cavity preparation basics
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
what is the conclusion of remineralization of white spot lesions
some white spot lesions are and aren’t remineralizable
are active (initial) or arrested (initial) lesions easier to remineralize
active initial lesions
minimally invasive cavity preparation is possible thanks to…
adhesive dentistry (bonded restoration)
amalgam or metal inlays require what type of preparation compared to and adhesive restoration
larger preparation- rely on mechanical support
the larger/more dental work you do on a tooth
the sooner you get to the end of the tooth
what is the GV back concept
the classifications of restorations (not the disease that is there)
what is a Class I restoration
restoration on one or more approximal surfaces added
what is a class II restoration
a class I restoration w one or more proximal surfaces added
what is a class III restoration
an approximal or proximal restoration in an anterior tooth; w/o incisal edge
what is a class IV restoration
a class III restoration involving the incisal edge
what is a class V restoration
a restoration on the B or L smooth surface, commonly in the gingival third
what is a class VI restoration
restoration of a cusp tip or incisal edge
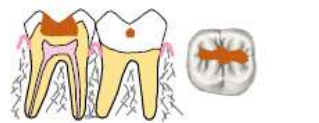
what restoration class is this
class I

what restoration class is this
class II

what restoration class is this
class III

what restoration class is this
class IV
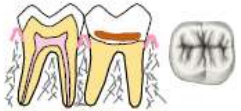
what restoration class is this
class V
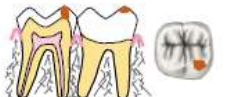
what restoration class is this
class VI
classic principles of cavity preparation
outline form
resistance form
retention form
convenience form
decay removal
finish cavity walls
clean cavity
how has the philosophies of surgical intervention changed over the last ~100 years
overtime we have become more and more conservative in cavity preparations- only do so when you absolutely have to drill
what was the ultra conservative “sealed restorations” introduced in the 80s
no prep, just bevel the enamel- don’t need to numb
what is the atraumatic restorative treatment that was introduced in the 90s
no rotary instrument, just scoop out decay and place GI
today, some preparation principals still apply but the traditional _______________________ is thought to be outdated
extension for prevention
____________________ angles are thought to be stress concentration points
sharp internal line angles- we want round now!
today, we want to rely on bonding, this is called…
adhesive dentistry
_________________ is essential placing margins in sound tooth structure
peripheral seal
you want to prioritize __________ health over complete caries removal and direct pulp cap
pulpal; want to preserve pulpal vitality
restorations are never as good as…
sound tooth tissue
redos of restorations usually result in…
larger restorations
more complex and bigger restorations have inc in cost, take more time, and are more likely to…
fail
what are the modern practice goals
prevent
reverse
preserve
retreat
update
in terms of out modern practice goals, prevent…
initial lesion or progression of any lesion that exists
in terms of out modern practice goals, reverse…
lesions as possible, identify lesions early to maximize the opportunity for reversal
in terms of out modern practice goals, preserve…
as much tooth structure as possible for the long-term, remove as little tissue as possible
in terms of out modern practice goals, retreat …
only is needed, as little as possible, and w preservation as much as possible
in terms of out modern practice goals, update…
KEEP LEARNING
what are the cavity preparation factors
which lesions
what tooth and site/surface
what material and restoration technique
what is the initial outline form
minimal surgical extension to eliminate defective tooth structure and provide a restorable surgical preparation; extent of disease and existing groove patterns are primary determinants of outline form
the initial outline form may be different depending on the…
restorative material
what is the caries-free DEJ outline form
should be caries free DEJ everywhere
what is the final outline form
clean periphery at the DEJ; accommodate the peripheral extent of the disease; may go beyond the initial form
the resistance form principals largely depend on…
the material that you are going to use
what is the resistance form principal
eliminate undermined enamel that is susceptible to fracture
avoid undermined cusps
enamel w no dentin support
allow adequate thickness of restorative material to avoid fracture
what do you want to check before doing a filling preparation
occlusion
goal of retention form
create a surgical preparation that will mechanically retain the restoration; convergence vs divergence
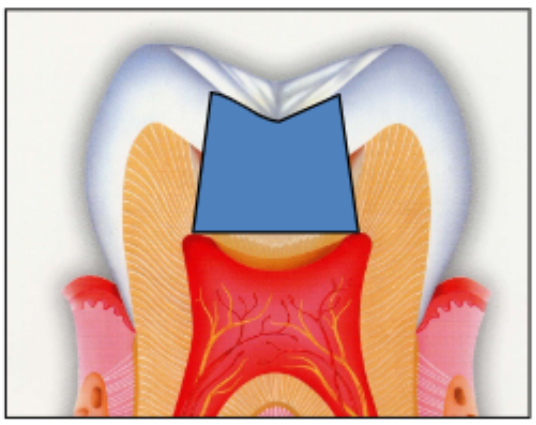
convergence or divergence
convergent walls
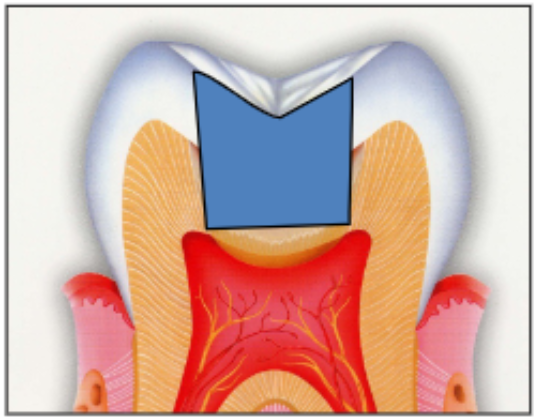
convergence or divergence
divergent walls
composite restorations rely on ___________ (mechanical or bonding) techniques, amalgam restorations rely on _____________ (mechanical or bonding) techniques
bonding; mechanical
what is convince form
extending the outline to improve access to caries and ease material placement; avoid unnecessary extension
what are the principals for deep caries removal
use:
visual
hardness of dentin
caries indicator dye
clinical judgement
knowledge of anatomy to consider pulp horn location
pt age
what are the questions you should be asking to ensure pulpal protection
how much dentin is left over the pulp
how can i help remineralize caries-affected dentin
was the pulp exposed, do we need IDP/DPC
what is DPC
placing the pulp cap directly in contact with the pulp tissue
what is IPD
placing the pulp cap not directly on the pulp tissue
what is routinely used for cleaning and disinfecting of the preparation
cavity cleanser such as 2% of chlorhexidine of di-gluconate
how are the chlorhexidine for cleaning the preparation vs the mouthwash different
mouthwash has detergent in them → contains no boning
when smoothing the outline form, you want to focus on what and why
the enamel walls and cavosurface margins; margins are frequently the site of restoration failure (restoration failure or recurrent decay)
good margin management is good ____________ dentistry
preventative
TERMINOLOGY PICTURES
what are the 4 external walls of a cavity preparation
distal
facial/buccal
lingual
gingival
what are the two internal walls of a cavity preparation
pulpal
axial
for composite, do you prefer sharp or round internal line angles
round
what did research show in the 1980-90s about a sharp internal line angles
where stress concentrates:
clinical load + viscoelasticity of dentin + stress concentration = higher risk of cusp fracture
what is a handpiece
a rotary device used to precisely modify enamel, dentin, and restorative mateials
what is a turbine
the part of the handpiece that turns the cutting bur; available in both air-driven and electrically-driven motors
advantages of electrical handpieces
quiter
more controllable rotations and torque
no need for air compressors
disadvantages of electrical handpieces
more expensive
more sensitive parts
heavier
what can the material of a bur be made of
SS- stainless steel
carbide
diamond
polishing: rubber, silicate
what are the parts of a bur
shank
neck
head
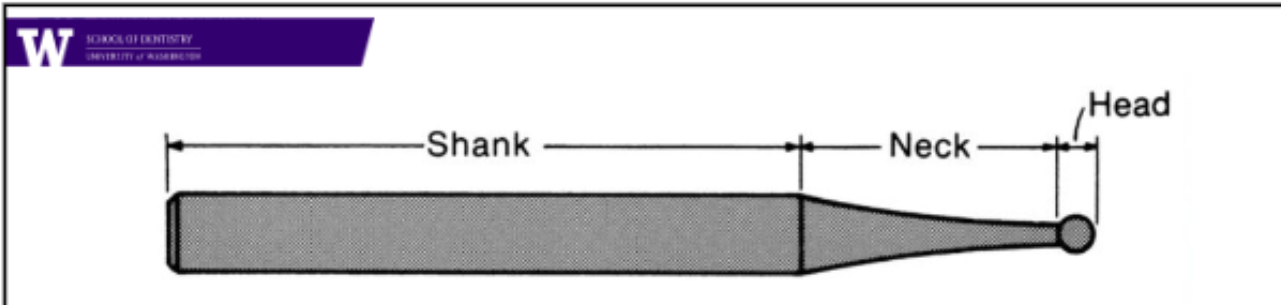
what are the parameters of the head of a bur
diameter
shape
length
taper
what are the parameters of shanks of burs
friction grip
latch
diameter
length
when removing caries in dentin, what handpiece is recommended to use vs enamel
enamel: high-speed
dentin: slow speed
what is the speed range of a slow speed
6-10000
what can the speed up to in a highspeed
up to 200000
what are the types of heads on burs
round
pear
straight fissure
tapered fissure
end cutting

bur type
round

bur type
pear

bur type
straight fissure

bur type
tapered fissure

bur type
end cutting
which bur would create sharp internal angles
straight fissure
funx of carbide bur
cutting
funx of diamond bur
grinding
why are diamond burs more commonly recommended nowadays over carbides
smooth finish on teeth → better enamel margins
less damage to cutting surface
less burn on tooth and soft tissue
better surface for bonding
wide spectrum of roughness and cutting efficiency
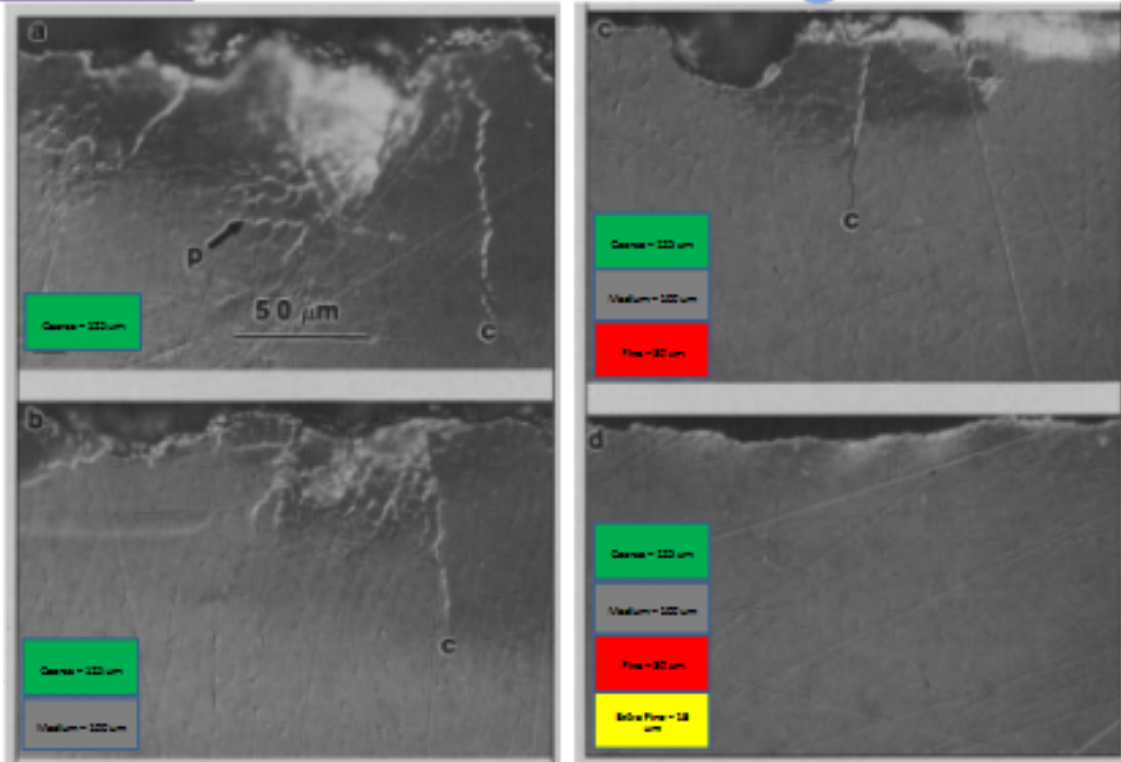
how are the roughness of diamonds classifies
diamond grits and colors based on their coarseness
super course is what color and grit #
black;150 microns
coarse is what color and grit #
green = 125 microns
medium is what color and grit #
gray = 100 microns
fine is what color and grit #
red = 30 microns
extra fine is what color and grit #
yellow = 15 microns
ultra fine is what color and grit #
white = 8 microns
how is enamel finishing effected by coarse grit
get a smooth effect the finner bur you use