Lipids (classification, fatty acids, steroids, eicosanoids, vitamin D)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
lipid molecules that act like hormones; regulate inflammation, pain, fever, and smooth muscle contraction (think childbirth)
prostaglandins
lipid molecules that promote blood clotting and vasoconstriction (made by platelets)
thromboxanes
lipid molecules that are involved in inflammation and allergic response - ASTHMA (not prostaglandins)
leukotrienes
lipid molecules that are pigments found in plants that give yellow, organge and red colours (some are precursors to Vit A)
carotenoids
group of lipid compounds with Vit E activity; act as antioxidants
tocopherols
lipid molecules that are involved in electron transport and energy production in cells
quinones
two features of all lipids
soluble in solvents with low polarity
are nonpolar
what type of lipids serve as protective coatings in plants and animals?
waxes
which type of simple lipids are composed of esters of long chain fatty acids and long chain alcohols (not glycerol)?
waxes
two types of simple lipids
triacylglycerols and waxes
what type of simple lipids is composed of esters of fatty acids and glycerol?
triacylglycerols
which type of lipids made up of multiple components, usually fatty acids, an alcohol and additional molecules such as phosphates, sugars or proteins?
complex lipids
name the two types of glycolipids and then the two types of phospholipids (based on which alcohol they have as the backbone)
glycosphingolipids and glycoglycerolipids and glycerophospholipids and sphingophospholipids
two common (but not necessary) features of derived lipids
hydrocarbon rings and a long hydrocarbon side chain
compounds produced from hydrolysis of simple and complex lipids
derived lipids
five examples of derived lipids
cholesterol, steroid hormones, fatty acids, glycerol and fat soluble vitamins
classification of lipids based on structure: what are the three classes of lipid structures?
simple, complex and derived lipids
classification of lipids based on function: what are the five major functions of lipids?
energy storage
membrane components and surface coverings
signalling
cofactors
pigments
example of lipid cofactors (think vitamins)
DEKA vitamins
if a fatty acid contains double bonds is it saturated or unsaturated?
unsaturated
carbons in fatty acids are numbered from which end?
carboxylic end
how would you name a saturated fatty acid with 18 carbons?
octadecanoate
how would you name an monounsaturated fatty acid with 18 carbons?
octadecenoic acid
what is the name of the C2 carbon in a fatty acid chain? (the first carbon after the carboxylic group)
alpha
how would you name the C3 carbon in a fatty acid chain? (second carbon after the carboxylic group)
beta
how would you name the last carbon in a fatty acid chain?
omega
how would you name an unsaturated fatty acid with 18 carbons and 2 double bonds?
octadecadienoate
how would you name an unsaturated fatty acid with 18 carbons and 3 double bonds?
octadecatrienoate
Δ9 is used to denote a double bond present between which two carbons (counting from carboxylic end)
C9 and C10
Δ12 is used to denote a double bond present between which two carbons (counting from carboxylic end)
C12 and C13
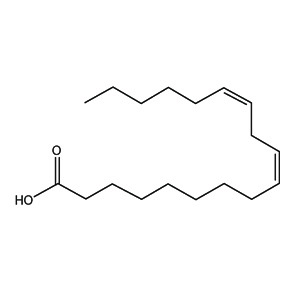
name of linoelic acid (LA) in delta notation
Δ9,12-octadecadienoic acid
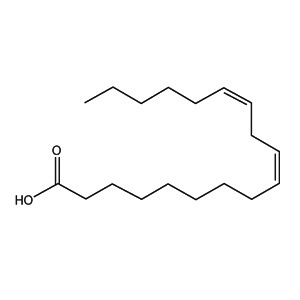
name of linoleic acid (LA) in shorthand notation
18:2-6
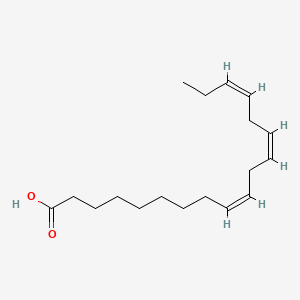
name of alpha linolenic acid (ALA) in the delta notation
Δ9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid
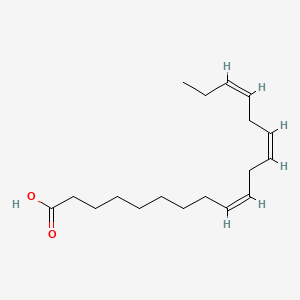
name of alpha linolenic acid (ALA) in the shorthand notation
18:3n-3
mammals cannot introduce double bonds beyond which carbon?
C9
is gamma linolenic acid (GLA) with the structure 18:3n-6 an omega 3 or omega 6 fatty acid?
omega 6
is alpha linolenic acid (ALA) with the structure 18:3n-3 an omega 3 or omega 6 fatty acid?
omega 3
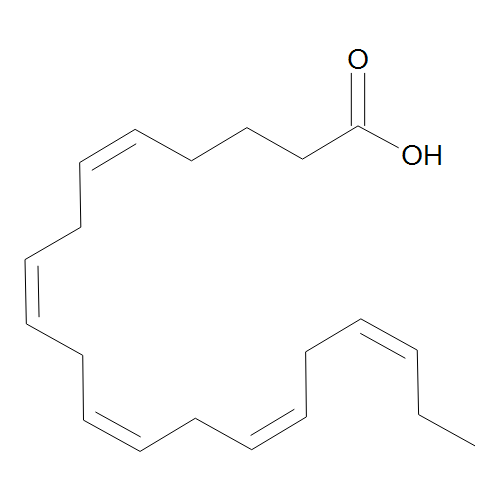
name of eicosapentaenoic acid in the shorthand notation
20:5n-3
how would you name a fatty acid with the structure 22:6n-3?
docosahexaenoic acid
how would you name a fatty acid with the structure 20:5n-3?
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
is linoleic acid omega 3 or omega 6?
omega 6
is alpha linolenic acid omega 3 or omega 6?
omega 3
example of an omega 6 PUFA synthesised by humans
arachidonic acid
example of omega 3 PUFAs synthesised by humans
epa and dha
do omega 6 PUFAs tend to produce pro or anti inflammatory metabolites? (answer with 3 words)
pro inflammatory metabolites
do omega 3 PUFAs tend to produce pro or anti inflammatory metabolites? (answer with 3 words)
anti inflammatory metabolites
are eicosanoids produced from omega 3 or omega 6 fatty acids or both?
both
3 common precursors for eicosanoids
arachidonic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid
classnof lipid based signalling molecules which act as local mediators
eicosanoids
unsaturated fatty acids are usually … at room temperature because the … interrupt regular packing of the …
liquid, double bonds, chains
the more unsaturated a fatty acid the lower of higher the melting point?
lower
components of triacylglycerols
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
two types of phospholipids
glycerophospholipids and sphingophospholipids
components of sphingophospholipids
sphingosine, 1 fatty acid, phosphate and an alcohol
components of glycerophospholipids
glycerol, 2 fatty acids, phosphate and an alcohol
four examples of alcohols found in glycerophospholipids
choline, ethanolamine, serine and inositol
components of glycosphingolipids
sphingosine, 1 fatty acid and a carbohydrate
do glycerophospholipids usually have a saturated or unsaturated FA on C1 of glycerol?
saturated
do glycerophospholipids usually have a saturated or unsaturated FA on C2 of glycerol?
unsaturated
components of lecithin (phosphatidylcholine)
glycerol, 2 fatty acids, phosphate and choline
although lecithin is sometimes used generically to refer to a wide variety of lipids it is most commonly associated with which molecule?
phosphatidylcholine
as all membrane lipids have both a hydrophobic andhydrophilic part they are said to be …
amphipathic
is cholesterol present in membranes of prokaryotic cells?
no
is cholesterol present in membranes of eukaryotic cells?
yes
is cholesterol present in membranes of chloroplasts?
no
is cholesterol present in membranes of mitochondria?
no
cholesterol is the precursor to which 5 major classes of steroid hormones?
progestogens
estrogens
androgens
glucocorticoids
mineralocorticoids
what class of steroid hormones regulates metabolism, stress response and suppress the immune system (are anti-inflammatory)?
glucocorticoids
what class of steroid hormones regulates electrolyte, salt and water balance (increase sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in kidneys)?
mineralocorticoids
cholesterol is the precursor to which three classes of biological compounds
steroid hormones
bile acids
vitamin D
leukotrienes are produced from arachidonate by which enzyme?
lipoxygenase (LOX)
prostaglandin synthase has which two distinct activities?
cyclooxygenase (COX) and peroxigenase (POX)
prostaglandin synthase produces prostaglandin H2 which is the precursor for… (3 words)
prostacyclin, thromboxanes and other prostaglandins
aspirin inhibits which enzyme
COX (1 and 2)
where are corticosteroids produced
adrenal cortex
prostaglandin H2 is converted to produce prostacyclin (PGI2) by which enzyme?
prostacyclin synthase
prostaglandin H2 is converted to produce thromboxane A2 (TXA2) by which enzyme?
thromboxane synthase
prostaglandin H2 is converted to produce various prostaglandins (PGE2, PGD2 and PGF2a) by which type enzymes? —> these enzymes are for example called PGE synthase
terminal prostaglandin synthases
the COX activity of prostaglandin synthase converts arachidonic acid to which intermediate?
PGG2
the peroxidase activity (POX) of prostaglandin synthase converts PGG2 into which molecule which acts as a precursor used by terminal synthases?
PGH2
which form of vitamin D is the active form
1,25 hydroxyvitamin D
UVB converts … to … in the skin (vit D synthesis)
7 dehydrocholesterol to cholecalciferol
in the liver … is converted to … ( first activation in vit D synthesis)
cholecalciferol to calcidiol
another names for calcidiol and calcitriol
25 hydroxy vitamin D and 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D
in the kidneys … is converted to … (second activation in vit D synthesis)
calcidiol to calcitriol
which two types of vitamin D do we get prom diets (D2 and D3)
ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol
what is the origin of ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) that we take in from the diet
fungi/yeast
what is the origin of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) that we take in from the diet
animal foods