Lecture 11 Pt. 1: Carbohydrate Biosynthesis in Plants and Bacteria
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
NADPH and ATP is used by carbon assimilation reactions to achieve what?
reduce CO2 and generate trios phosphates and more complex compounds
What kind of compounds are synthesized from trios phosphates?
glucose, sucrose, cellulose
Water is the source of what that get passed via what to the ultimate what?
electrons
chain of protein transporters
electron acceptor, NADP+
Light energy is used to what in the context of photophosphorylation?
separate charges on chlorophyll
generate NADPH and phosphorylate ADP
What is the byproduct of water oxidation?
oxygen
Catabolic
generate chemical energy via oxidation of biomolecules
Anabolic
synthesize cellular components from simple precursor molecules using chemical energy
associated with reduction
Plants are autotrophs that rely on what to utilize what for what result?
anabolic reactions
inorganic carbon
synthesize organic compounds
CO2 in an anabolic reaction is converted to what?
trios phosphates and hexose phosphates
What are trios phosphates and hexose phosphates used for?
synthesis of sucrose, starch, cell wall components, pentose phosphate pathway
make other metabolic intermediates
Starch
high molecular weight polymer of D-glucose
alpha 1,4 linkage
Where is starch made?
chloroplasts → short term storage
amyloplasts of non photosynthetic parts i.e., roots, seeds, tubers → long term storage
Starch provides the bulk of what for plants?
stored energy
Where is sucrose made?
cytosol for transport
Sucrose is considered what for plants?
“blood glucose” of plants
Starch synthesis proceeds similarly to what process?
glycogen synthesis
Gluconeogenesis of two glyceraldehyde-3-phosphates result in what?
glucose-6-phosphate
Phosphoglucomutase converts glucose-6-phosphate to what?
glucose-1-phosphate
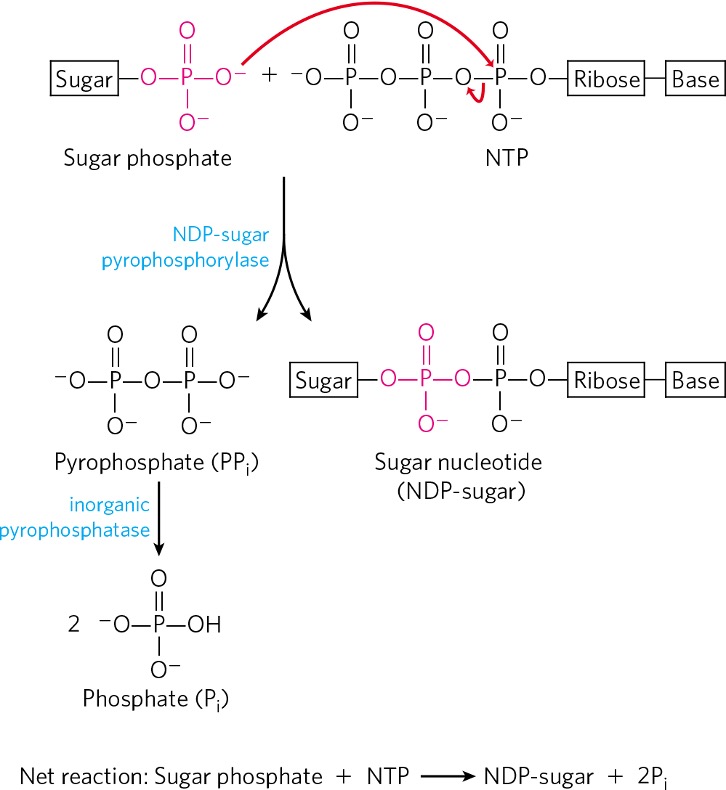
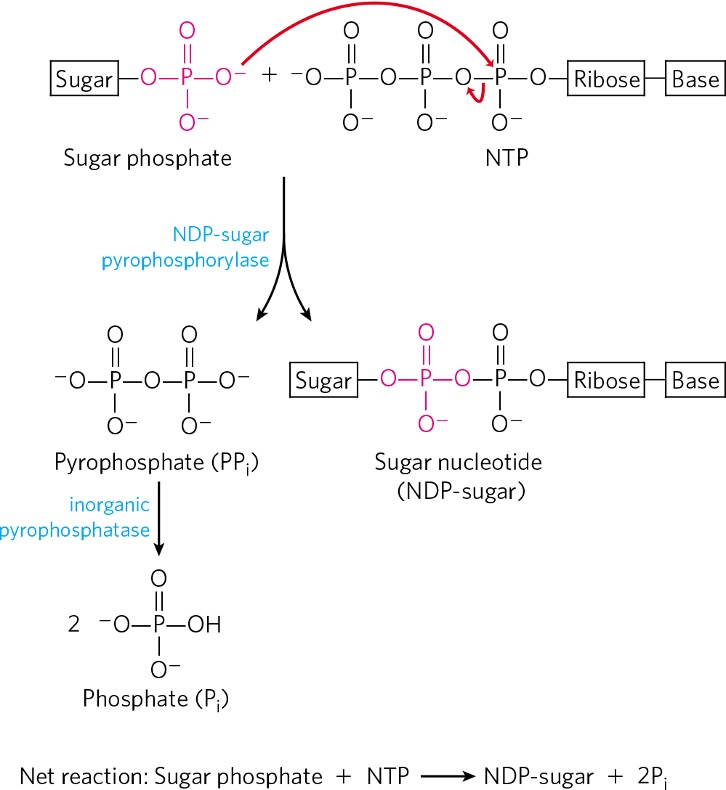
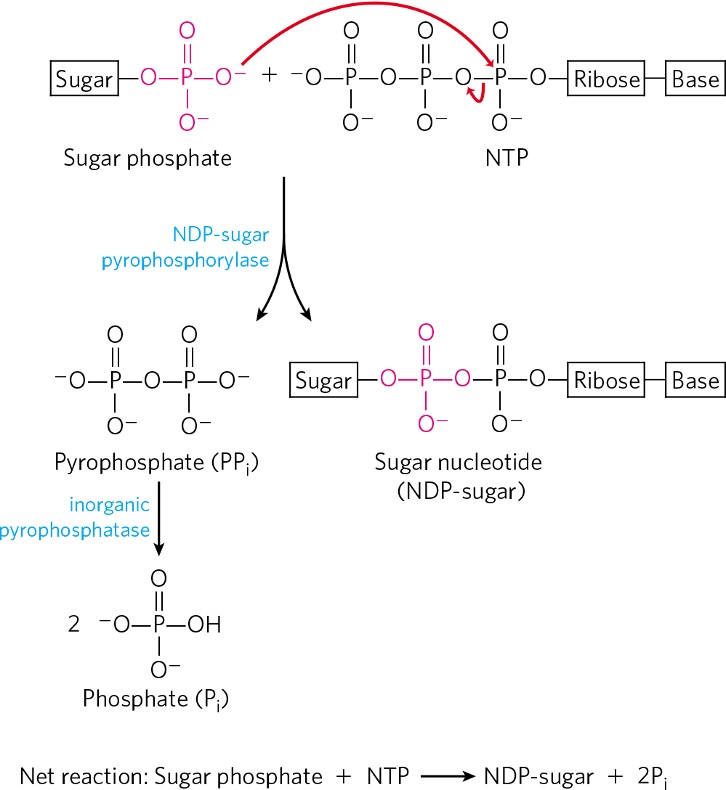
Condensation of glucose-1-phosphate and NTP forms what?
nucleotide sugar (NDP)
In the case of starch synthesis, the NDP-sugar is what?
ADP-glucose
via ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
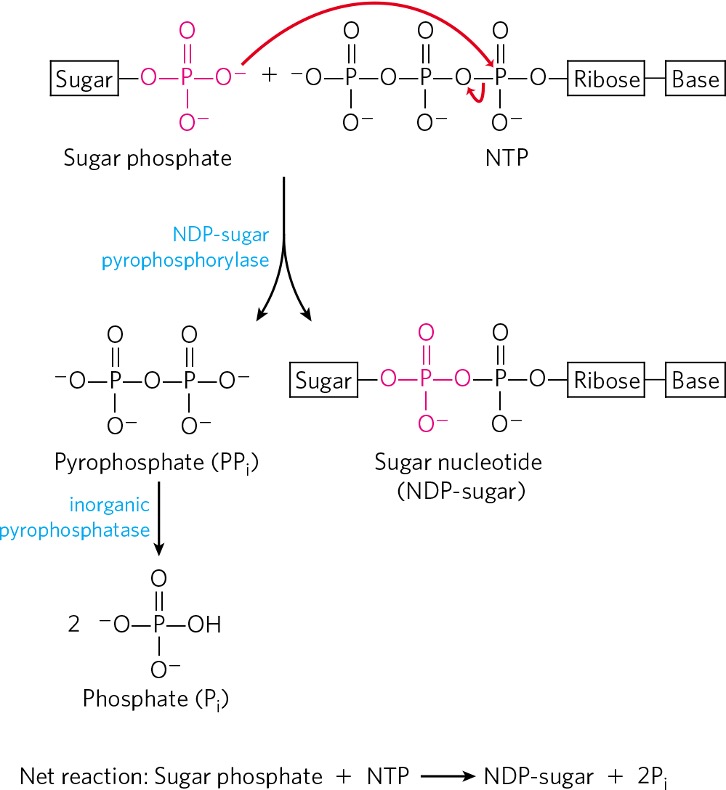
Difference between glycogen and starch synthesis?
glycogen → glucose monomers are UDP-glucose
starch → glucose monomers are ADP-glucose
Starch synthase
creates alpha 1,4 bonds i.e., amylose and catalyzes the addition of ADP-glucose to the growing starch molecule.
Amylopectin
numerous alpha 1,6 branches
added via branching enzyme
similar to branching enzyme in glycogen synthesis
Amylose in starch is what?
unbranched
Sucrose synthesis uses UDP-glucose to create…?
alpha 1 → B2 bond
Most triose phosphates generated by CO2 fixation in plants is converted to…?
starch
sucrose
Sucrose is the transporter of what?
carbon sources
Synthesis of sucrose occurs where?
cytosol
What two compounds are transported out of the chloroplast into the cytosol during sucrose synthesis?
DHAP i.e., dihydroxyacetone phosphate
glyceradehyde-3-phosphate
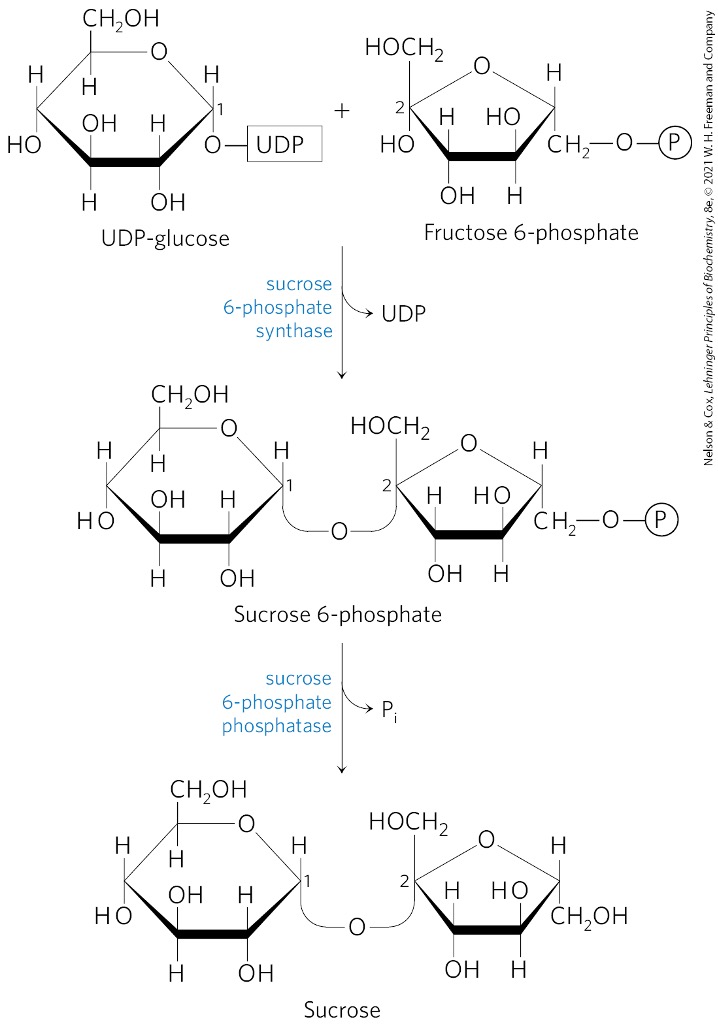
Once DHAP and G3P are in the cytosol, what reaction do they undergo?
condensation via aldolase
forms fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
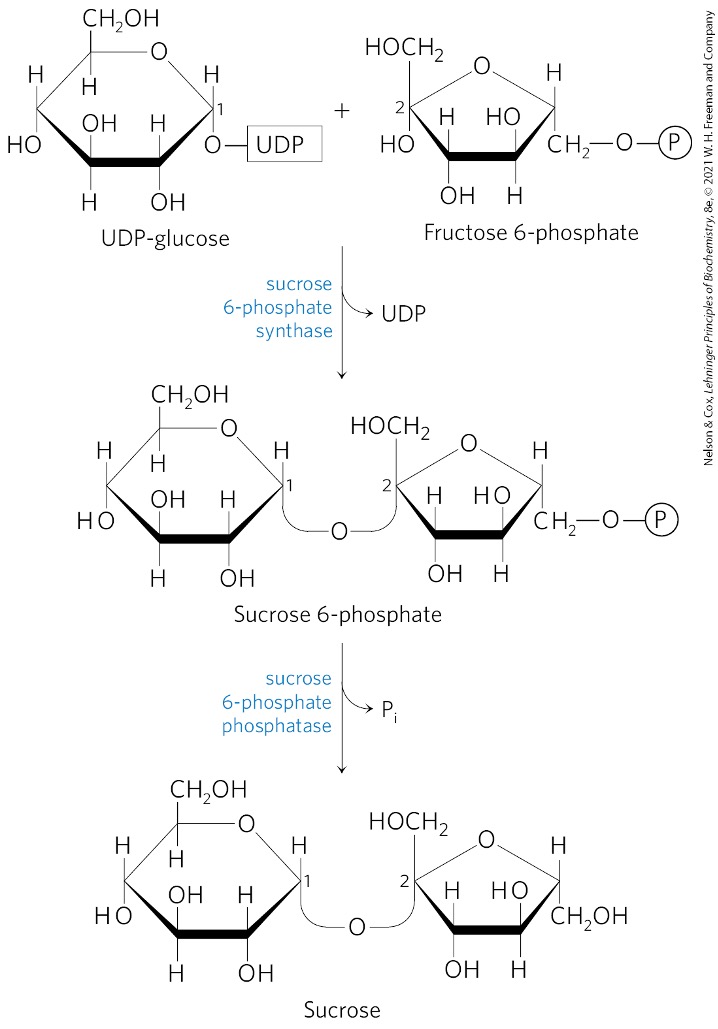
What happens to the fructose 1,6-bisphosphate?
hydrolyzed to fructose 6-phosphate
via fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
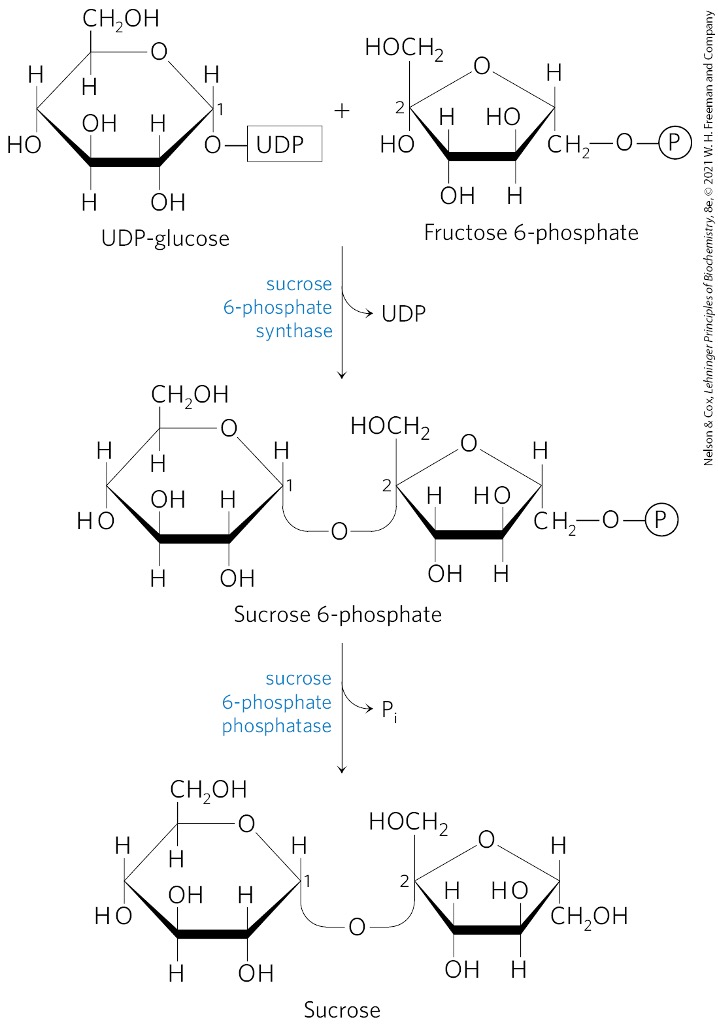
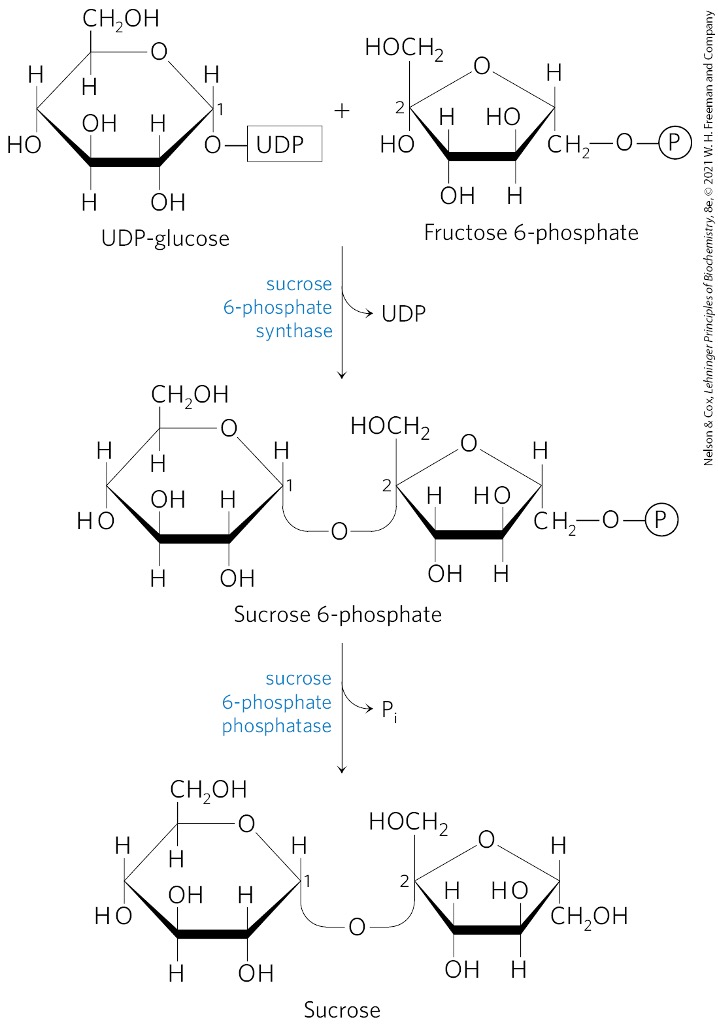
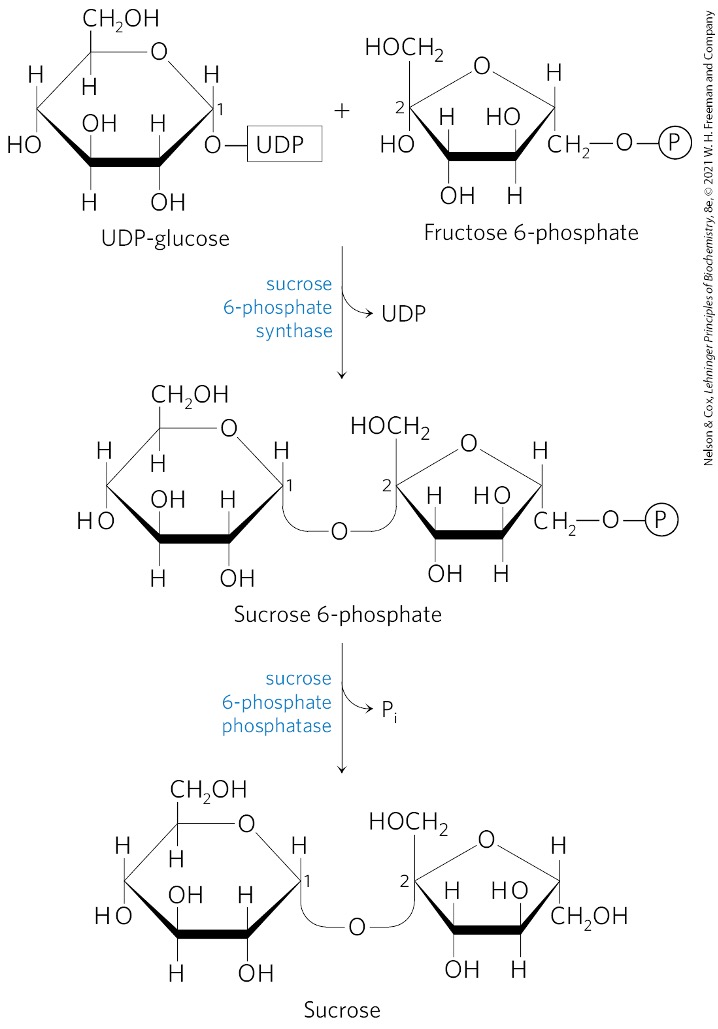
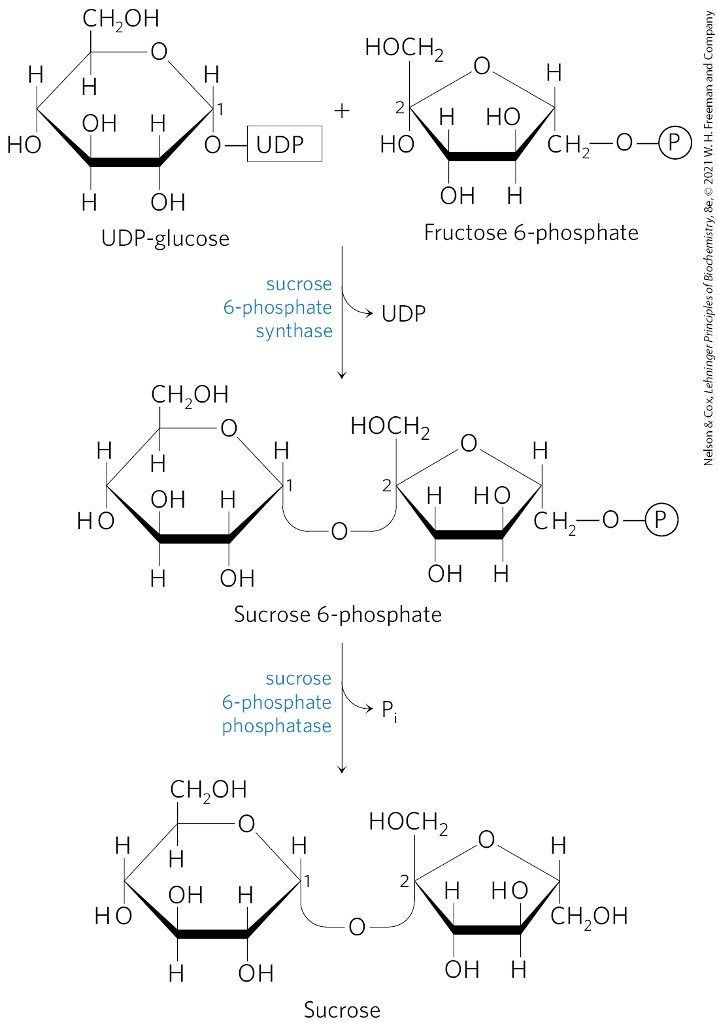
Fructose 6 -phosphate + UDP-glucose → ?
sucrose 6-phosphate
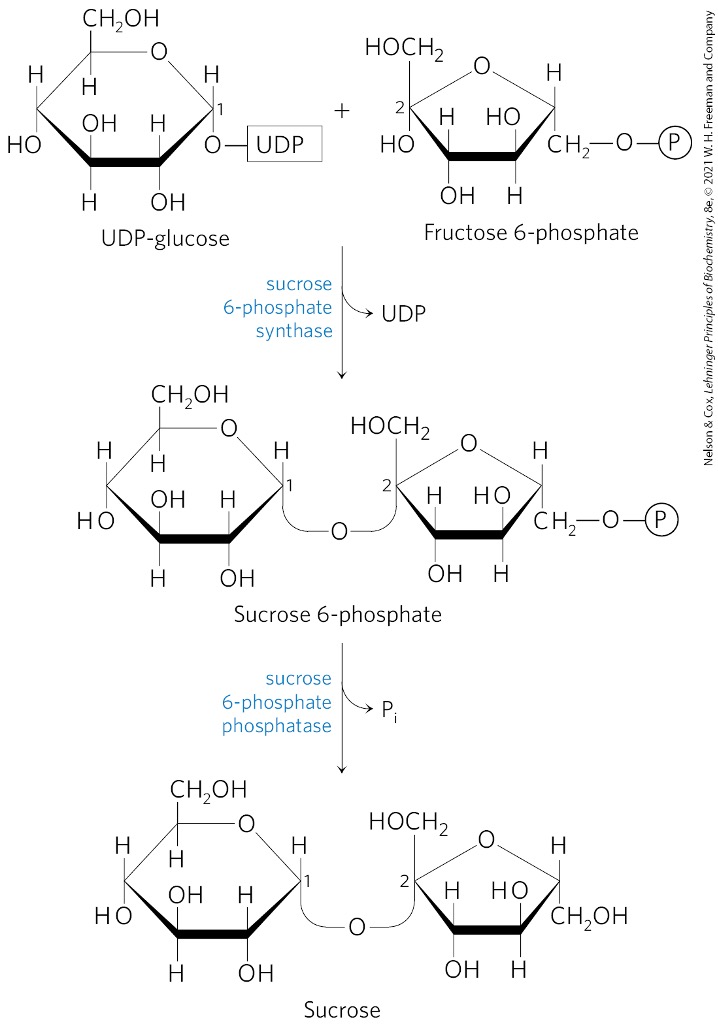
What catalyzes the formation of sucrose 6-phosphate?
sucrose 6-phosphate synthetase
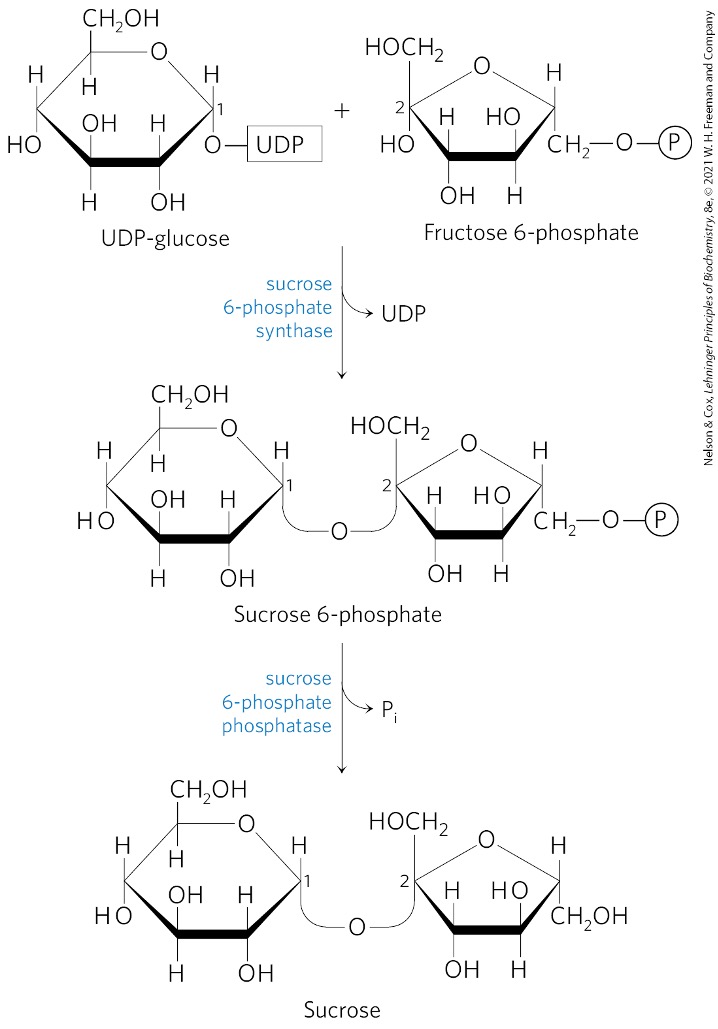
Sucrose 6-phosphate is converted to what? via what enzyme?
sucrose
sucrose 6-phosphate phosphatase
1) Aldolase combines ? to form ?
DHAP + G3P
fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
2) Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is ? by ? to form ?
dephosphorylated
fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
fructose 6-phosphate
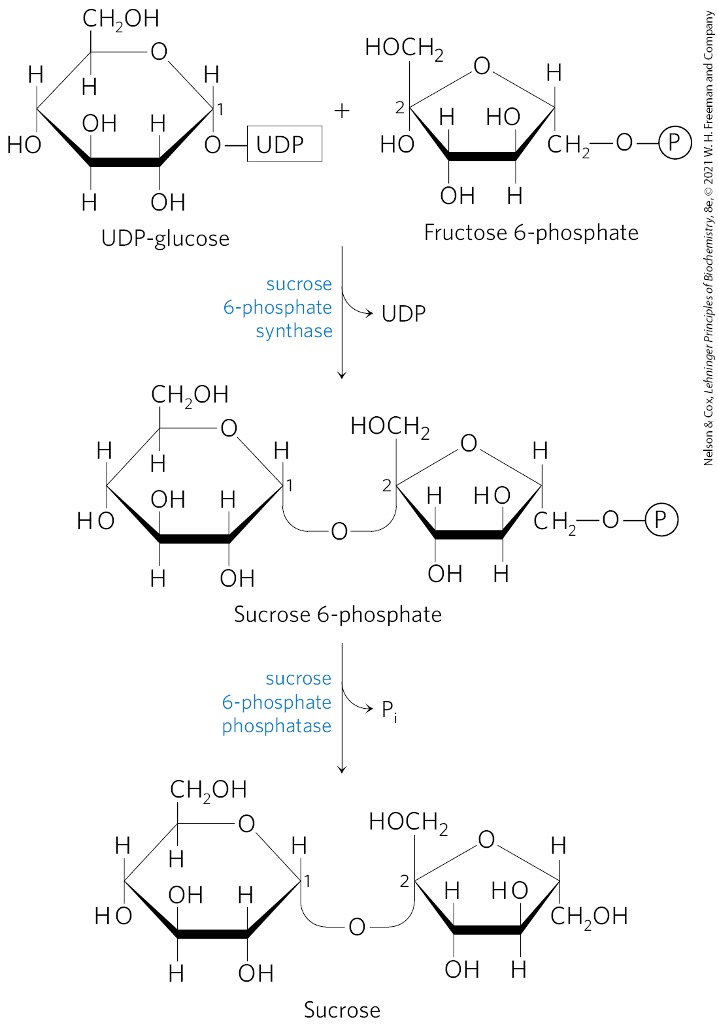
3) Sucrose 6-phosphate synthase adds ? to ? to make ?
UDP-glucose
fructose 6-phosphate
sucrose 6-phosphate
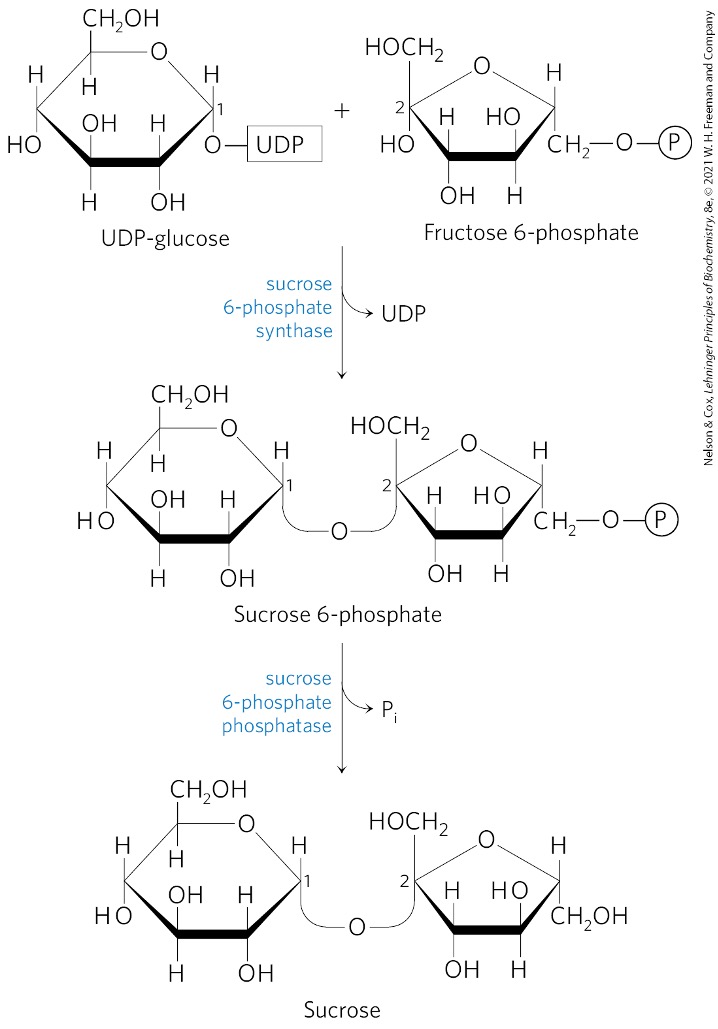
4) Sucrose 6-phosphate cleaves ? to yield ?
a phosphate group (PO43-)
sucrose
Cellulose provides what to prevent what of the cell and plasma membrane?
strength and rigidity
swelling and rupture
What is a major component of cell walls in plants?
cellulose
Cell wall of plants is composed of cellulose…?
microfibrils
Cellulose microfibrils are composed of…?
linear polysaccharide > 1000 glucose units
linked via 1,4 beta linkages i.e., cellulose chains
Cellulose is synthesized via ? but assembled where?
intracellular precursors
outside of plasma membrane
Of microfibrils, these polymers are bundled consisting of…? which aggregate…? and…? forming…? which then assemble into…?
at least 18 chains
side by side
co-crystallize
microfibrils
macrofibrils
Cellulose biosynthesis: At the cytosolic end, there is…?
a substrate binding site UDP-glucose
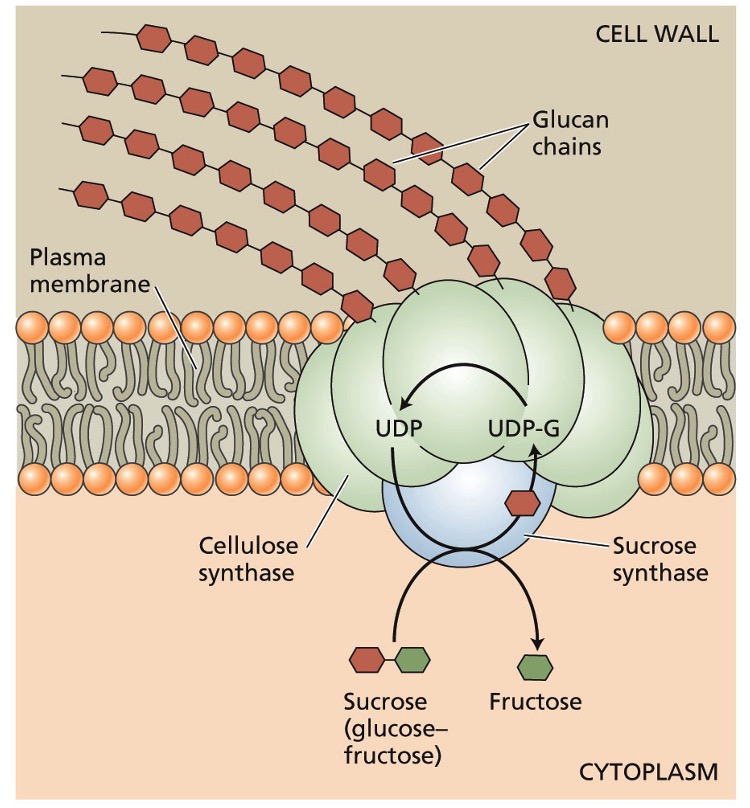
Cellulose biosynthesis: At the extracellular space…?
cellulose molecules are elongated and crystallized
The enzyme complex involved in cellulose biosynthesis is composed of what?
a catalytic sub unit with 8 transmembrane segments
several other sub units involved in packaging the cellulose chains
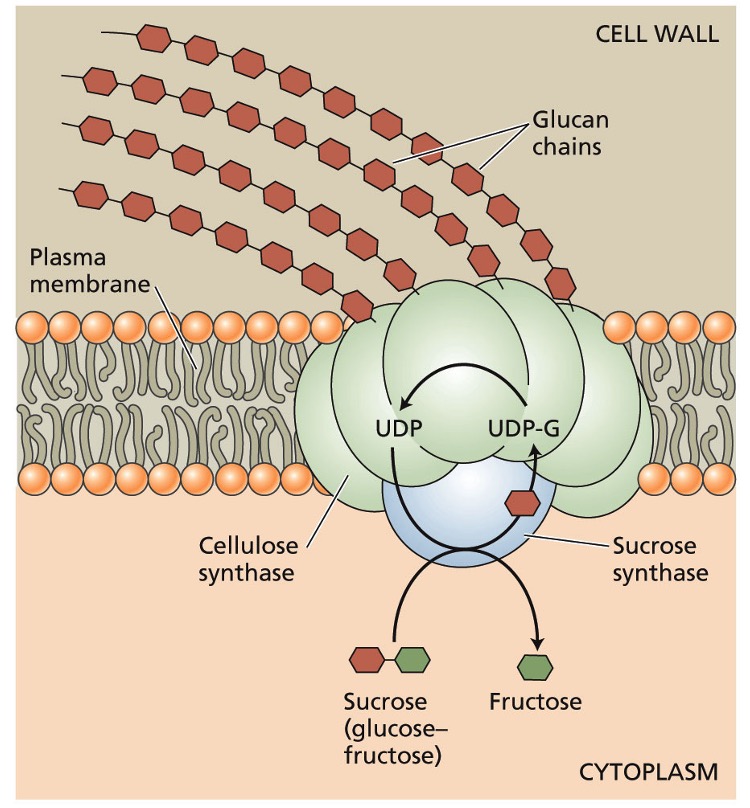
UDP-glucose is used for?
cellulose biosynthesis
via cellulose synthase
adds glucose monomers to non-reducing ends
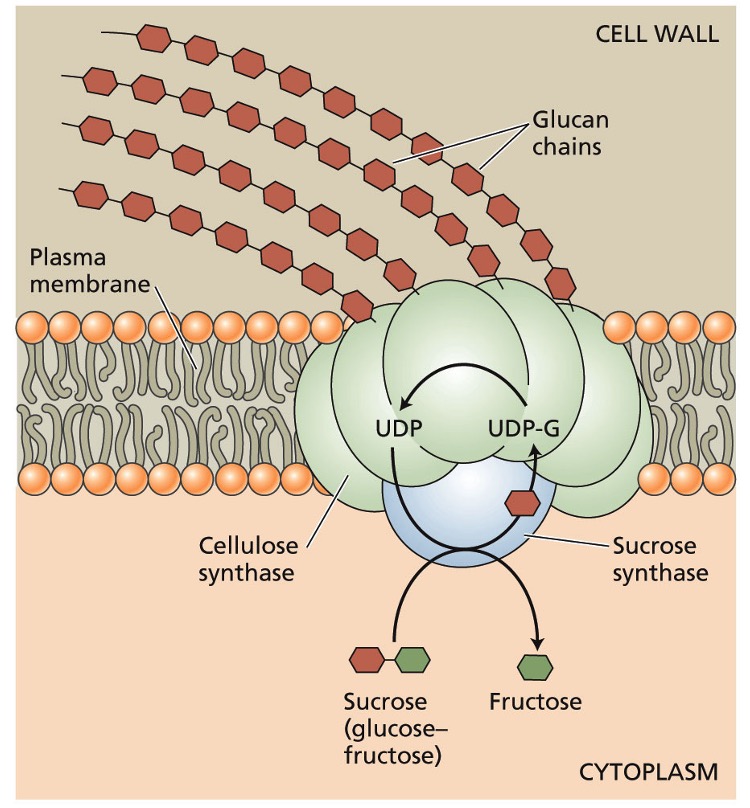
Sucrose + UDP → ?
UDP-glucose + fructose
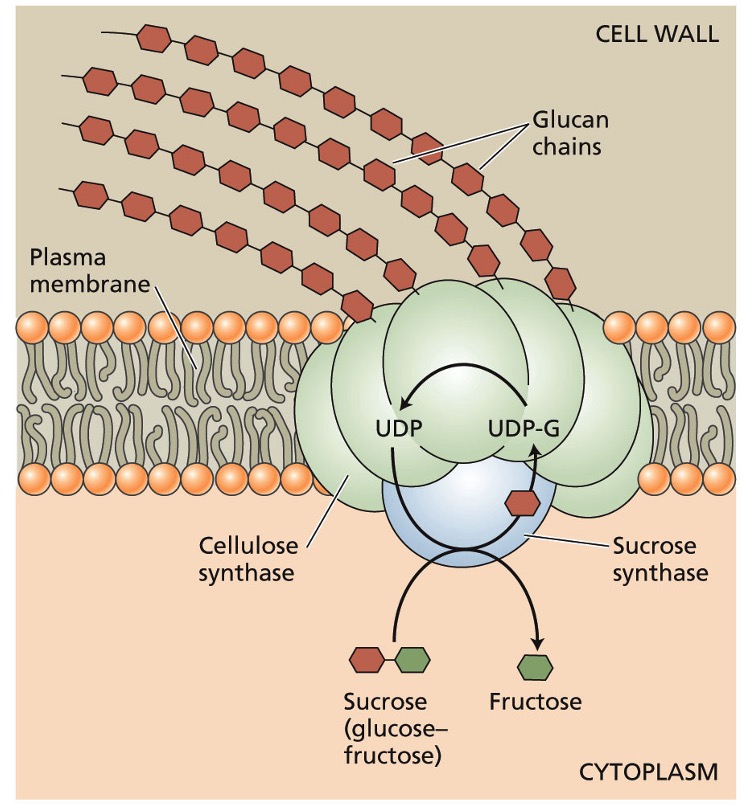
UDP-glucose is produced from what during what?
sucrose synthase
photosynthesis
Catalytic sub units of cellulose synthase are found in?
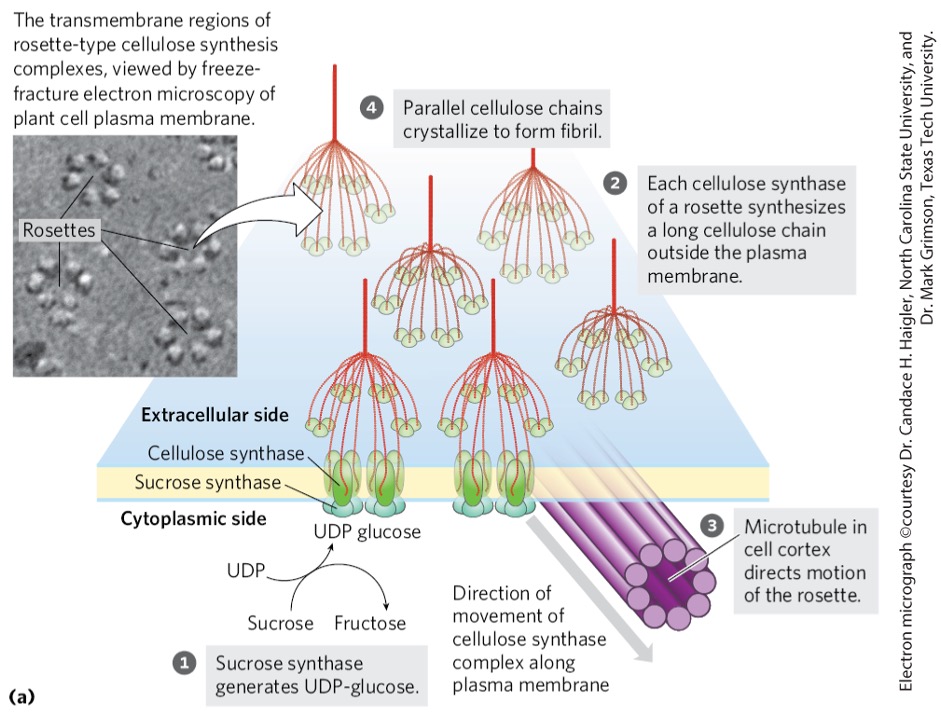
terminal complexes aka rosettes
Rosettes
cellulose synthesis complex
6 large particles arranged in a hexagon
UDP-glucose is generated from?
sucrose by-product during photosynthesis
catalyzed via sucrose synthase on cytosolic end
What is required for cellulose synthesis?
lipid primer
Initiation
glucose from UDP-glucose associates with lipid primer
i.e., sitosterol
inner face of plasma membrane
displacement of UDP
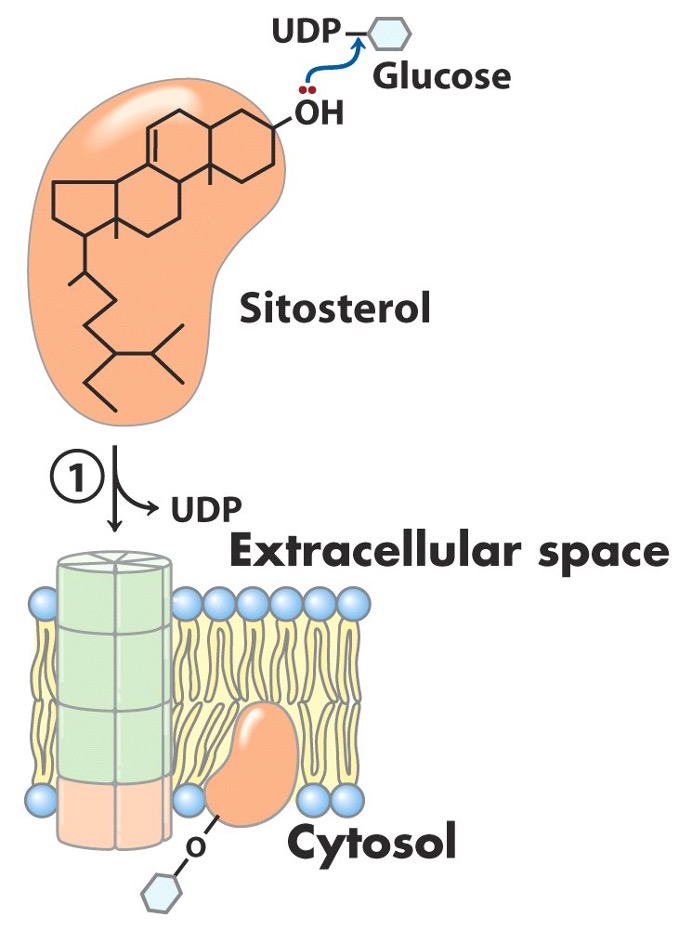
Carbohydrate chain is extended with continuous addition of what? received from what?
glucose
oncoming UDP-glucose
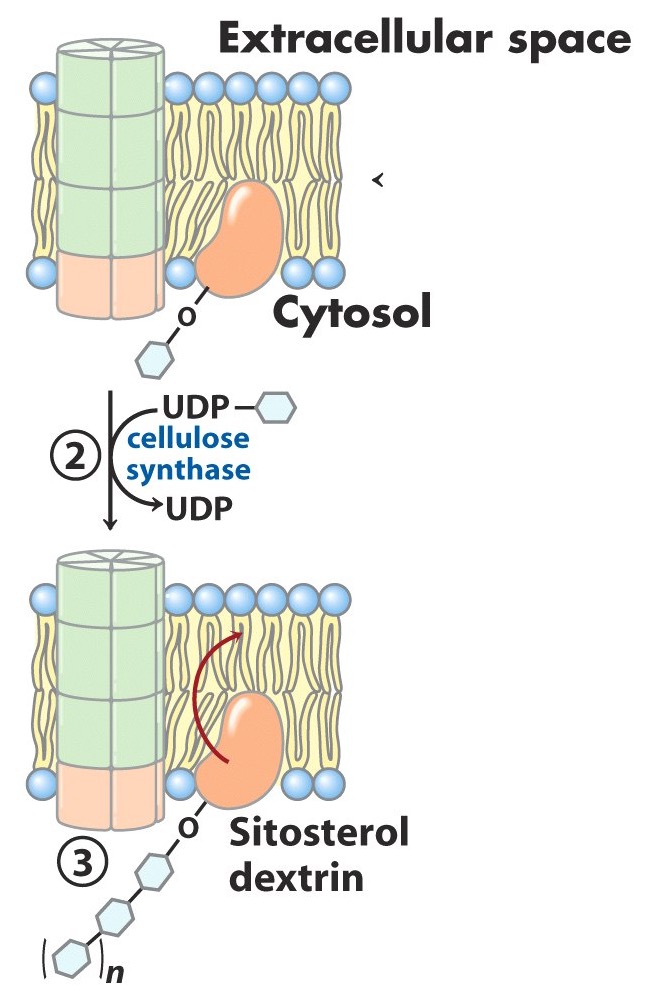
Intracellular cellulose synthase adds several more what? in what?
glucose residues
B1,4 linkages
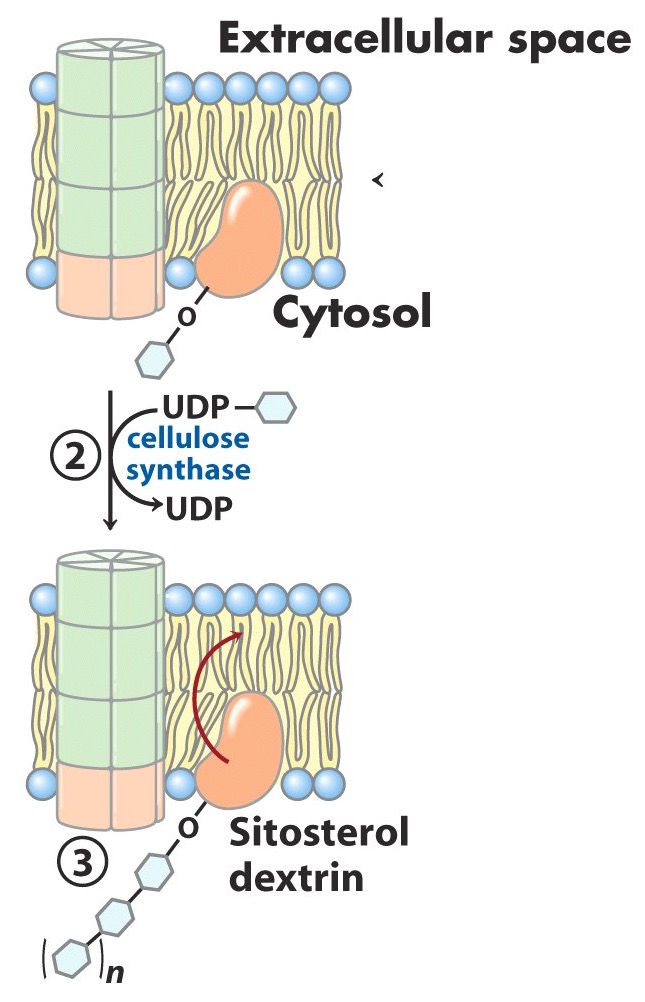
What does the constant addition of glucose eventually yield in the initiation process with the lipid primer?
short oligosaccharide chain
attached to the sitosterol dextrin
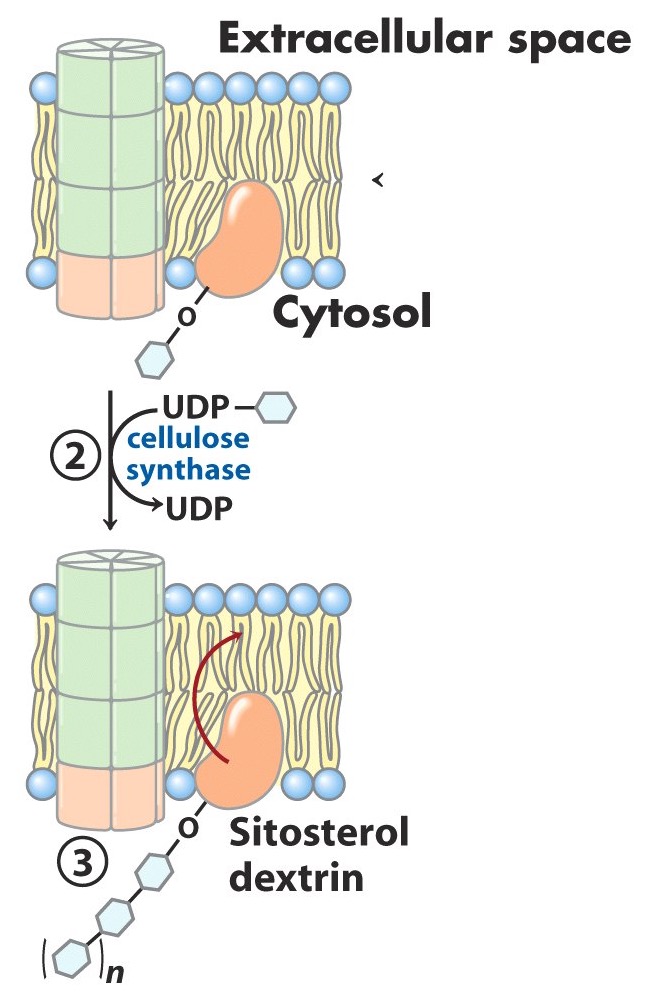
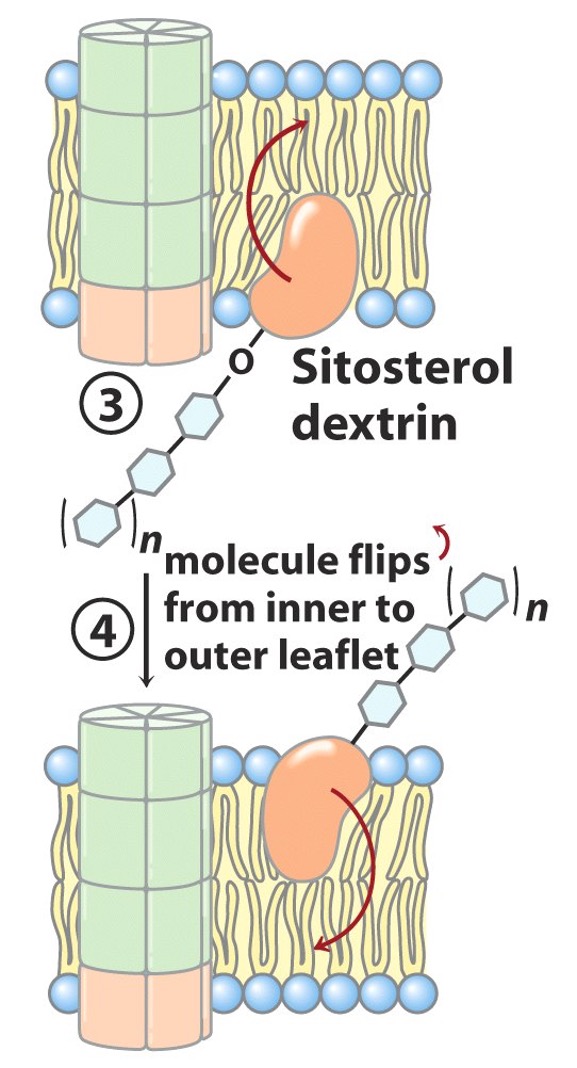
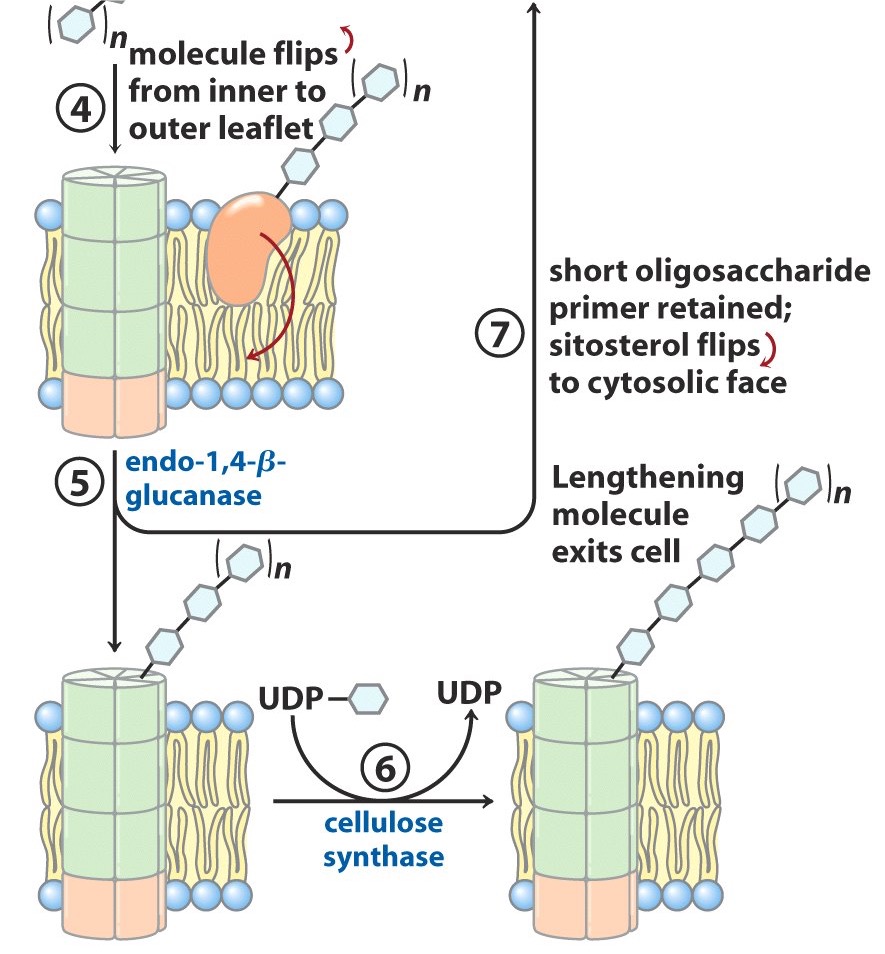
Once an appropriate length of the oligosaccharide is reached, what happens?
entire sitosterol dextrin flips from inner plasma membrane surface to outer plasma membrane surface
Endo-1,4-B-glucanase separates the…? from…?
growing chain
a short oligosaccharide attached to the sitosterol
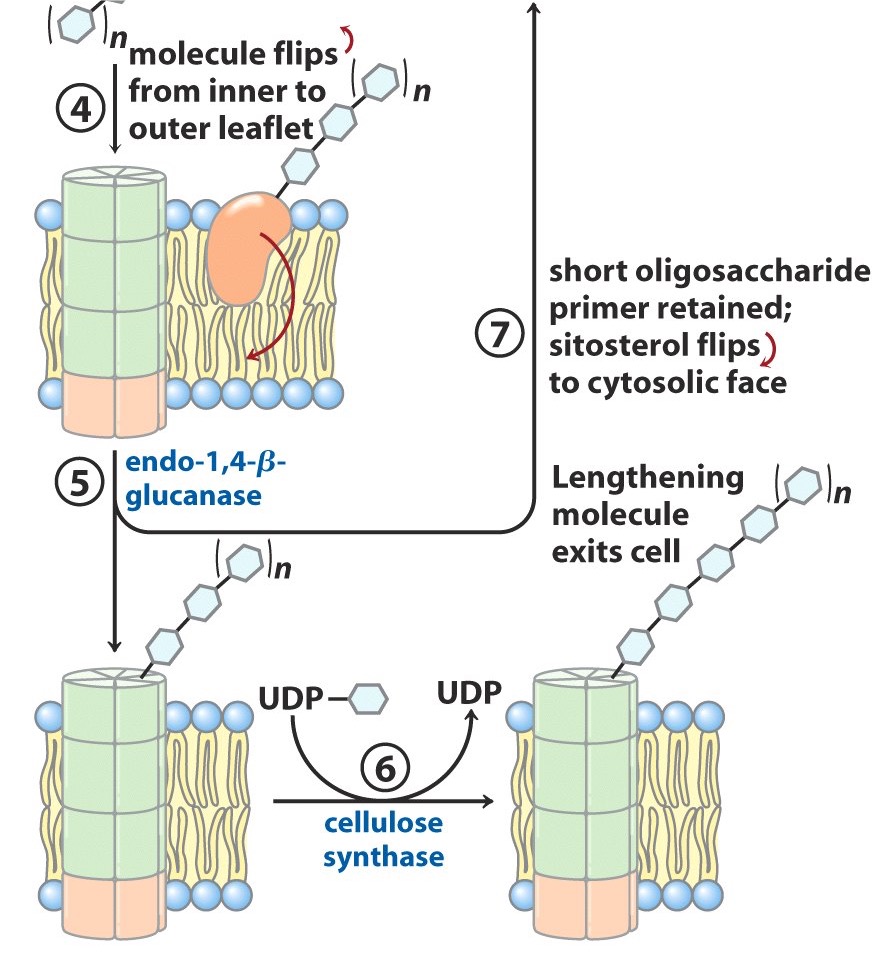
The sitsterol-free polymer of what? is extended further by what enzyme? with what substrate?
glycosyl
cellulose synthase
UDP-glucose
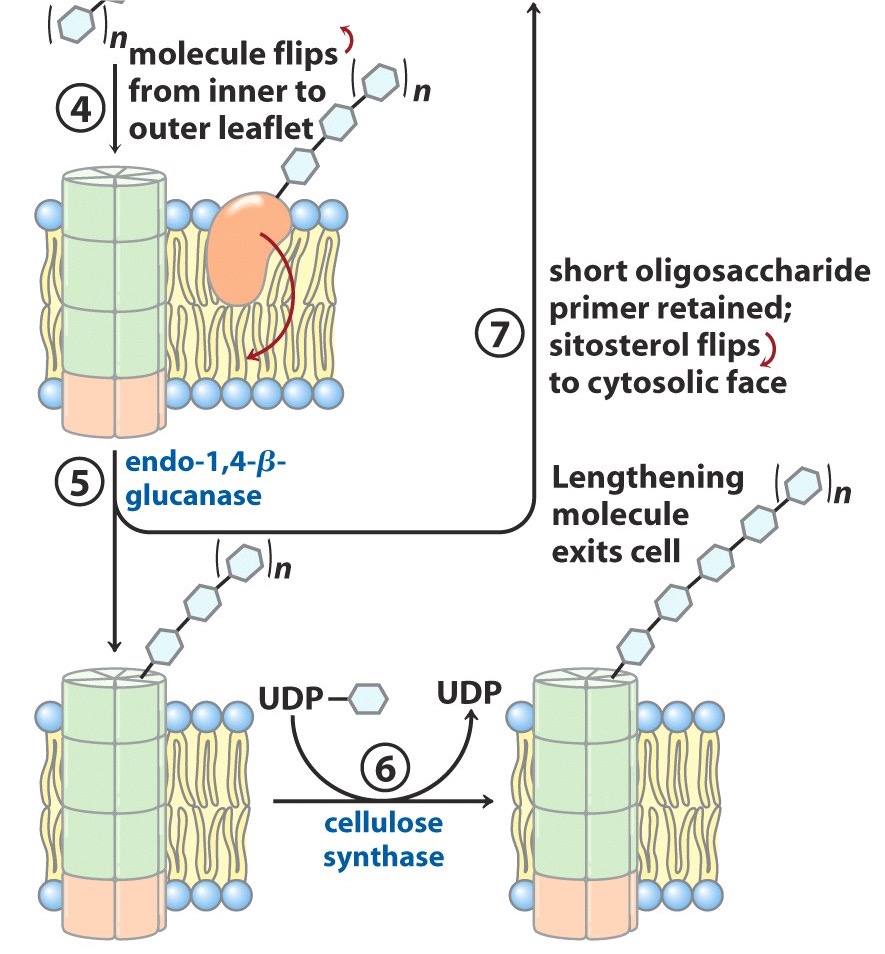
The sitosterol-linked short oligosaccharide returns back to where? to be reused as what?
cytosolic face
primer for another chain of cellulose synthesis
1) Glucose attaches to ? in the cell membrane
lipid
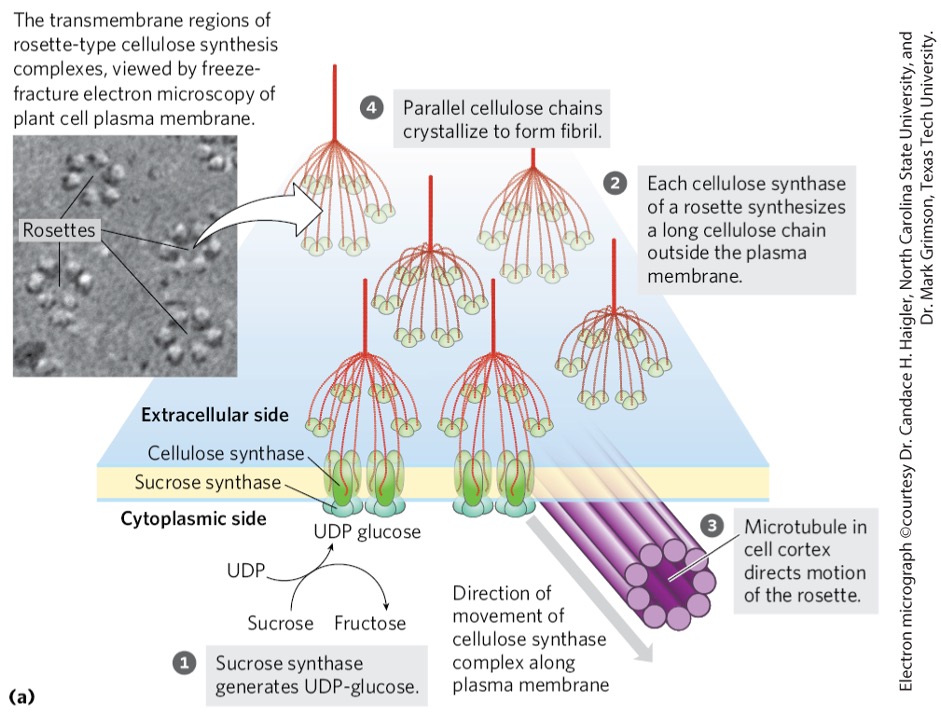
2) Sucrose synthase generates ? with the help of ? to create?
UDP-glucose
cellulose synthase
six chains

3) Cellulose synthase continues to ? outside of the ?
extend the chain
plasma membrane
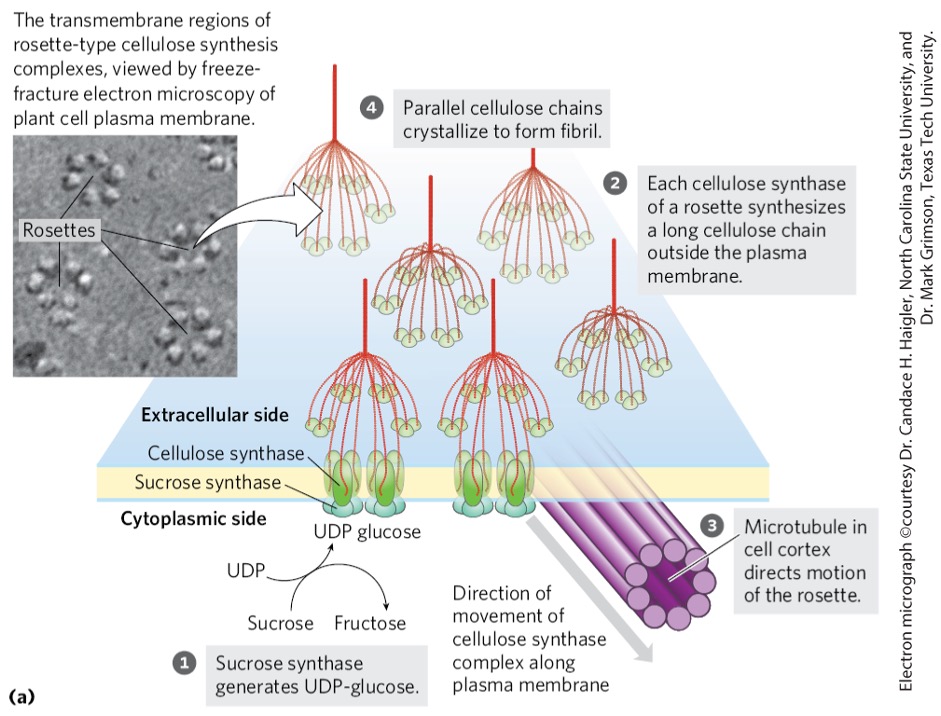
4) Chains ? to form ? and eventually form ?
crystallize
microfibrils
macrofibrils