Anatomy exam chapters 1 - 4 mcgraw hill
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What is anatomy?
study of structure
What is physiology?
Study of function
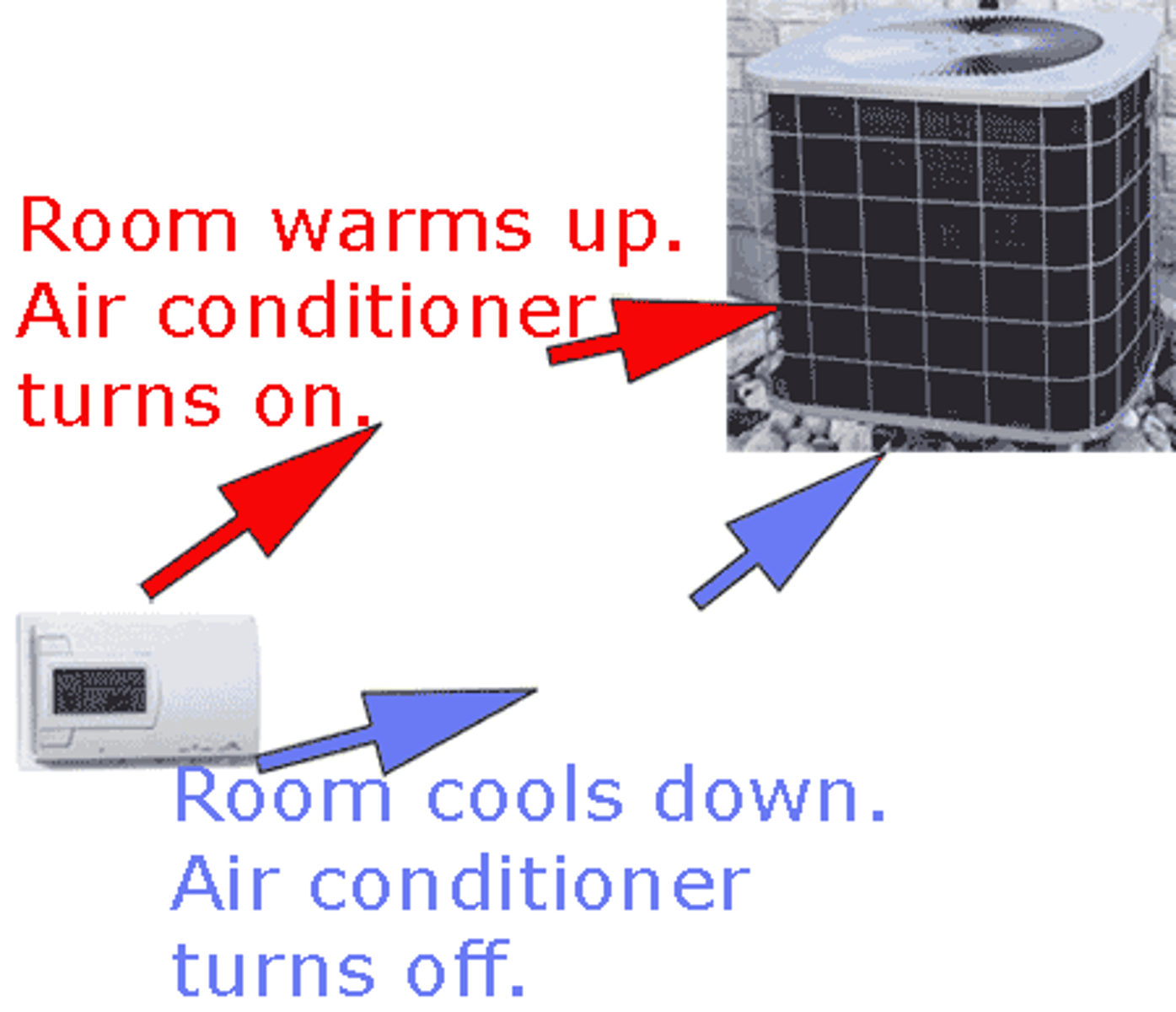
What is meant by the term homeostasis?
It is the ability of an organism to monitor conditions and maintain them
Negative feedback
The mechanism is used to maintain homeostasis primarily.
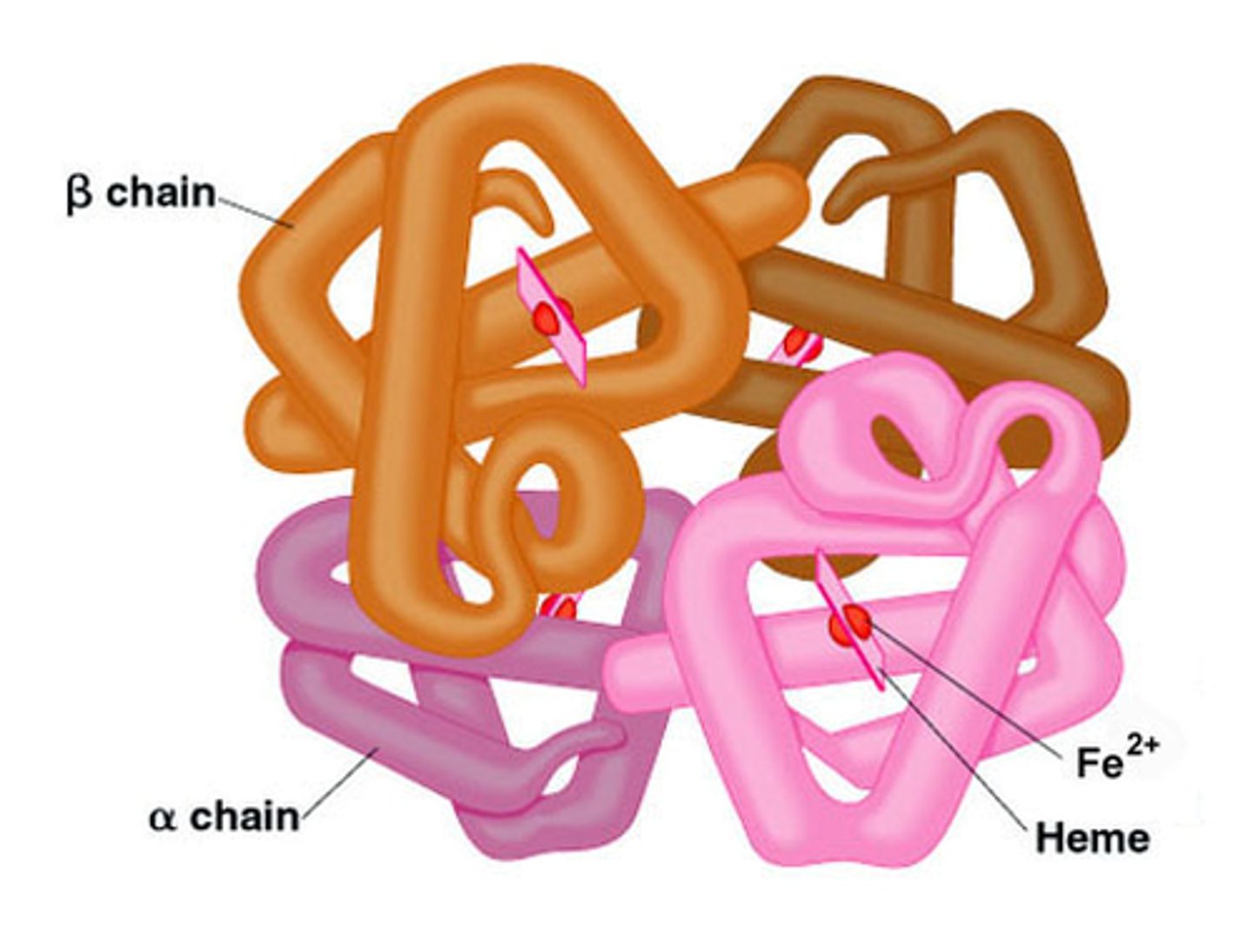
What happens if homeostasis is lost?
sickness - disease - death
Place in order, from simplest to most complex, the organization of the body.
Chemical Level
Cellular Level
Tissue Level
Organ Level
Organ system level
Organismal Level
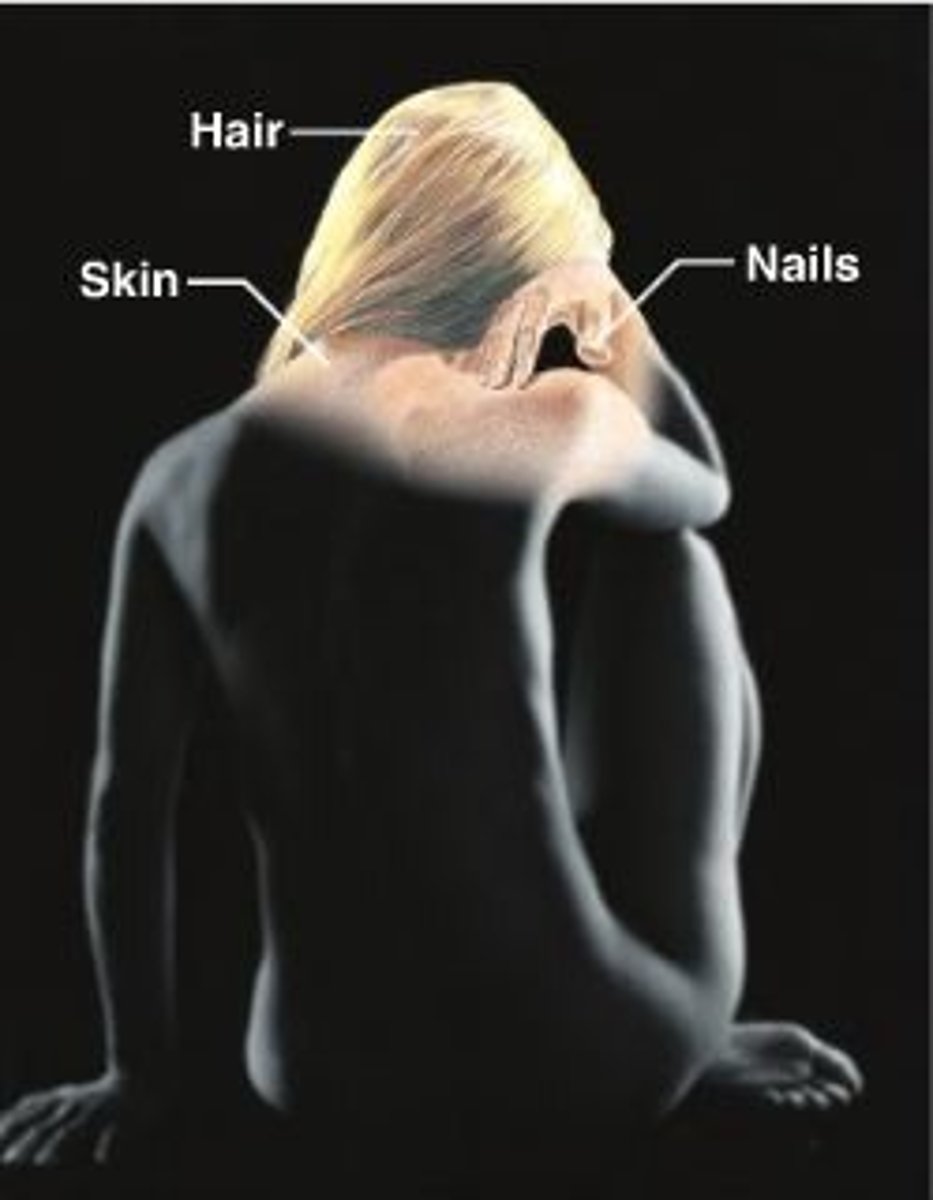
integumentary system
Protects and regulates body temperature. Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail
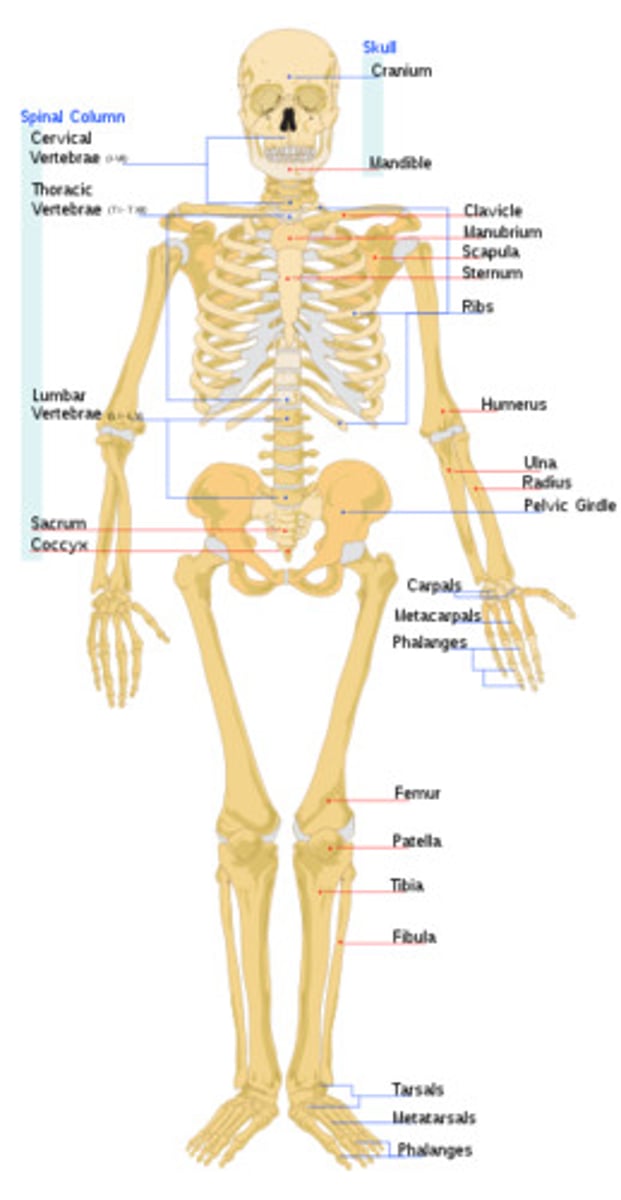
skeletal system
Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to support movement. Made up of bones and joints
Muscular System
Consists of skeletal muscles, tendons that connect muscles to bones, and ligaments that attach bones together to form joint. Allows manipulation of the environment, movement, maintains posture, and produces heat.
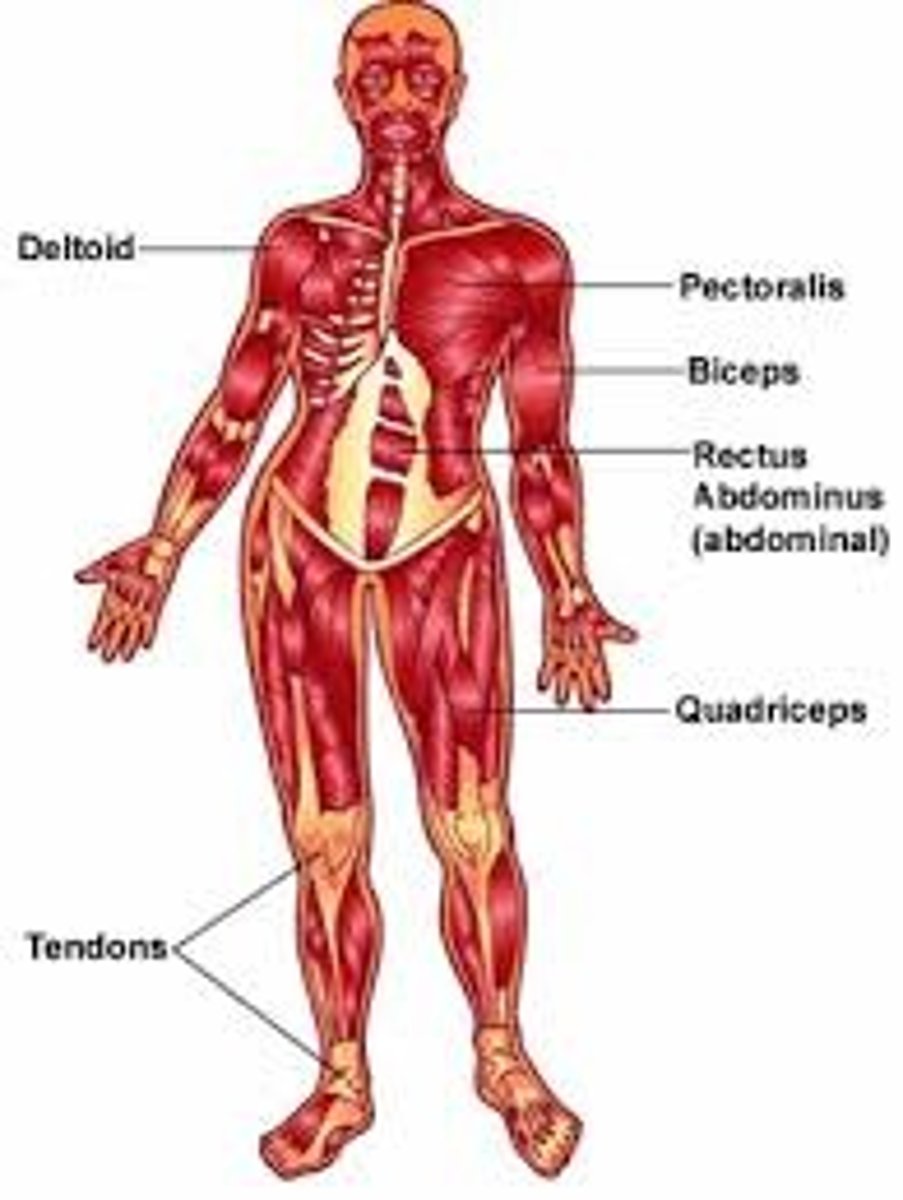
nervous system
A conglomeration of billions of cells specifically designed to provide a communication network within the human body. Brain, spinal cord, peripheral and central nervous system
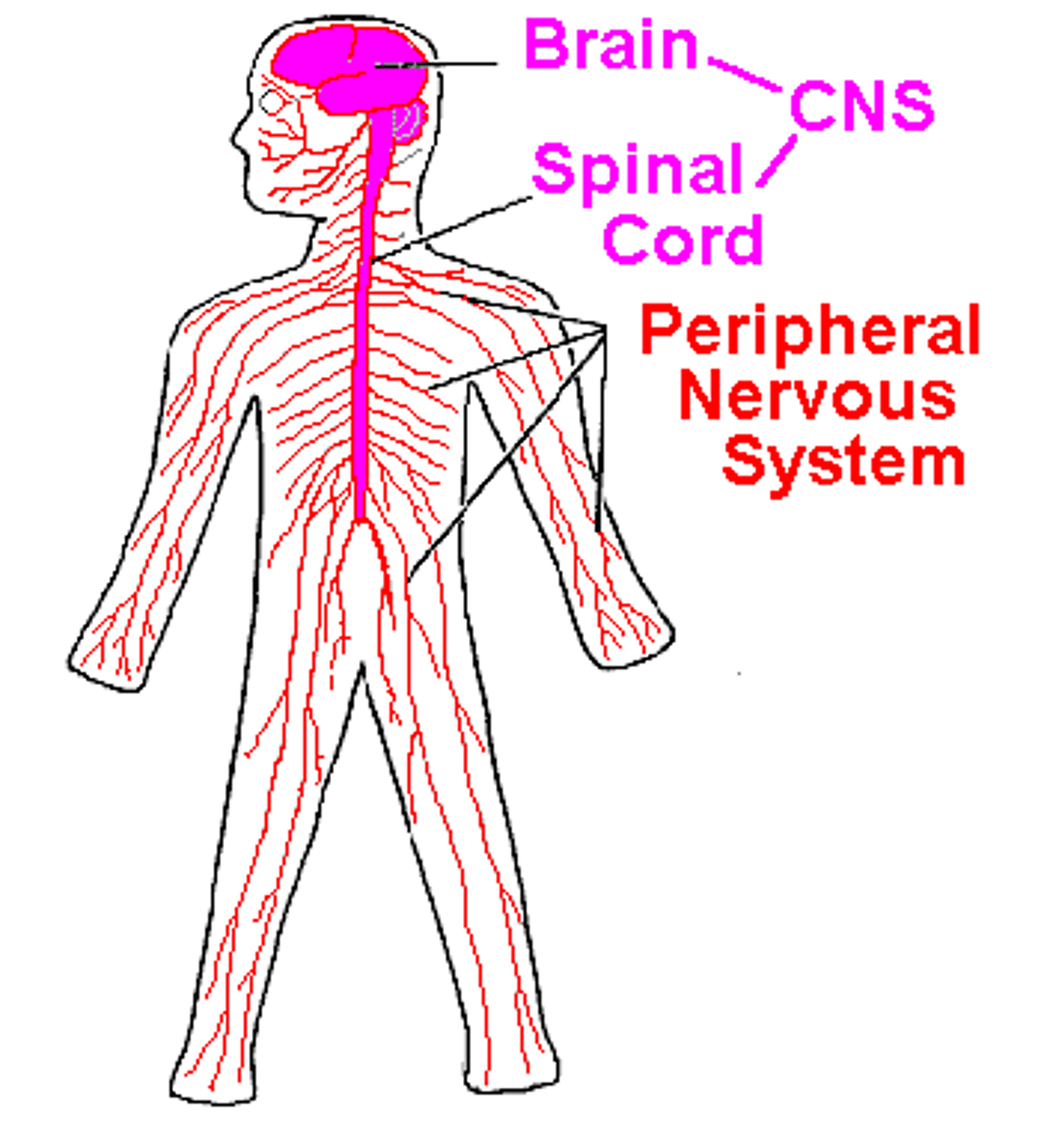
endocrine system
Consists of glands that control many of the body's activities by producing hormones such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells.
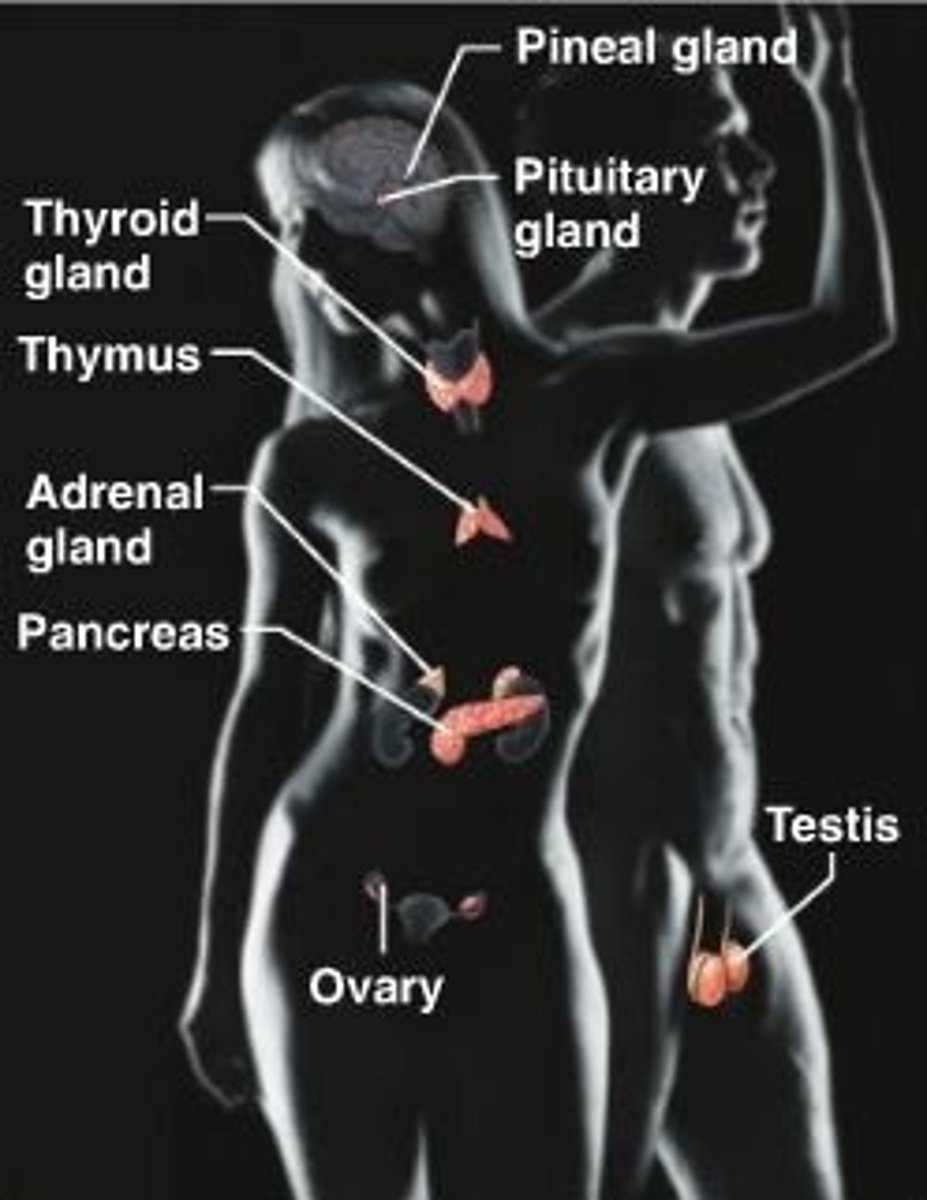
lymphatic system
Composed of a network of vessels, ducts, nodes, and organs. Provides defense against infection. Transports and filters lymph from the tissues into the blood.
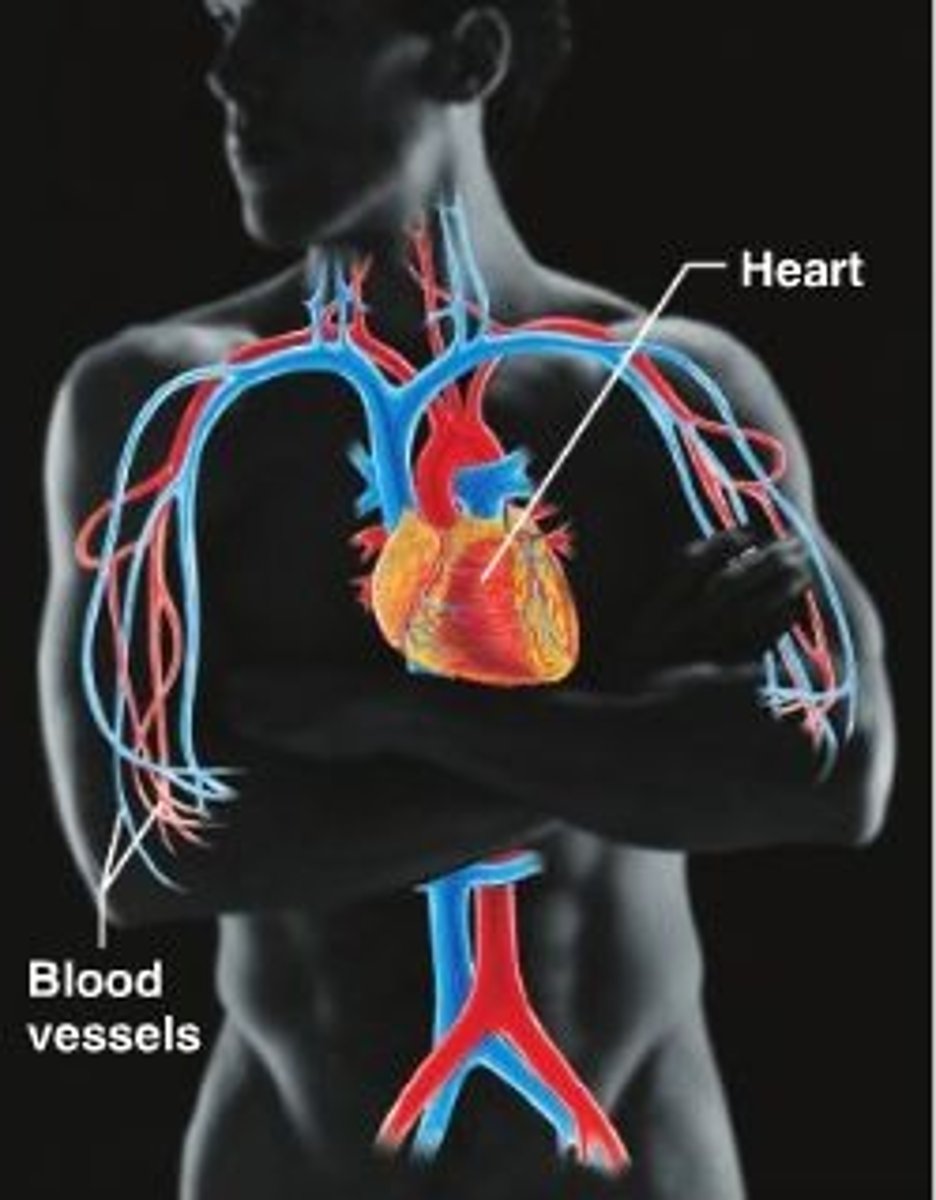
cardiovascular system
The transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes; composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
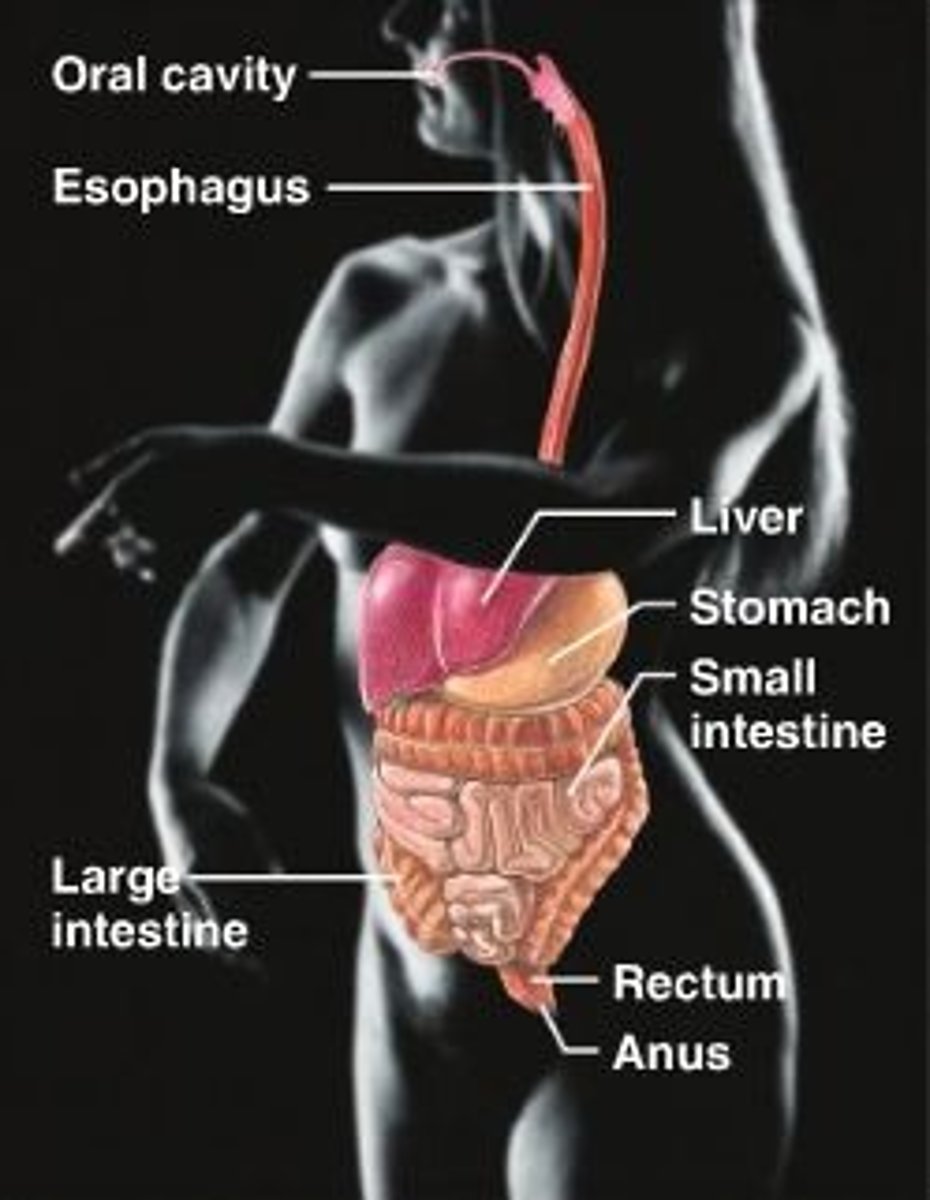
digestive system
Breaks down food into smaller molecules. Absorbs these nutrients into the body. Oral cavity, liver, stomach, intestines
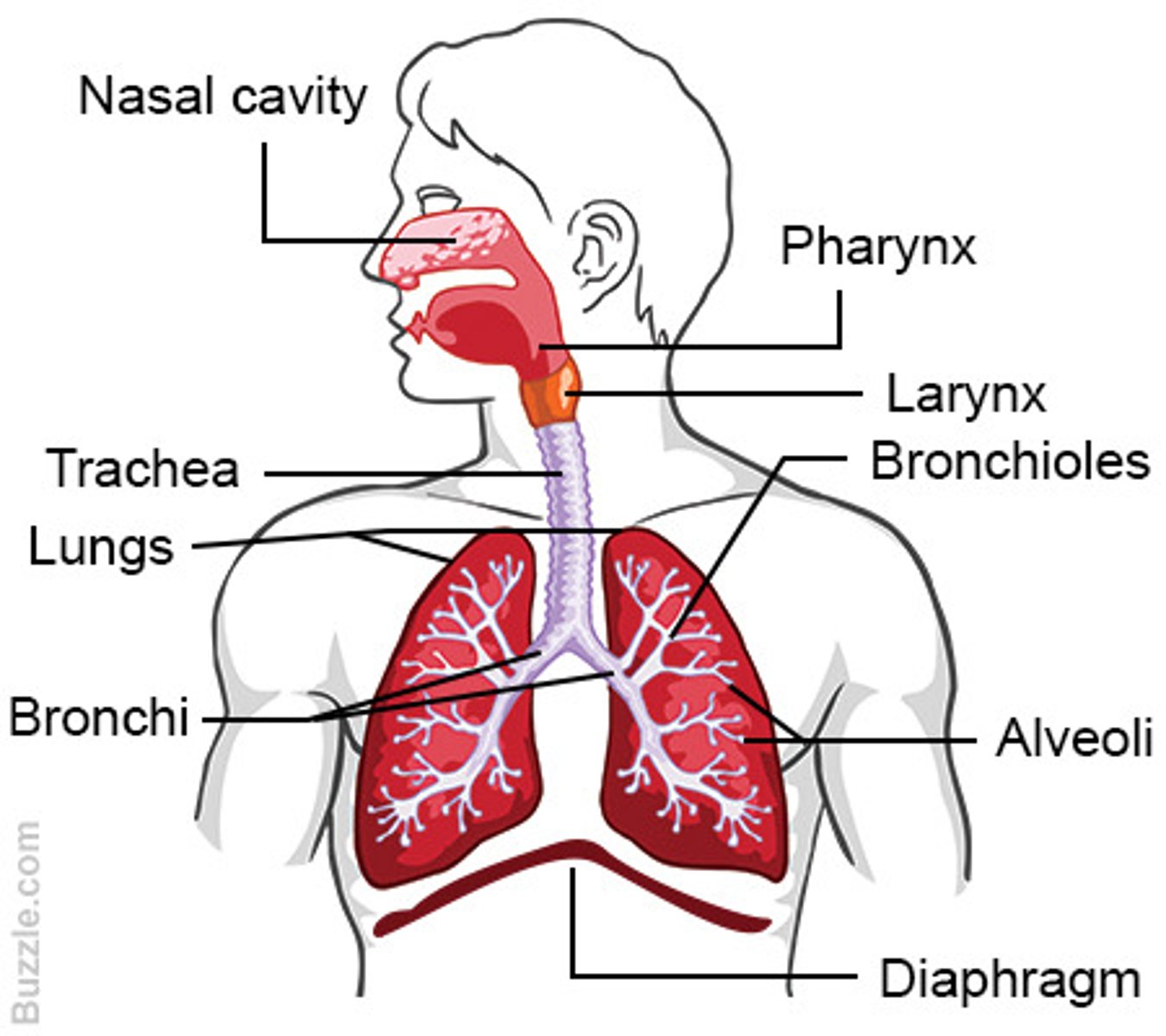
Respitory system
the organ system that brings oxygen to body cells and removes waste gas. Lungs, bronchi, trachea
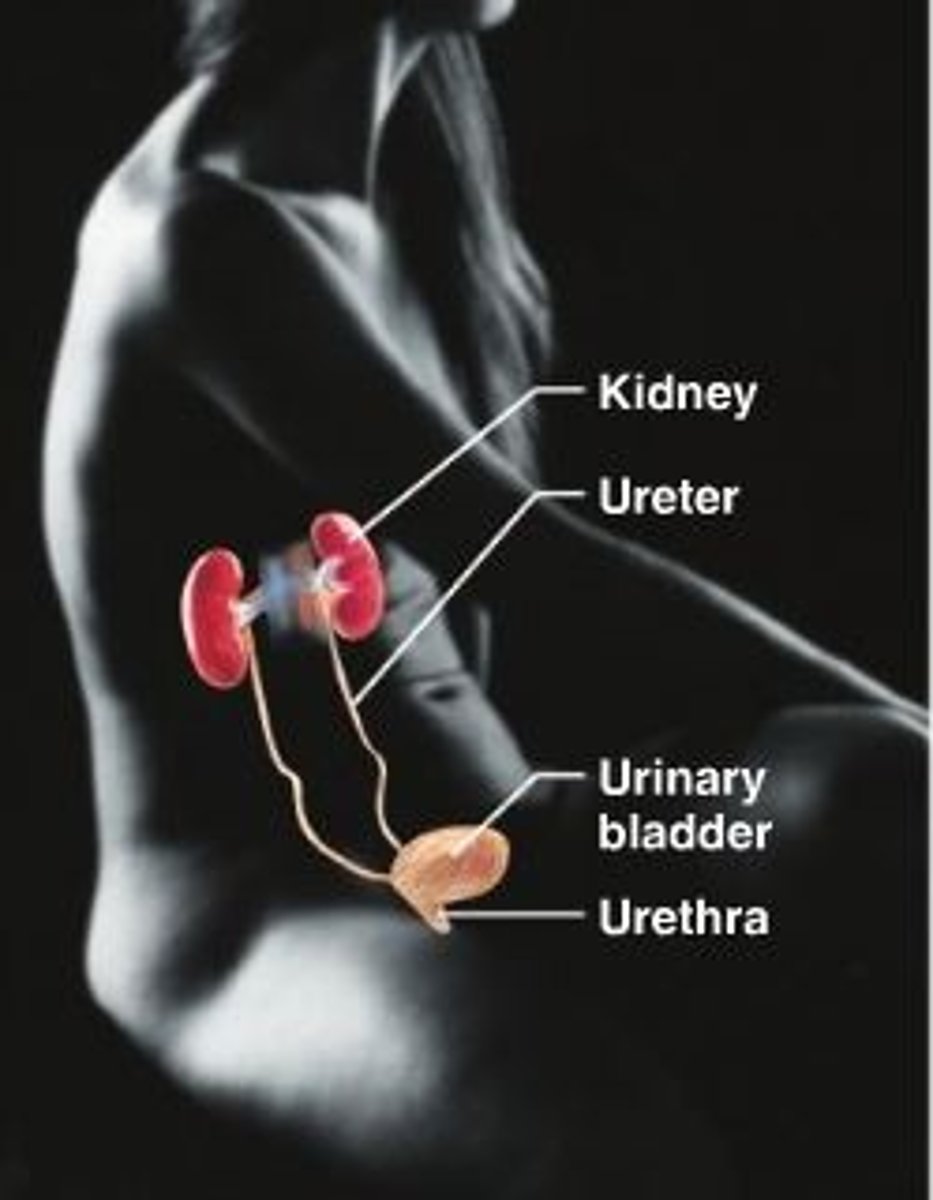
urinary system
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body. Regulates water and salt balance, electrolyte and acid-base balance of the blood.
reproductive system
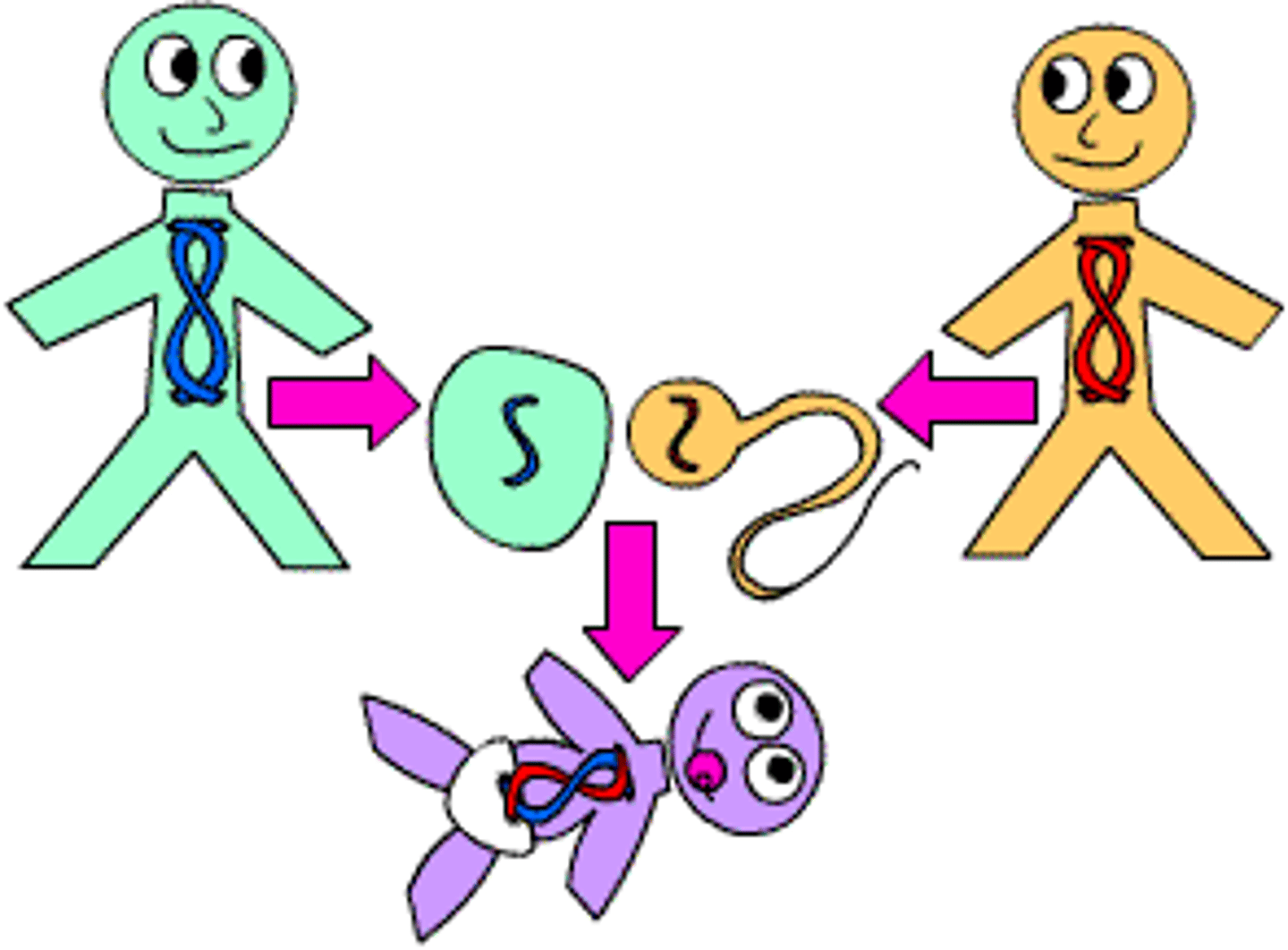
Reproduce offspring- produce male sex cells and female sex cells
Atom
Basic unit of matter
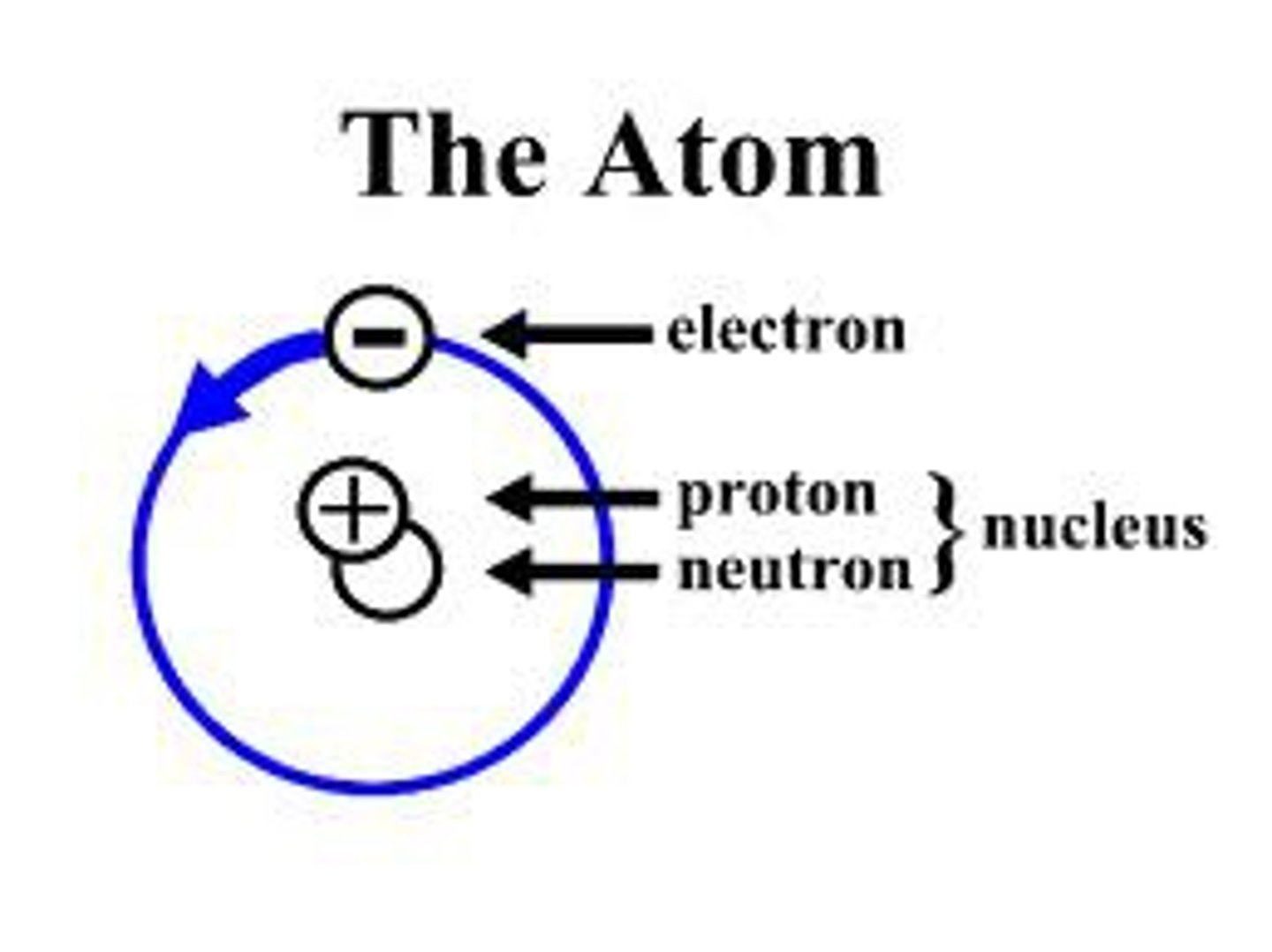
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom

Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge that orbits the nucleus of an atom
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
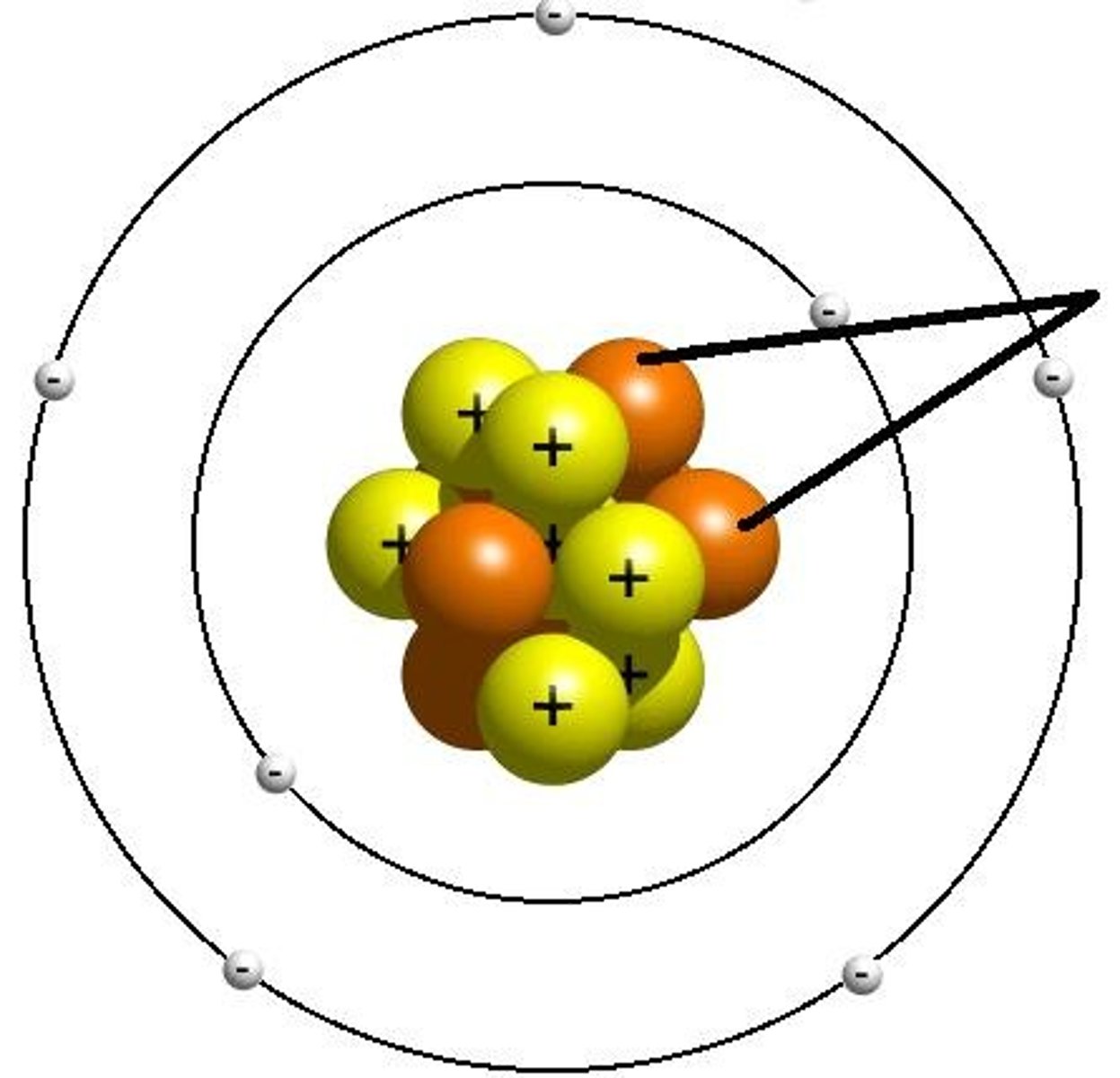
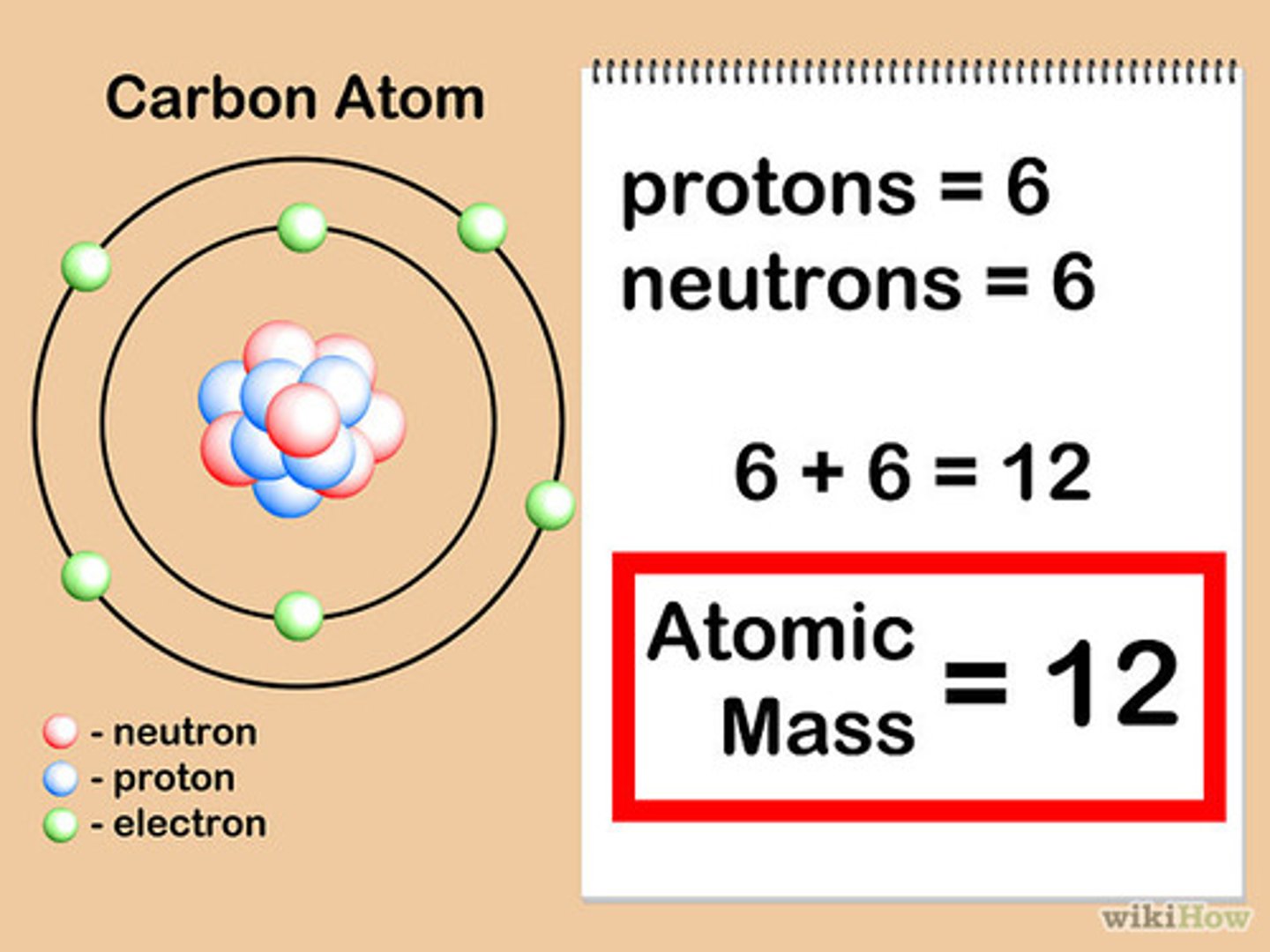
How is an atomic number determined?
By the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines an element's atomic number.
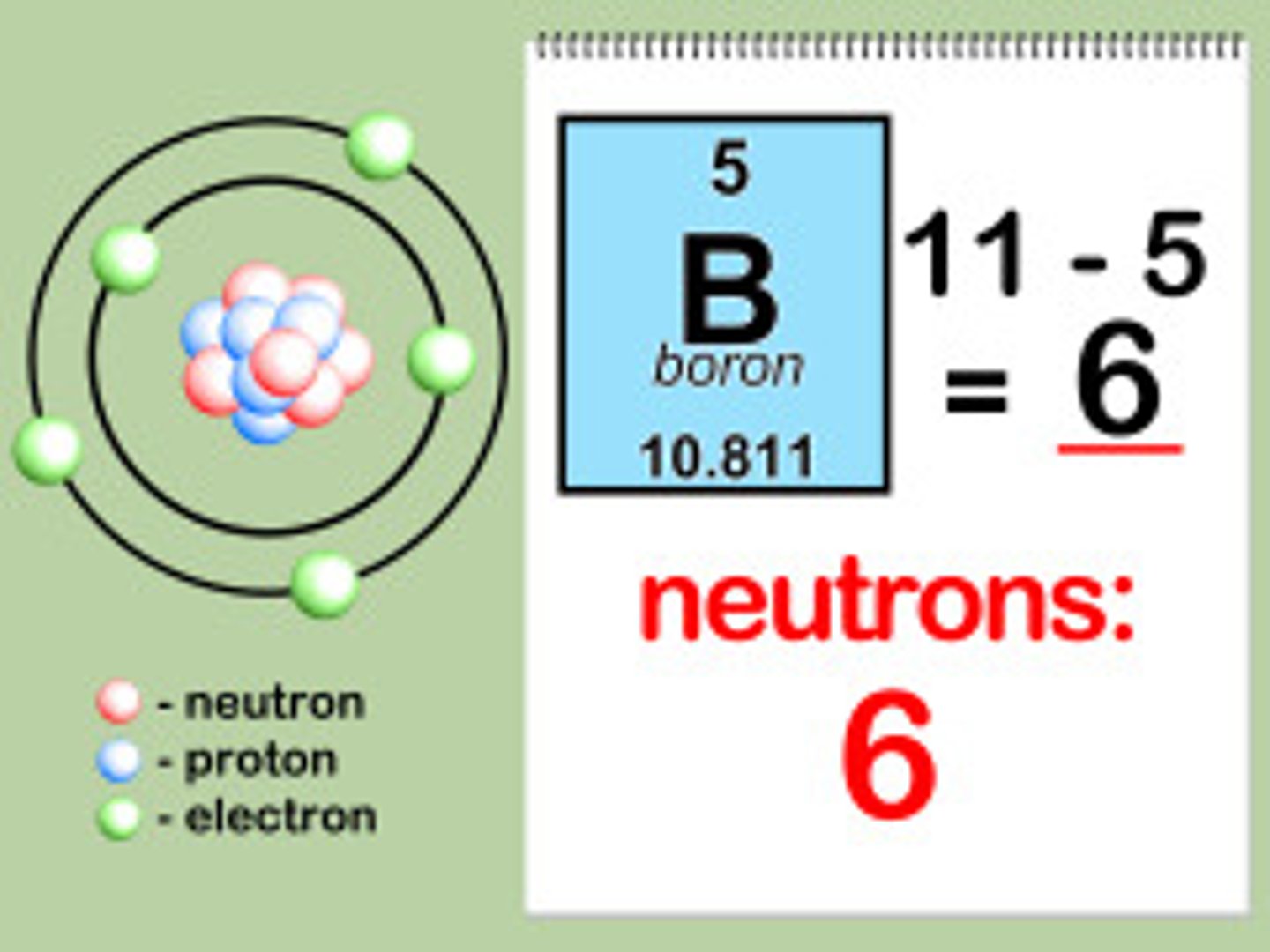
How is atomic mass determined?
By adding the numbers of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Ions
positively or negatively charged atoms due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
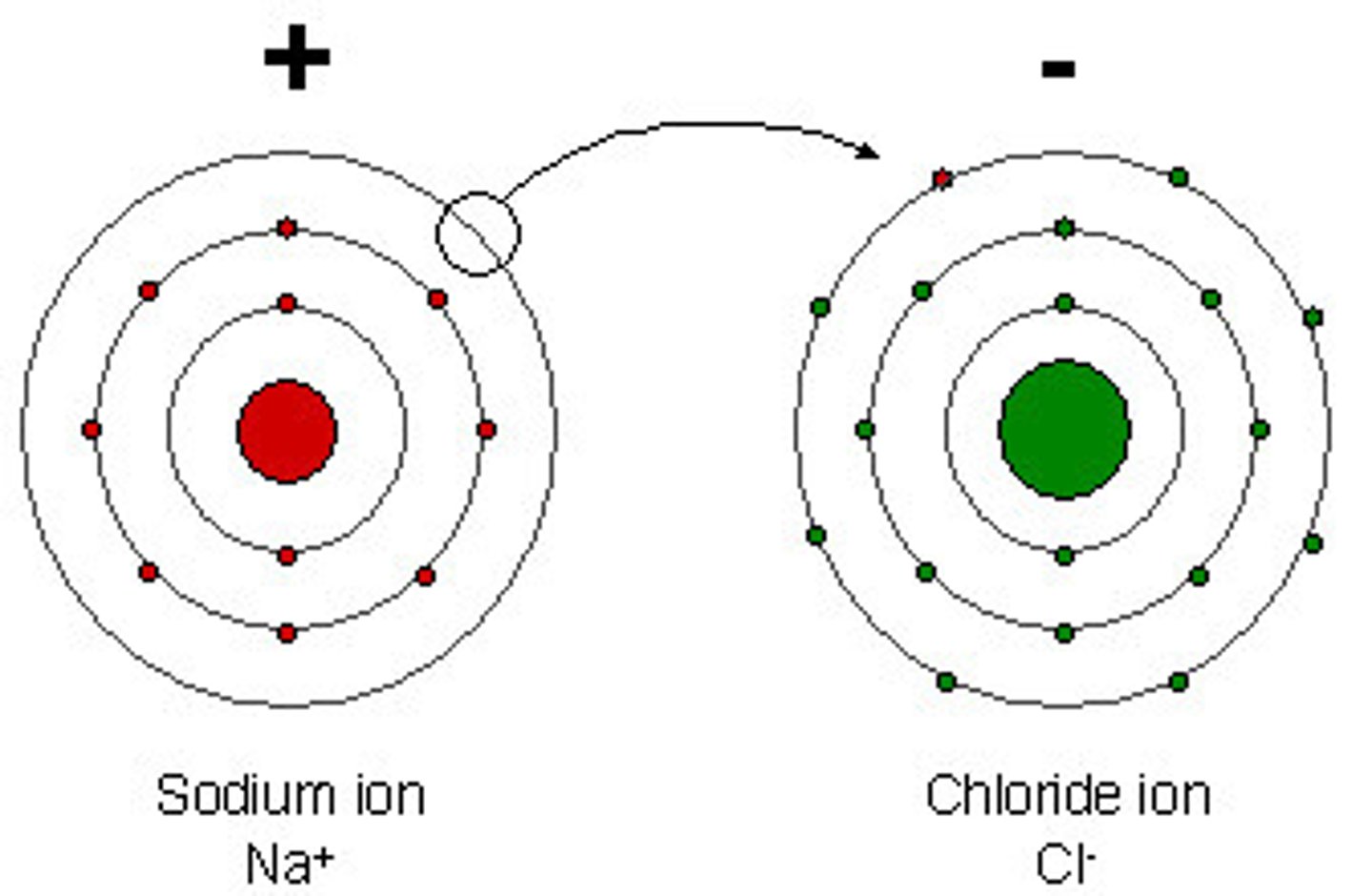
Anion
a negatively charged ion due to gaining one or more electrons
Cation
A positively charged ion due to gaining one or more protons

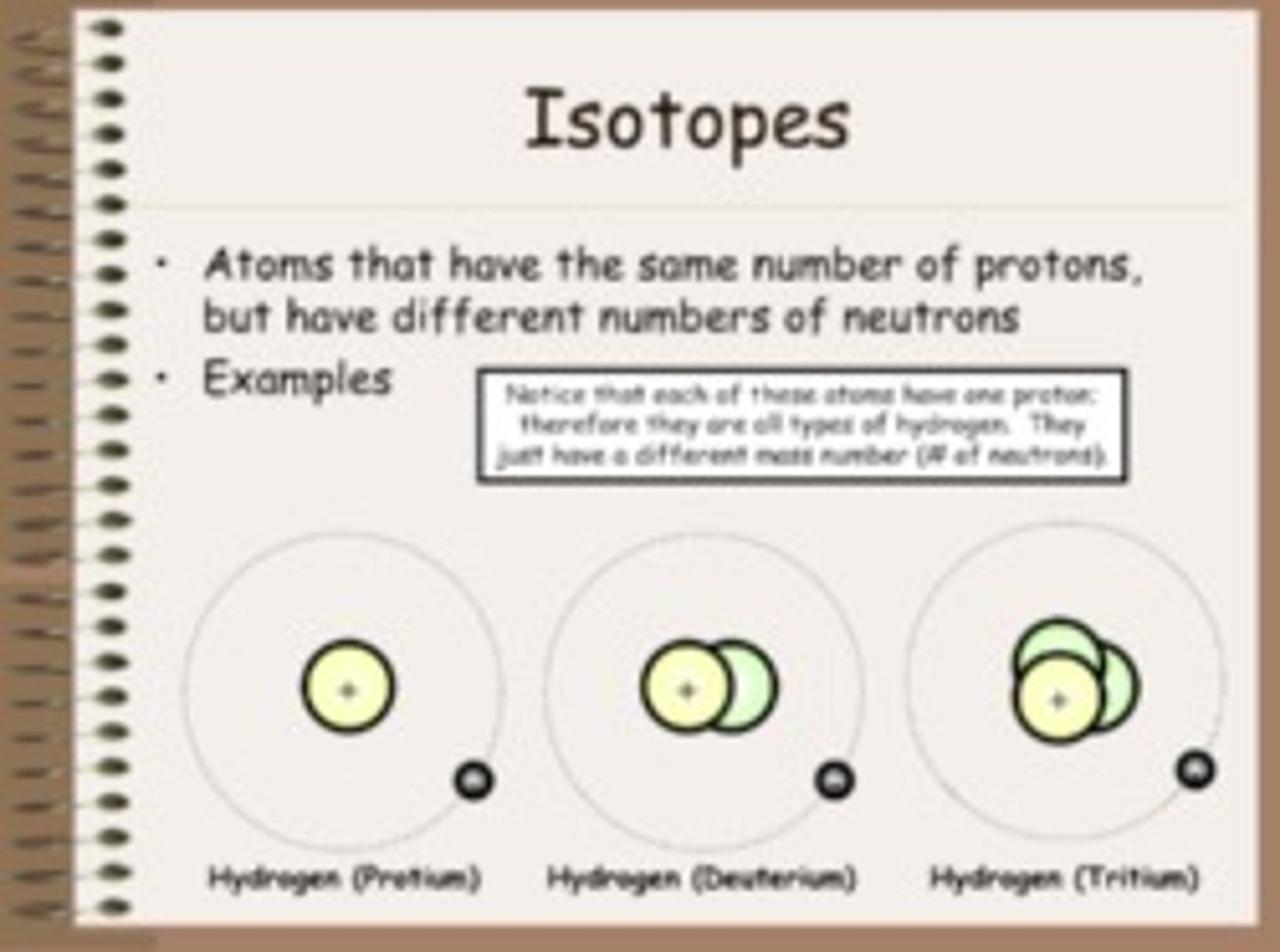
Isotope
An atom with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons from other atoms of the same element.
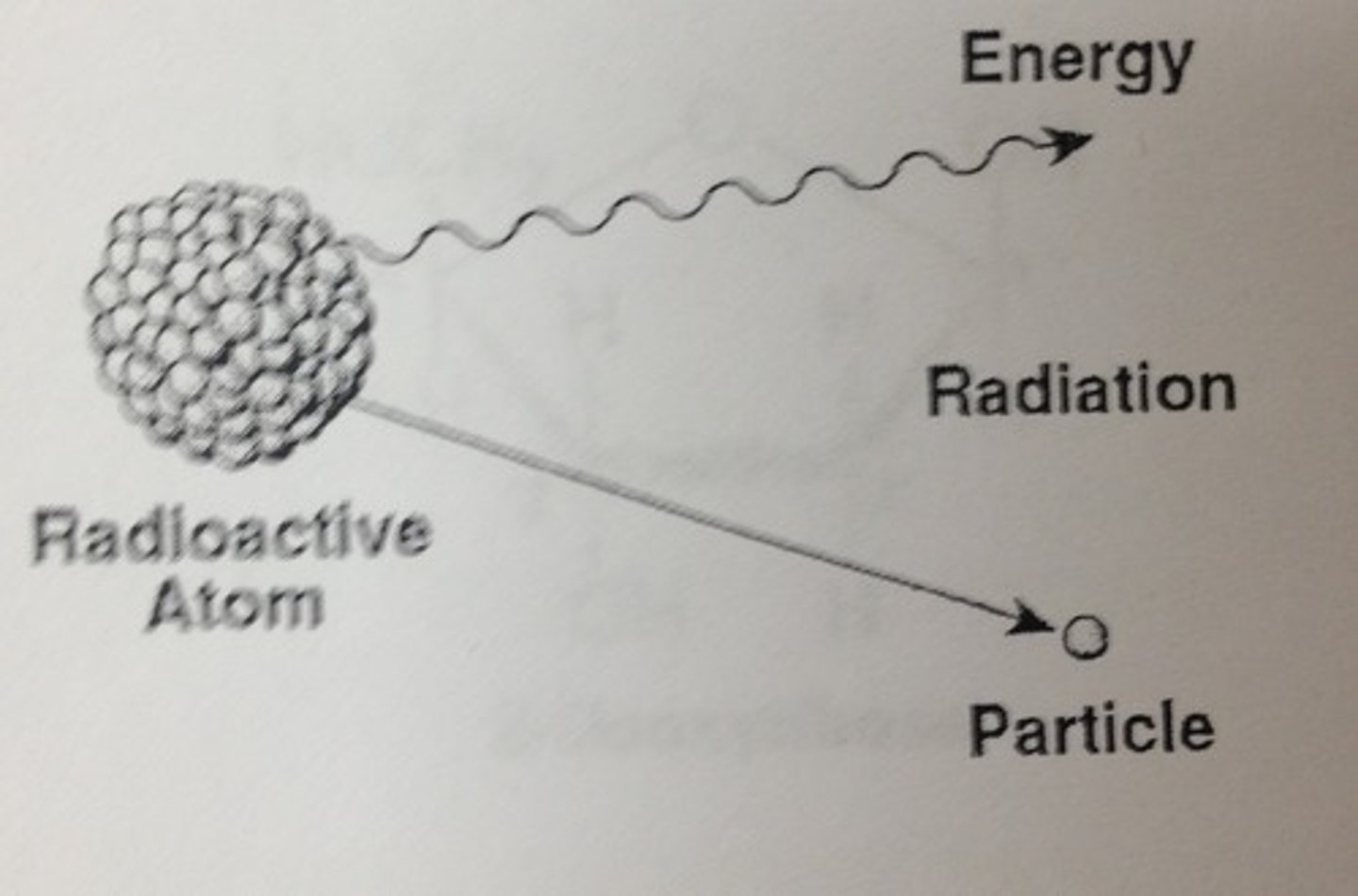
What are isotopes used for?
Unstable Isotopes undergo spontaneous decay where they emit radiation to achieve a stable state. Measuring the speed of decay allows scientists to date archaeological finds. Stable isotopes can be used to give a record of climate change. Isotopes are also commonly used in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
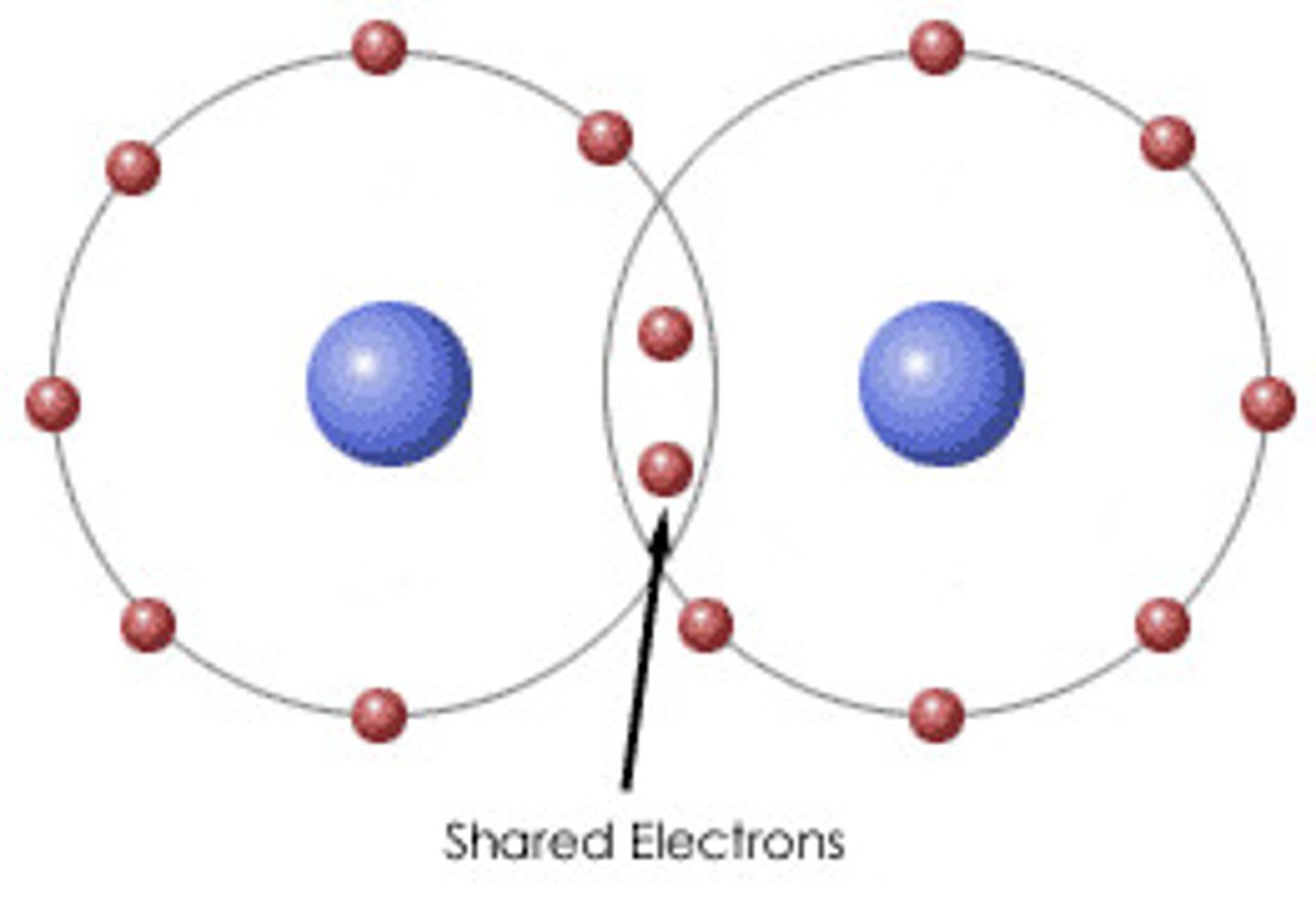
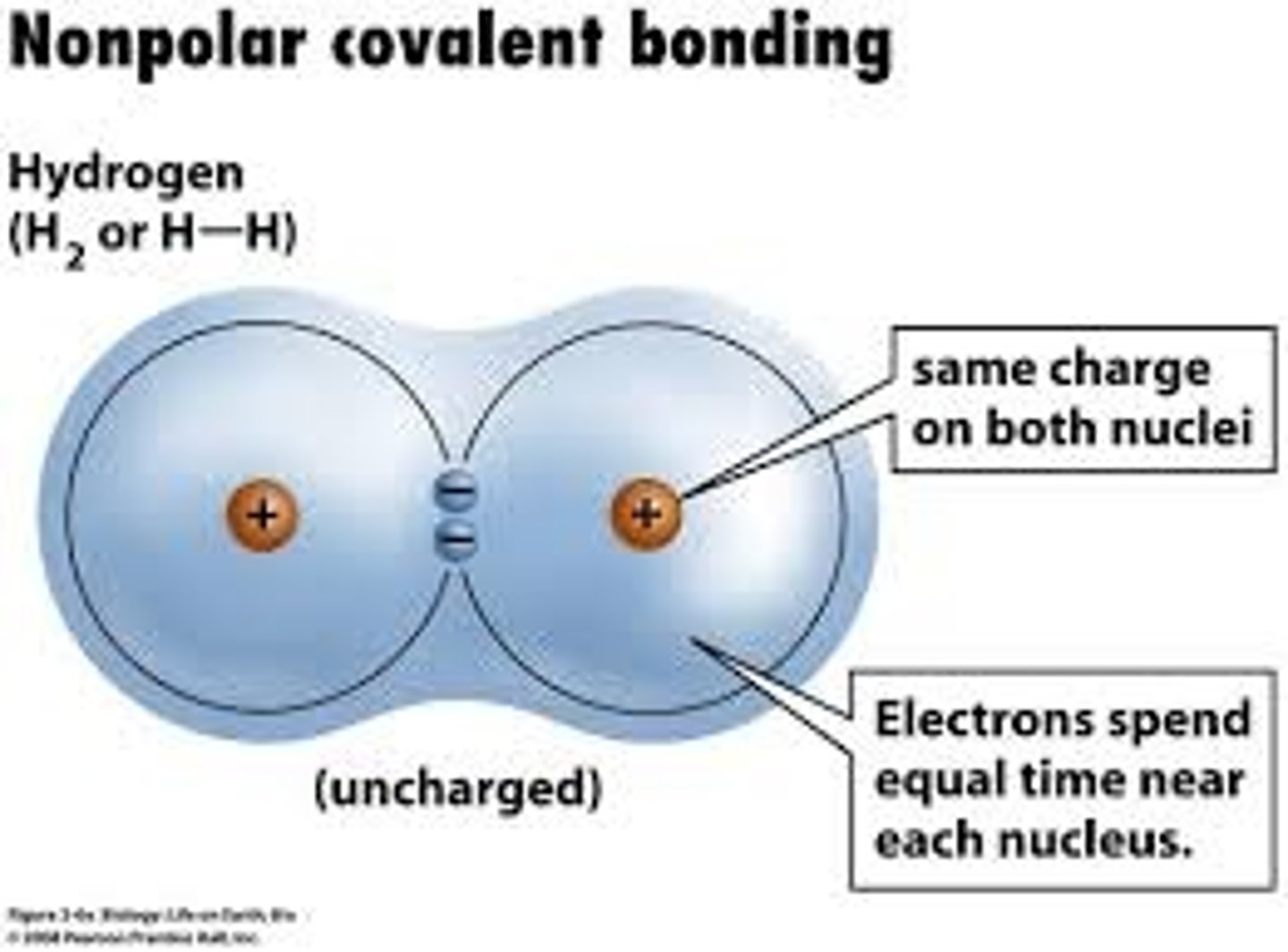
convalent bond
A chemical bond formed when when atoms share electrons
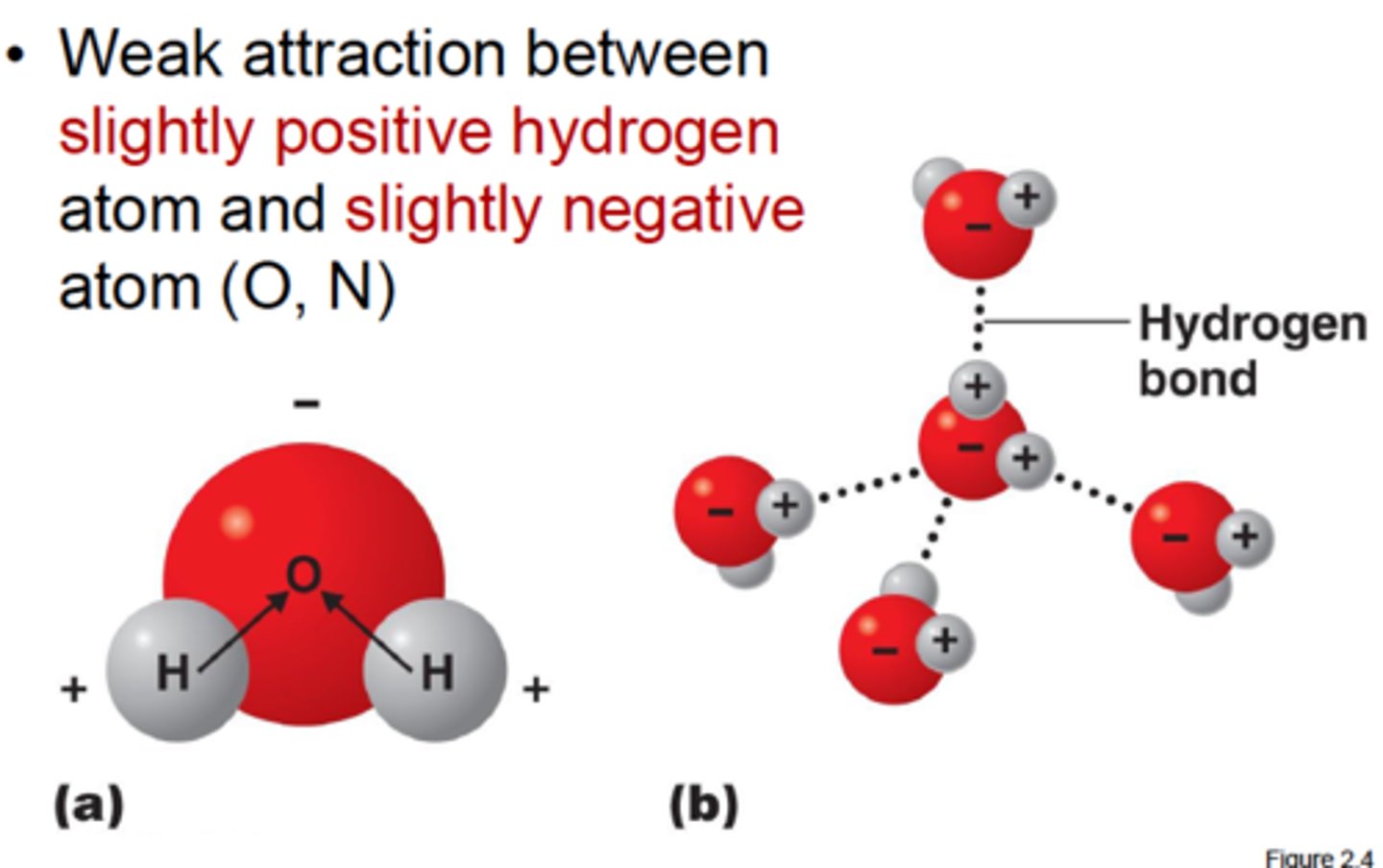
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom. Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom.
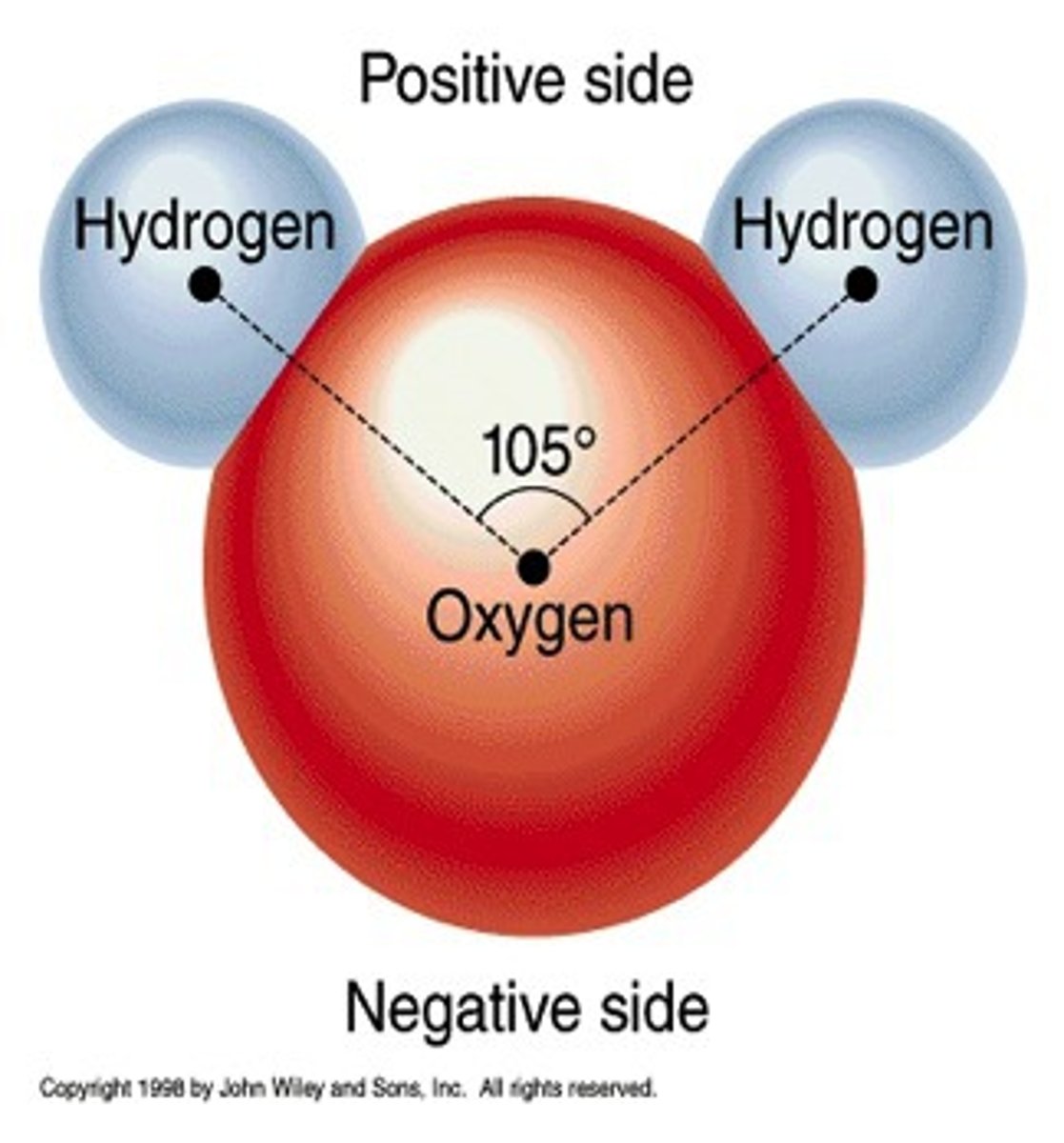
polar molecule
molecule with an unequal distribution of charge, resulting in the molecule having a positive end and a negative end
nonpolar molecule
molecule that shares electrons equally and does not have oppositely charged ends
Phases of water
solid (ice), liquid (water), gas (water vapor)
Functions of water in the body
- Carries nutrients and waste products
- Lubricant between body structures
- Cushions and absorbs force of body movements
- Excretes waste
Properties of Water
cohesion - attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding
surface tension - inward pulling of cohesive forces at surface of water - causes moist sacs of air in the lung to collapse
adhesion - attraction between water molecules and a substance other than water
Temperature
A measure of kinetic energy of atoms or molecules within a substance
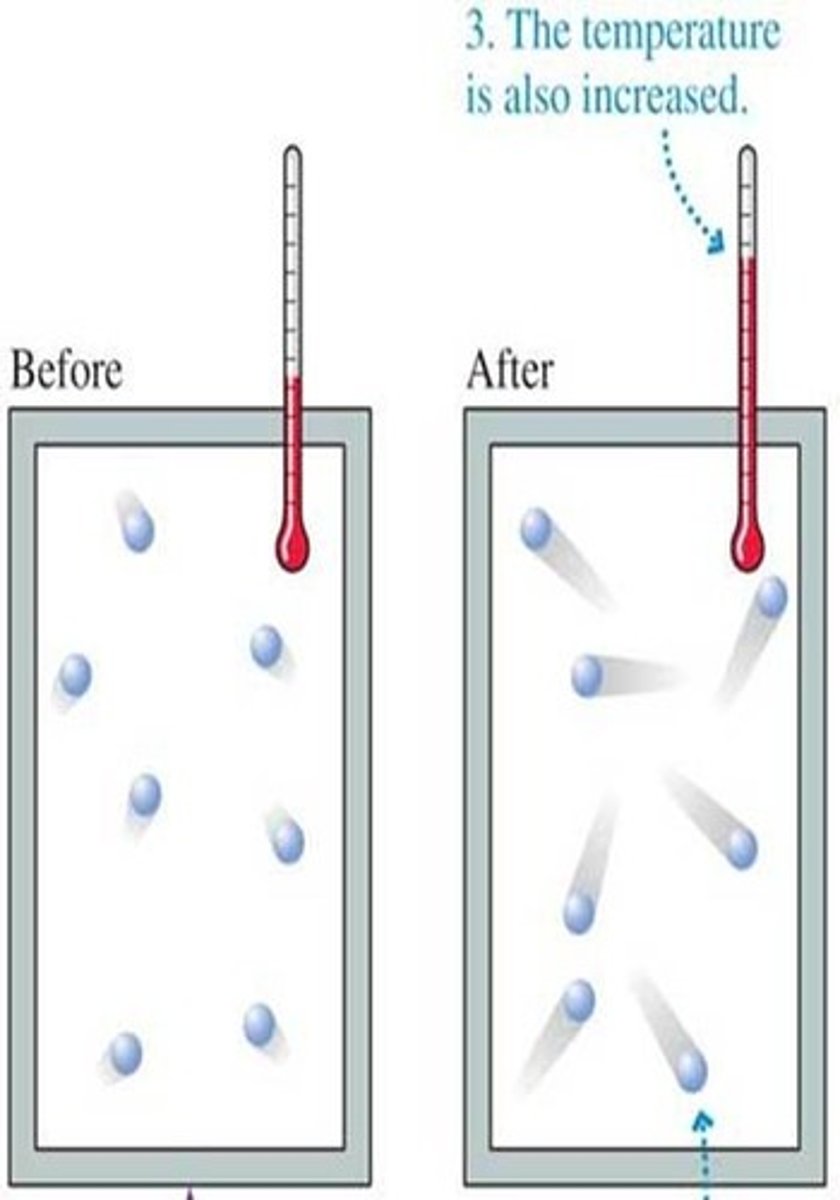
specific heat
- The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius
- Water's value is extremely high due to the amount of energy needed to break hydrogen bonds and this helps keep body temperature regulated
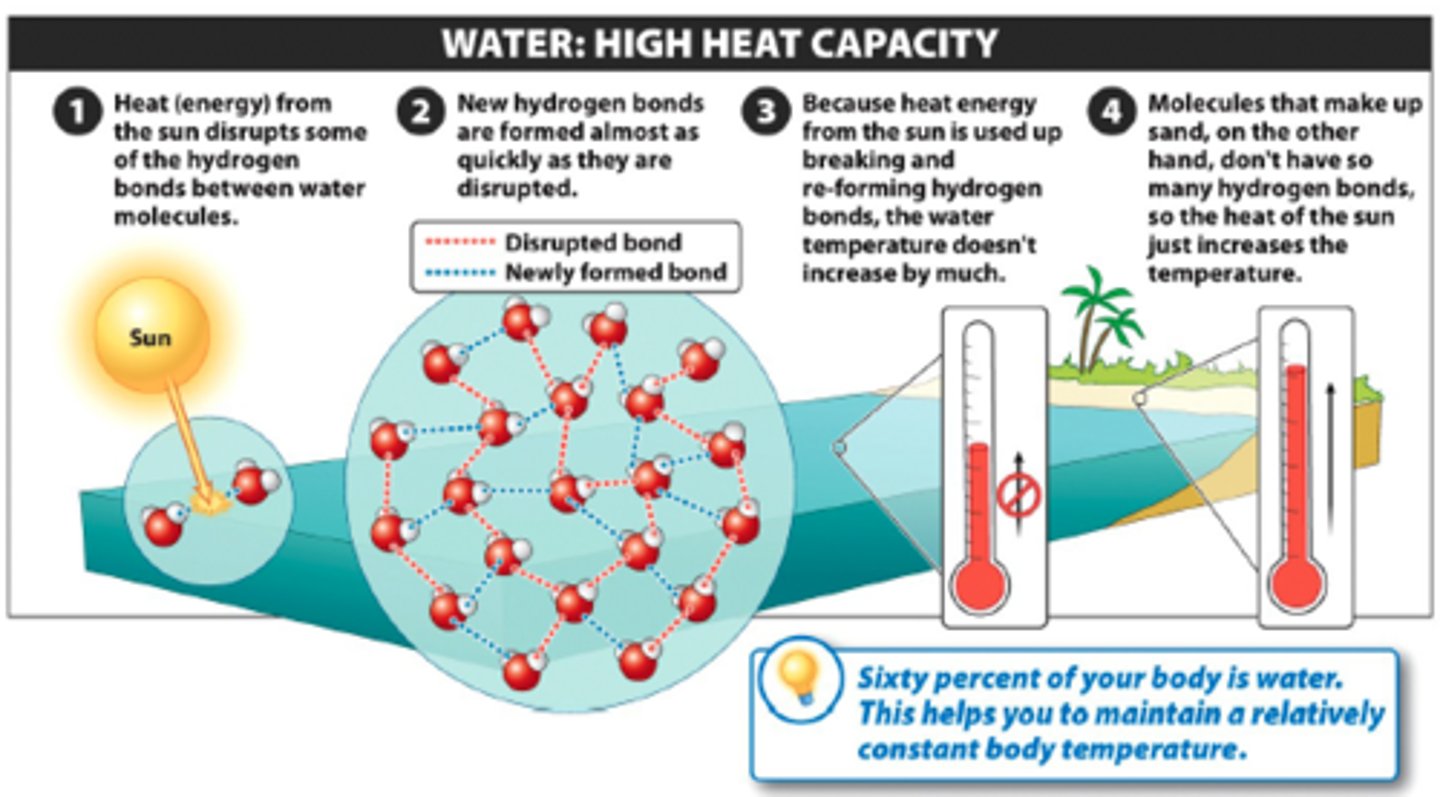
heat of vaporization
- The amount of heat a liquid must absorb for 1g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state
- Water's value is extremely high due to the amount of energy needed to break hydrogen bonds
- When we sweat and the water evaporates excess heat dissipates

ph
a measure of hydrogen ion concentration, a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The pH scale usually ranges from 0 to 14. Aqueous solutions at 25°C with a pH less than 7 are acids or acidic, while those with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline.

Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Base
A substance that decreases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
How are salts formed?
When acids react with bases ( Neutralisation reaction)
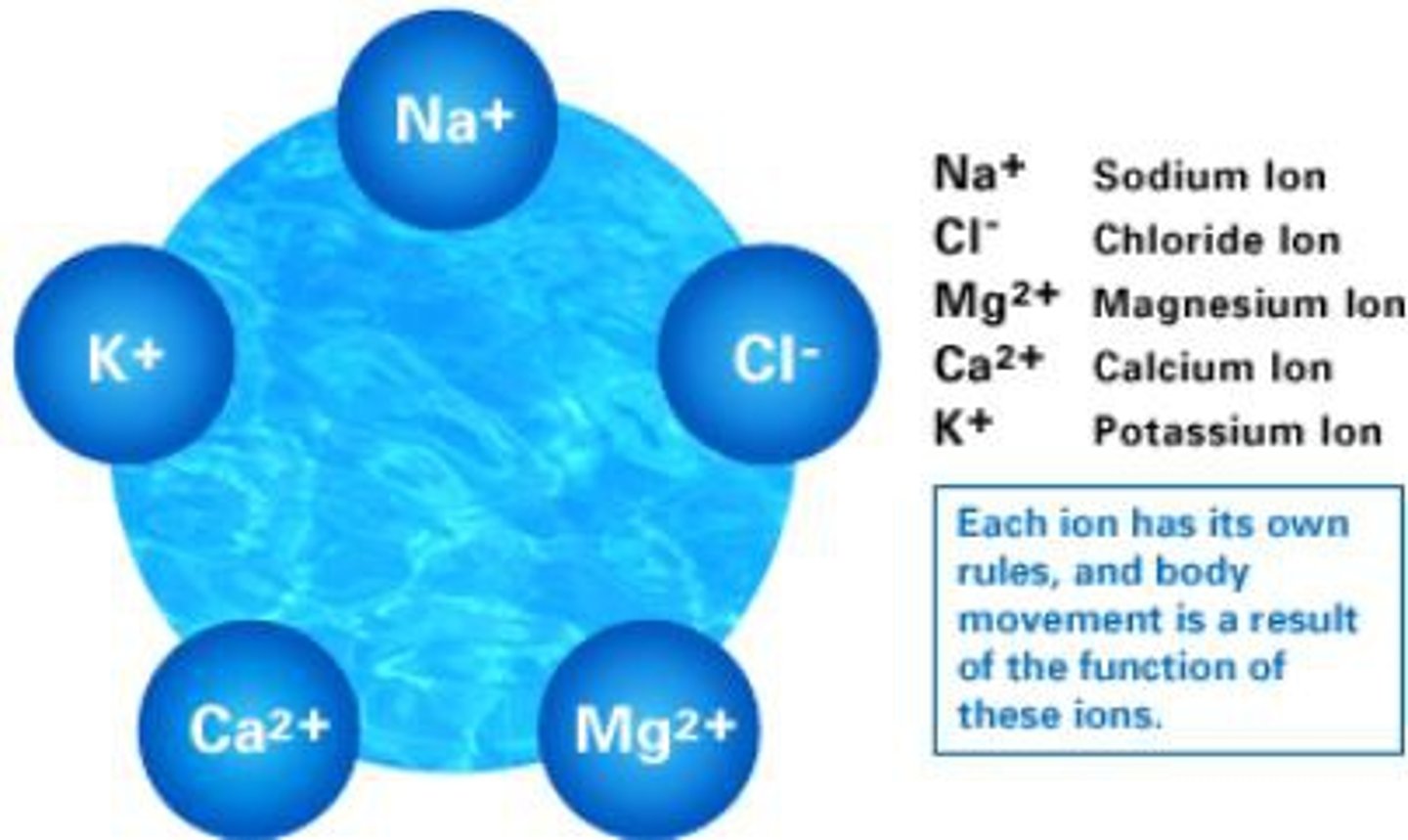
Electrolyte
A substance that produces an electrically conducting solution when dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. The dissolved electrolyte separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly through the solvent. Electrically, such a solution is neutral
Sodium, calcium, potassium, chloride, phosphate, and magnesium are all electrolytes (release ions in water)
organic molecules
- contain hydrogen and carbon
- usually larger than inorganic
- dissolve in water and organic lipids
- are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids
inorganic molecules
- generally do not contain carbon
- usually smaller than organic molecules
- usually dissolve in water or react in water to release ions
- are water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and inorganic salts

Four major classes of macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
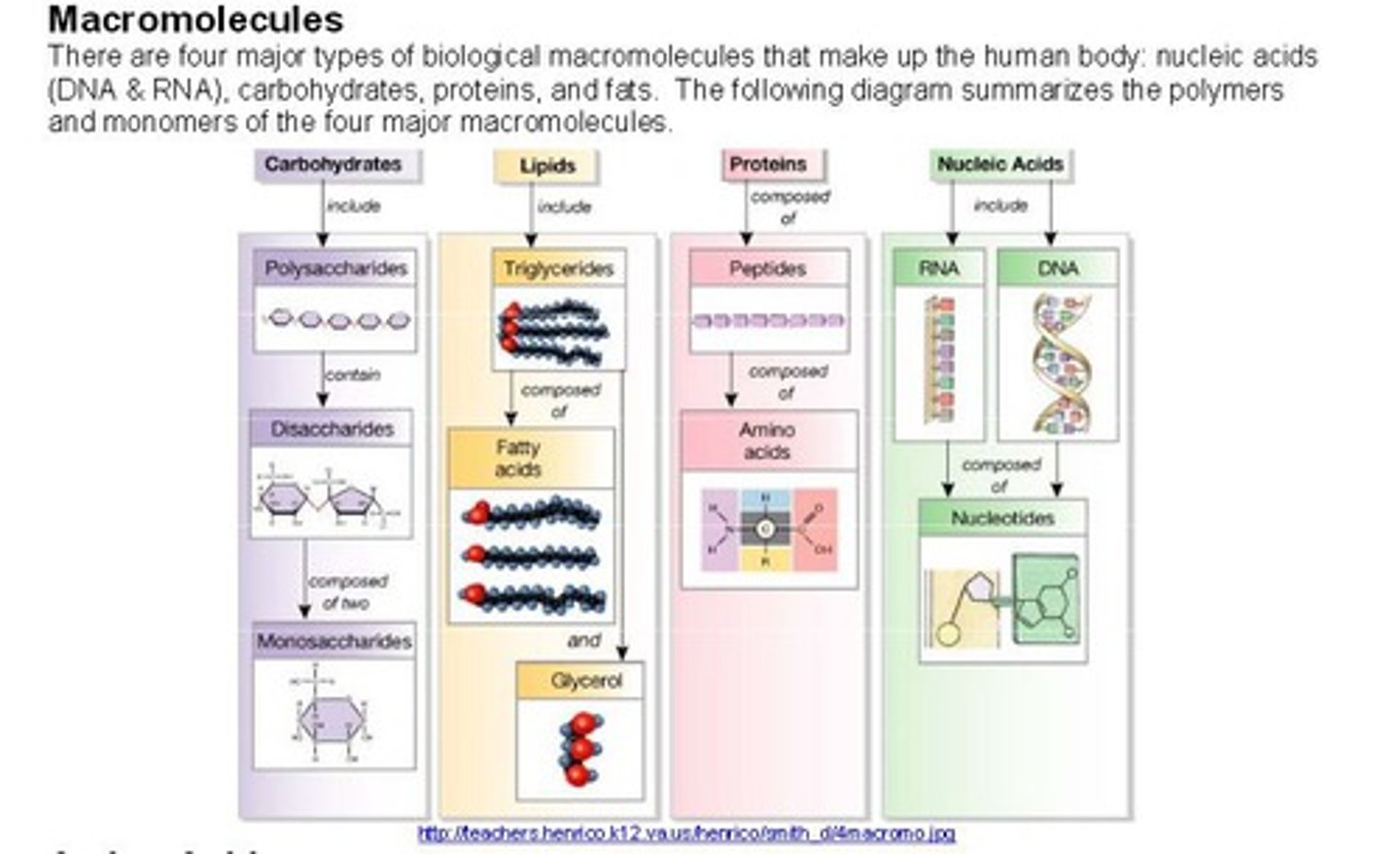
Carbohydrates function & building blocks
main source of energy & monosaccharides
Lipids function & building blocks
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen & glycerol and fatty acids
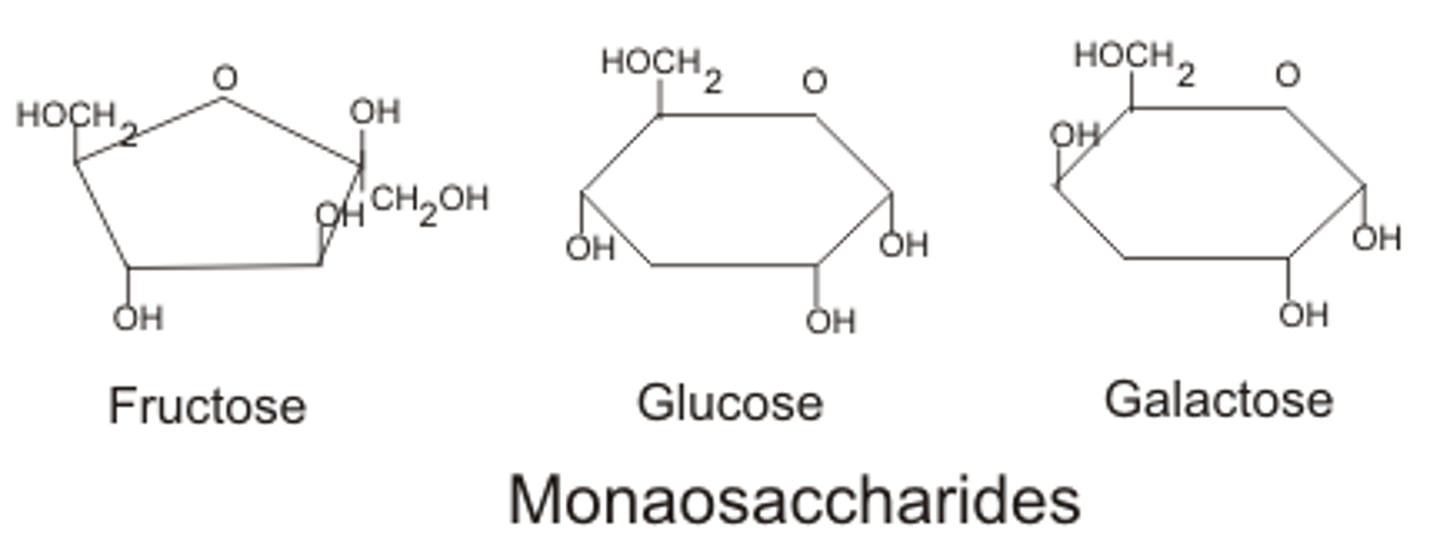
Monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
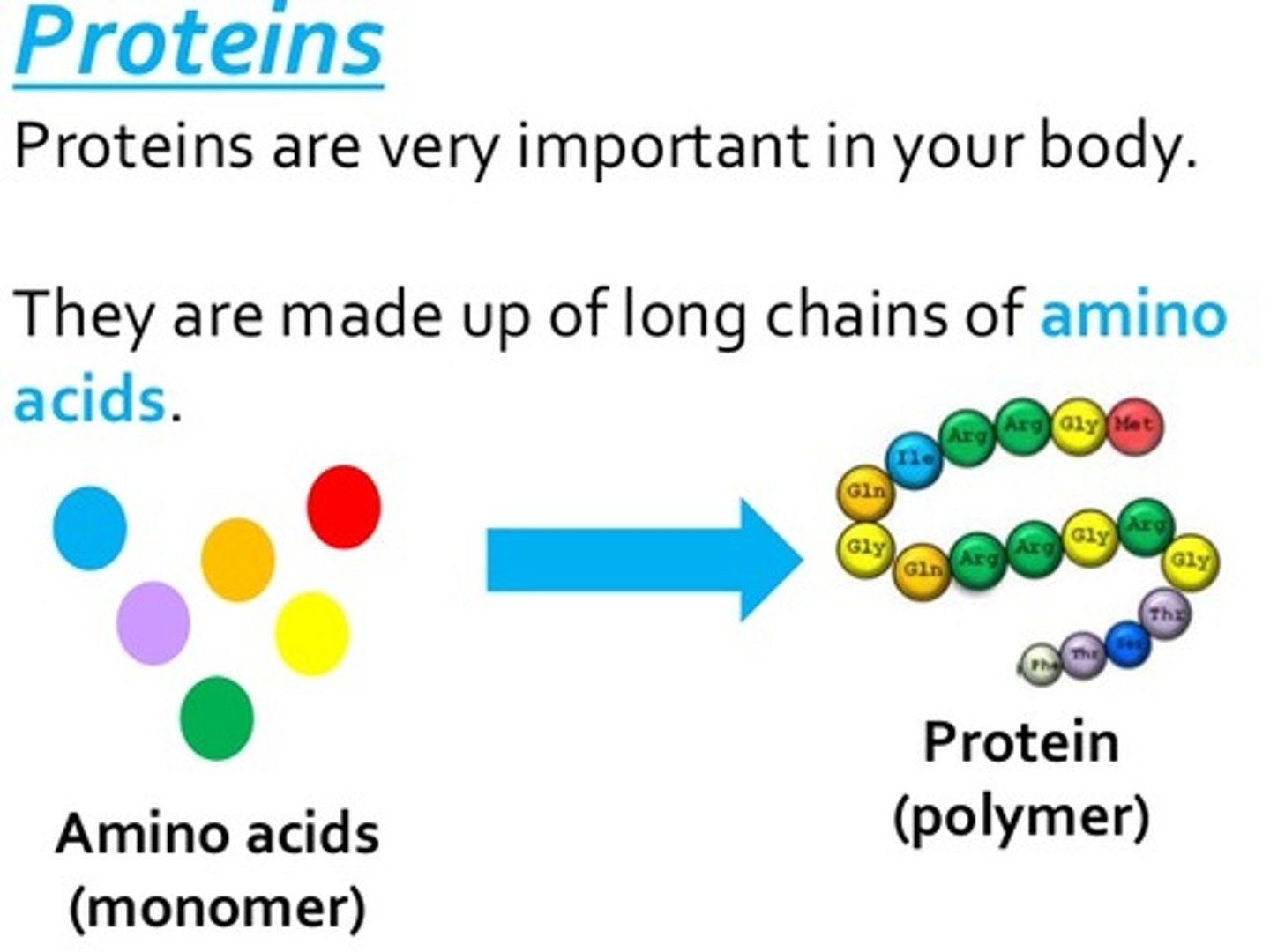
Proteins function & building blocks
Structure, storage, defense, transport, and speeding up reactions & amino acids
function of nucleic acids & building blocks
store and transmit genetic information & nucleotides
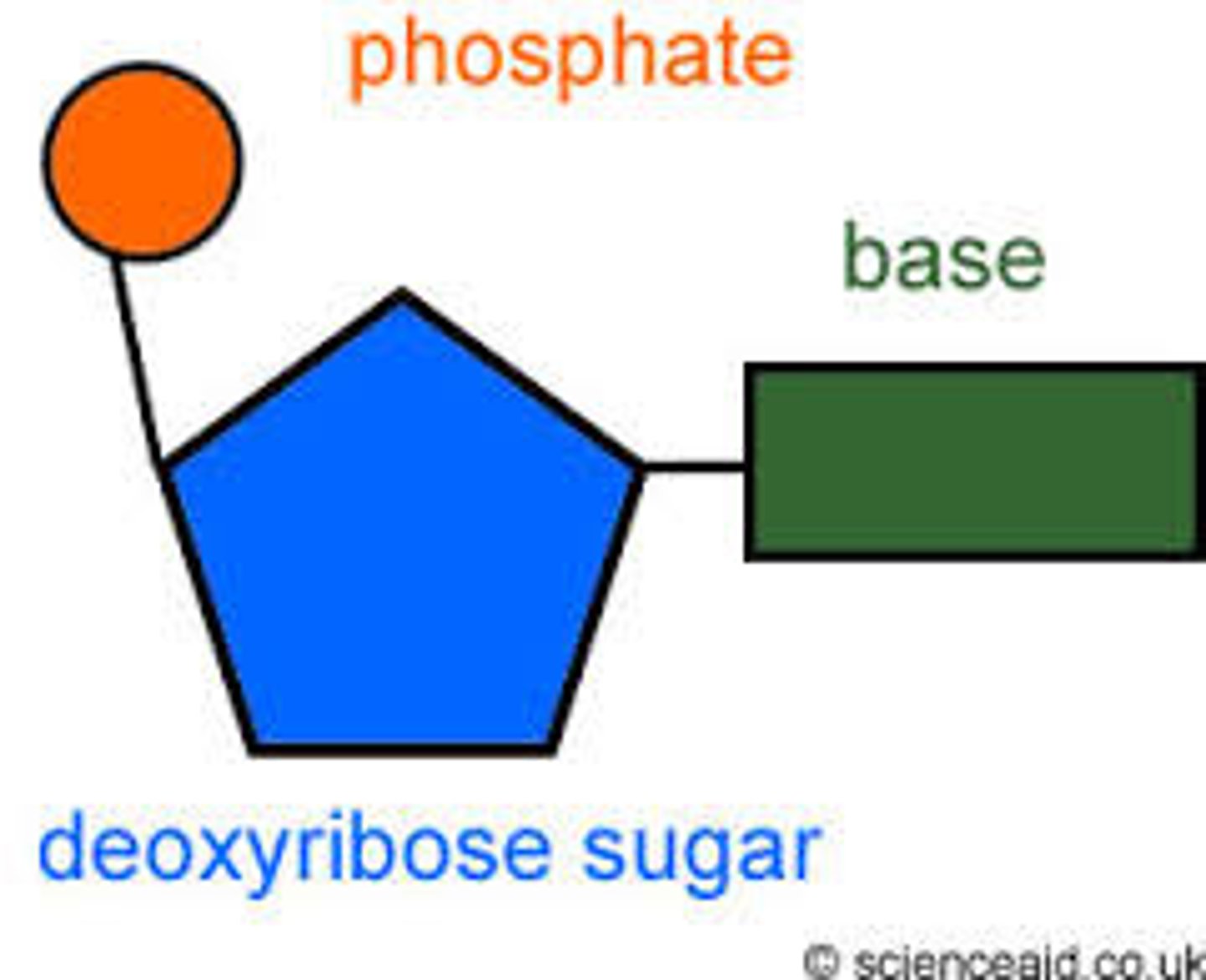
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
What are the 4 protein shapes?
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
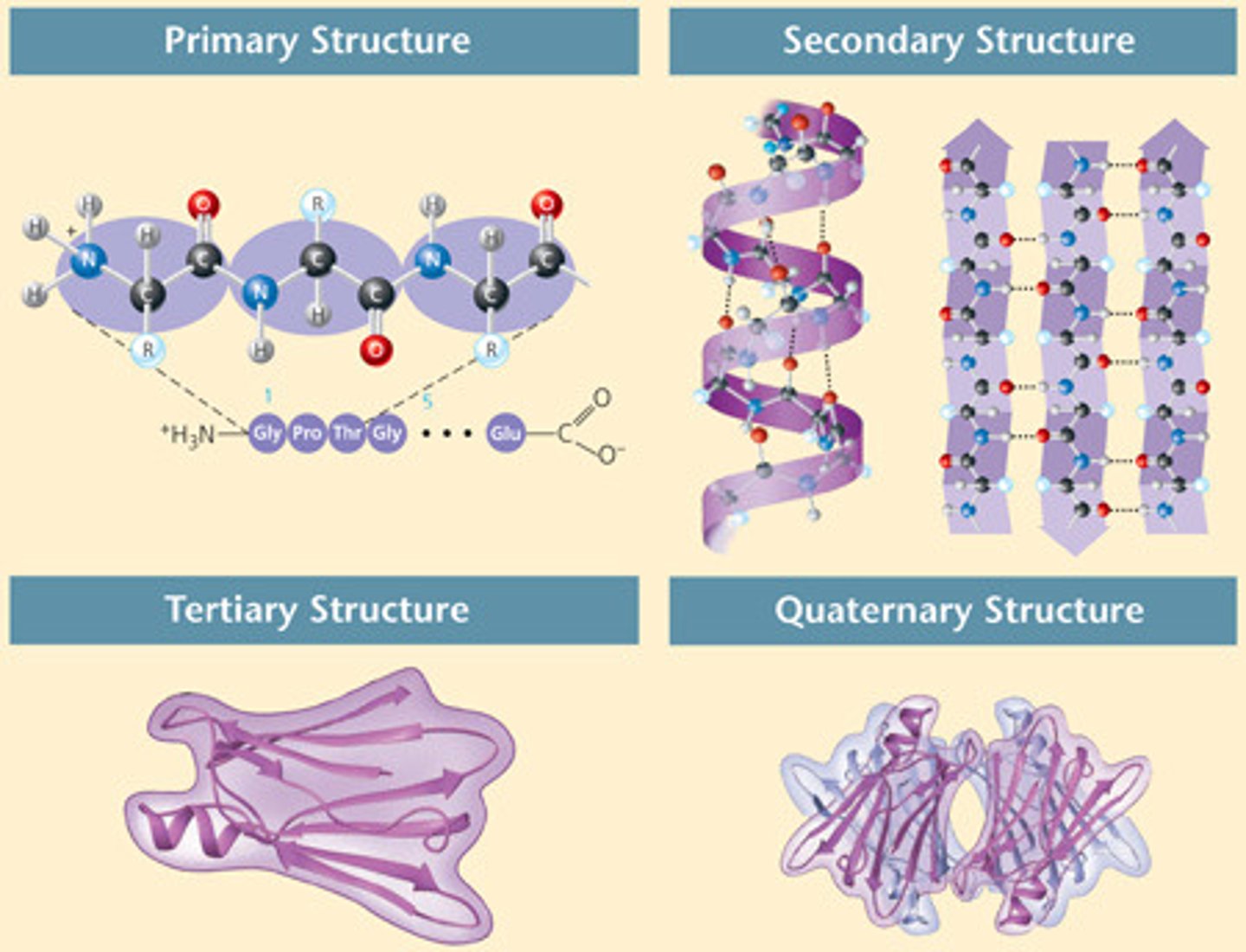
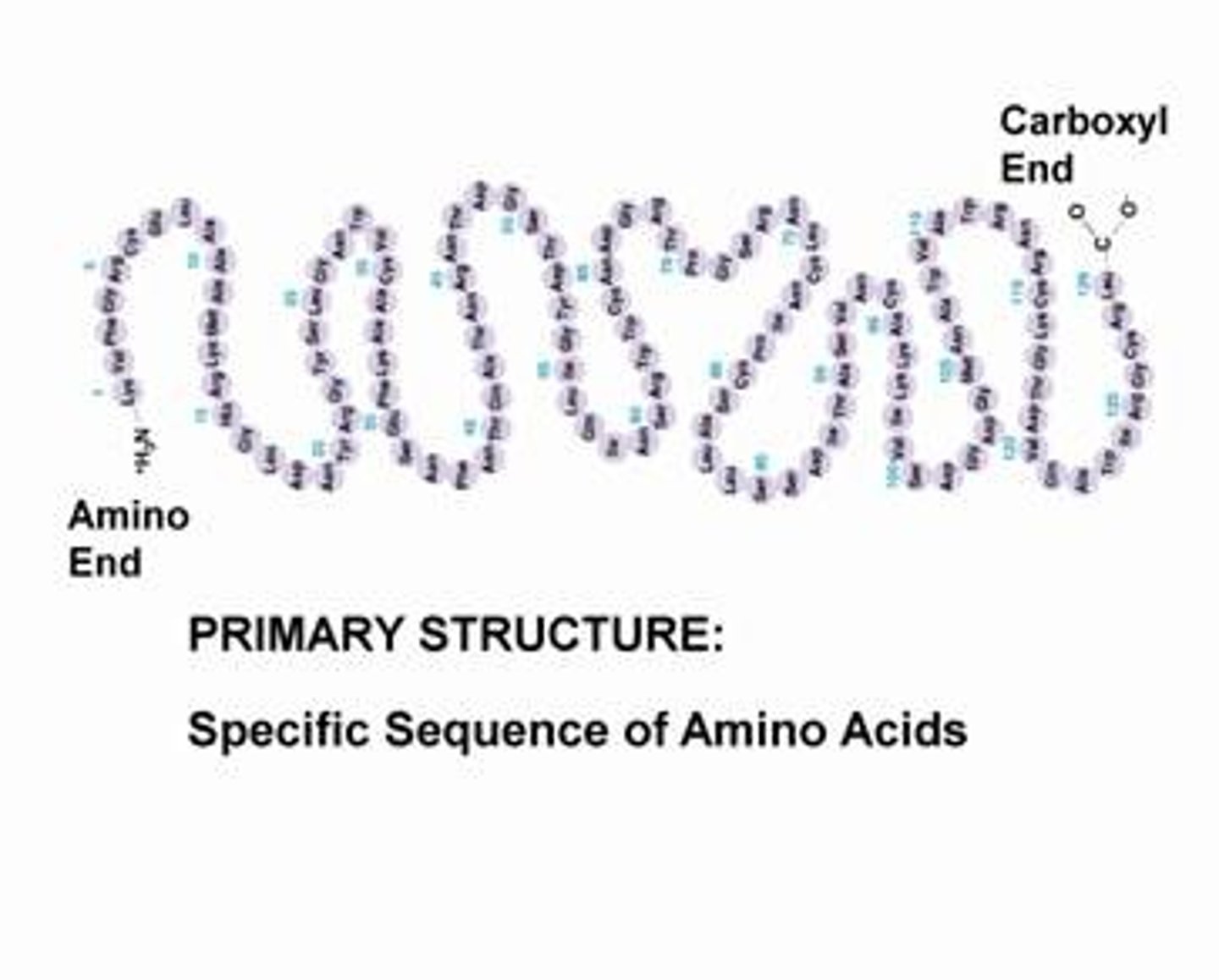
primary protein structure
sequence of a chain of amino acids
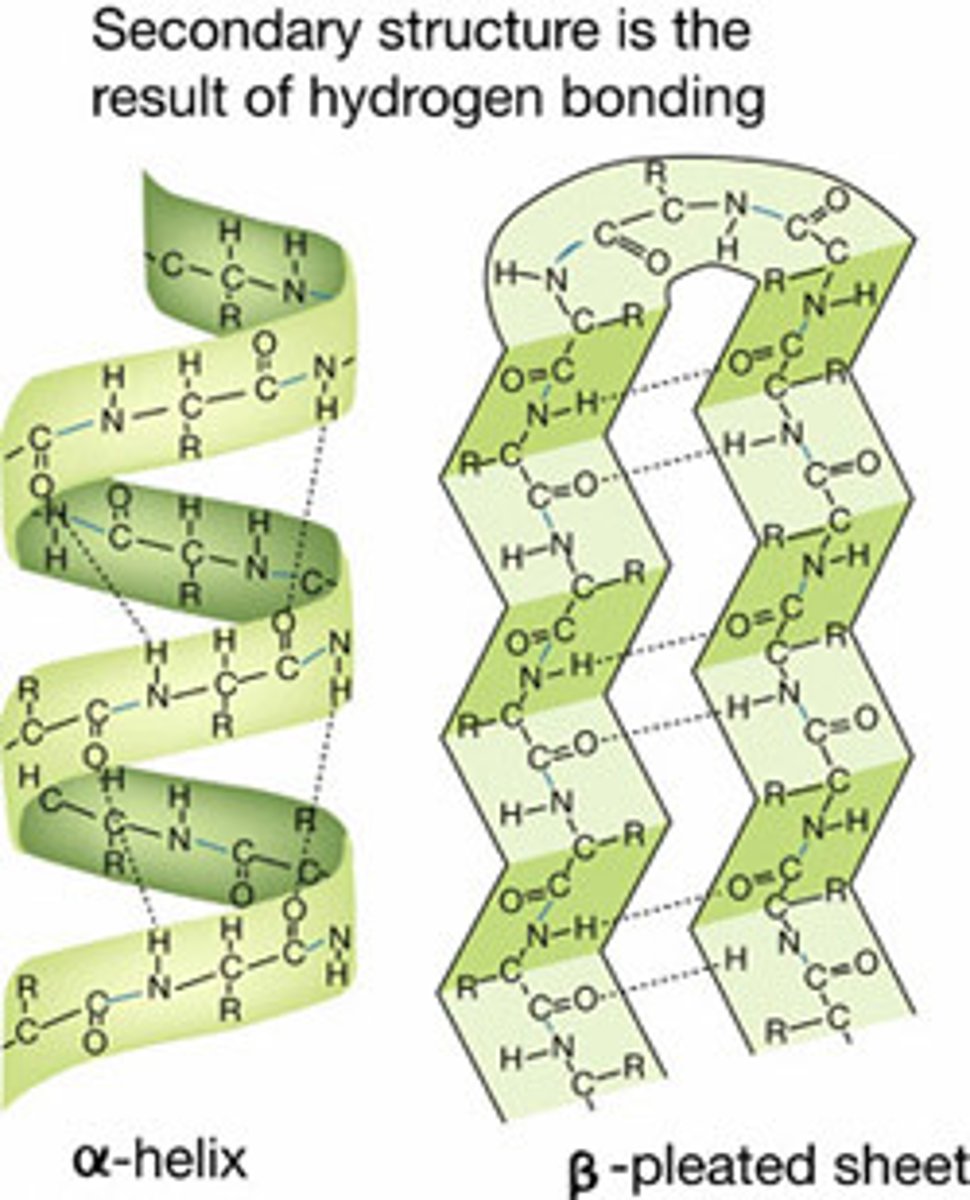
secondary protein structure
hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone causes the amino acids to fold into a repeating pleated pattern
tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide from protein chain due to hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and disulfide bridges; interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
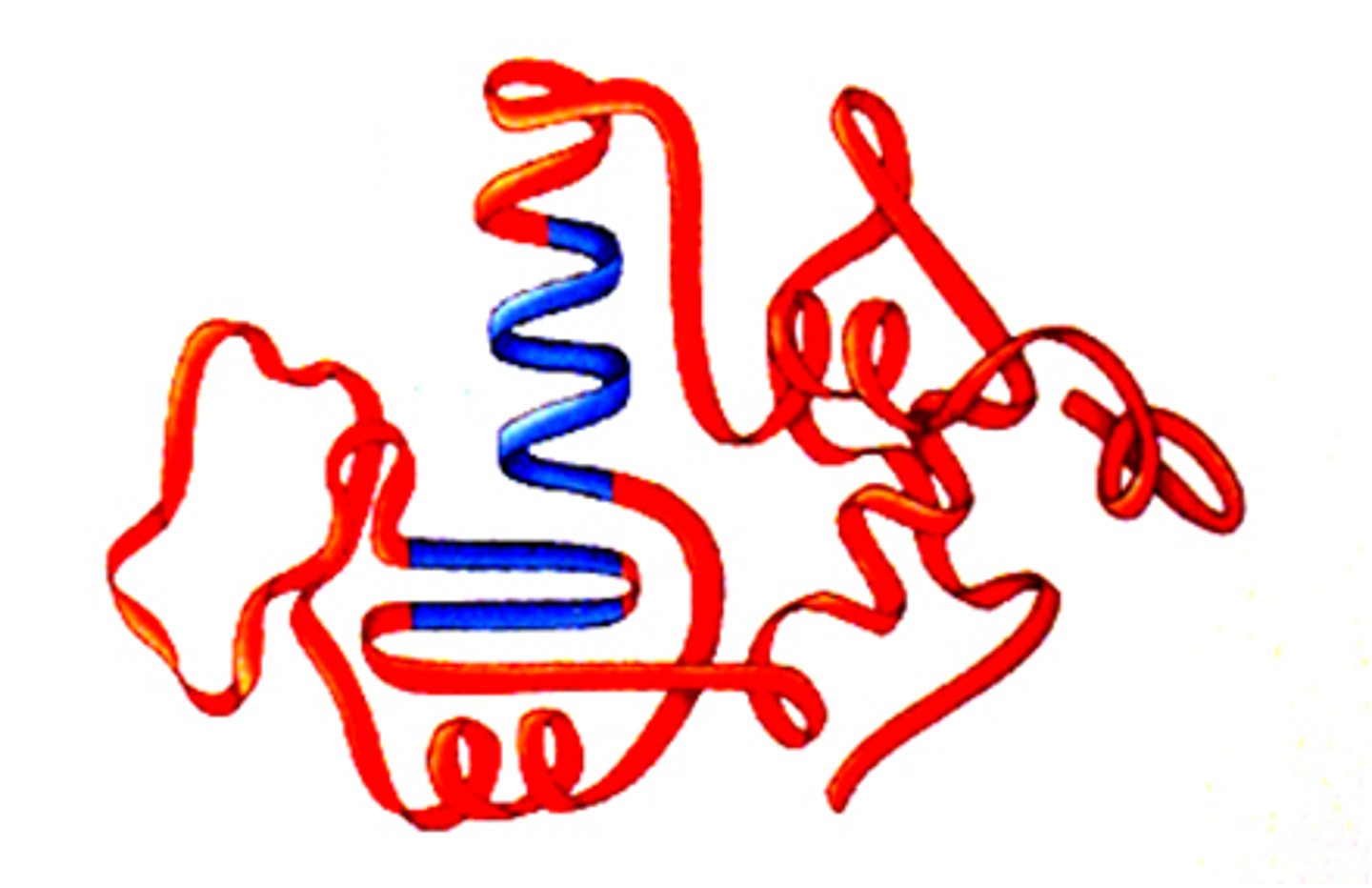
protein shape
determines function, the more complex the structure = complexity of function from none - hair - muscle - hemoglobin
Metabolism
the combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down materials
Anabolism
Constructive metabolism; the process of building up larger molecules from smaller ones. (hulk hogan)
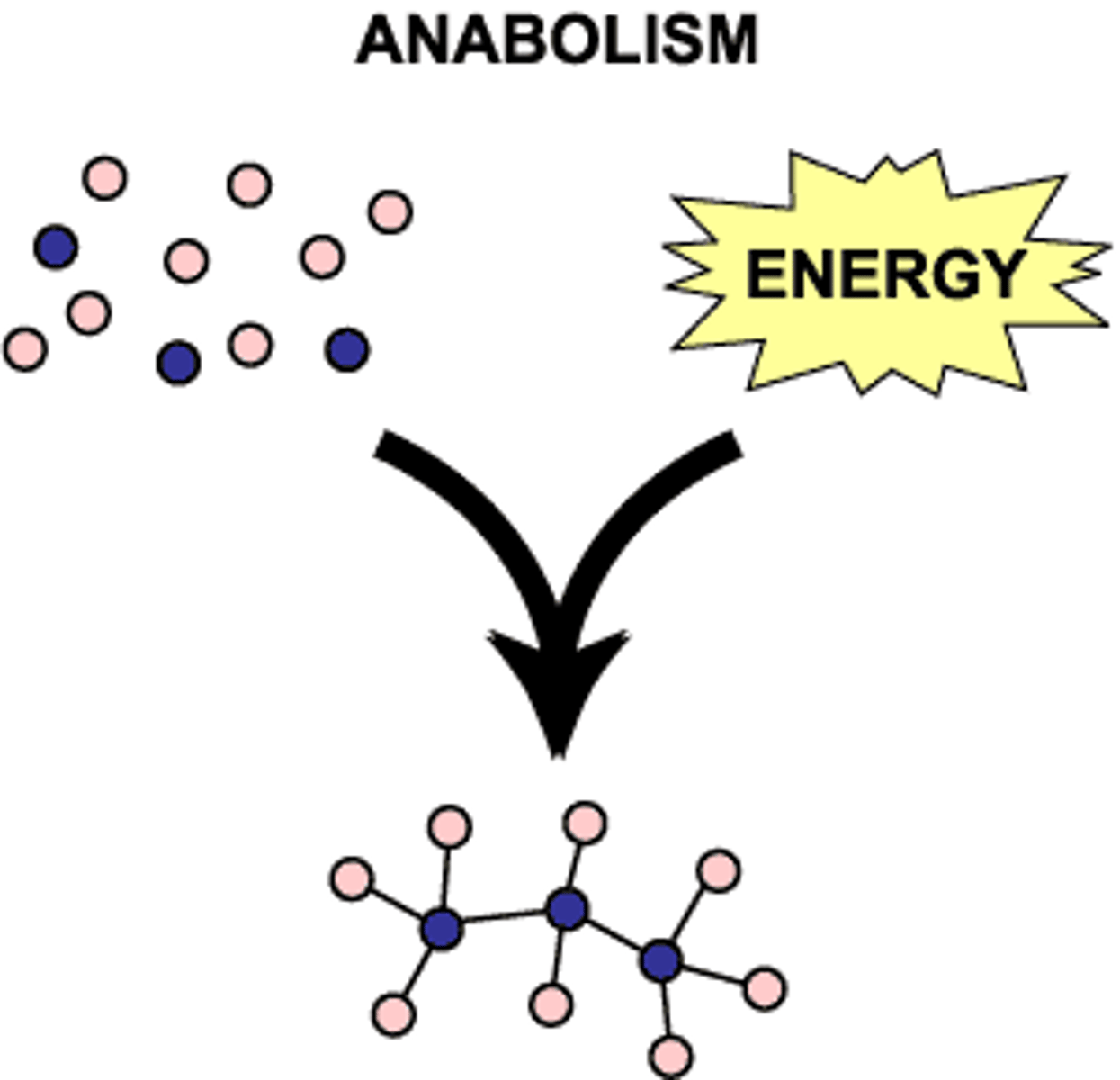
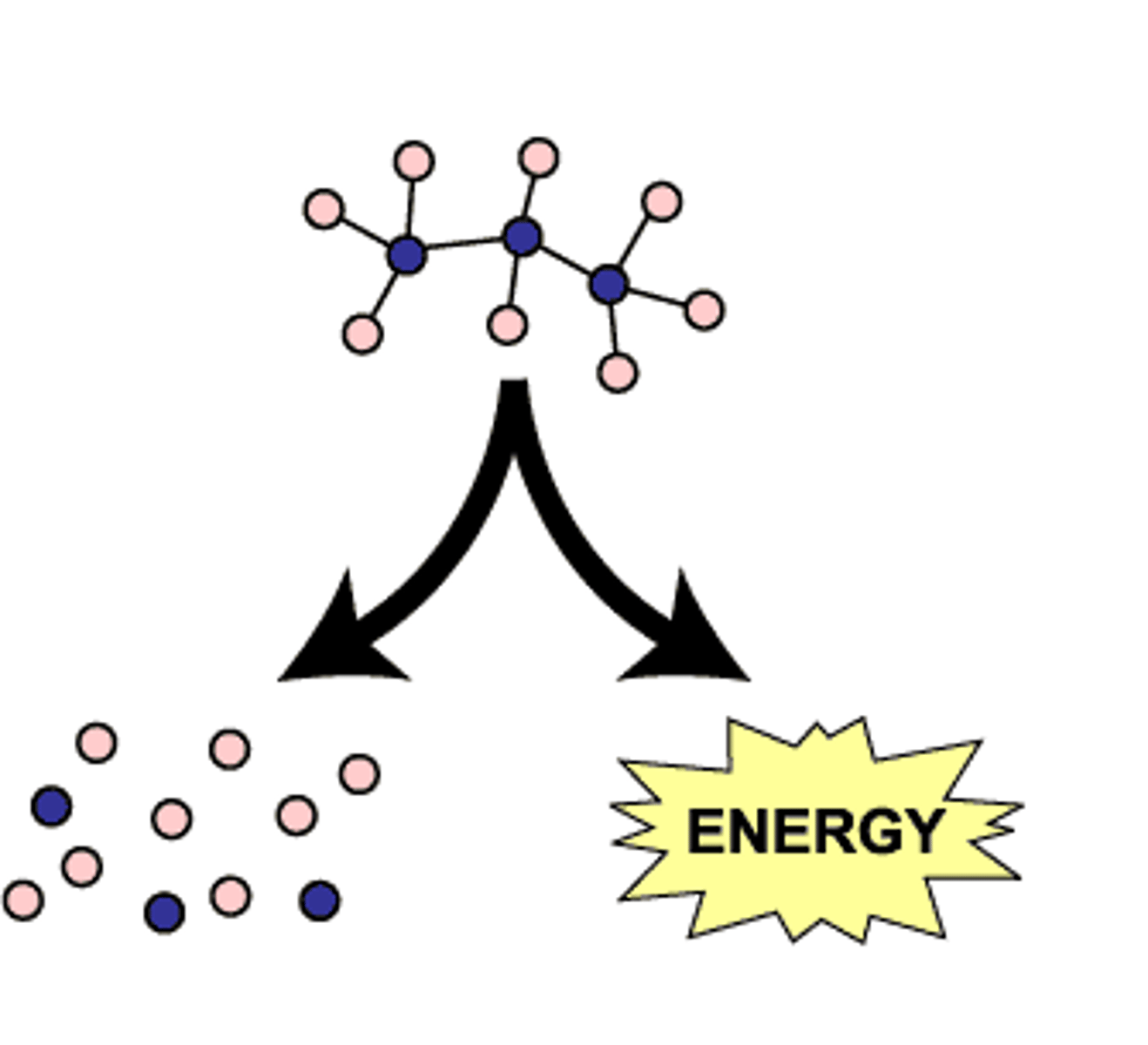
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules, releasing energy.
condensation reaction
a chemical reaction in which two or more molecules combine to produce water or another simple molecule
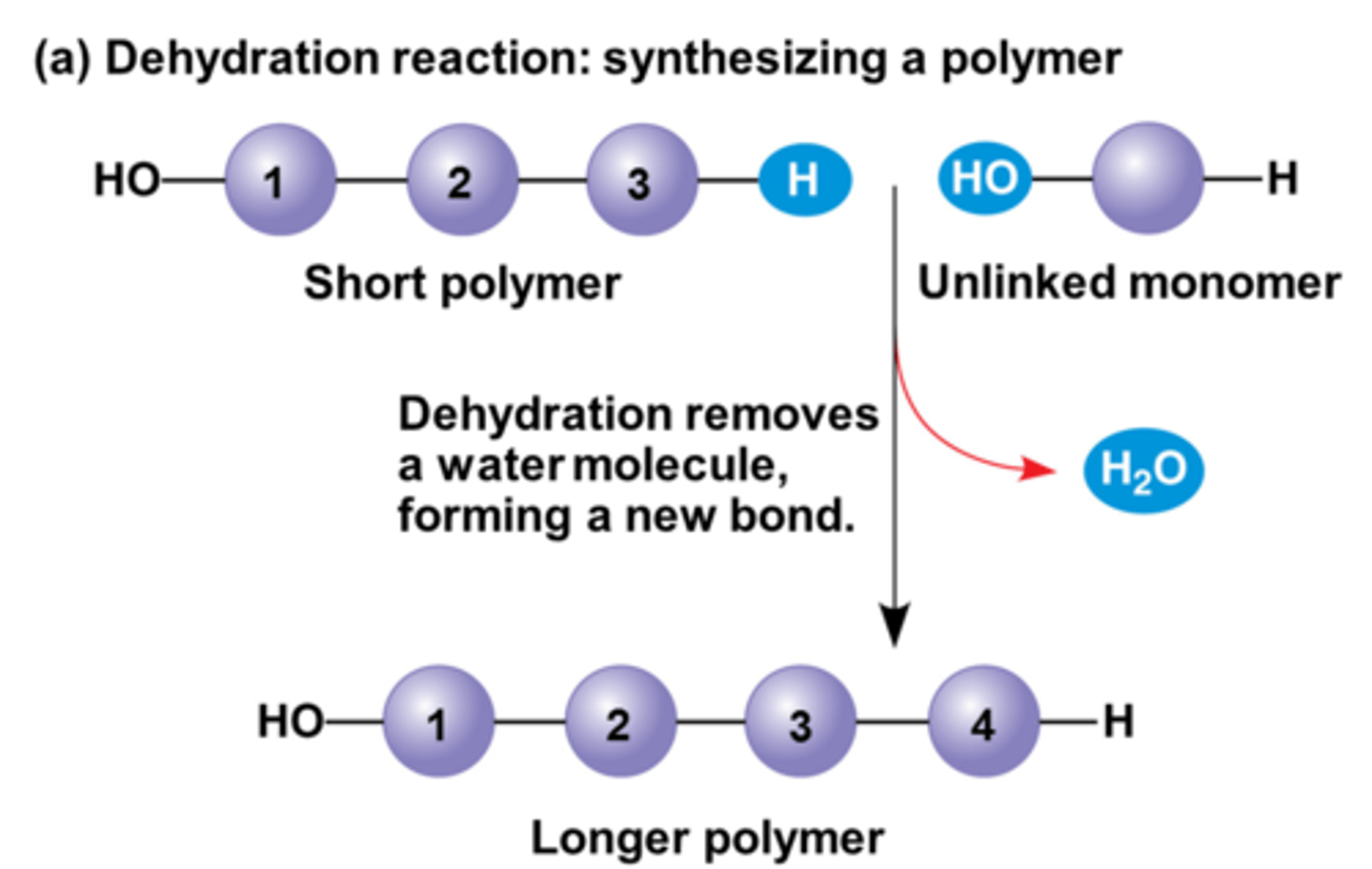
decomposition reaction
a chemical reaction that occurs when a single compound breaks down into two or more elements or new, smaller compounds
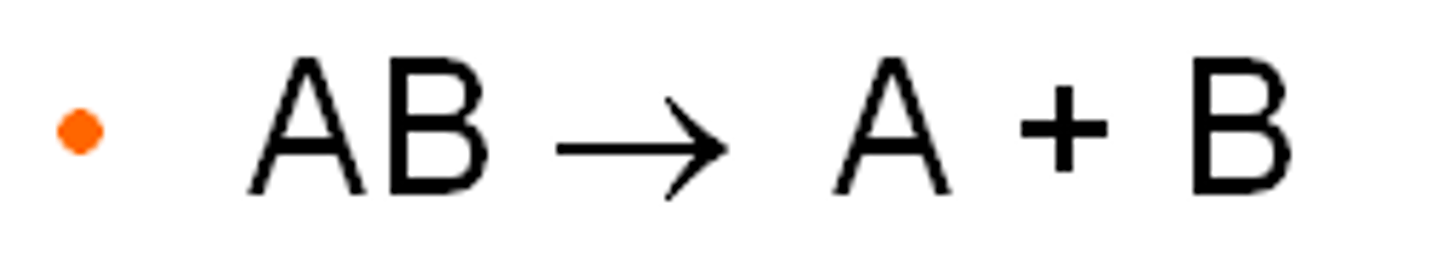
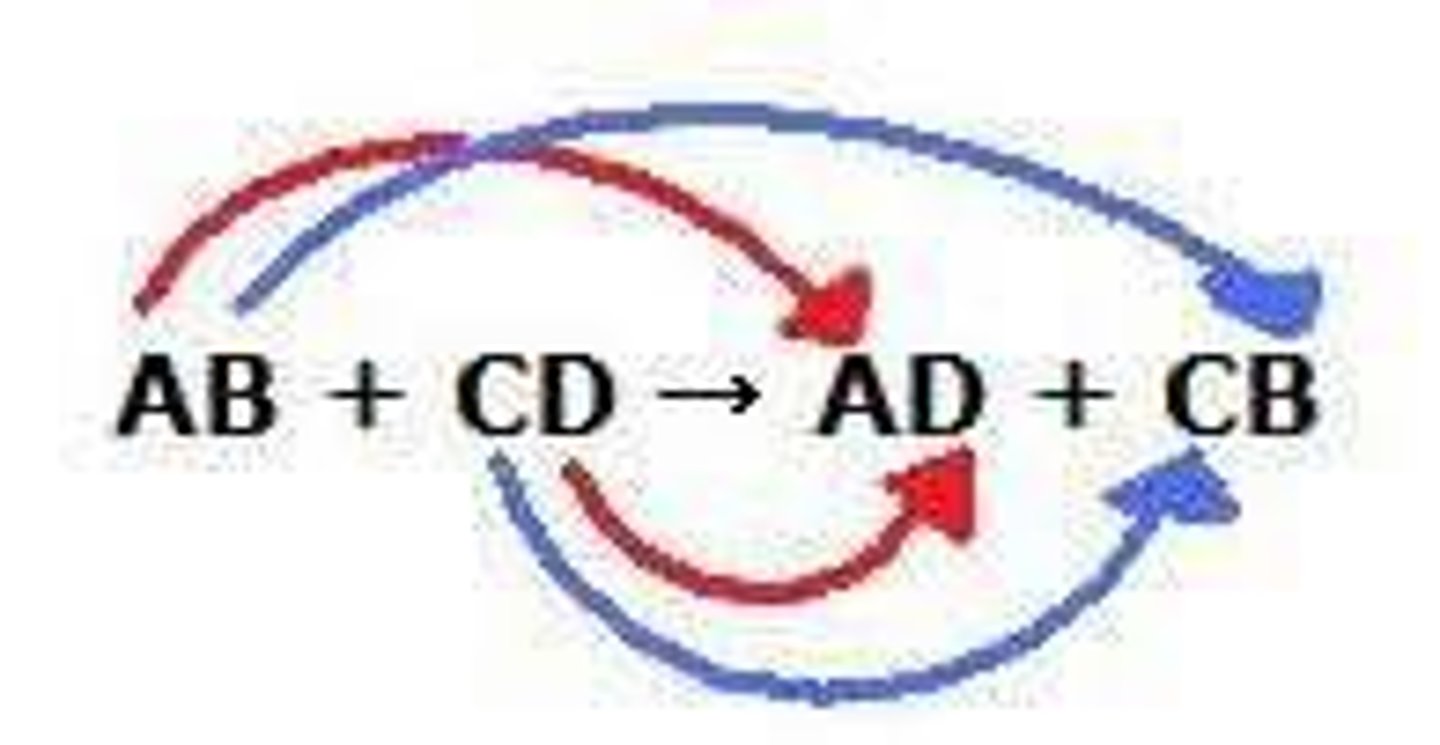
exchange reaction
Chemical reaction in which bonds are both made and broken; atoms become combined with different atoms.
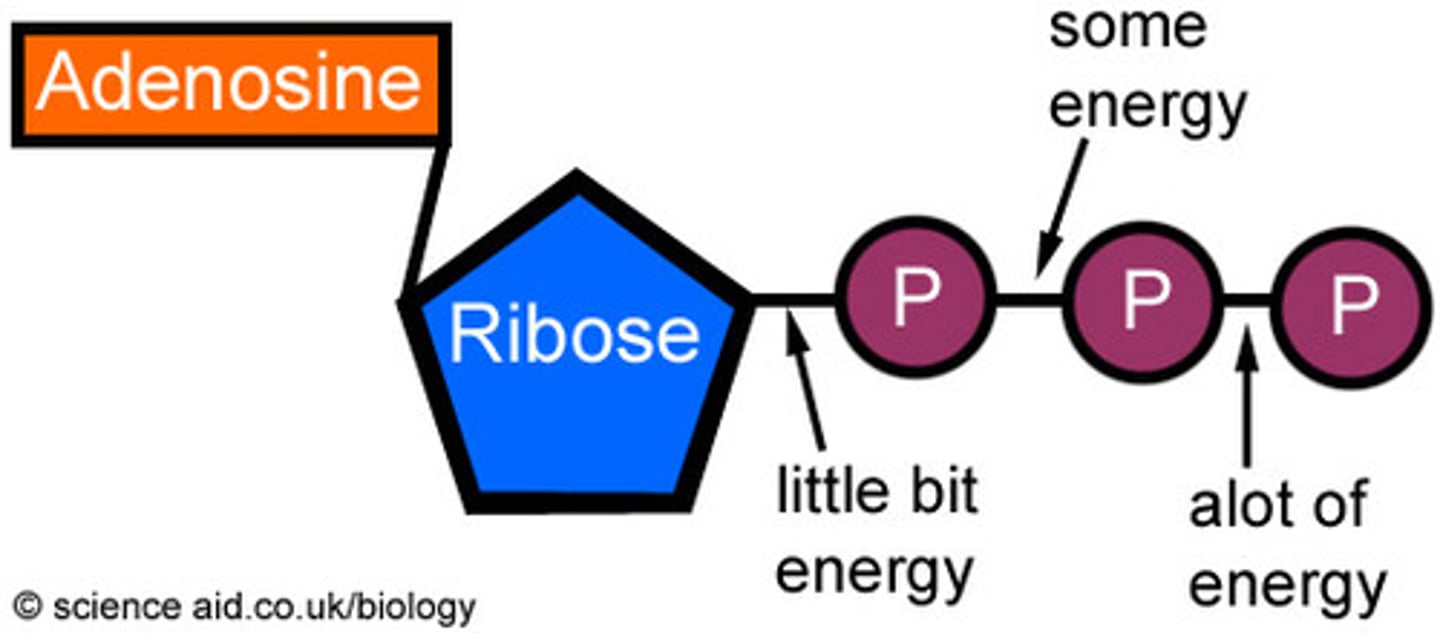
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work, 30 ATP made from 1 glucose
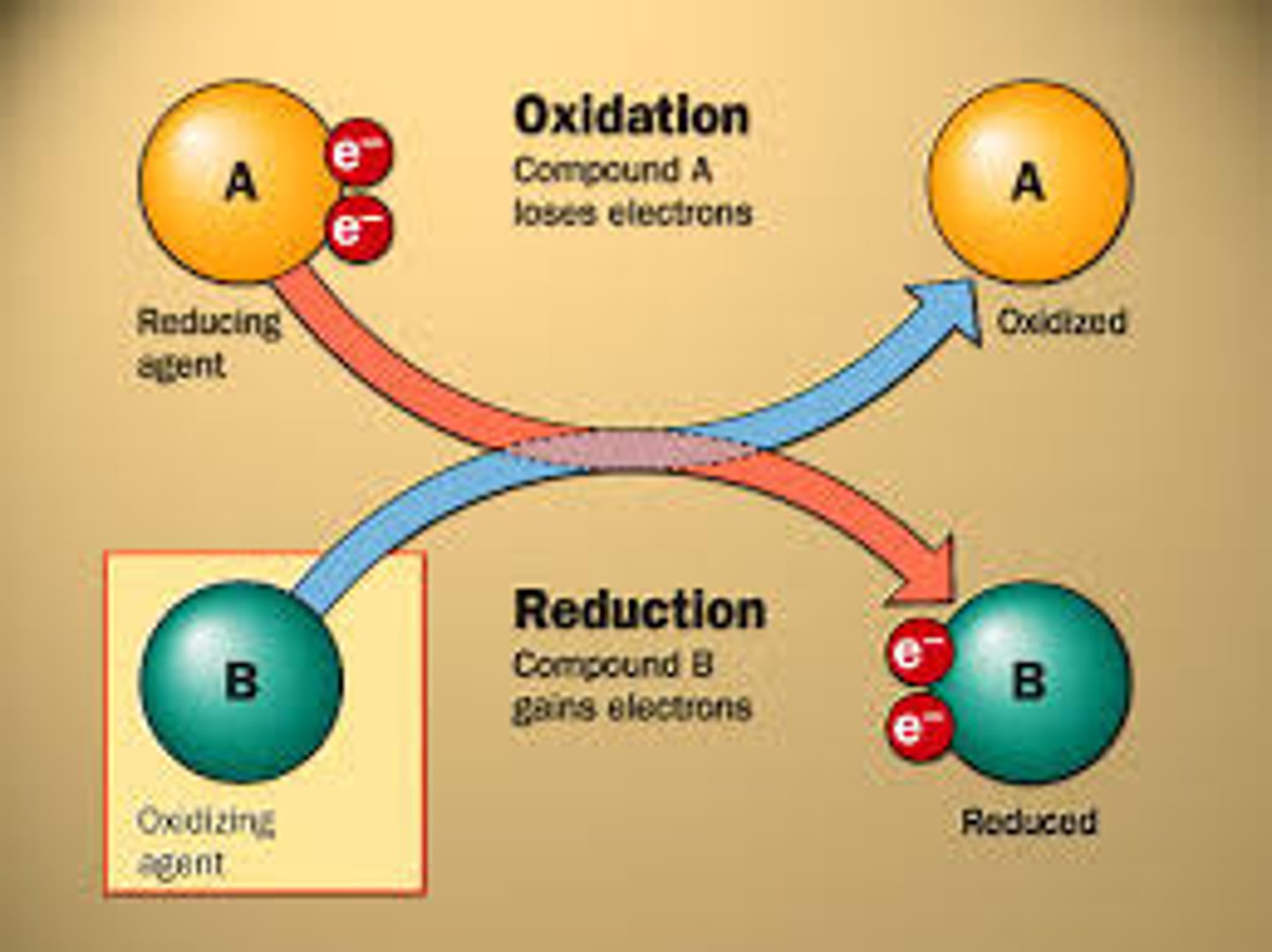
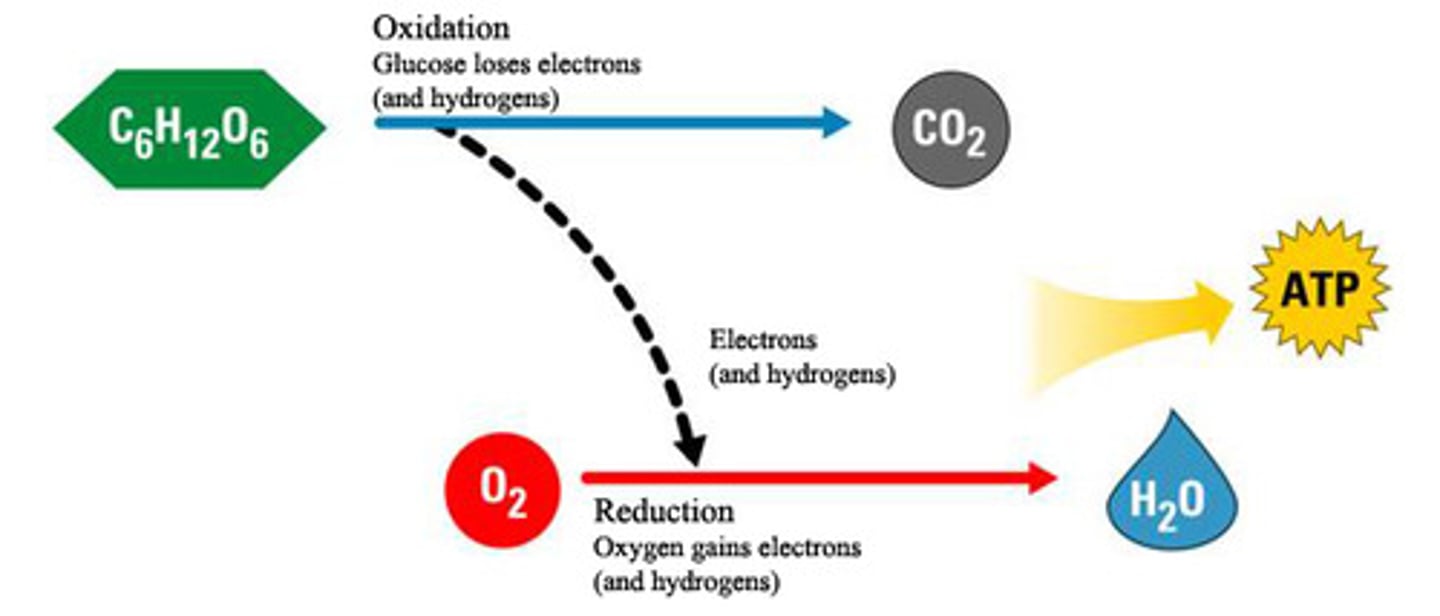
redox reactions (oxidation-reduction reactions)
electron transfers, oxidation being the loss of electrons and reduction being the gain of electrons (OIL RIG)
exergonic reaction
A spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy.
endergonic reaction
A non-spontaneous chemical reaction in which free energy is absorbed from the surroundings.

Enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things - speeds them up
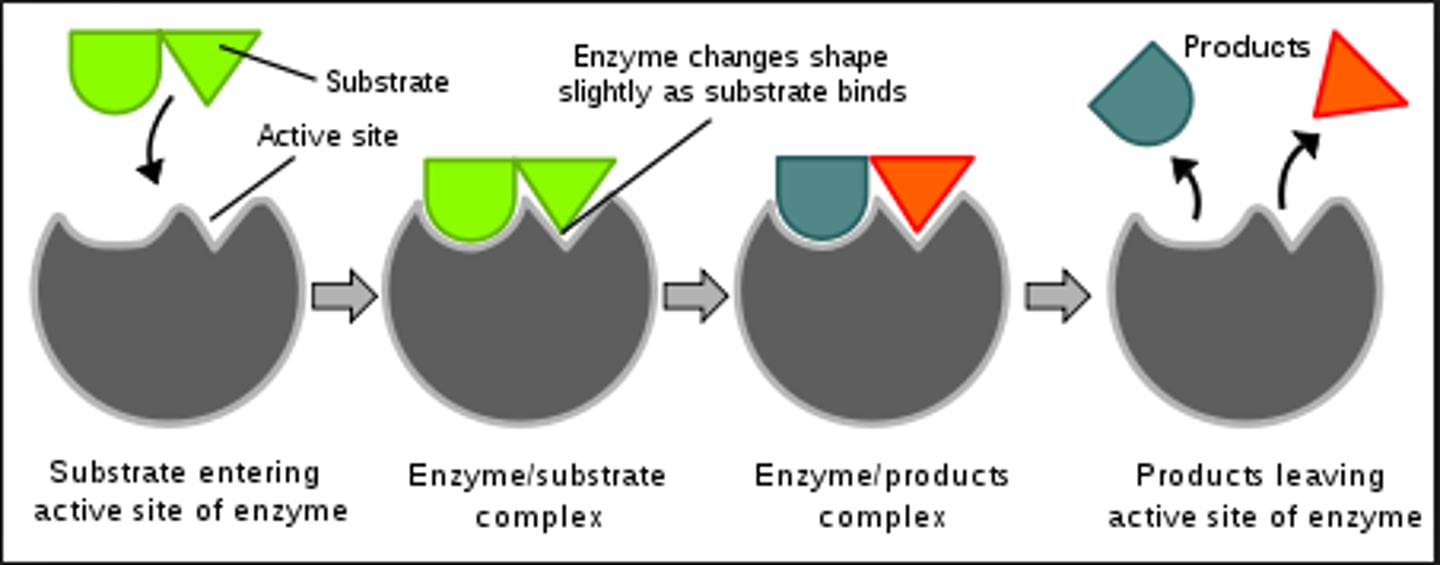
Enzymes are composed of
amino acids = proteins
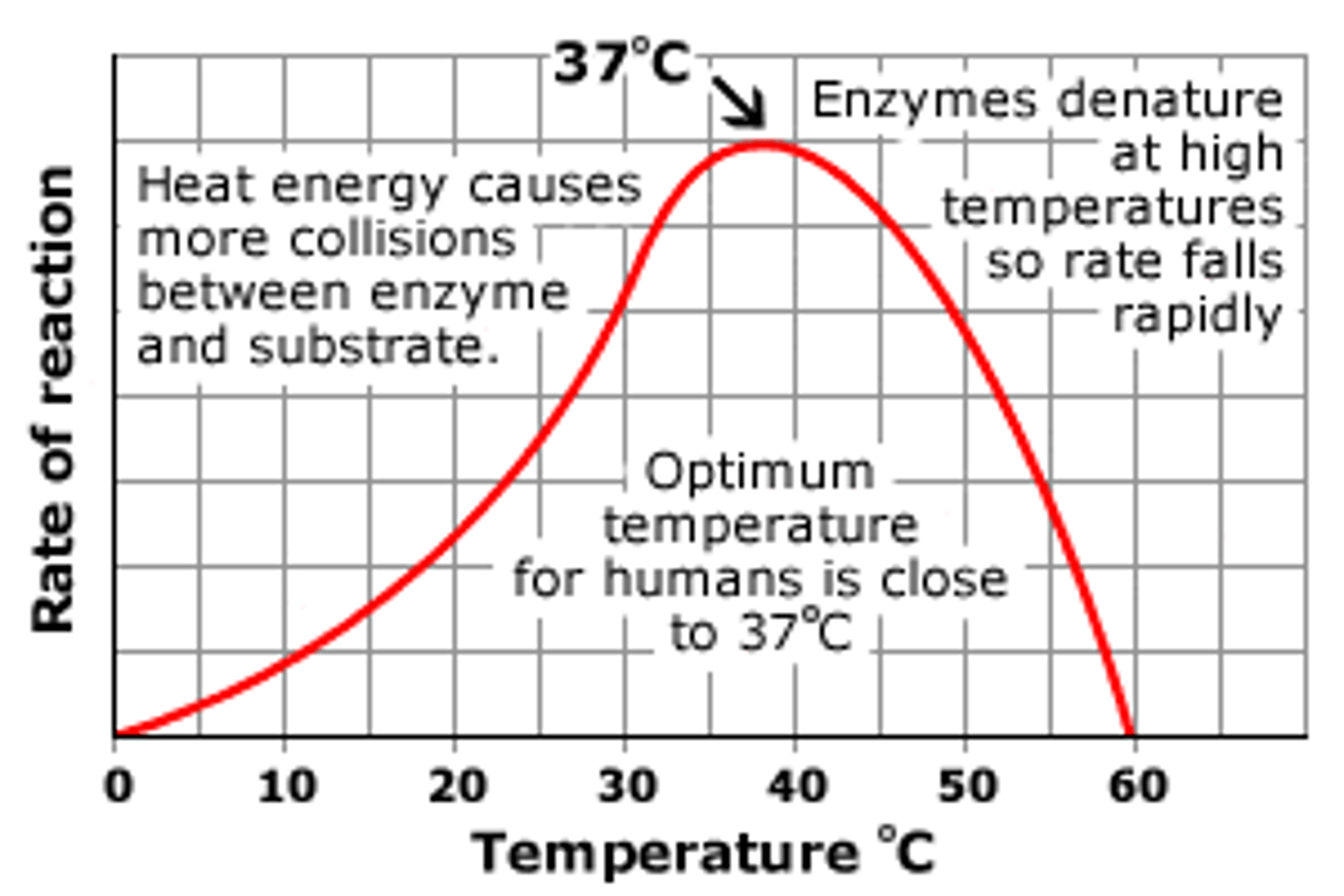
Factors that effect enzyme activity
more or less enzymes
temperature
ph
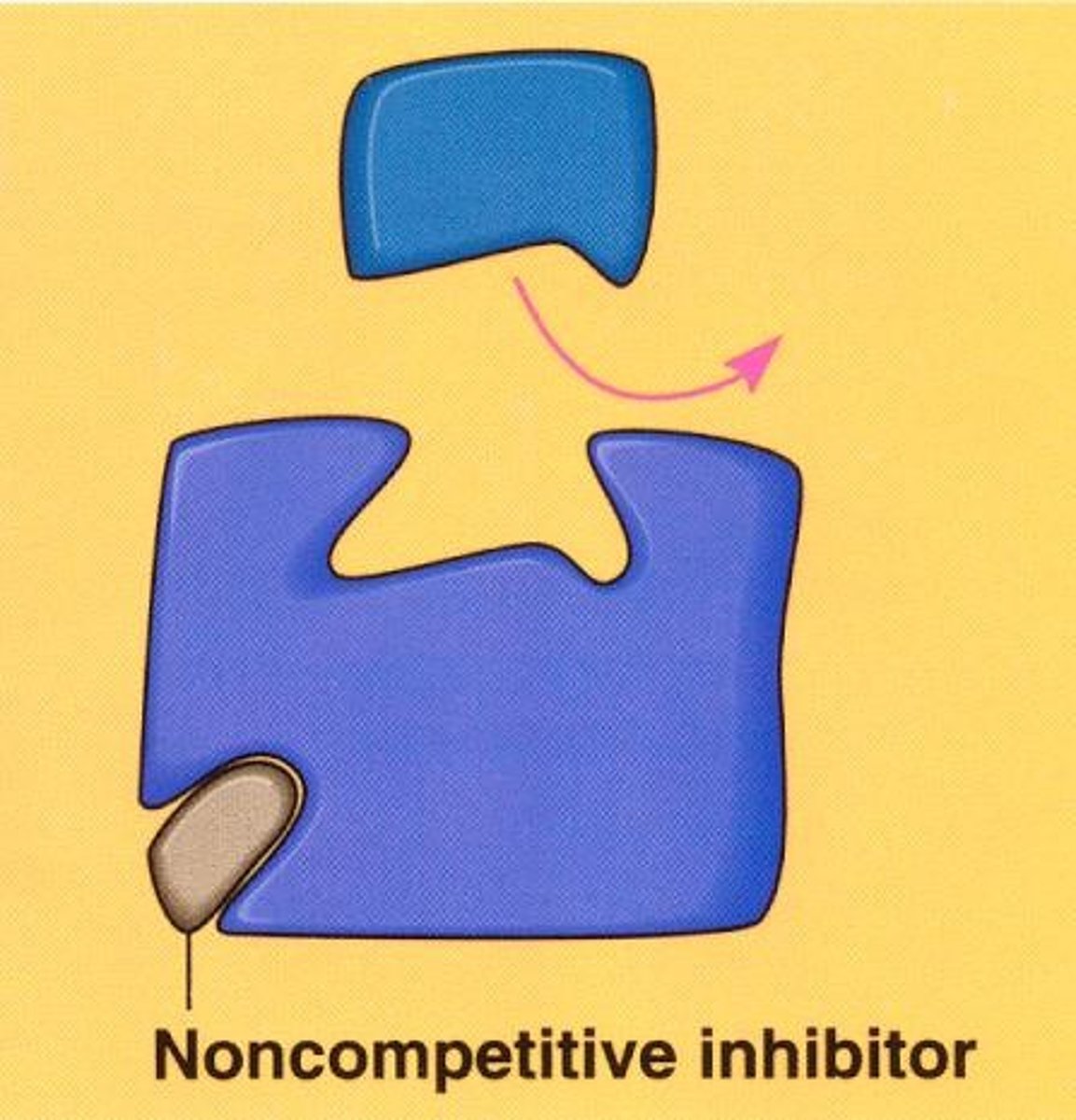
inhibitors
Inhibitor
A substance that slows down or stops a chemical reaction
Four steps of energy production
- Glycosis
- intermediate stage
- Citric acid cycle
- the electron transport system
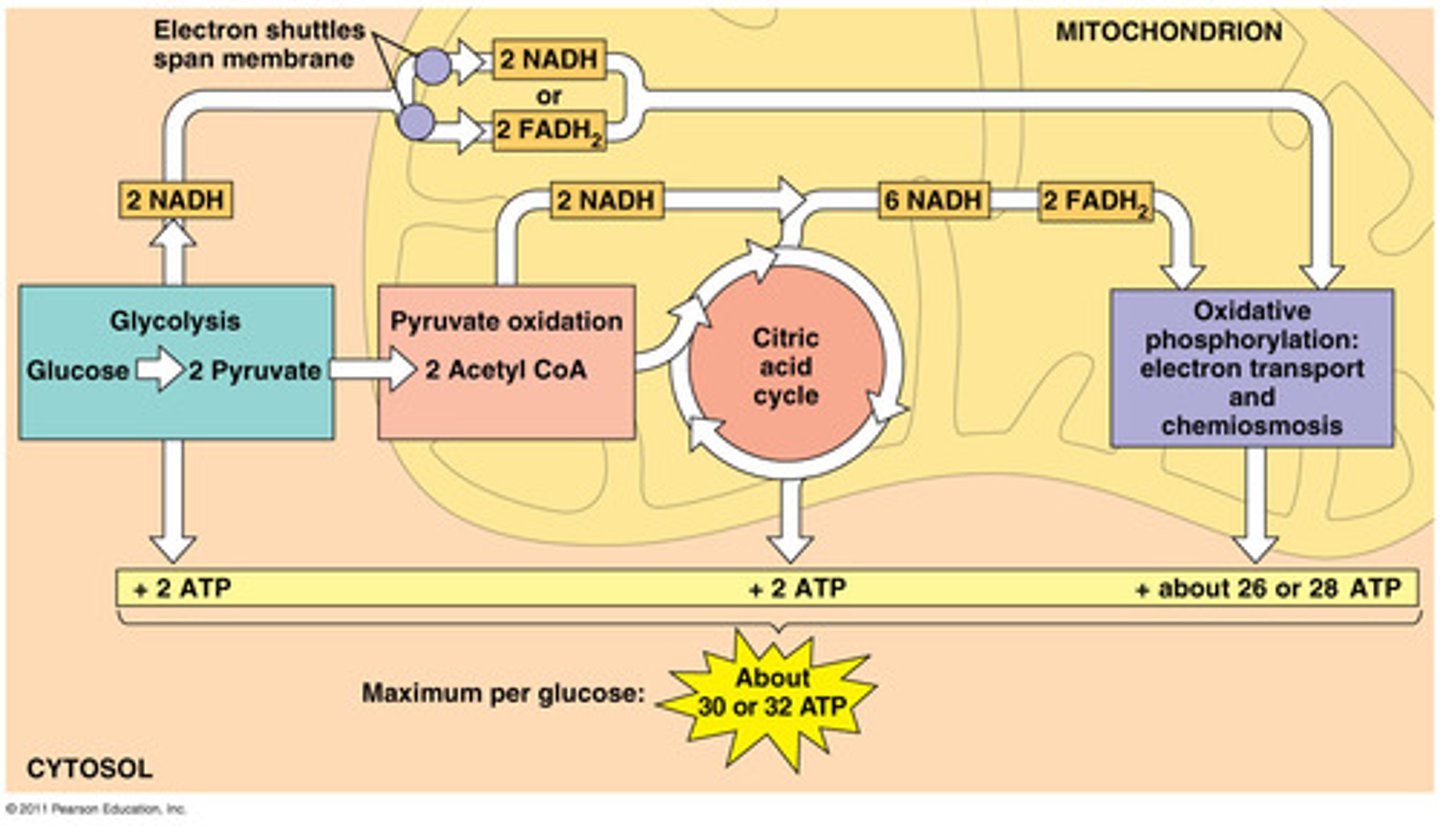
Glycosis
first step in releasing the energy of glucose and occurs in the cytosol; in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvate molecules. making 2 ATP and 2 NADH per glucuse
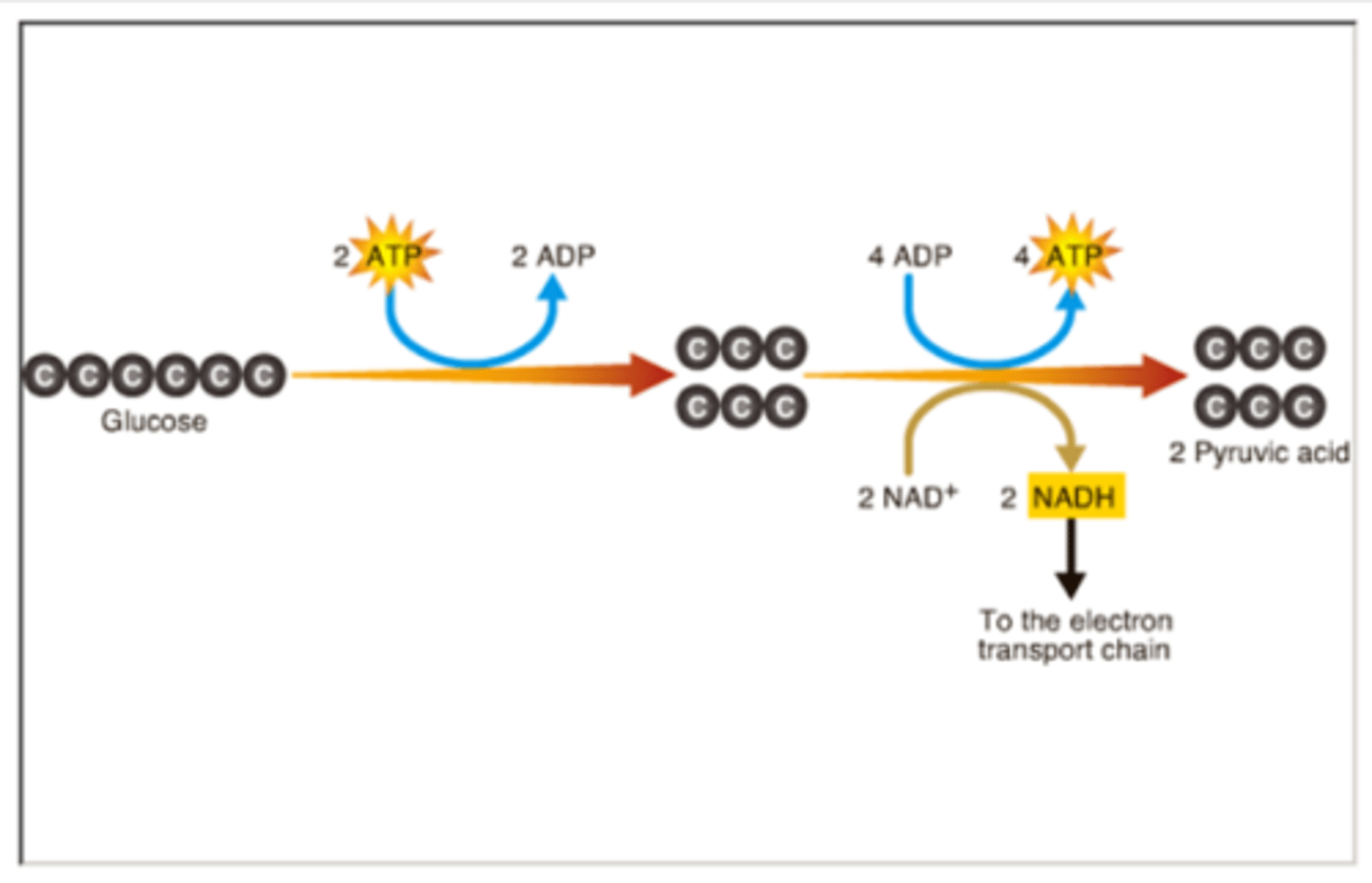
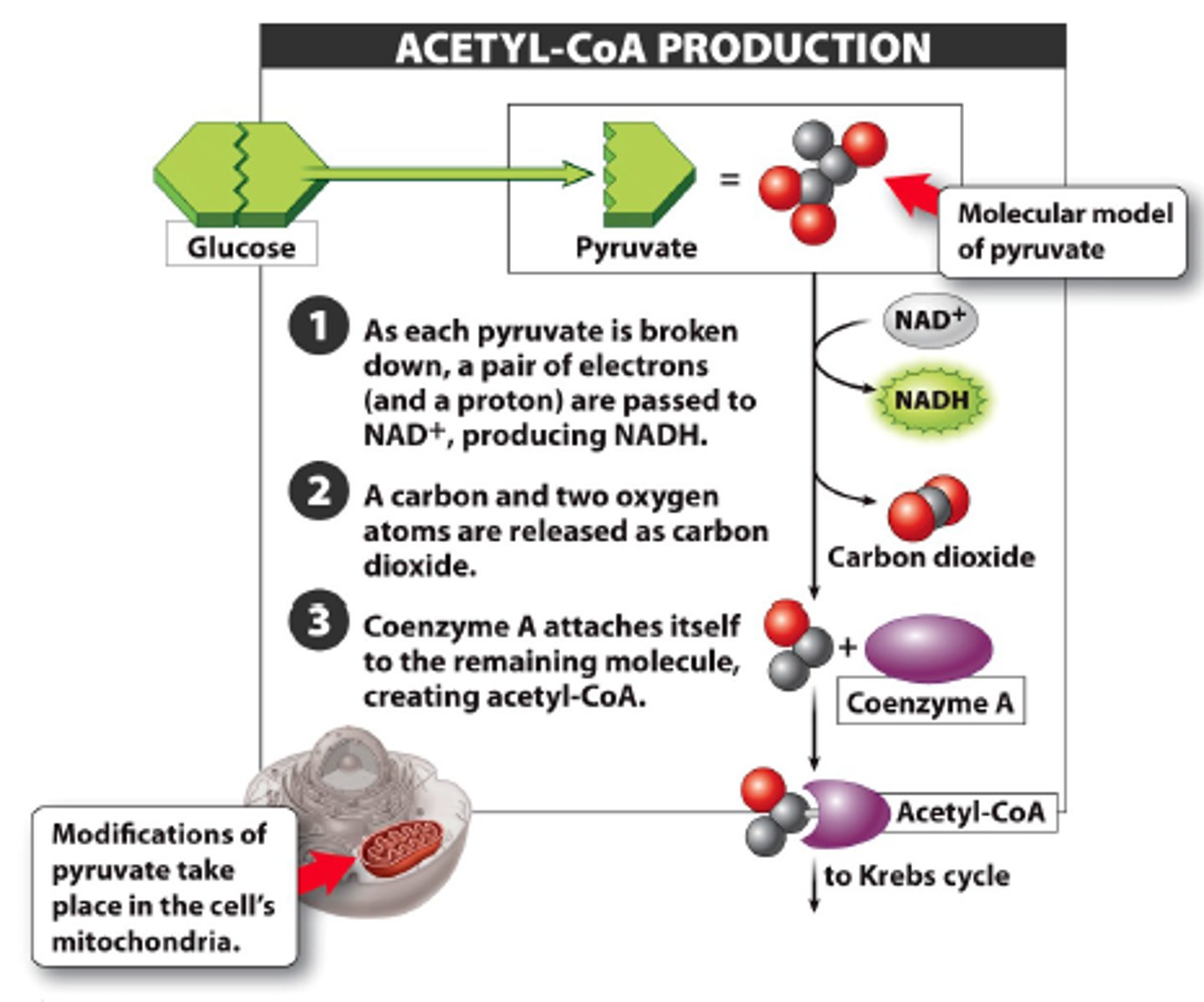
intermediate stage energy production
occurs in mitochondria, pyruvate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA and releases 1 CO(2), 1 NADH is produced per pyruvate
occurs 1x per original glucose
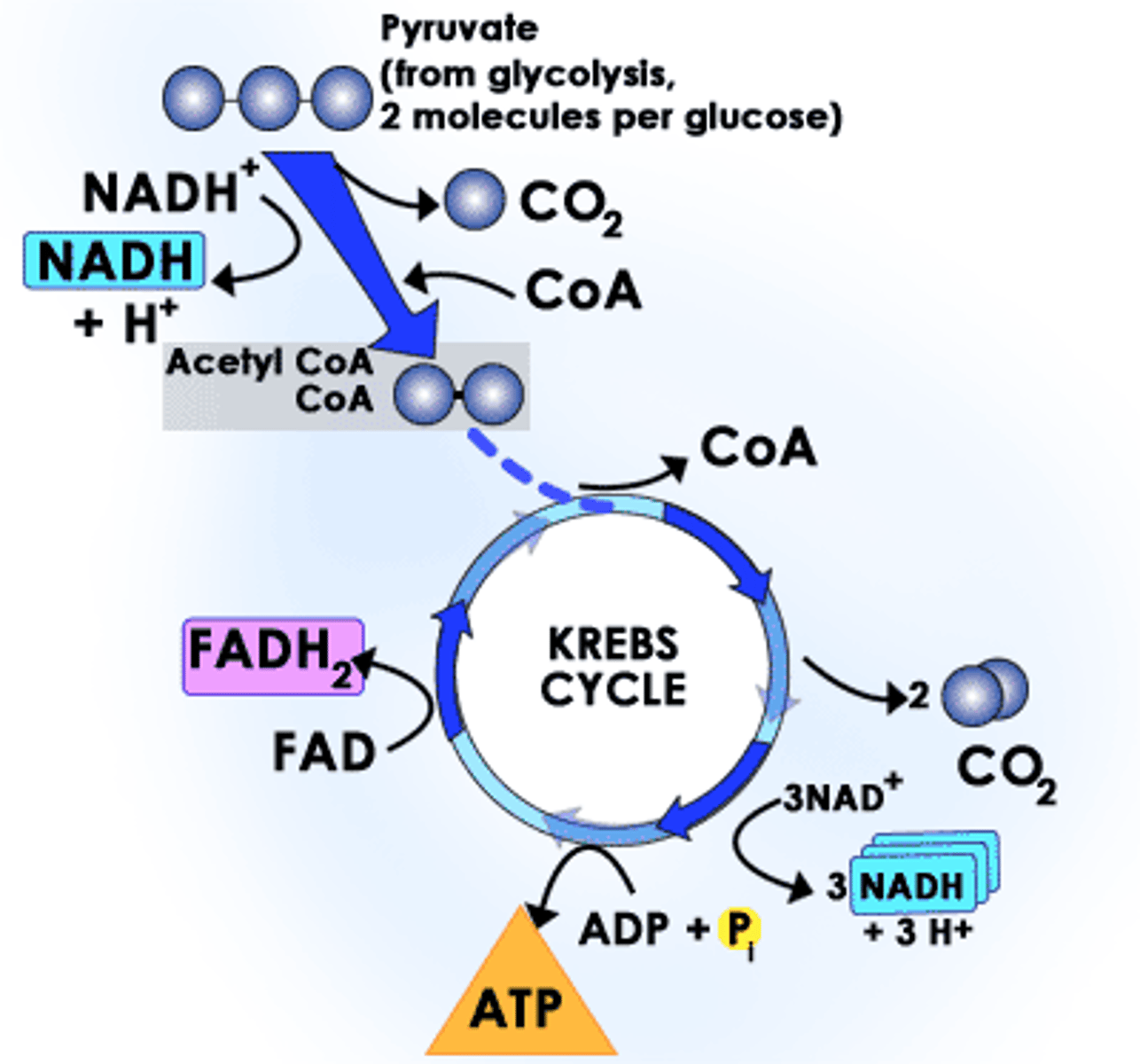
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
occurs in mitochondria, breaks down acetyl and creates 1 ATP, 3 NADH & 1 FADH(2)
occurs 2x per original glucose
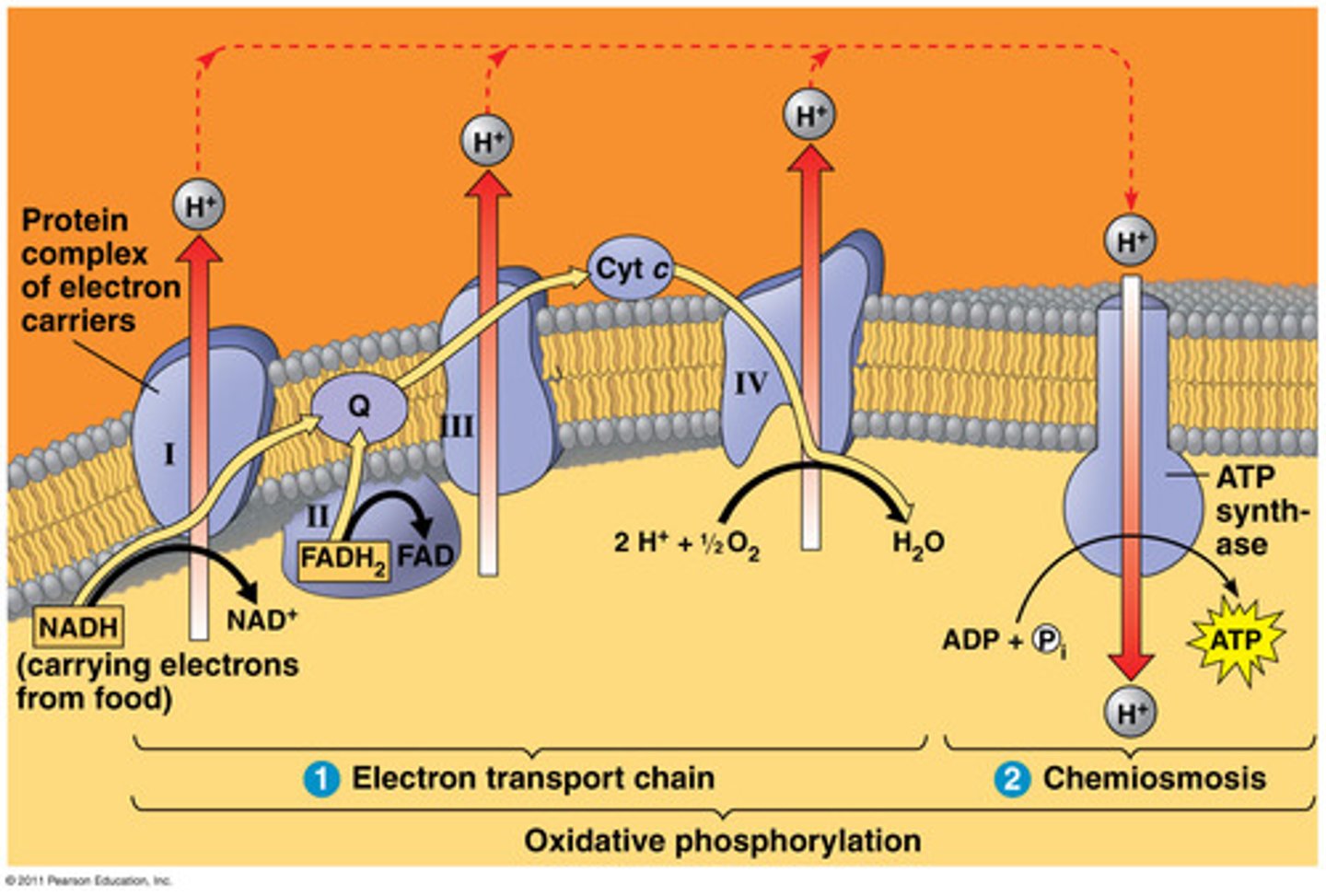
the electron transport system
Takes the electrons from NADH & FADH(2) to electron carriers in the electron transport chain of a mitochondria and O(2). The electron, hydrogen and oxygen ions form H(2)O. A H+ ion gradient is formed and an H+ ion flows down the gradient and the energy harnessed by ATP synthase to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation
Oxygen in Cellular Respiration
pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation—require oxygen in order to occur. Only oxidative phosphorylation uses oxygen directly, but the other two stages can't run without oxidative phosphorylation.
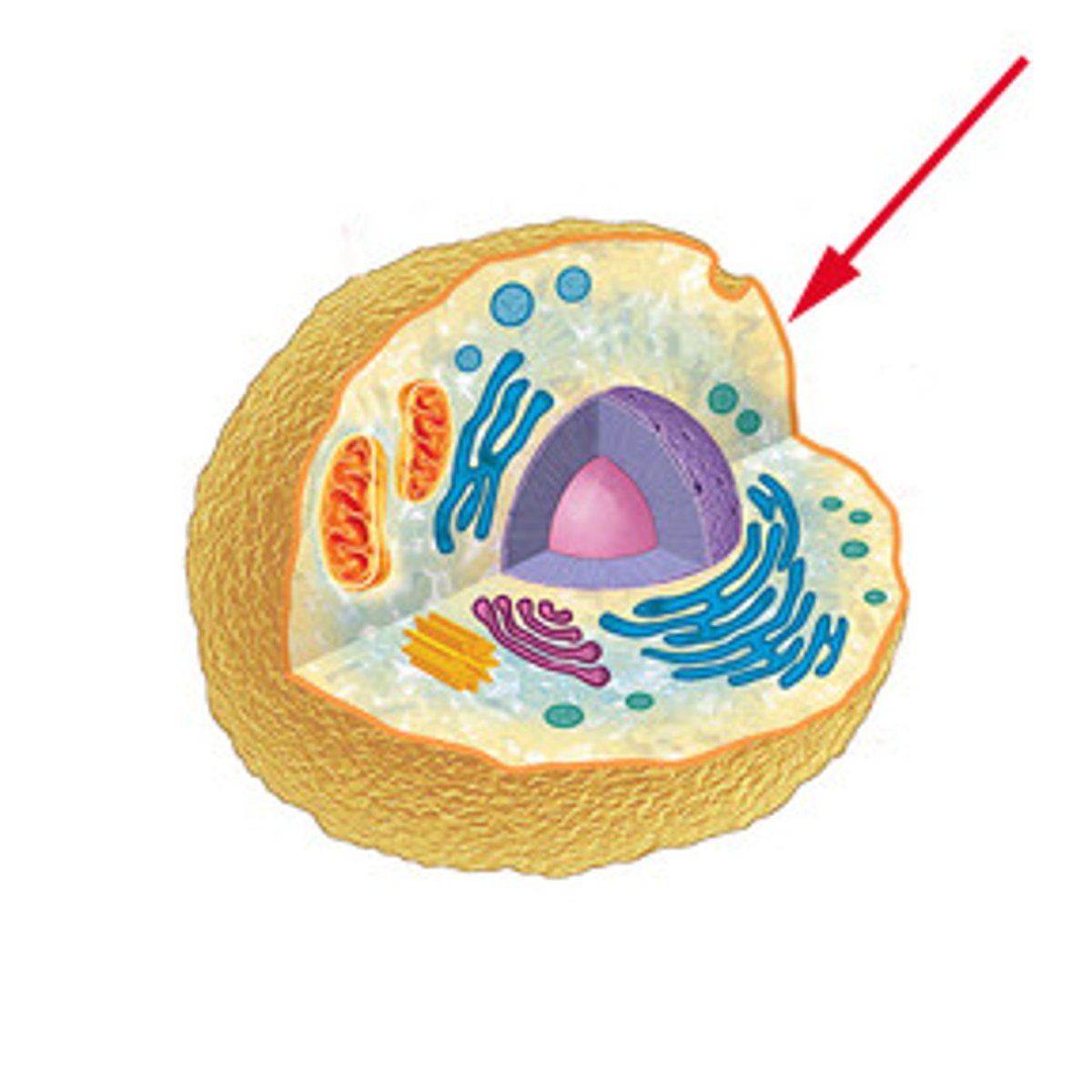
cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
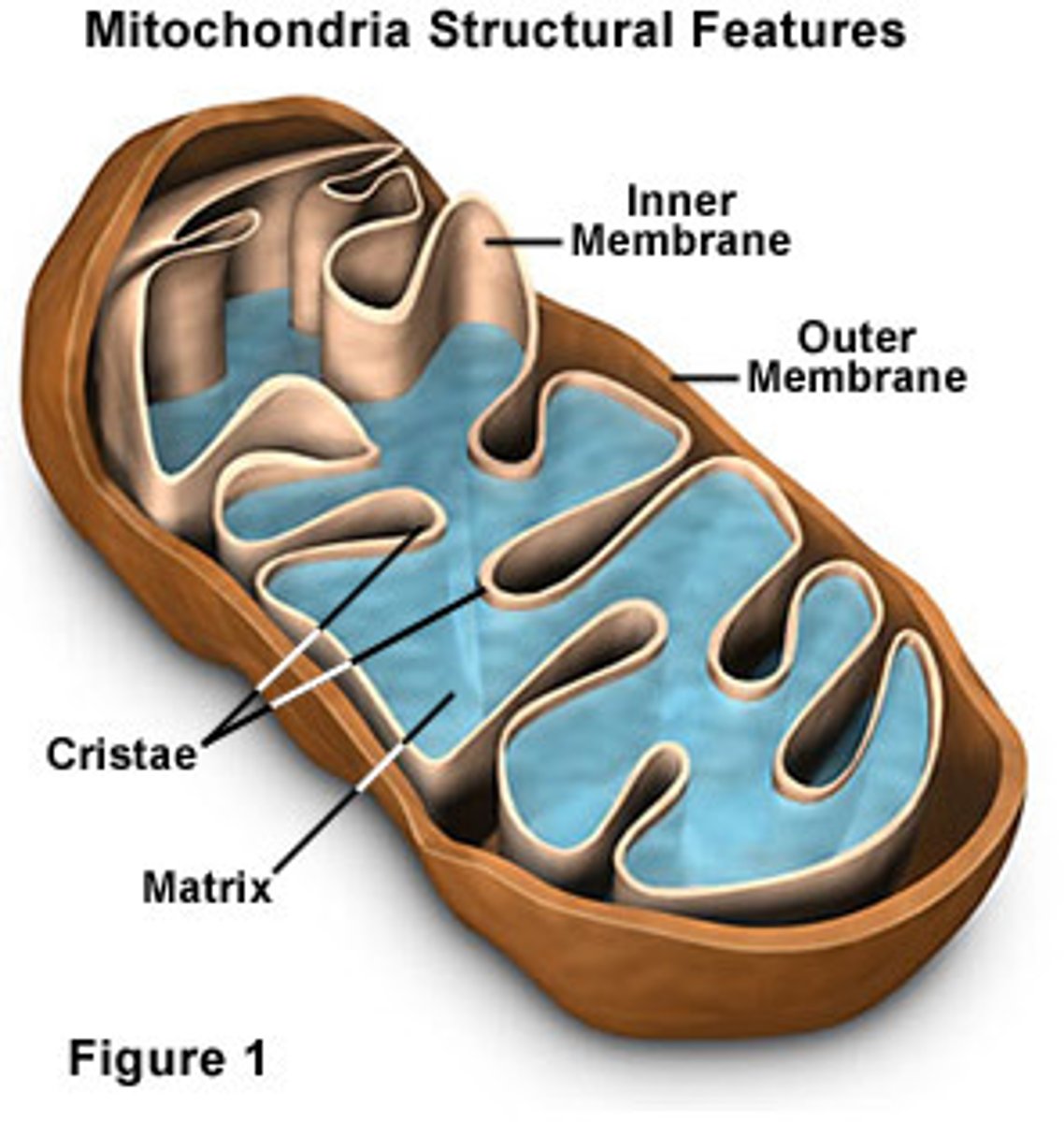
Mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
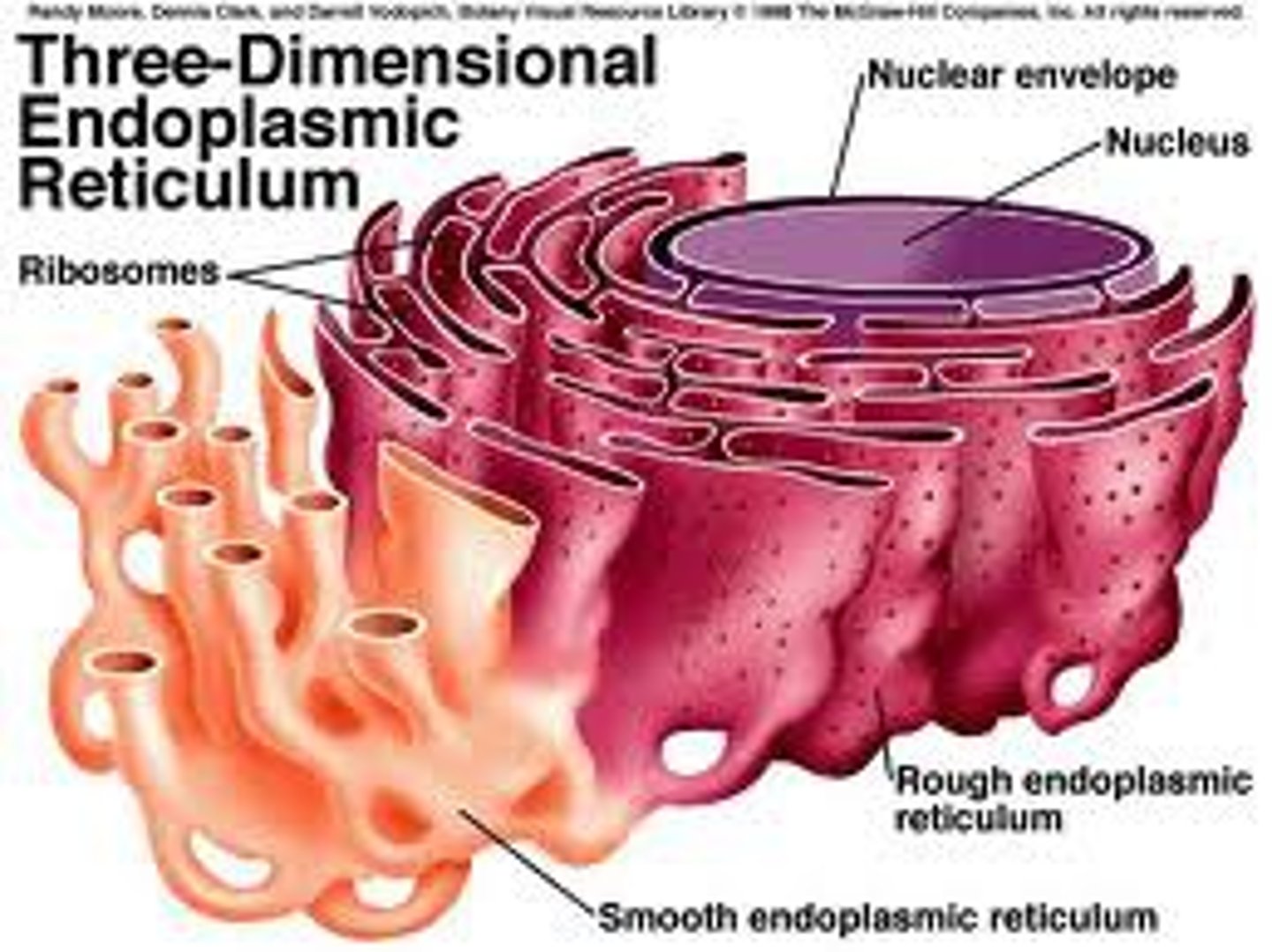
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. functions in transport of substances such as proteins within the cytoplasm
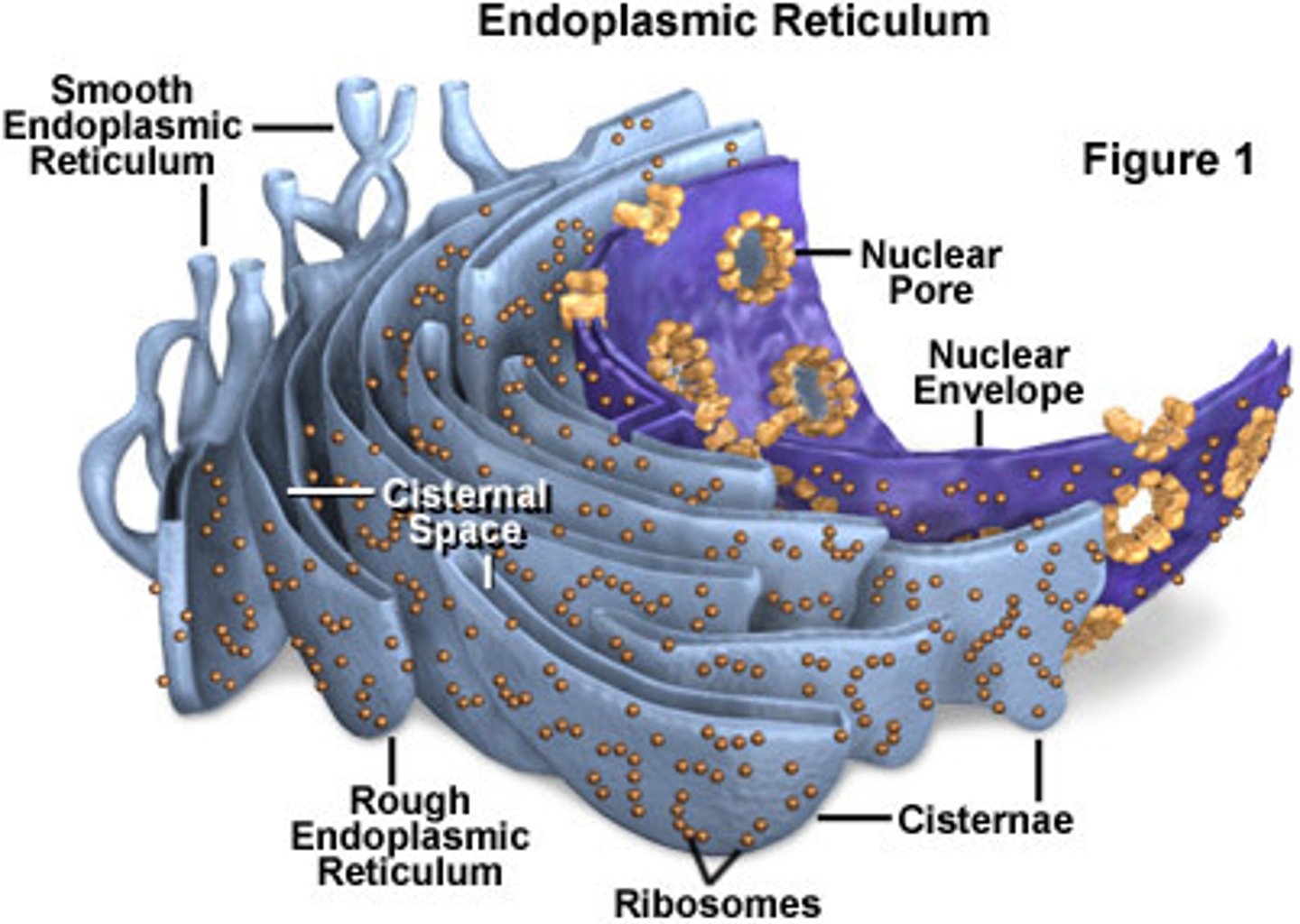
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
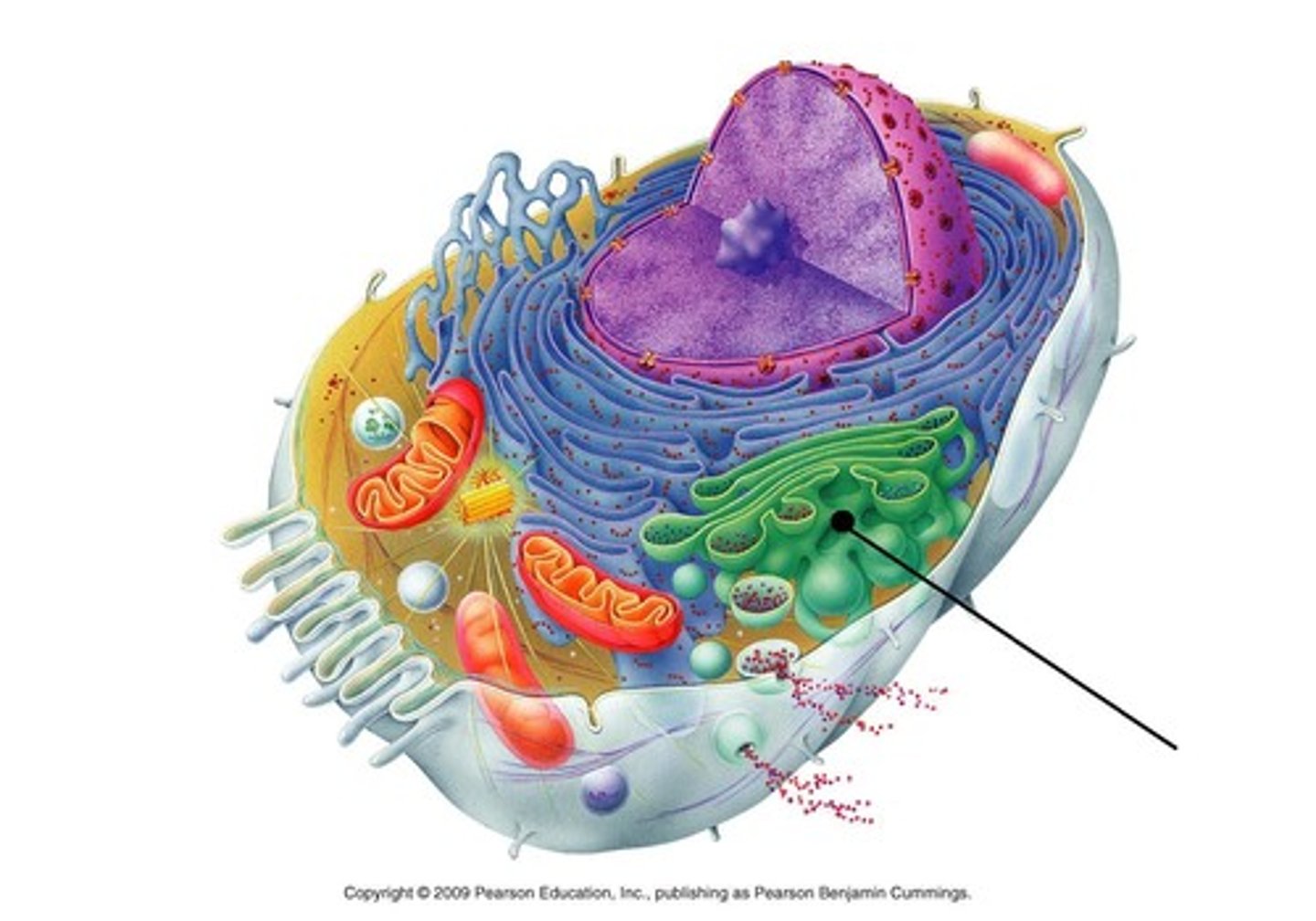
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
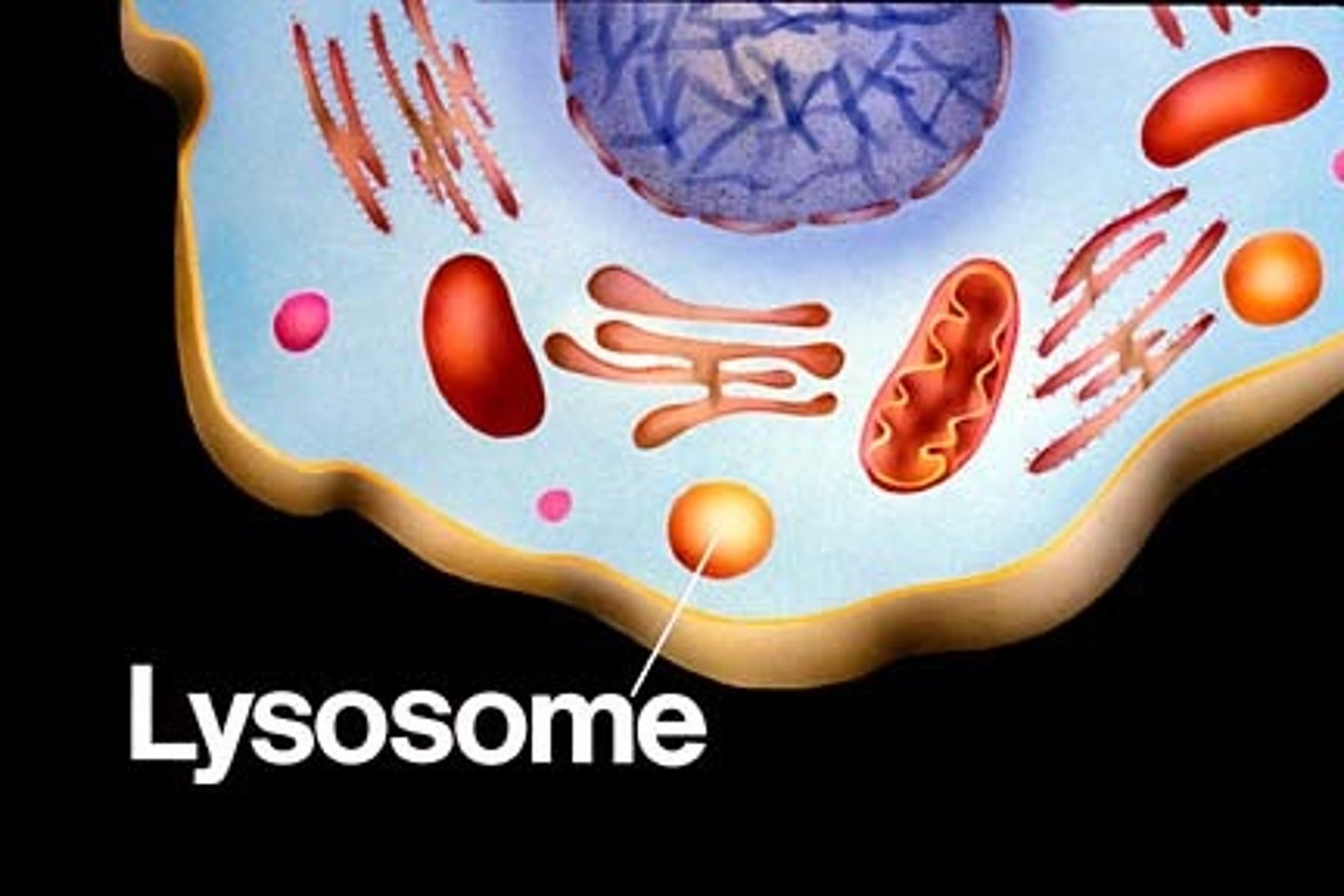
Lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down food and worn out cell parts
Peroxisomes
break down fatty acids to be used for forming membranes and as fuel for respiration; and transfer hydrogen from compounds to oxygen to create hydrogen peroxide and then convert hydrogen peroxide into water.
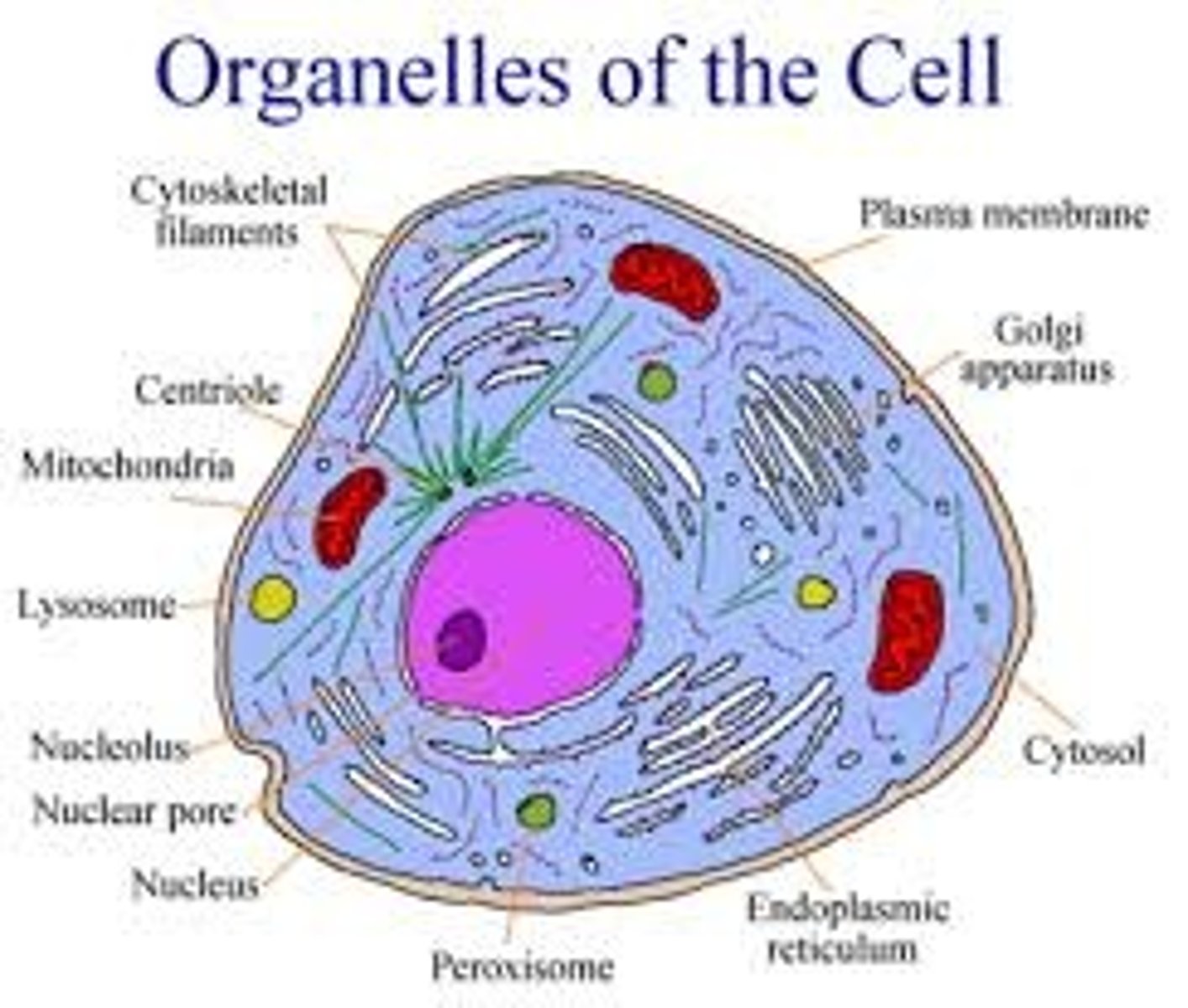
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
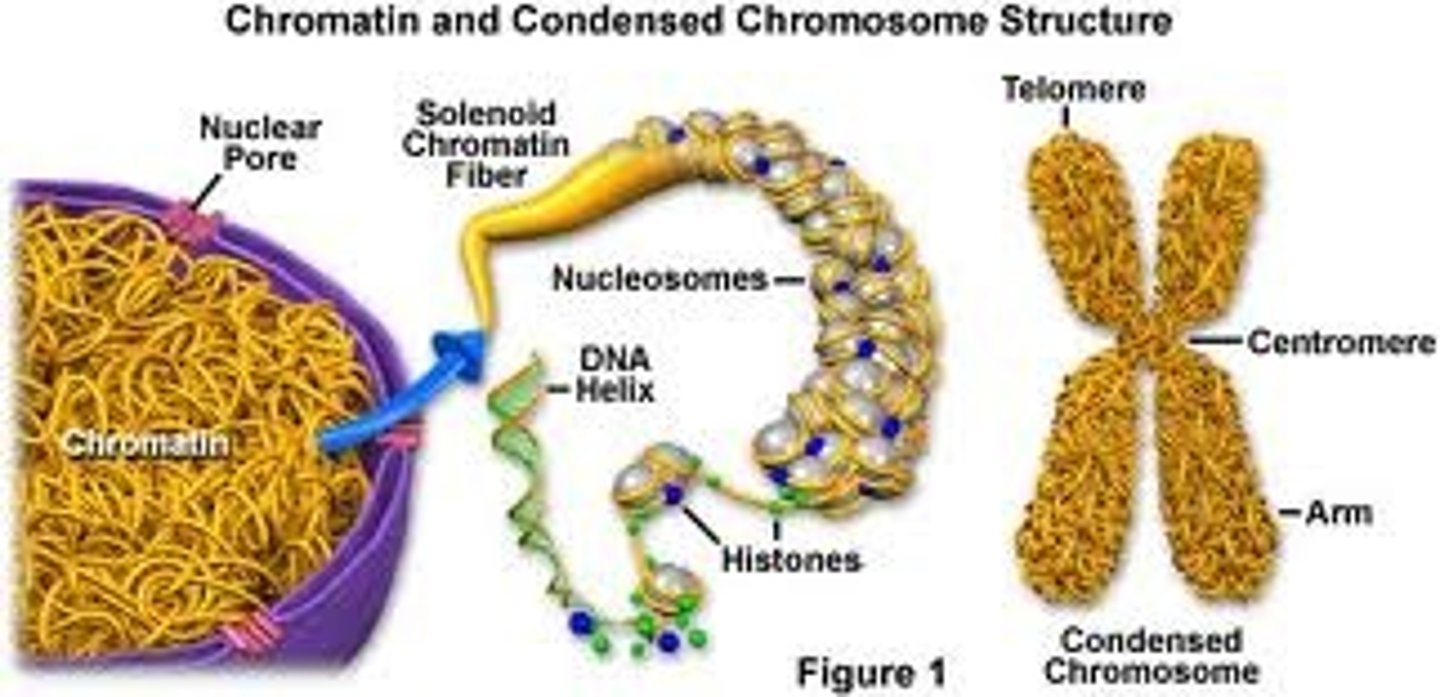
Chromatin
granular material visible within the nucleus; consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins
Stages of the cell cycle
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
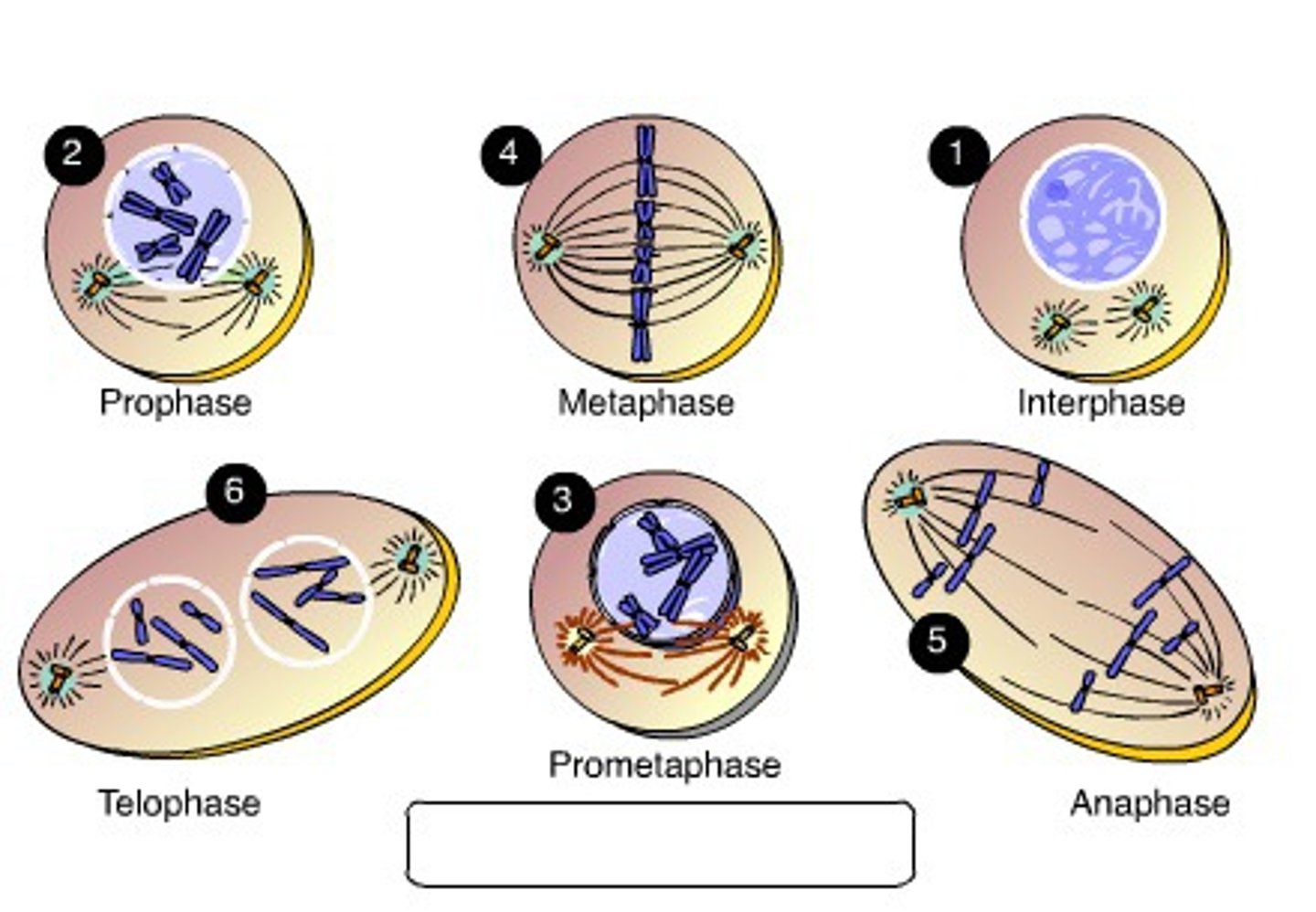
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division
Prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus
Metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
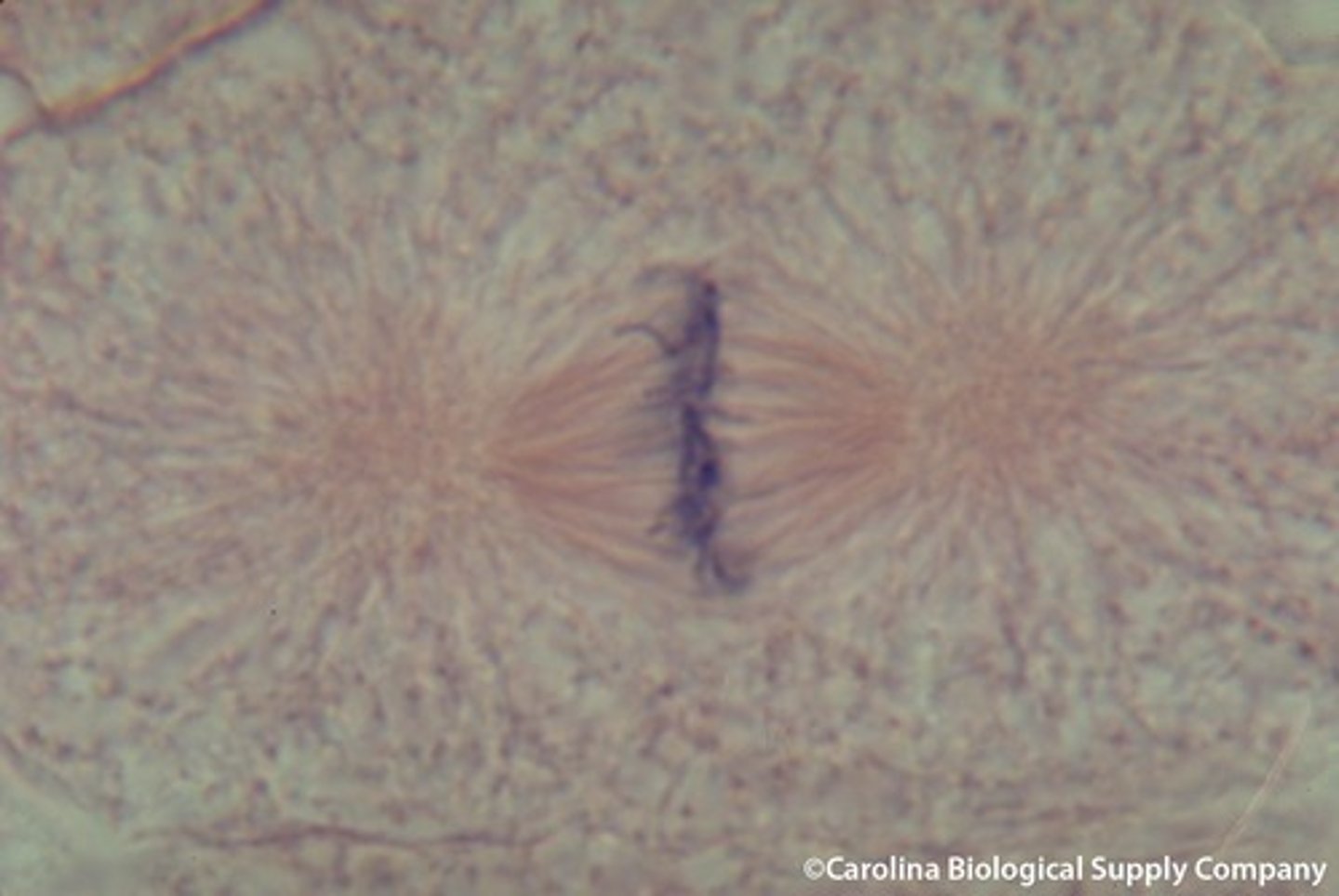
Anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
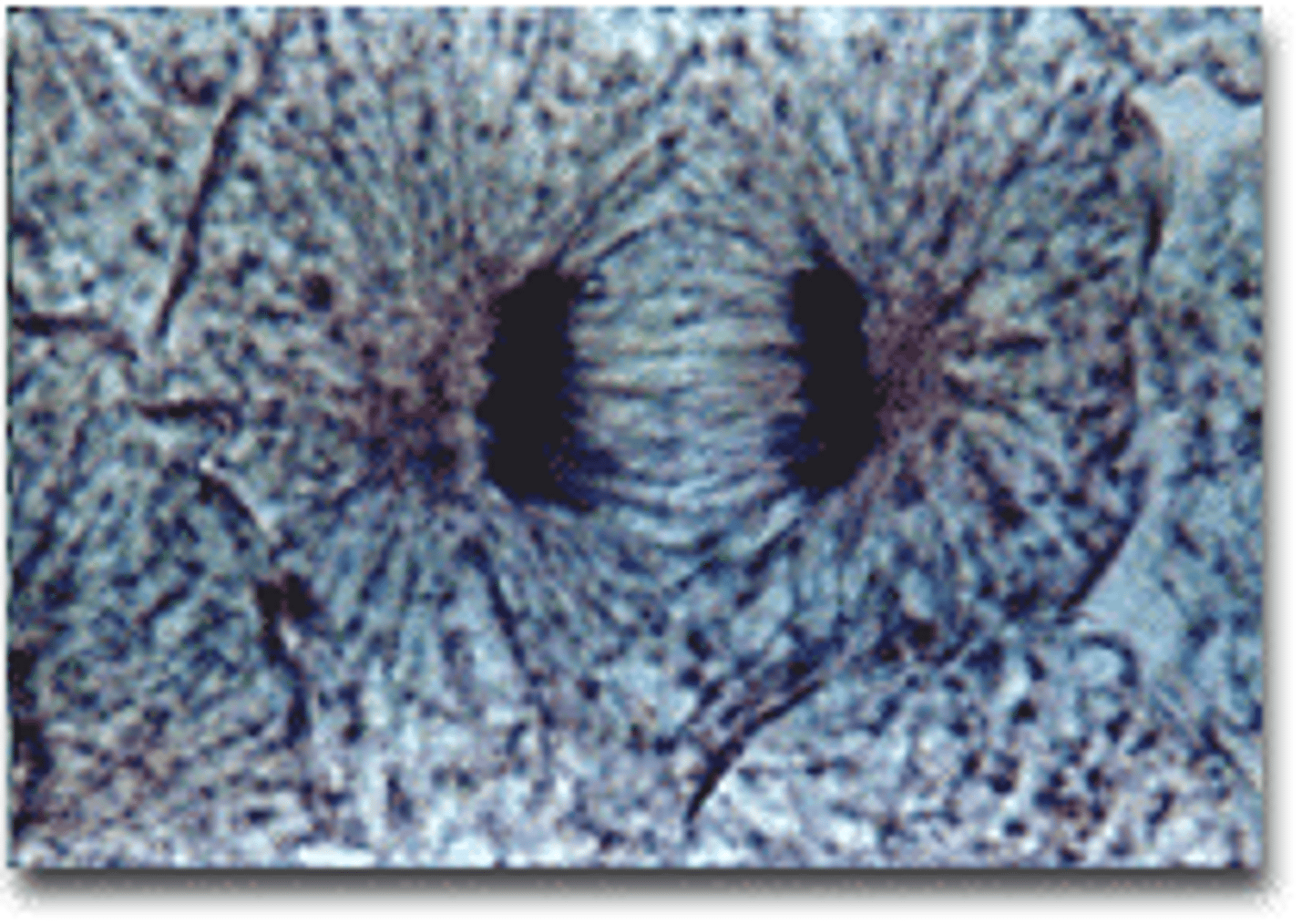
Telophase
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.
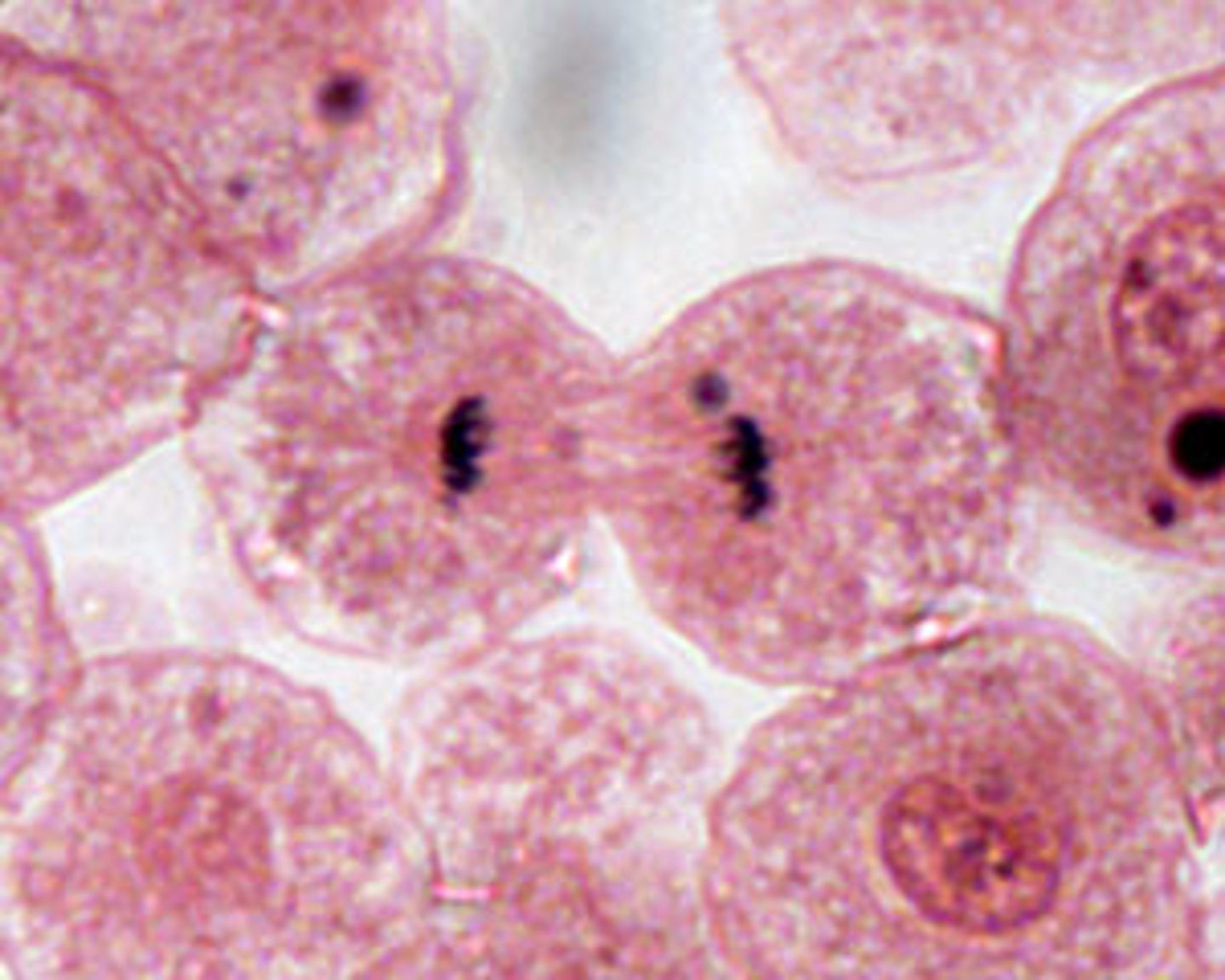
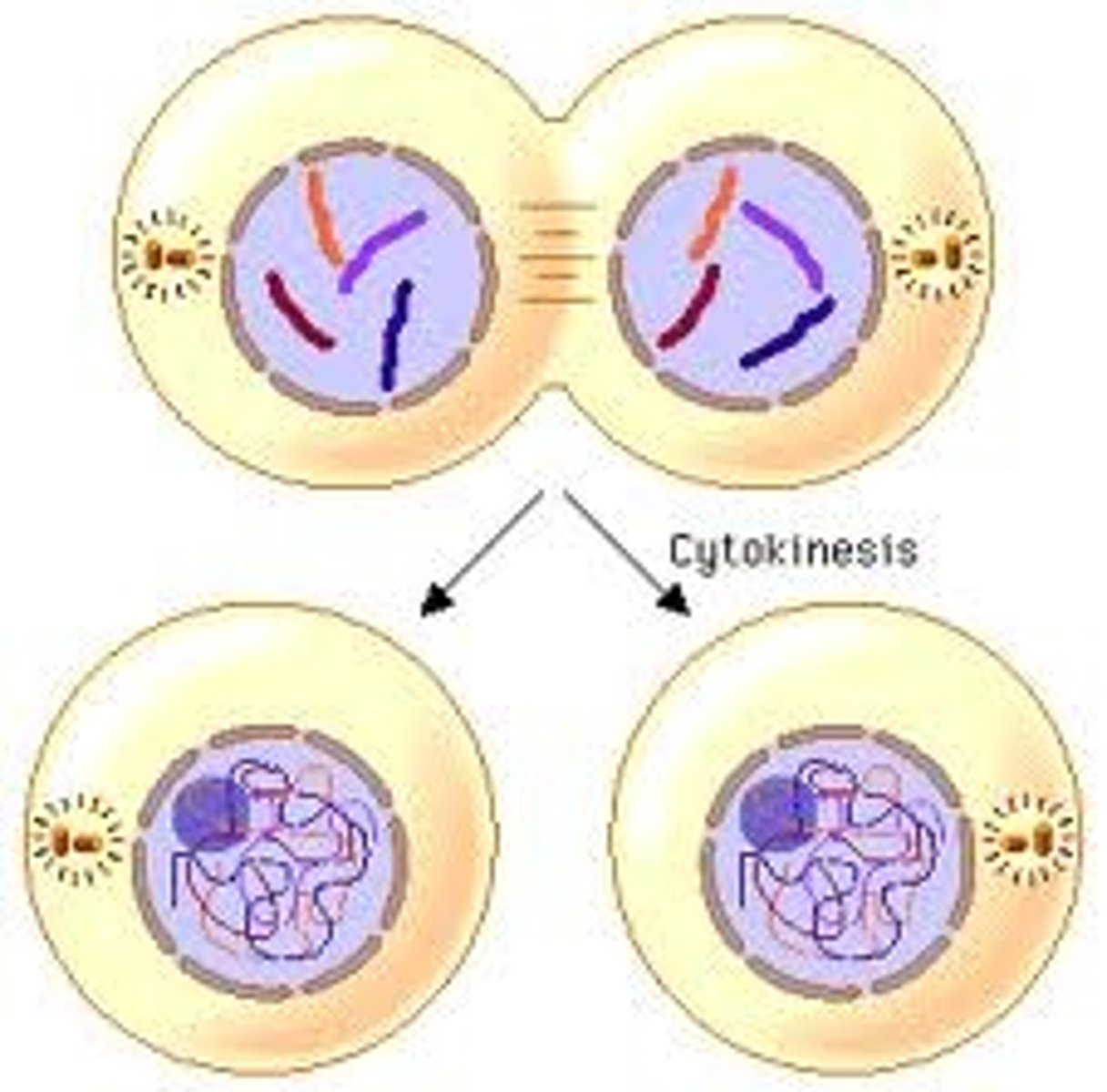
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
Transcription
(genetics) the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
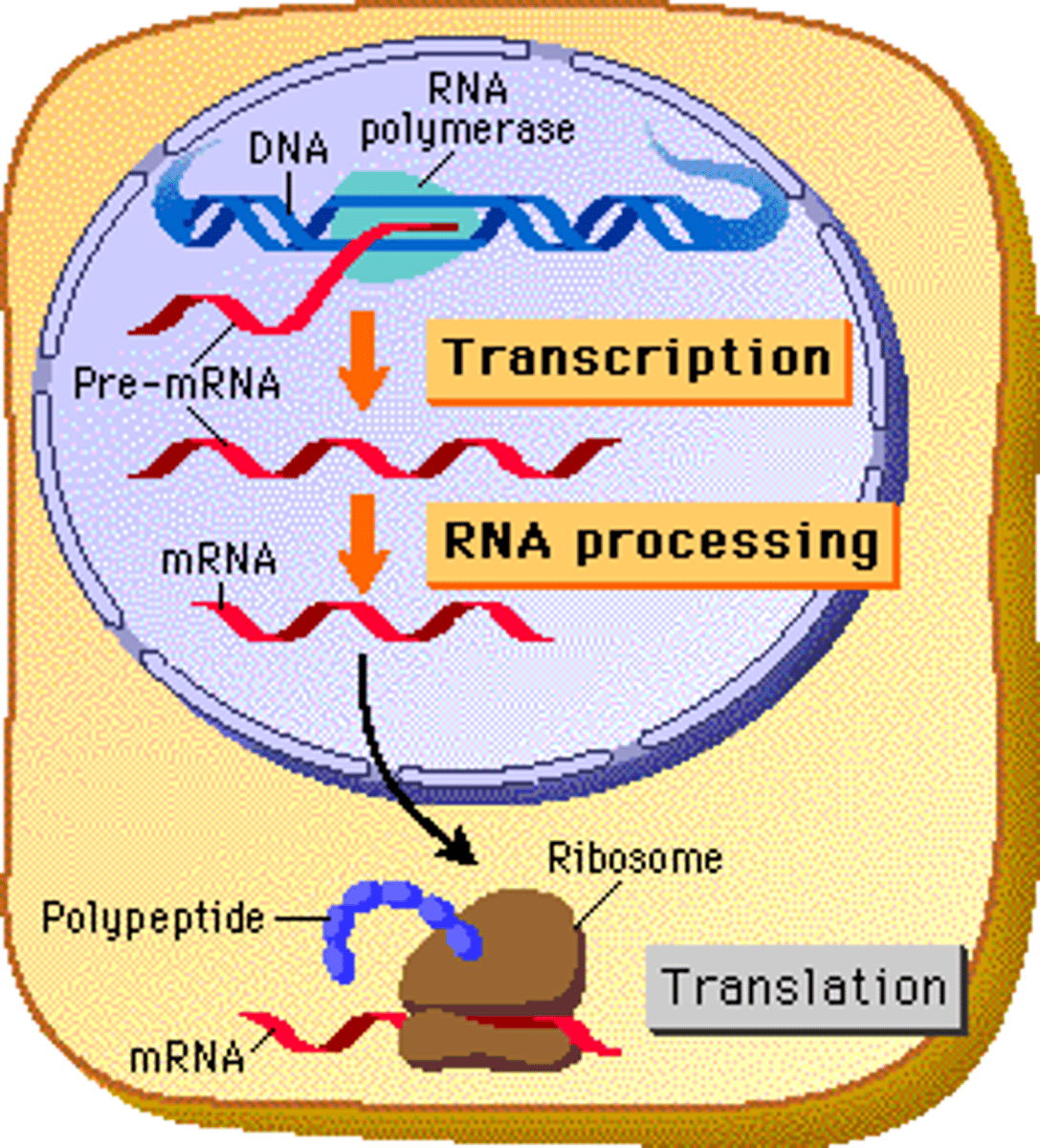
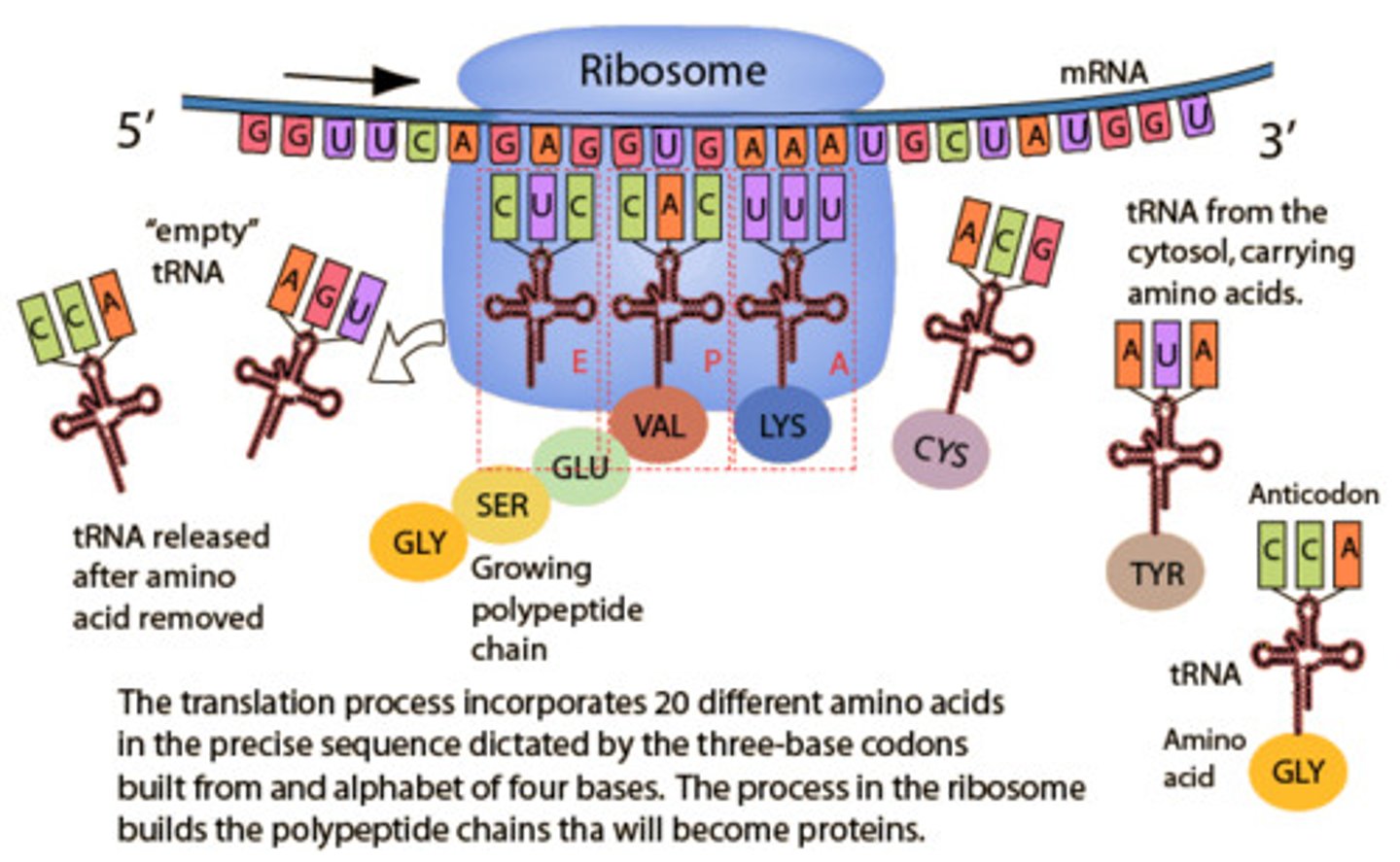
Translation
(genetics) the process whereby genetic information coded in messenger RNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosome in the cytoplasm
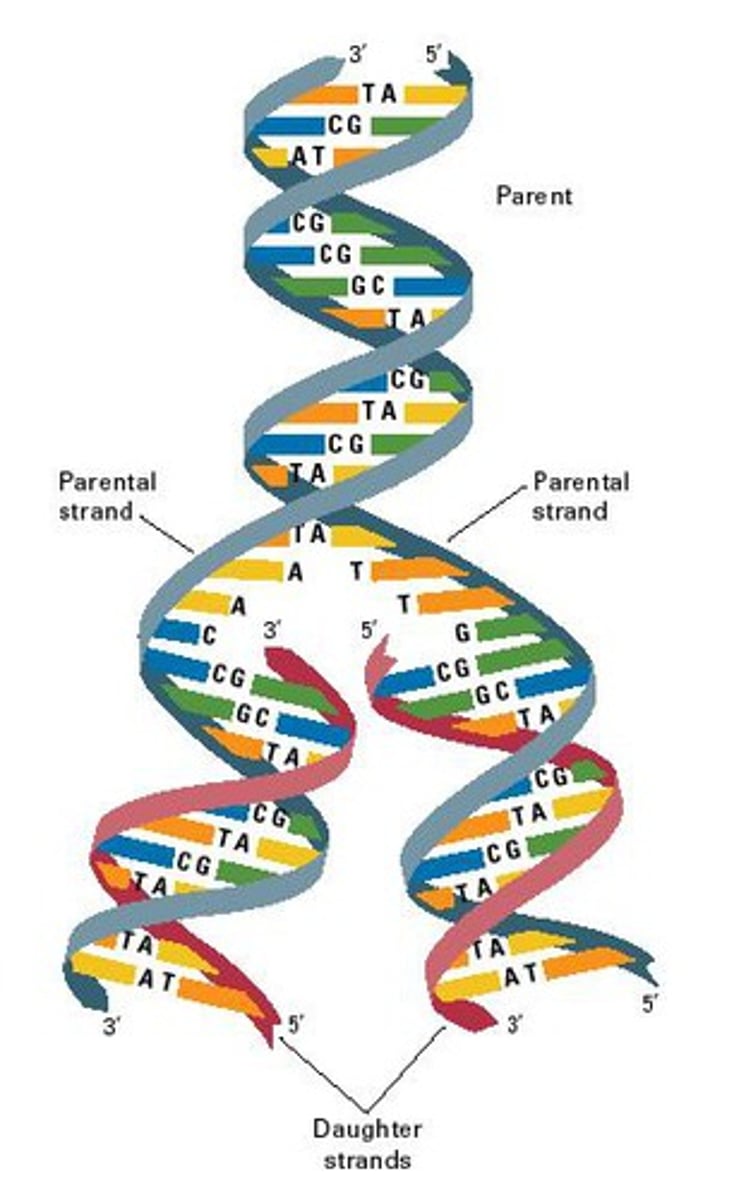
DNA replication
DNA unzips into two parts and splits with the cell. In it's new home each side of the DNA strand attach to matching nucleotide to create 2 exact copies. It is important in puberty and other times of growth as it is the reproducing of your cells.
quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.