Ochem 257-Pennington Flashcards
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
How many step(s) is E1 and Sn1?
2 steps
How many step(s) E2 and Sn2?
1 step
when we see Sn2 think…?
Stereochemistry
when we see Sn1 think….?
carbocation
when we think E1 think…..?
carbocation
when we think E2 think ..…?
strong base
What are the Leaving Groups for Sn2?
1°, 2°
What are the Leaving Groups for E2?
1°, 2°, 3°
What are the Leaving Groups for Sn1, E1?
2°, 3°
What is polar protic?
polar, and have N-H or O-H bonds
What is polar aprotic?
polar, but no O-H or N-H bonds
how to identify non polar solvent?
it has the same atoms around the central atom ex: (CH4) and it has no lone pairs
how to identify polar solvent?
it has different atoms around the central atom ex:(Cl2O) and it has lone pairs
how do I quickly identify is something is acidic?
if it has OH, NH, or SH bonds
how do I quickly identify if something is a strong base?
if its a metal combined with a hydroxide ex: NaOH, KOH, LiOH, Ca(OH)2
how do I quickly identify if something is a weak base ?
they have a pH of 7-10 Ex: pyridine (C5H5N), ammonia (NH3)
What is a rate limiting step?
the first step and it
What’s a carbocation
a positively charged carbon
What is a nucleophile?
Any atom (-) or neutral that has an unshared pair of electrons
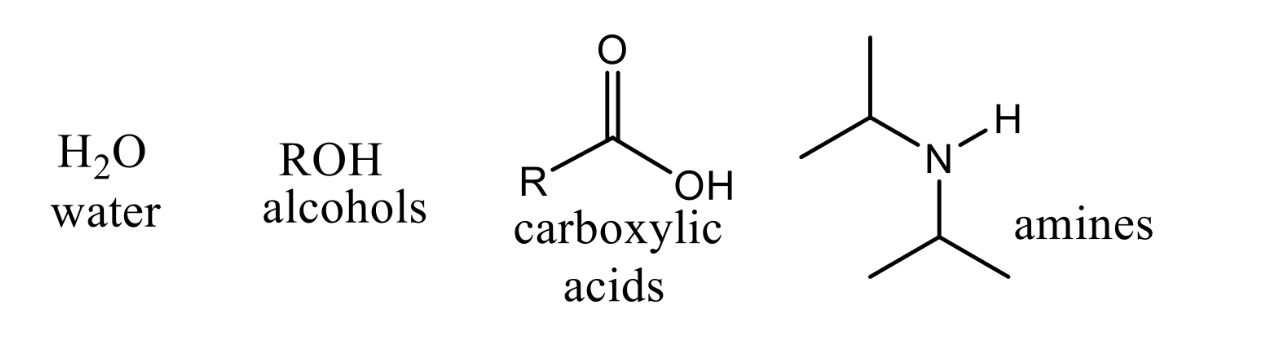
What kind of solvents are these?
Polar-Protic Solvents
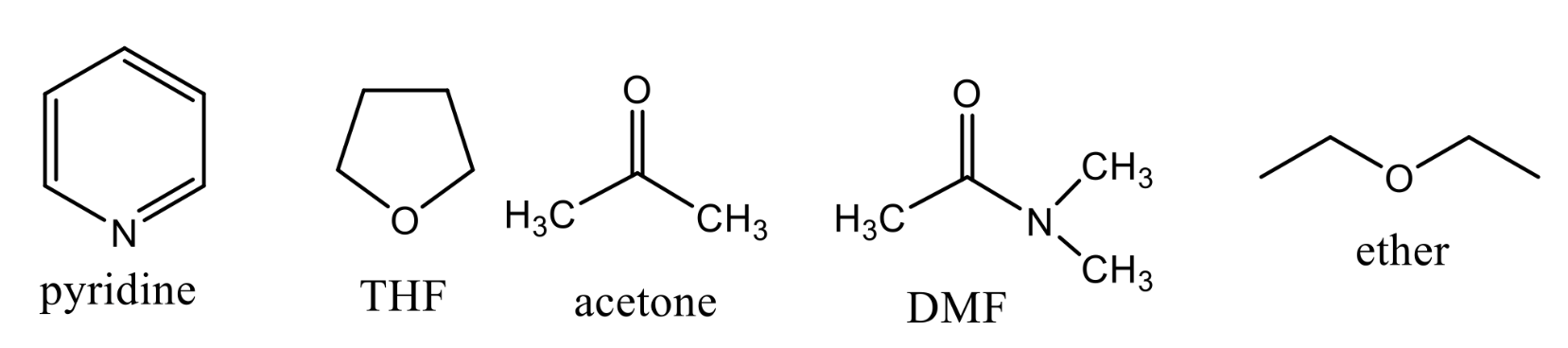
What kind of solvents are these ?
Polar-Aprotic
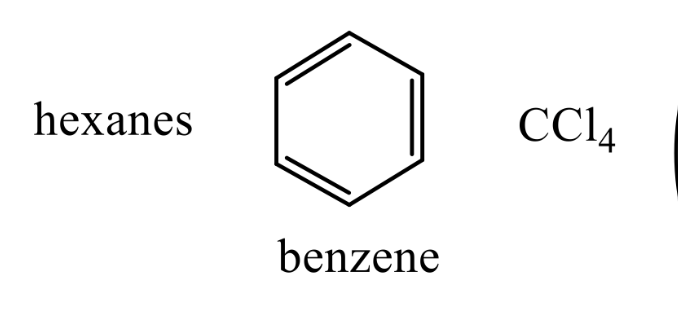
What kind of solvents are these ?
Non-Polar
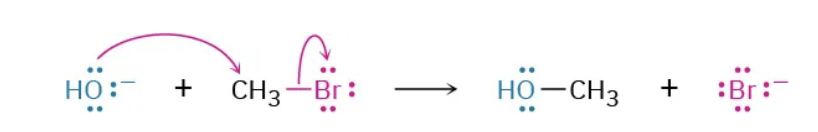
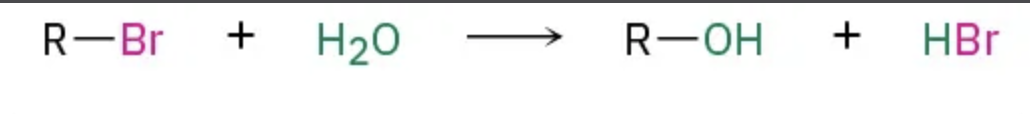
What kind of reaction is this ?
SN2
What kind of reaction is this ?
SN1
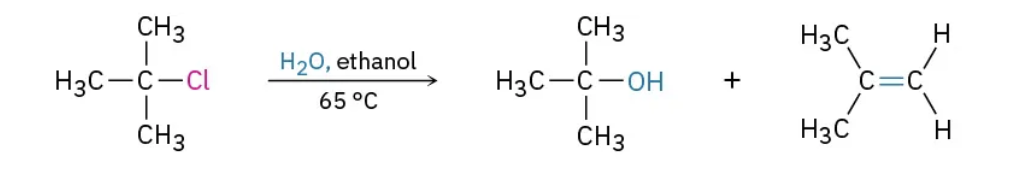
What kind of reaction Is this ?
E1
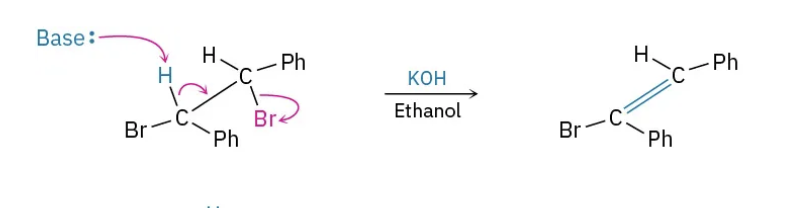
What kind of reaction is this?
E2
What’s an Alkane ?
hydrocarbon with only single carbon-carbon bonds
What’s an Alkene?
hydrocarbon with at least one carbon-carbon double bond
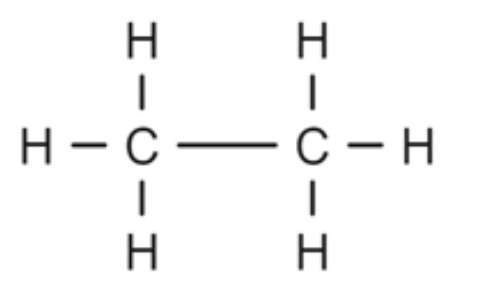
Alkane or Alkene?
Alkane
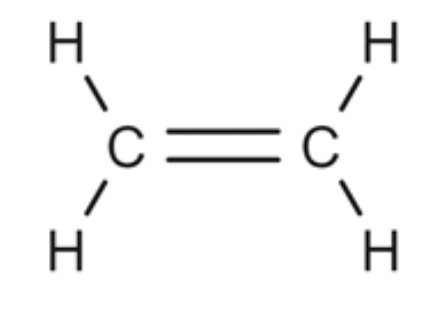
Alkane or Alkene?
Alkene
What is Allylic position?
When an atom is 2 bonds away from a double bond
Parent name for 1 carbon?
methane
Parent name for 2 carbons?
ethane
Parent name for 3 carbons?
propane
Parent name for 4 carbons?
butane
Parent name for 5 carbons?
pentane
Parent name for 6 carbons?
hexane
Parent name for 7 carbons?
heptane
Parent name for 8 carbons?
octane
Parent name for 9 carbons?
nonane
Parent name for 10 carbons?
decane
What does chiral mean?
not superimposable (it is asymmetrical)
What is a monochlorated product?
a compound that has been created by replacing a hydrogen with a chlorine atom
What is a chiral center ?
an atom that is bonded to 4 different groups
If you see a double bond what reactions should come to mind?
Elimination and bromination
What position does bromination happen at?
Allylic position
What reagents should we use for alcohol ?
HCl, HBr, or HI
What reagents should we use for Bromination?
Br2, NBS, PBr3, HBr
What reagents should we use for Allylic Bromination?
NBS
What reagents are used for Gringard reagents?
Ether or THF
What is a Gringard Reagent reaction?
When either (Cl, Br, or I) react with (Mg) and either (THF or Ether) to form (R-Mg-X) products
What is Alcohol ?
when an alkyl group is bonded with an OH
(R-OH)
What reagents should be used for SN1, E1, and E2 reactions?
Water (H2O), Alcohols (ROH), Carboxylic Acids (ROOH), Amines
What reagents should be used for SN2 reaction?
pyridine, THF, Acetone, DMF, Ether, DMSO, Acetonitrile
What is an isomer ?
a molecule with the same formula but different arrangement
What is a enantiomer ?
molecules that are mirror images of each other (non-superimposable)
What is a stereoisomer?
same formula and arrangement just have different 3-dimentional orientation
What is achiral?
symmetrical arrangent aka meso compounds
What is “S” configuration?
(sinister) “left” counter clockwise configuration around chiral center
What is “R” configuration?
“right” clockwise configuration around chiral center
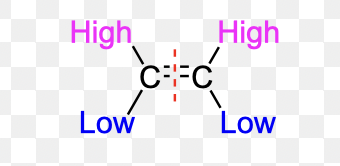
What is Z configuration?
When 1st priority substituents are on the same side of the double bond
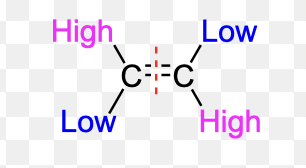
What is E configuration?
When 1st priority substituents are on the opposite sides of the double bond.
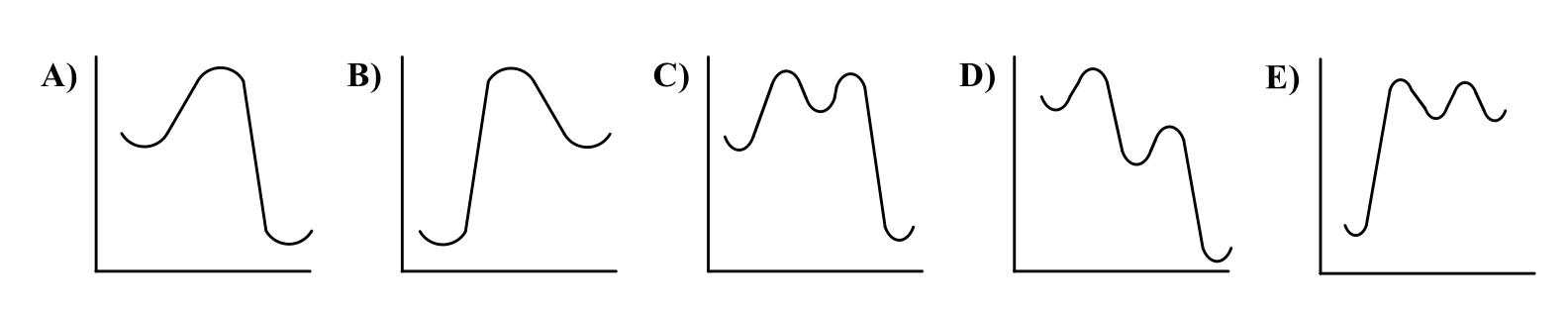
Which reaction energy curve is consistent with an SN1 reaction?
C
If the reagent concentration is doubled what would happen to the rate of the reaction?
The rate would not change