Module 7 - Leader Values and Ethics
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards created based on the lecture notes covering leader values, ethics, and related concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the definition of Values?
Values are things that people consciously or unconsciously want or seek to attain
What does Value-Percept Theory state?
It argues that job satisfaction depends on whether employees perceive that their jobs supply the things that they value.
What are the 5 things that determine Job Satisfaction?
Pay Satisfaction (Paywant - Payhave) * Payimportance
Promotion Satisfaction (Promotionwant - Promotion have) * Promotionimportance
Supervision Satisfaction (want - have) * importance
Coworker Satisfaction (w - h) * i
Satisfaction with the work itself (w - h) * i
Of the 5 things that determine Job Satisfaction, what is the order of importance from least important to more important. Why?
Pay (~ 20%)
Promotion (~40%)
Coworker (~50%)
Supervision (~52%)
Satisfaction with the work itself (~70%)
The things that are most important are the things that you deal with on a daily basis, and what you spend the majority of your time doing.
What are Cultural Values?
Shared societal beliefs about appropriate conduct
Cultures provide societies with their own distinct personalities
Cultural values reflect the way people think things should be done in a given society
Cultural values affect the expression of personality traits and belief systems
What is Personality?
The structures and propensities inside a person that explain his or her characteristic patterns on thought, emotion, and behavior
What are Personality Traits?
Recurring trends for people’s responses to their environment
What are Ethics?
The degree to which behaviors are in accordance with generally accepted moral norms
What is Moral Identity?
The degree to which a person views himself or herself as a moral person
What are Moral Principles?
Prescriptive guides for making moral judgments.
What are the two types of Moral Principles, and what are the descriptions of the specific principles of them?
Consequentialist
Utilitarianism - Is the act “good”? An act is moral right if it results in the greatest amount of good for the most people
Egoism - Is the decision maker is free to decide? An act is morally right if the decision maker freely decides to pursue either short-term or long-term interest.
Nonconsequentialist
Ethics of duties - Does the act do harm? An act is morally right if it fulfills the “categorical imperative” - an unambiguously explicit set of three crucial maxims: (a) the act should be performable by everyone with no harm to society; (b) the act should respect human dignity; (c) the act should be endorsable by others
Ethics of rights - Do you respect the rights of others? An act is morally right if it respects the natural rights of others, such as the right to life, liberty, justice, expression, association, consent, privacy, and education
Virtue Ethics - Are you trying to be a good person? an act is morally right if it allows the decision maker to lead a “good life” by adhering to virtues like wisdom, honesty, courage, friendship, mercy, loyalty, modesty, and patience
What is Ethical Leadership?
Leadership processes that demonstrate a pattern of moral and normatively appropriate behavior
Conform with moral norms
Engage in values-based behaviors
Build trust
What are Ethical Leader Behaviors?
Do you care, and do you try
Focus on processes and outcomes
Make informed decisions
Serve as a role model
What are the four components of Ethical Decision-Making?
Moral Awareness - when an authority recognizes that a moral issue exists in a situation
Moral Judgment - when an authority can identify the “right” course of action
Moral Intent - the extent to which the authority is committed to the moral course of action
Ethical Behavior.- following through with the potential consequences of your decisions
What are the Individual Factors and Situational Factors of Ethical Decision Making?
Individual Factors: Good Apples vs Bad Apples
Specific People engaging in behaviors
Situational Factors: Good Barrels vs Bad Barrels
Organizations engaging in behaviors
What does Communication involve?
The process by which information and meaning is transferred from a sender.
What are examples of Communicator Issues?
Communication competence - skills
Noise - interferences (what is happening in the background?)
Information richness - amount and depth of information. Being concise is important (pack in info without leaving out info - balance)
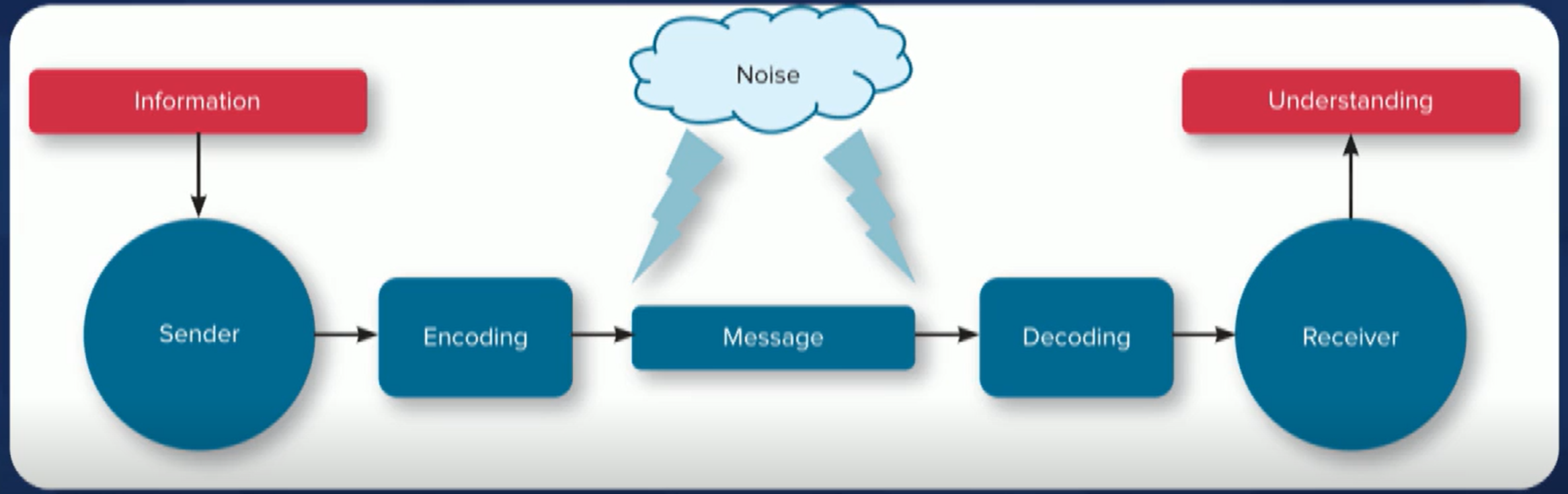
What is the Communication Process?
Information → Sender → Encoding
→ (NOISE) MESSAGE (NOISE) →
Decoding → Receiver → Understanding
What is Essentialism according to Greg McKeown?
The weight of overcommitment can decrease your well-being
Focus on prioritizing what truly matters
Lead an intentional and meaningful life
The disciplined pursuit of less by prioritizing what truly matters and leading an intentional and meaningful life.
What are the key challenges to Essentialism?
Overwhelming amounts of choices, information, opportunities, and obligations that lead to a lack of focus and purpose.
What are the Key Principles of Essentialism?
Eliminate or reduce nonessential commitments and distractions
Choose to engage in intentional decision-making that is aligned with your values and ethics
Learn how to say “no”
What are (Mac)Key Takeaways?
Busyness does not equal productivity
Protect your time and energy for your priorities
Focus on simplicity, purpose, and play