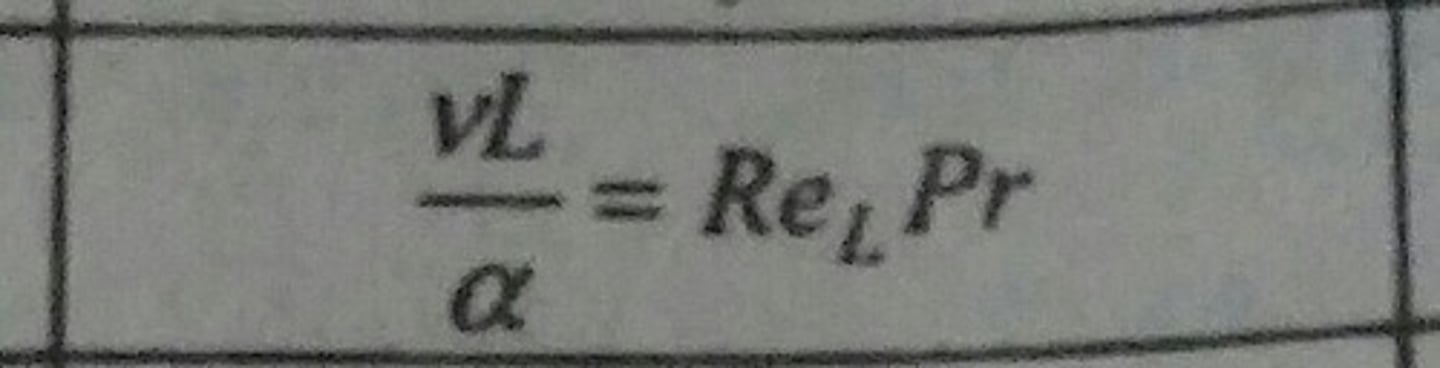
Power Number (Po)
Relates resistance forces to inertia forces in agitators. Known also as Newton Number.
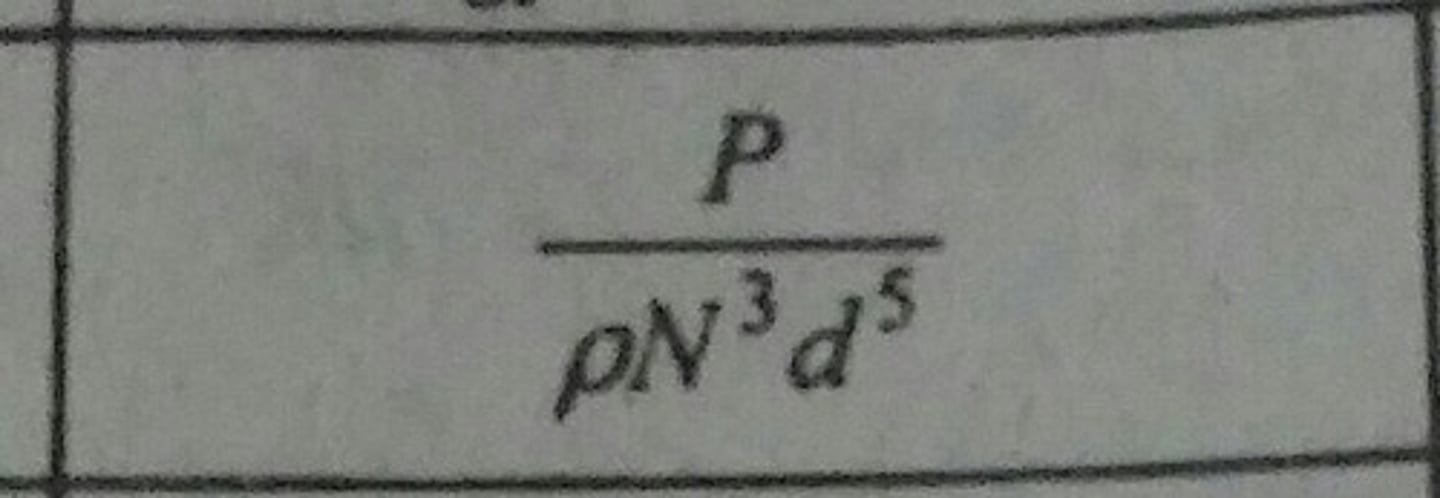
Prandtl Number (Pr)
Ratio of momentum and thermal diffusivities.
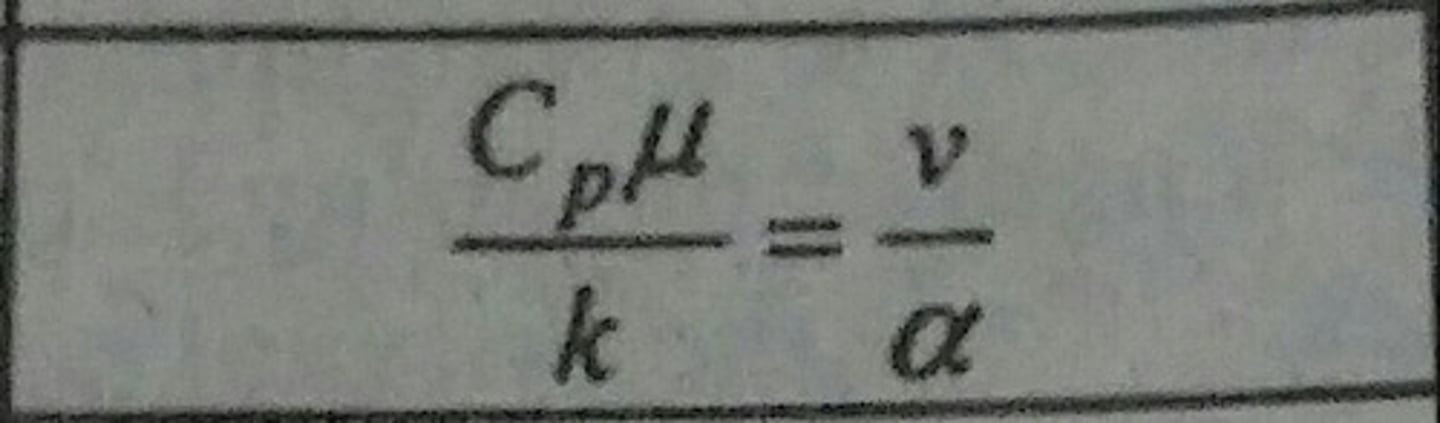
Rayleigh Number (Ra)
Determines free heat convection effects relative to the effect of fluid motion.
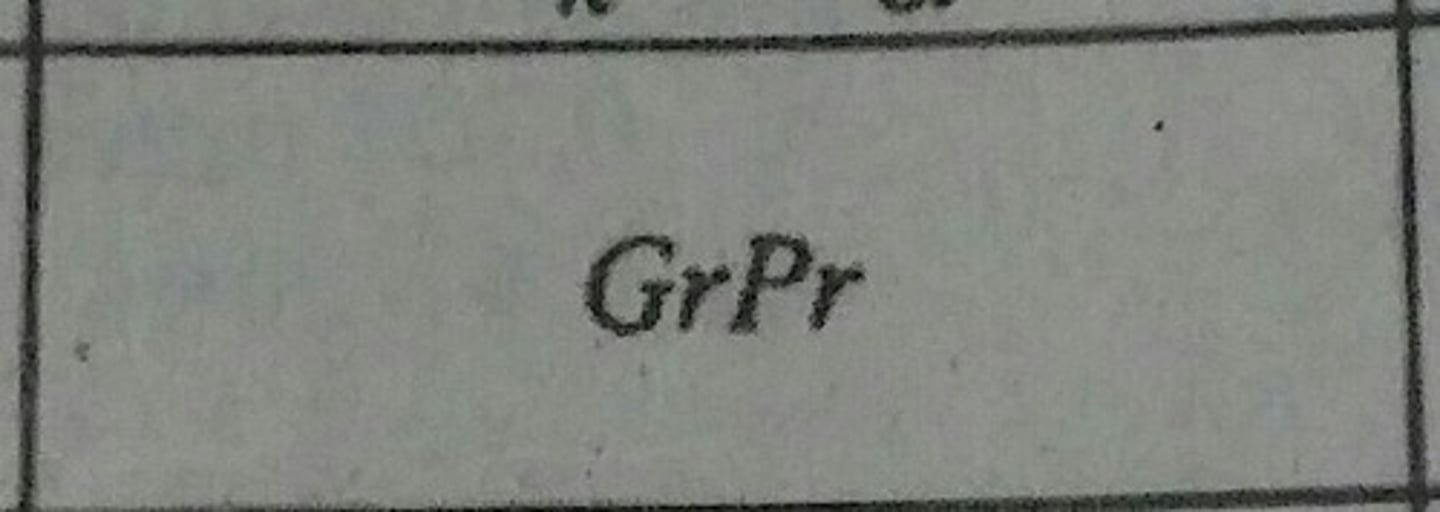
Reynolds Number (Re)
Ratio of inertia and viscous forces

Schmidt Number (Sc)
Ratio of momentum and mass diffusivities.
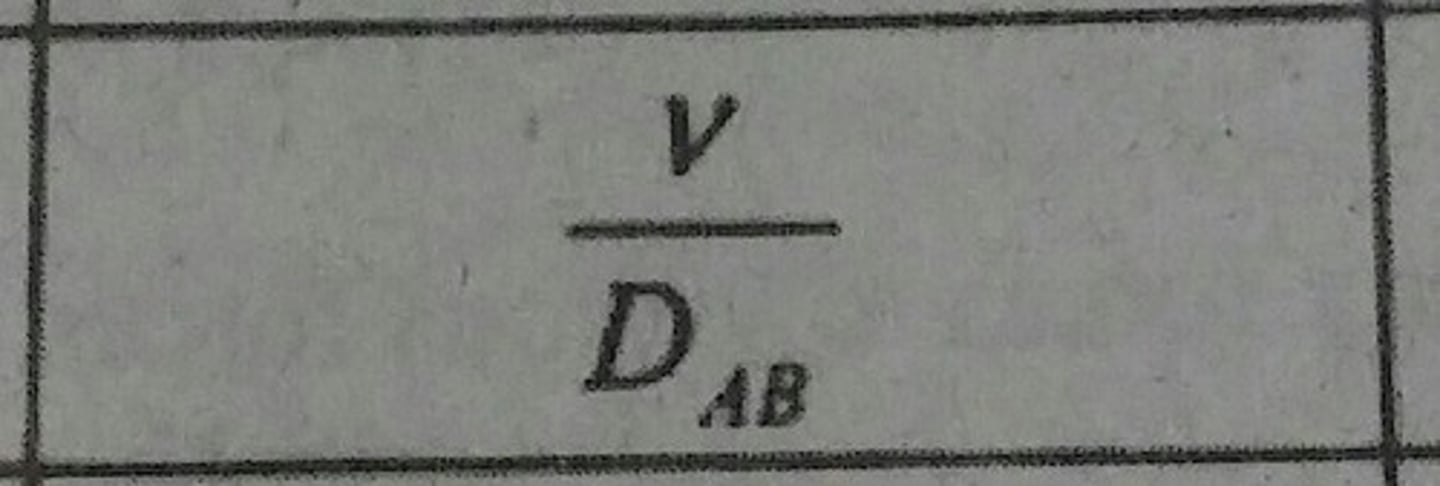
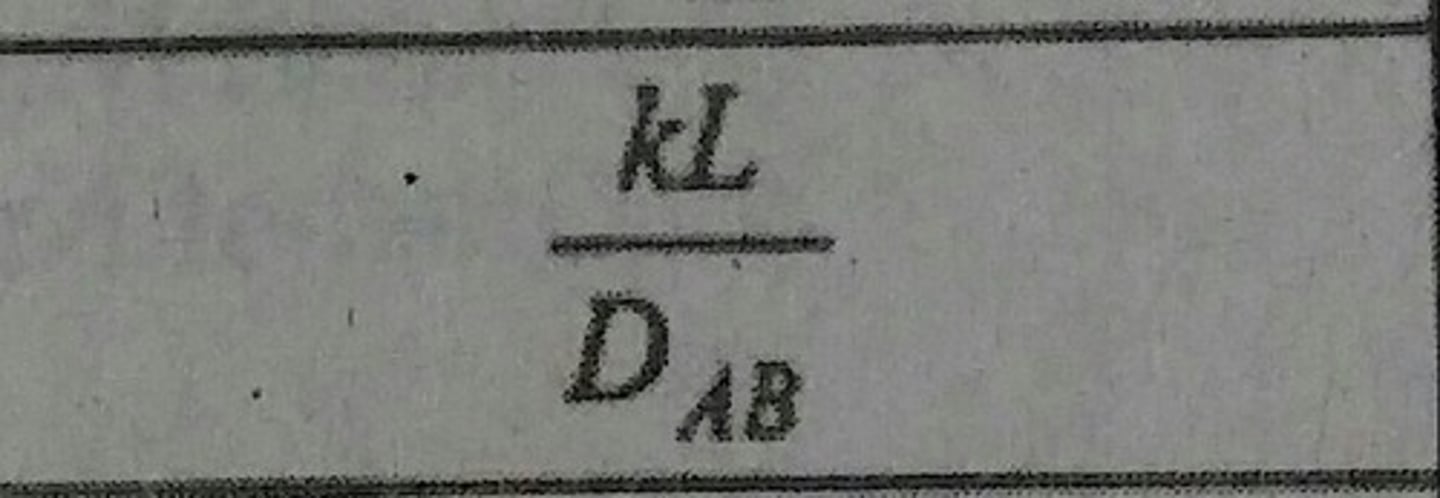
Sherwood Number (Sh)
Dimensionless concentration gradient at the surface.
Stanton Number (St)
Modified Nusselt Number
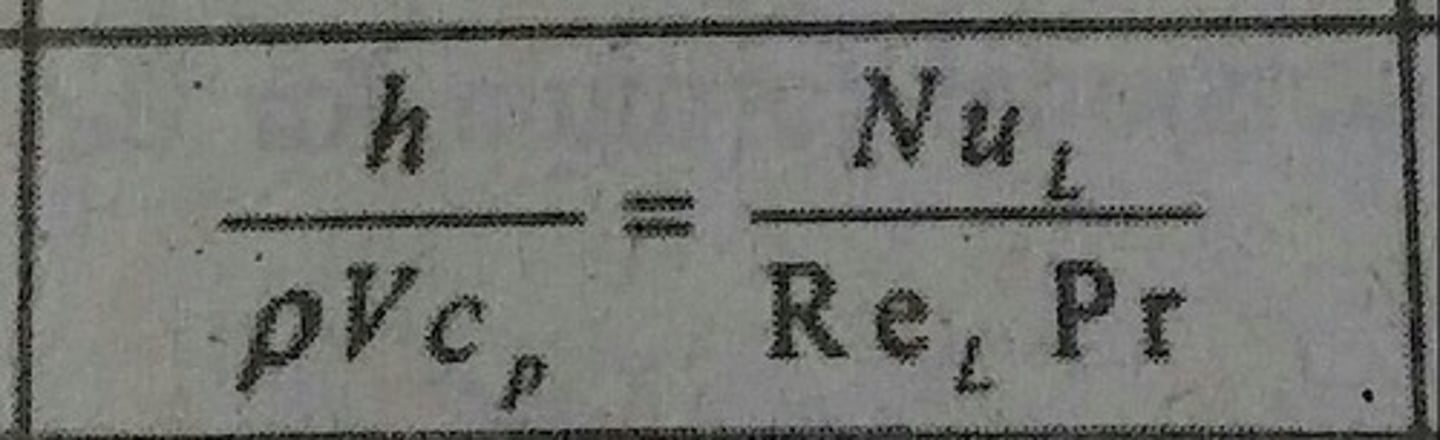
Weber Number (We)
Ratio of inertia to surface tension forces.