peptide bonds and primary structure
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
How are proteins formed
Amino acids link together via peptide bonds (amide bond)
What parts of the amino acid form the peptide bond
a-COOH of one amino acid reacts with the a-NH2 of another
Peptide backbone
NH-CH-CO
Everything but the side chain
Nomenclature of peptides
Written from N terminus to C terminus
Ex) alanylglutamylserylglycine
Characteristics of a peptide bond
Delocalized pi binding making the bond planar (not the peptide)
Rotation around the C-N bond is restricted due to its double bond character
Length of peptide bond
Shorter than its surrounding bonds at 1.32 A
Rotation around the peptide bond
At psi and phi
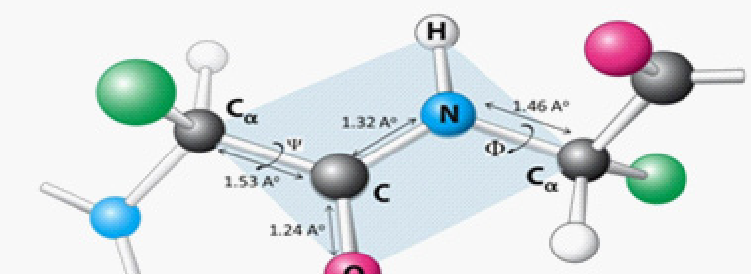
What configuration is the peptide if the R groups are on the same side
Cis
How much do amino acids weigh
One residue is 110 g/mol
Dalton
1 g/mol
How much does a protein with 64 amino acids weigh?
64 aa x 110 g/mol= 7040 g/mol
= 7040 Da x 1kDa/1000 Da
= 7.04 kDa
Polypeptide
Polymer of amino acids
10 or fewer amino acids is called
Oligopeptide
More than 10 amino acids is called
Polypeptide
Chain length of 50 or more amino acids is called
Protein
Why is Cysteine special
Can create disulfide bonds (covalent) to force a certain type of folding of the protein
What kind of links can cysteine make
Interchain and intrachain
Sangers results of insulin
Sequenced 2 chains of insulin and found that all molecules of a given protein have the same sequence
Primary structure of proteins
Amino acid sequence that forms the polypeptide (backbone)
What is the directionality of the primary structure
N terminus towards C terminus
Influences of the primary structure
Interactions between the aa side chain and water and the polypeptide
3D structure of the protein