Science 9: Projectile-Motion
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Projectile Motion
is a form of motion in which an object or particle is thrown near the earth's surface, and it moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only.
Projectile
an object in projectile motion.
Trajectory
path that the projectile follows.
Peak
highest point that the projectile could reach during its motion.
Range
the horizontal displacement of the projectile from its initial position in which its vertical displacement is zero.
Parabola
shape of the path of a projectile.
Horizontal
Motion of a ball rolling freely along a level surface.
always
Horizontal velocity is___ constant.
Vertical
Motion of a freely falling object and its force occurs due to gravity.
Vertical component
of velocity changes with time.
Parabolic
Path traced by an object accelerating only in the vertical direction while moving at constant horizontal velocity.
(v_x)_0 = (v_0) cos(theta)
When an object is projected at an angle with respect to the horizontal, the velocity of the projectile along the x – axis is given as (formula).
(d_x) = (v_x)_0 t
The displacement along the x-axis is given as (formula).
(v_y) = (v_y)_0 - gt
The velocity of the projectile along the vertical axis is given as (formula).
(v_y)_0= (v_0) sin(theta)
If an object is thrown at an angle with respect to the horizontal, its initial velocity along the y – axis is given as (formula).
(d_y) = (v_y)_0 t1/2 gt²
Hence, the object’s displacement along the vertical axis is given by the (formula).
R = [(v²_0) sin 2(theta)] / g
When a projectile is launched at a certain angle above the ground, its range is calculated using the equation (formula).
H = [(v²_0) sin(theta)] / 2g
The maximum height can be solved using the equation (formula).
Objects Projected Horizontally
In finding these, consider the equations below. Remember to treat the horizontal and vertical components of the motion independently.
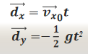
horizontal component of motion
[ORA]: The ___ of motion is the same throughout the duration of motion.
vertical component
[ORA]: The ___ decreases in magnitude on the first half of the projectile since acceleration due to gravity is in the opposite direction of motion.
zero
[ORA]: When the object reaches the peak of its trajectory, its velocity becomes ___.
increase
[ORA]: The horizontal component starts to ___ as the object moves downward.