compsci paper 1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
CPU purpose
processes data and instructions by repeating FDE.
CPU Registers
Control Unit
ALU
Program Counter
Memory Address Register
Memory Data Register
Current Instruction Register
Accumulator
Control Unit
directs the operations of the CPU. Manages FDE
It has the following jobs:
Controlling and coordinating the activities of the CPU
Managing the flow of data between the CPU and other devices
Accepting the next instruction
Decoding instructions
Storing the resulting data back in memory
ALU (Arithmetic and Logic Unit)
performs all arithmetic and logical operations inside the CPU
Register
small memory cells that operate at a very high speed. They are used to temporarily store data and all arithmetic, logical and shift operations occur in these registers.
Cache memory
temporary storage space for frequent accessed data
FDE
Fetch phase: - Address from the PC is copied to the MAR - Instruction held at that address is copied to MDR by the data bus - Simultaneously, the contents of the PC are increased by 1 - The value held in the MDR is copied to the CIR
Decode phase: - The contents of CIR are split into operand and opcode
Execute phase: - The decoded instruction is executed
Program Counter (PC)
Holds the address of the next instruction to be executed.
Accumulator (ACC)
Stores the results from calculations
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Temporarily stores data that has been read or data that needs to be written.
Current Instruction Register (CIR)
Holds the current instruction being executed, divided up into operand and opcode.
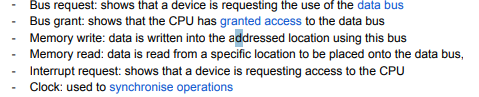
Busses
f parallel wires which connect two or more components inside the CPU
Busses name
Data bus, control bus, address bus
all called system bus
Data Bus
This is a bi-directional bus (meaning bits can be carried in both directions). This is used for transporting data and instructions between CPU, memory and components.
Address Bus

Control bus

Control signals
Pipelining
process of completing FDE (three step instructions) simultaneously, while holding data in a buffer in close proximity to CPU untill required, while one instruction executed, another can be decoded and another fetched. aimed to reduce amount of CPU which is idle.
Types of pipelining

Pipelining advantages
Increases instruction throughput (more instructions per unit time)
Reduces CPU idle time by overlapping stages
Improves overall efficiency of processor use
Speeds up execution of long programs, especially loops
CPU performance effected by:
The performance of the CPU is affected by three main factors:
• Clock speed is the number of cycles per second, so a higher clock speed means more instructions can be executed per second.
The number of cores is important as more cores allow a CPU to carry out multiple instructions simultaneously, improving multitasking and parallel processing.
• Cache memory is small and very fast memory inside the CPU that stores frequently used instructions, reducing the time needed to access RAM.
what is clock speed determined by
system clock. This is an electronic device which generates signals, switching between 0 and 1. All processor activities begin on a clock pulse, and each CPU operation starts as the clock changes from 0 to 1
core
independent processor that is able to run its own fetch-execute cycle. A computer with multiple cores can complete more than one fetch-execute cycle at any given time
why might a dual core processor not work twice as fast as one core processer
However, not all programs are able to utilise multiple cores efficiently as they have not been designed to do so, so this is not always possible
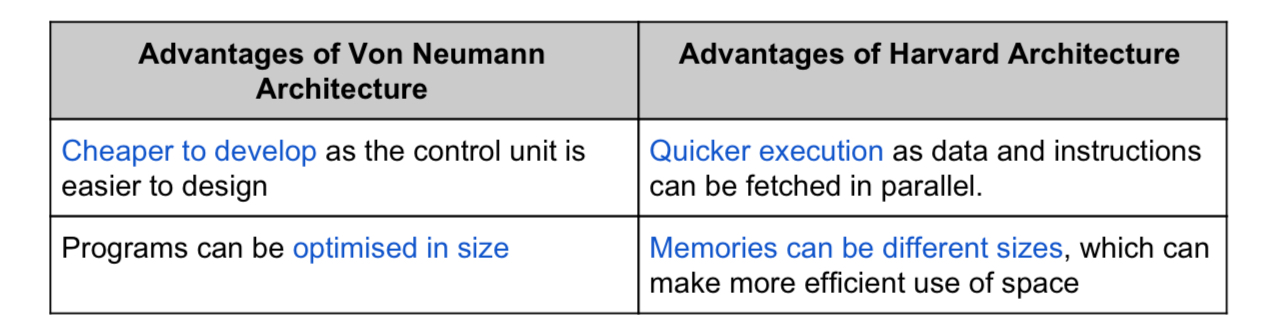
vonn neuman architectire
Includes basic computer components (CU, ALU, registers and memory units) shared memory and shared data bus used for both data and instructions
Could lead to bottleneck
harvard architectire
Physically seperate memories for instructions and data
Useful when memory has different characteristics allowing optimisation of the size of individual memory cells and their bases depending on your needs.
Vonn neuman vs Harvard adv
Contemporary processing
