Unit 2: Basics of Animal Cell and Organelles
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
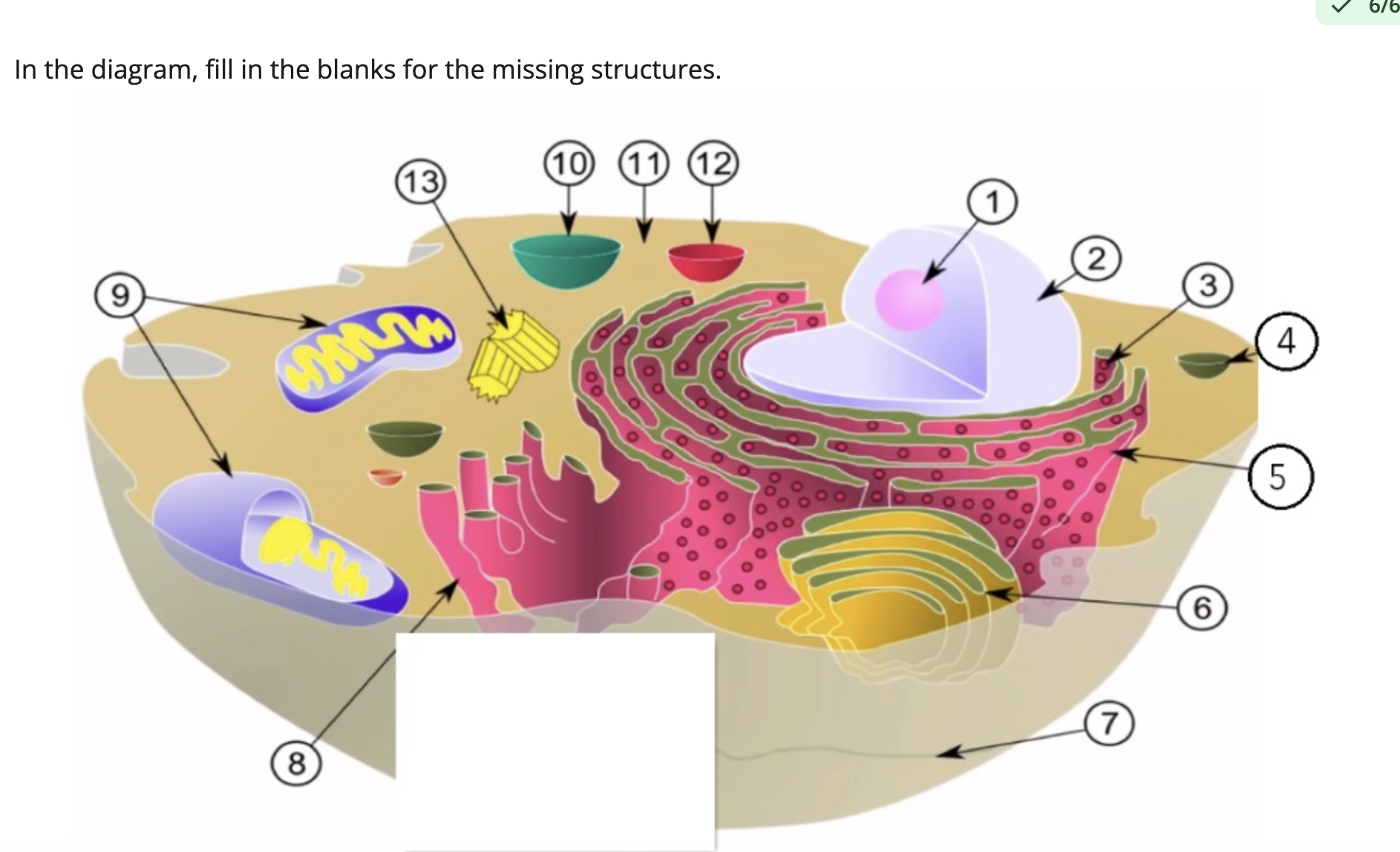
1: nucleolus
3: rough ER
6: golgi apparatus
8: smooth ER
9: mitochondria
13: centrioles
name structures 1, 3, 6, 8, 9, and 13
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms
cell → organism order
actin (provide structure), tubulin (work together w/ centrioles when cell is ready to replicate itself)
microfilaments with blank, microtubules with blank
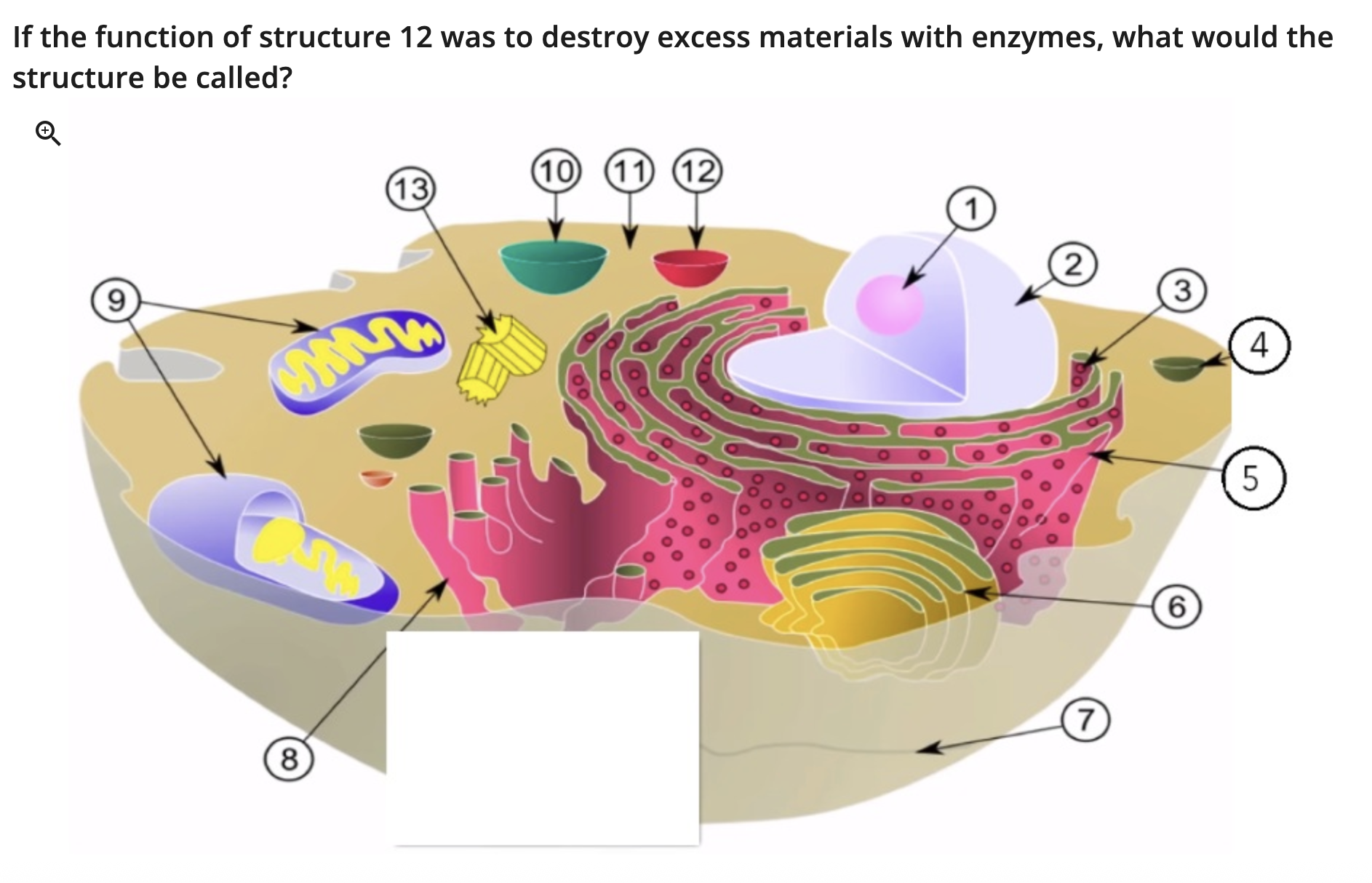
lysosome
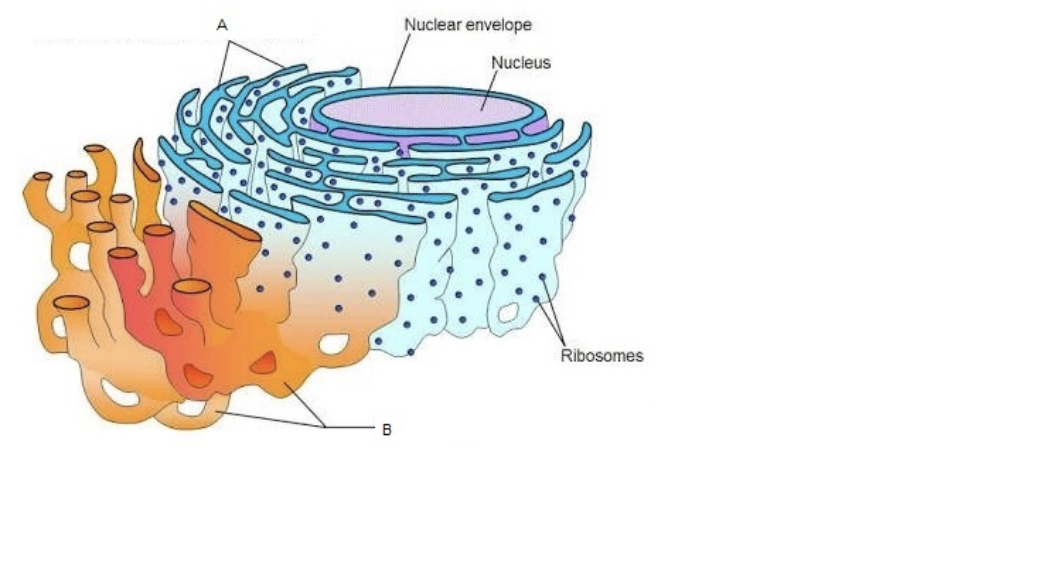
A: rough ER; aids ribosomes with protein synthesis
B: smooth ER; synthesize lipids and detox body from harmful chemicals
what are structures A and B? what are their functions?
cilia: in our throats because the cilia move mucus
microvilli: in our abdominal cavity because the organs in it need more surface area to function properly
Where in the human body would we find cells with microvilli, and where would we find cells with cilia?
exocrine
exocrine or endocrine: Sweat glands secrete water and salts onto the surface of the skin to release heat.
endocrine
exocrine or endocrine: The pancreatic islets release insulin into the bloodstream when blood glucose is too high.
exocrine
exocrine or endocrine: Parietal cells secret hydrochloric acid (HCl) into the stomach when food is present.
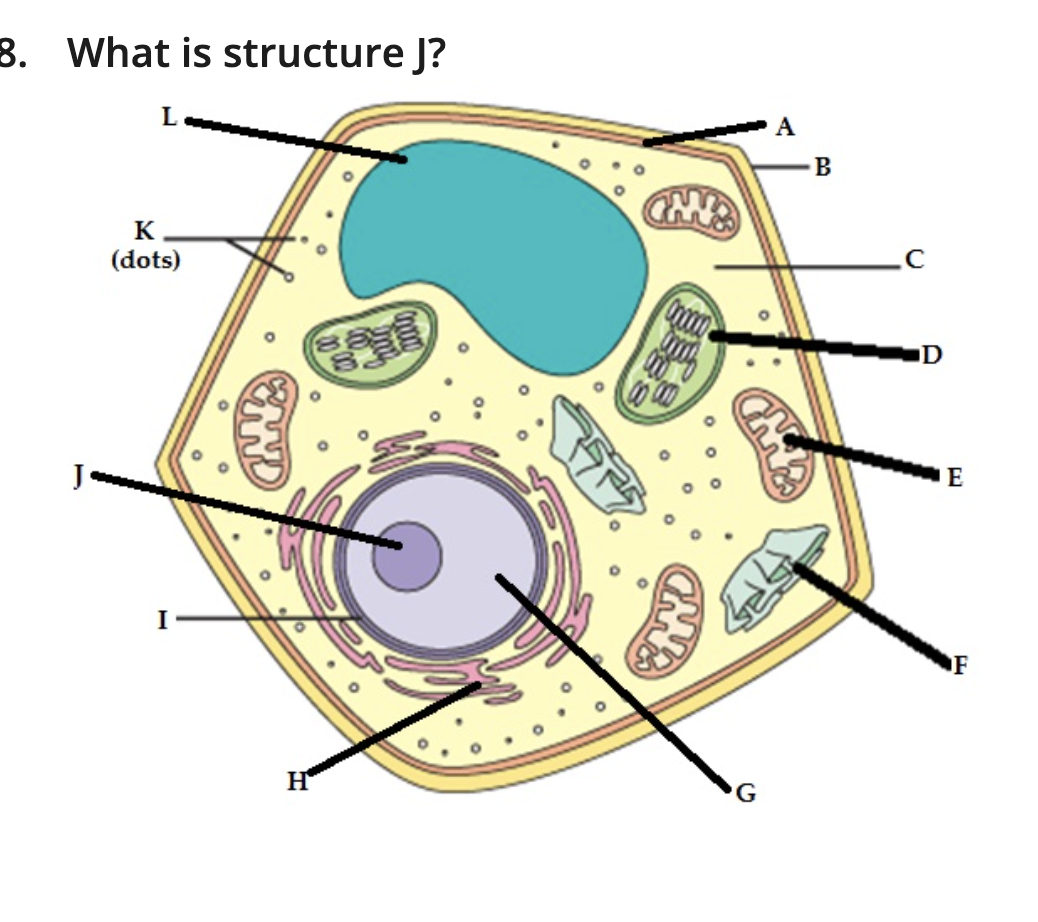
nucleolus
ribosomes
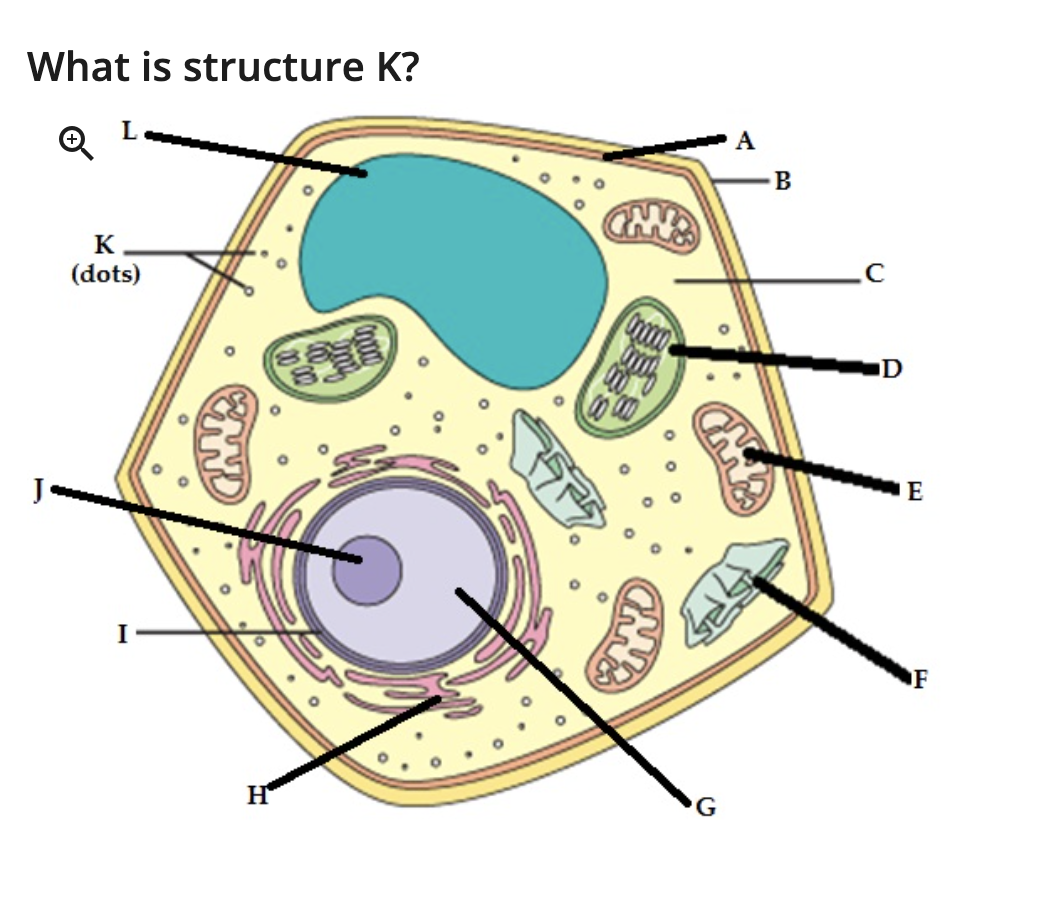
microvilli
fingerlike extensions that increase surface area
centrioles
cylindrical structures that direct chromosomes during mitosis
cilia
long, slender extensions of plasma membrane that can move independently
flagella
long, slender extensions of plasma membrane that can move independently
ribosomes
tiny particles made of RNA that build proteins
rough ER
Network of membranes covered in ribosomes; “Protein factory”
smooth ER
Membranes with no ribosomes that build lipids and carbohydrates
golgi
Flattened discs of membrane that package proteins in vesicles
vesicles
temporary storage organelles made of a phospholipid bilayer
secretory vesicle
Contain material to be released outside the cell via exocytosis
lysosomes
Digestive enzymes that break down worn cell parts, bacteria, or viruses
perioxisomes
Smaller than lysosomes; Digest fatty acids and amino acids