Kinetic Theory of Gases
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
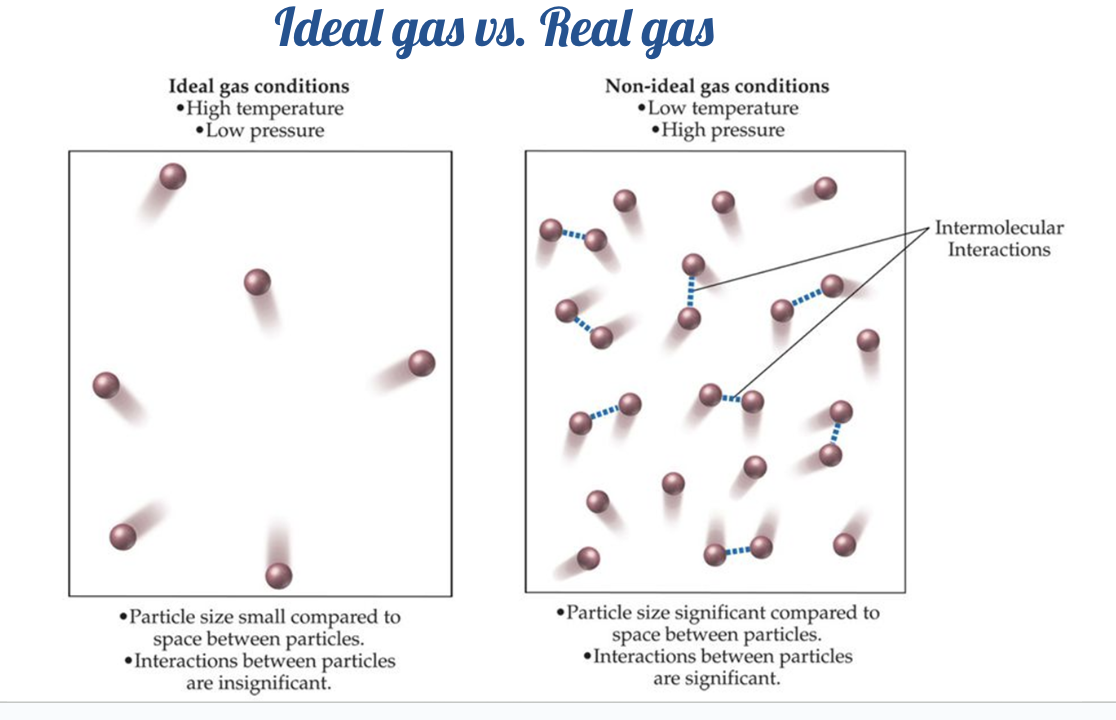
Ideal gases
ideal gas equation
AN IDEAL GAS”
Particles are in constant and random motion.
All collisions between particles are elastic
The volume of gas particles is negligible compared to the volume of container
There are no intermolecular forces between gas particles
The kinetic energy of gas particles is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas
pV = nRT
p = pressure in pascals (Pa)
T = temperature in kelvins (K)
V = volume in cubic meters (m3)
n = the amount of gas (mol)
R = gas constant (8.3145 (J)/(mol × K))
Avogadro’s law
Equal volumes of gases contain the same number of particles at the same temperature and pressure!
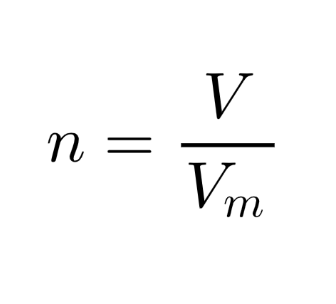
n = Amount of substance (mol)
V = Volume of gas (l = dm3)
Vm = Molar volume of a gas (22.7 L) in STP
STP = Standard Temperature and Pressure
Temperature 273.15 K = 0 oC
Absolute pressure of exactly 1 bar = 100 000 Pa
Combined gas law
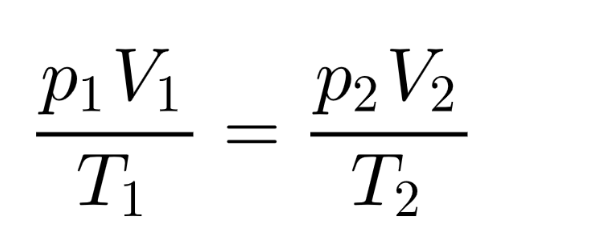
p1 = initial pressure p2 = final pressure
T1 = initial temperature T2 = final temperature
V1 = initial volume V2 = final volume
e