IB ESS HL/SL - Topic 2 (Populations, Niches, Tropic Systems, & Succession)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
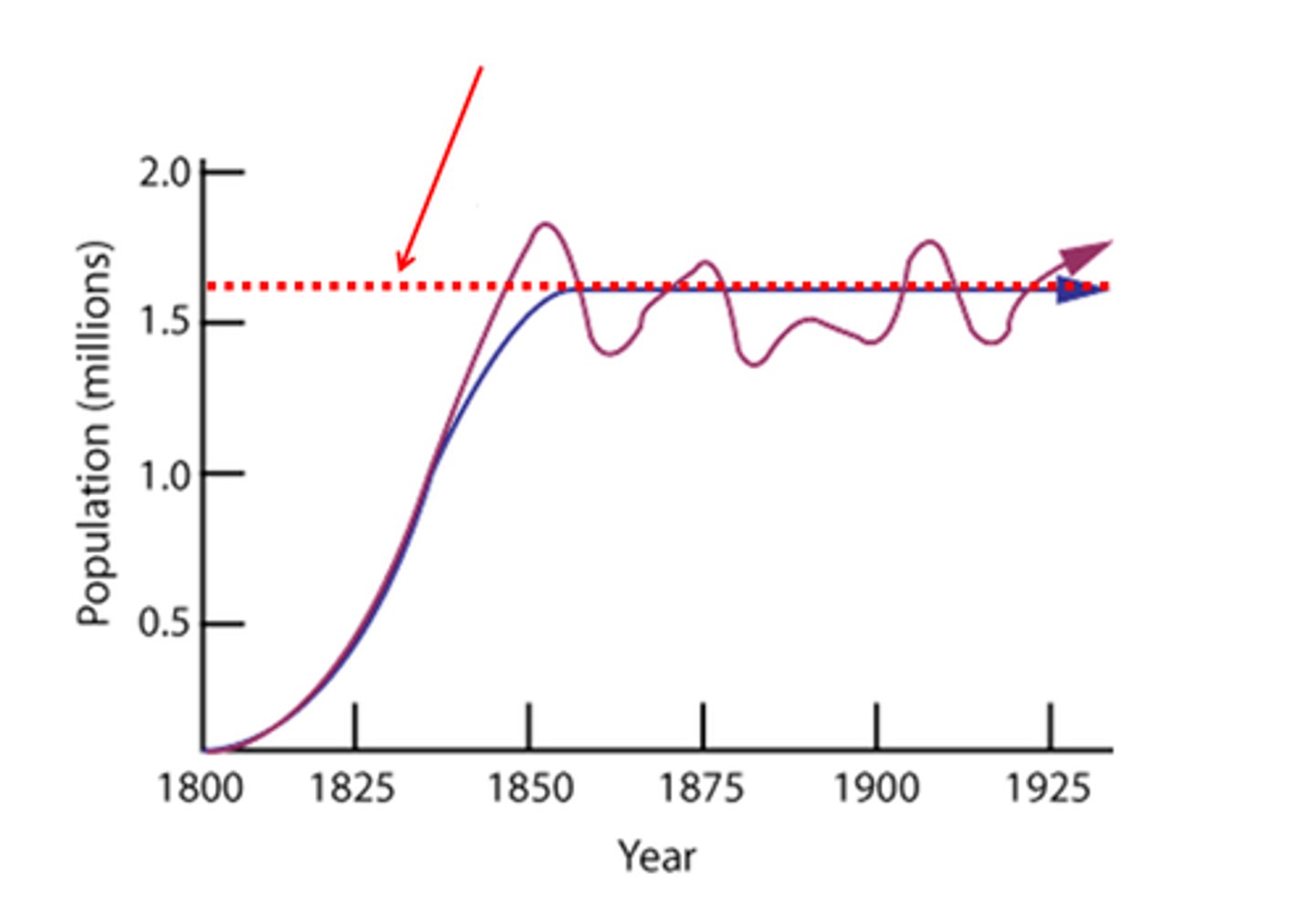
carrying capacity
the largest number of individuals an environment can sustainably support
producer
any autotrophic organism; the base of any trophic system.

autotroph
an organism that makes its own food

heterotroph
an organism that cannot make its own food and obtains energy from other organisms.
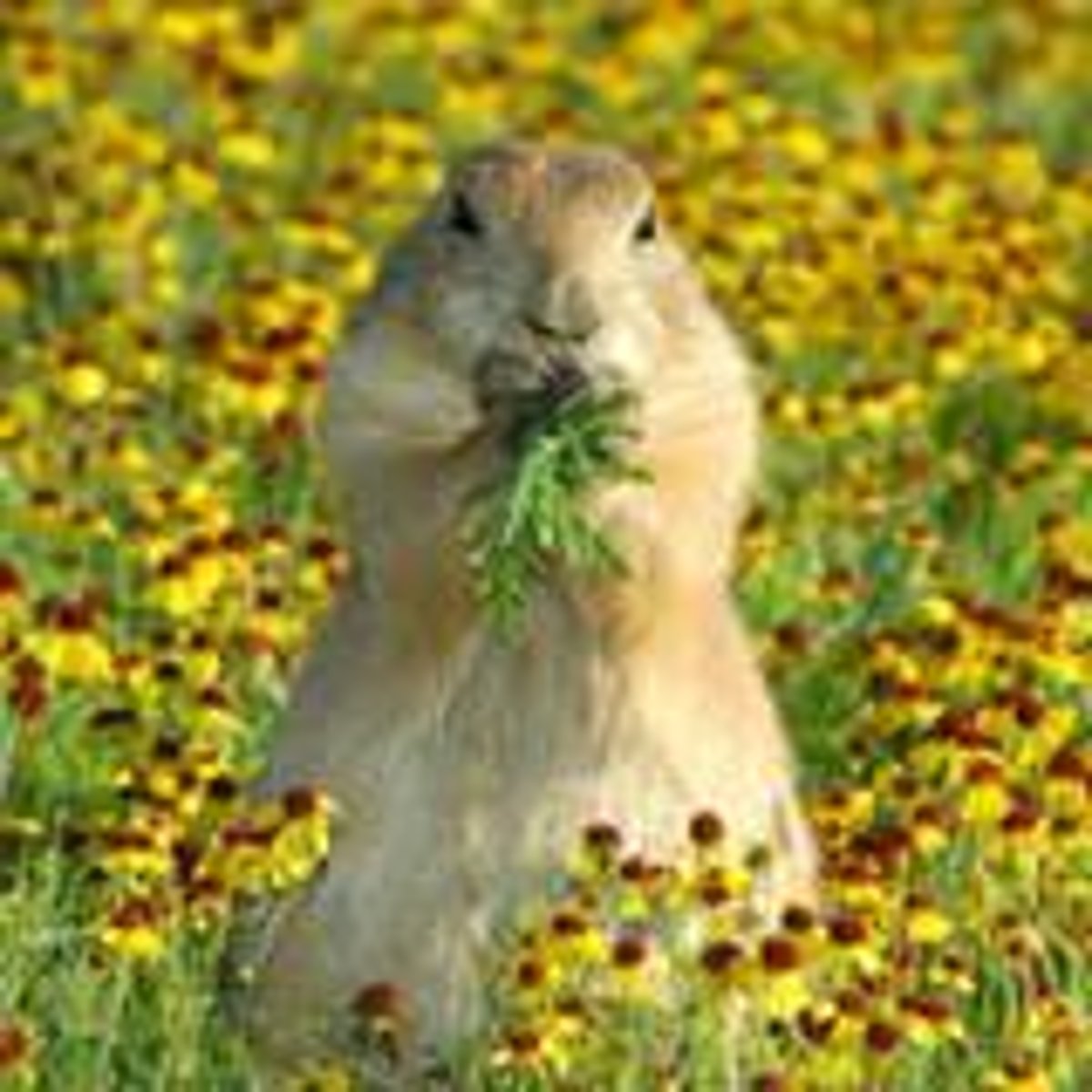

primary consumer
any organism that feeds on producers; the second tier of the trophic system
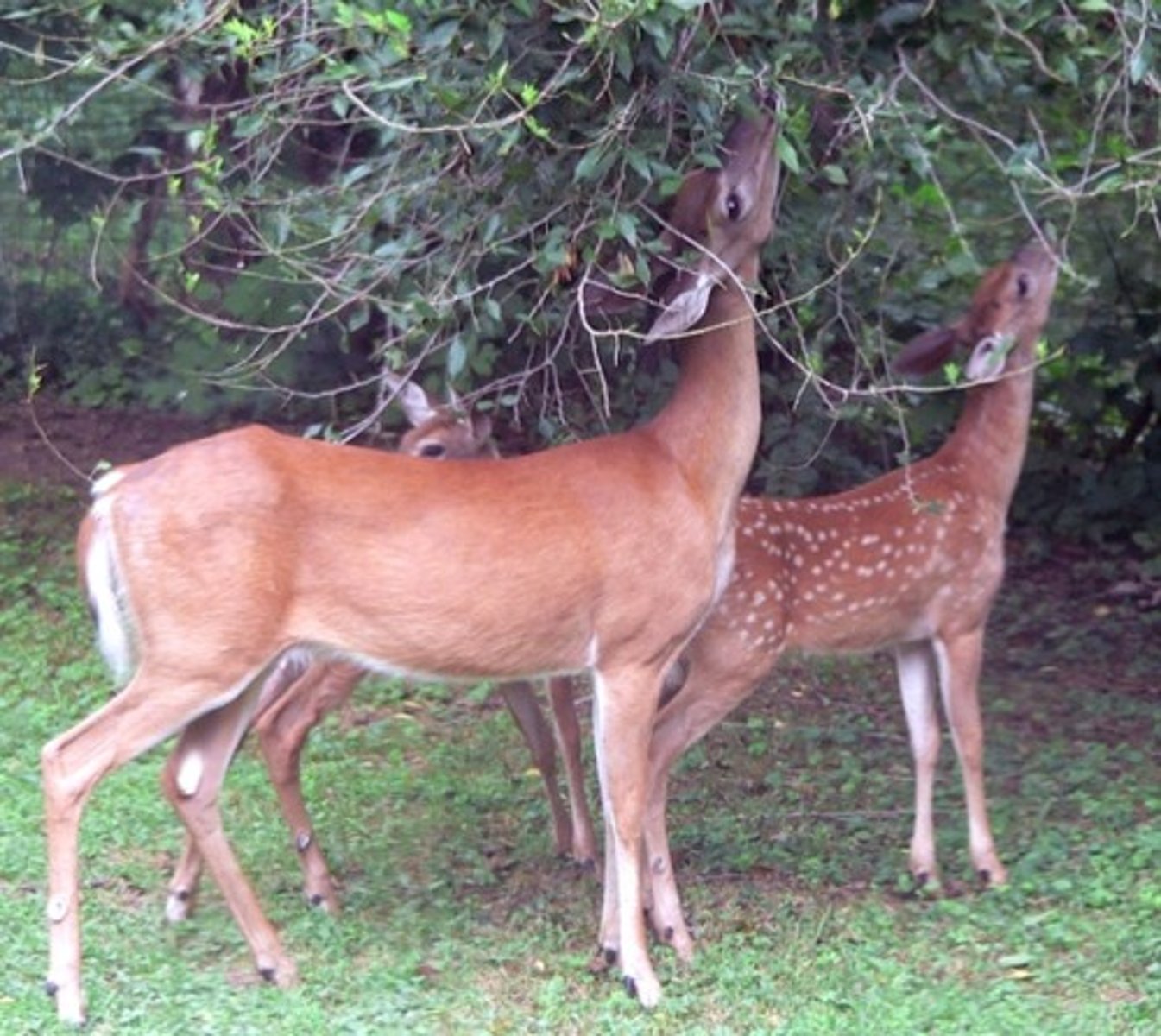

secondary consumer
any organism that feeds on herbivores; the third tier of the trophic system
carnivore
an animal that obtains energy by eating other animals
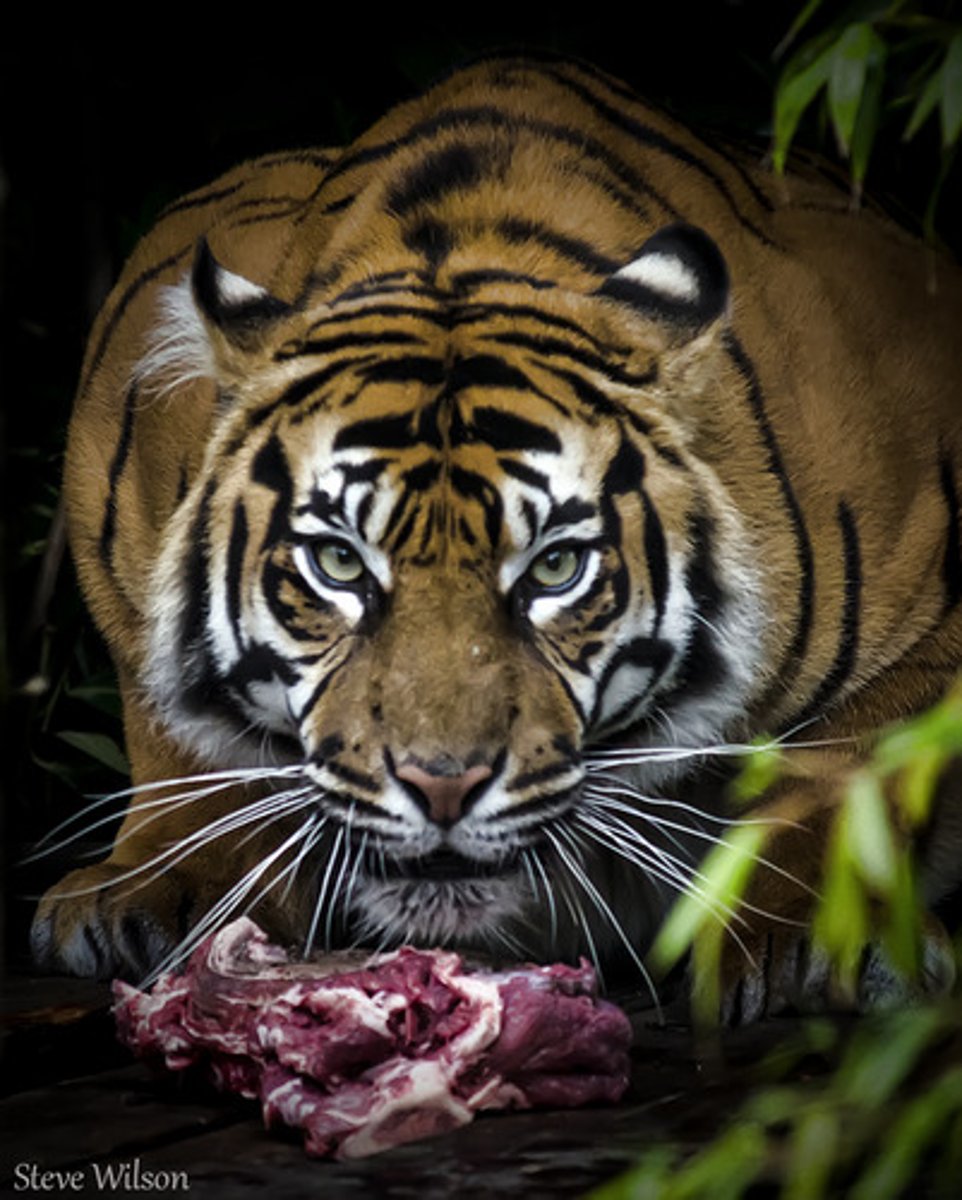

herbivore
an animal that obtains energy by eating only plants

decomposer
any organism that breaks down and obtains energy from dead organic matter
saprotroph
a decomposer that secretes digestive enzymes and absorbs the products of digestion

detritivore
a decomposer that digests dead organic matter internally

energy (kJ)
what is lost (to the system) along a trophic pyramid
biomass
what decreases along a trophic pyramid
nutrients
what is recycled along a trophic pyramid
population
group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area

primary succession
type of succession that begins on surfaces where no soil exists, such as volcanic rock
secondary succession
type of succession that occurs in an area with existing soil substrate that was only partially destroyed by disturbances, such as a fire.
pioneer species
first species to populate an area during succession

biotic
a living aspect of an environment
abiotic
a non-living aspect of an environment (eg: pH, water, temperature, wind, salinity, etc.)
GPP (gross primary productivity)
the total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
NPP (net primary productivity)
the energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
deflected succession
succession that is stopped or interfered with such as by grazing or lawn mowing
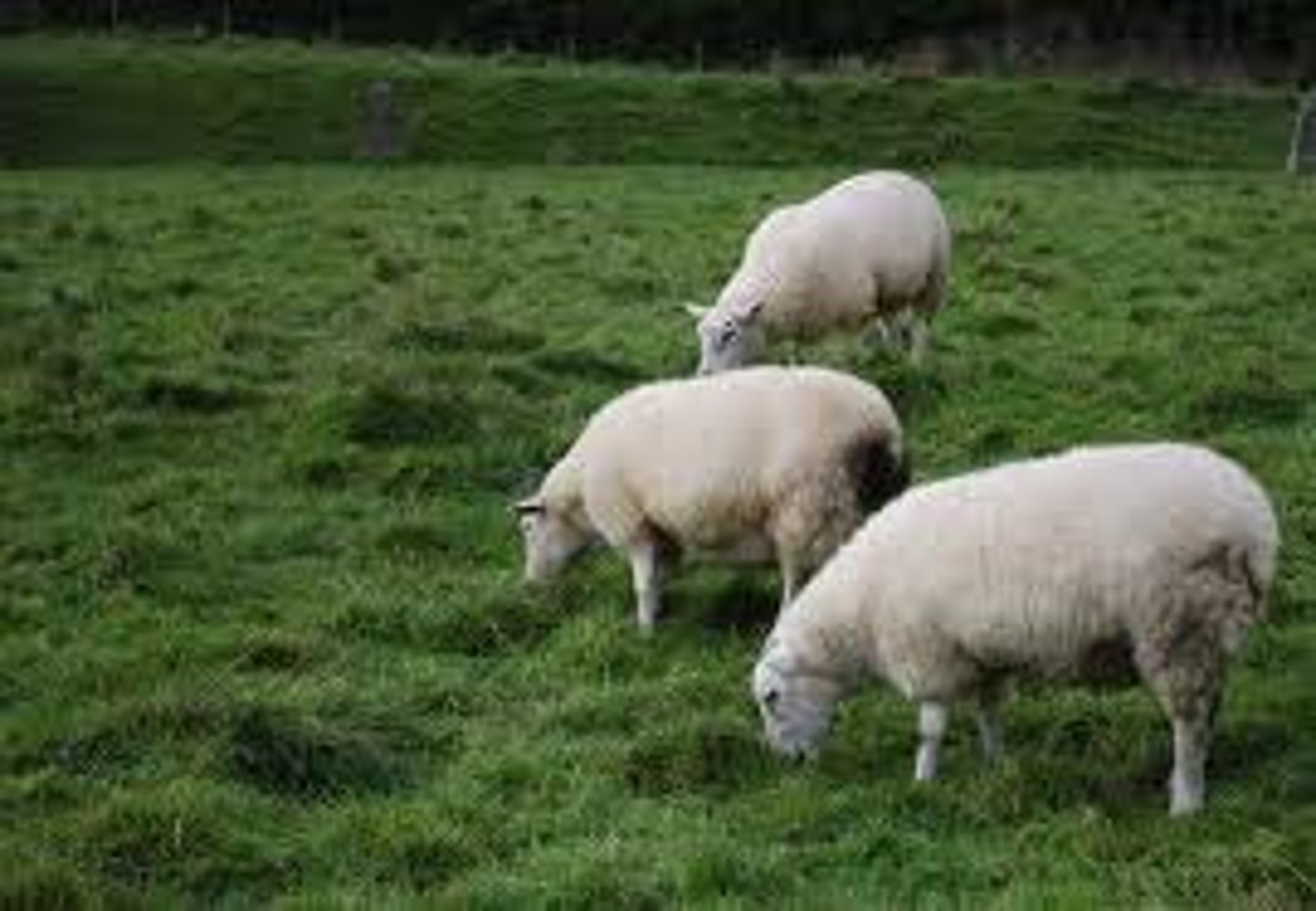

niche
an organism's particular role in an ecosystem
symbiosis
any niche relationship in which two species interact closely together
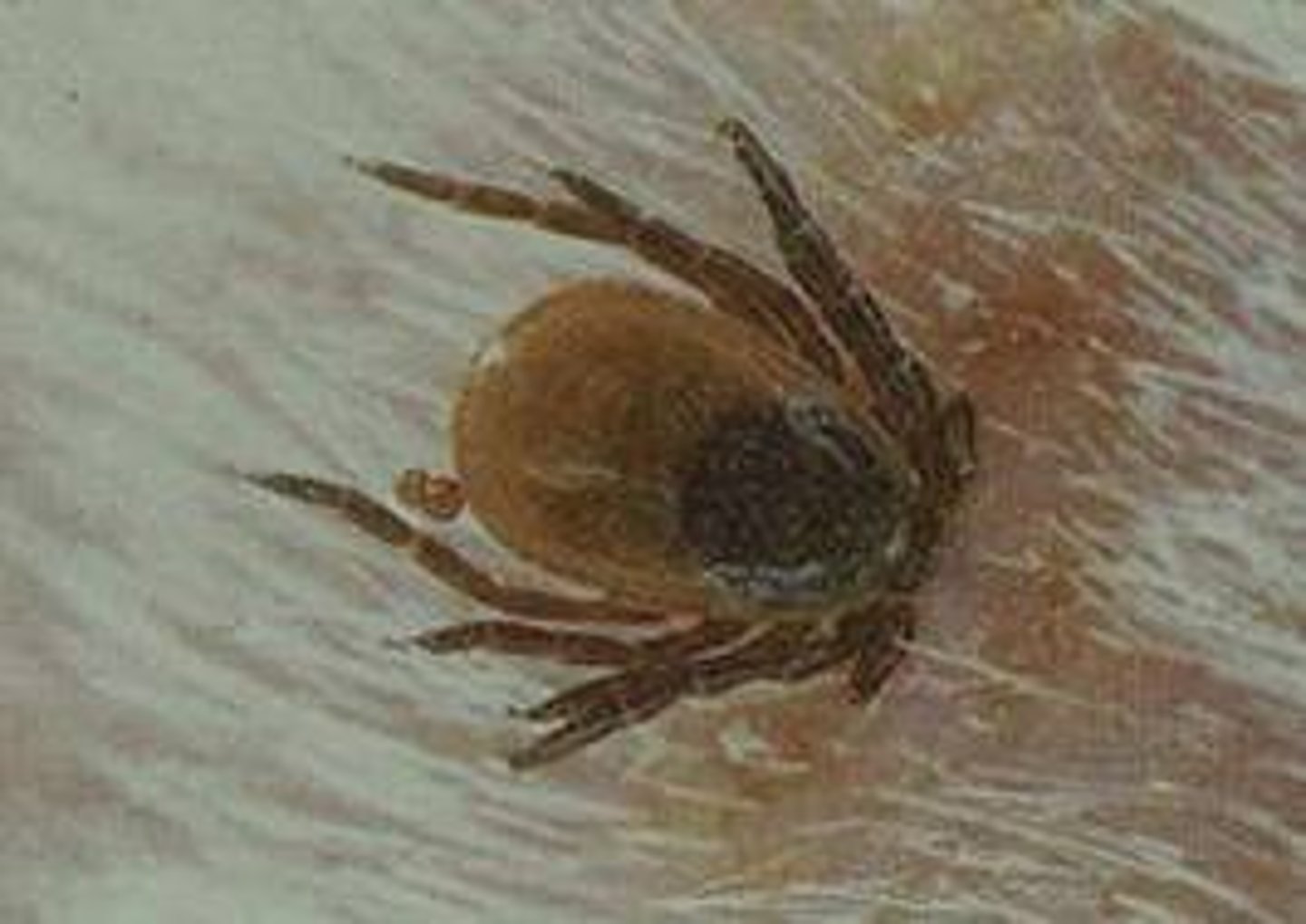
parasitism
a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and the other is harmed

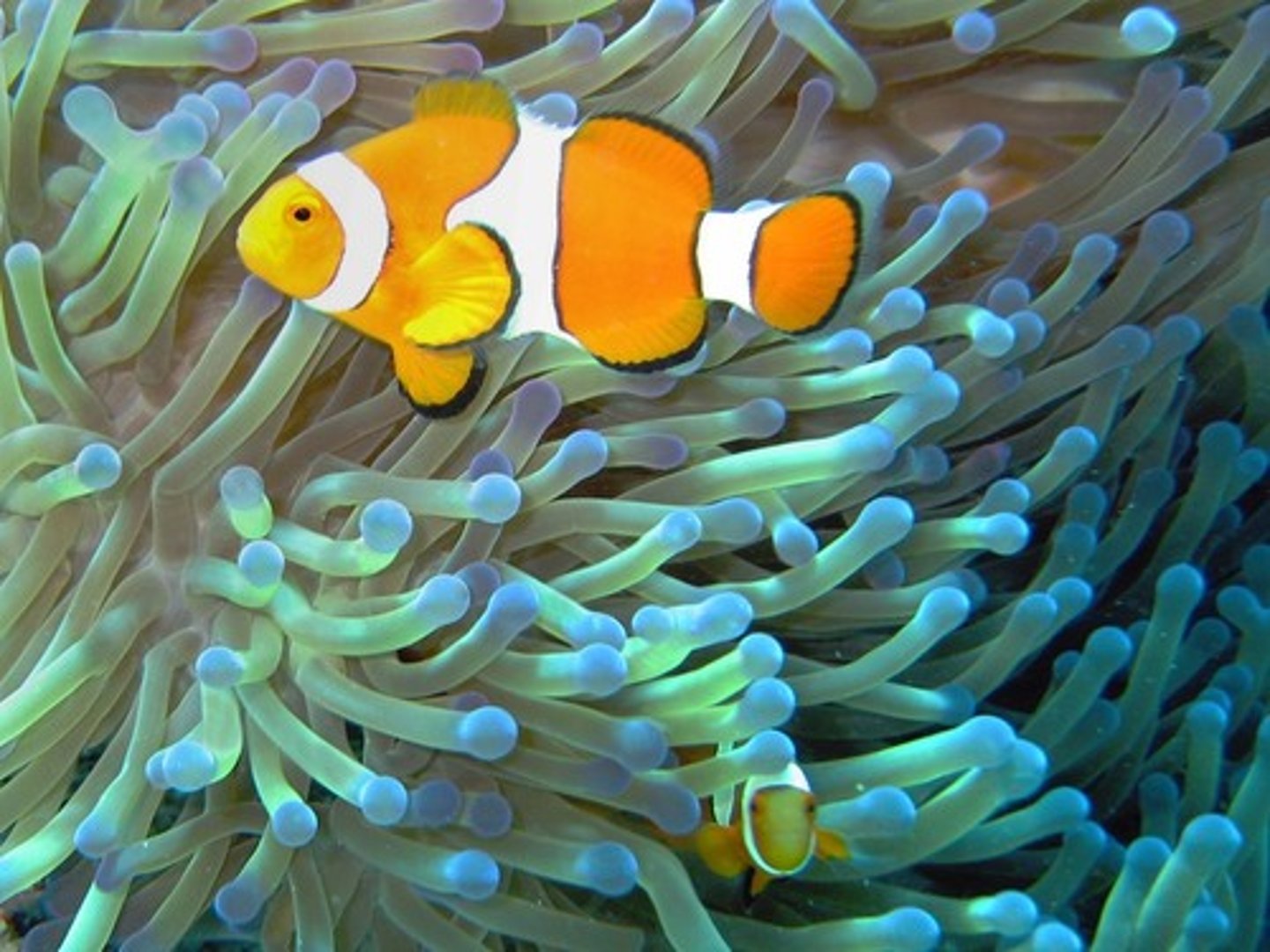
mutualism
a symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit

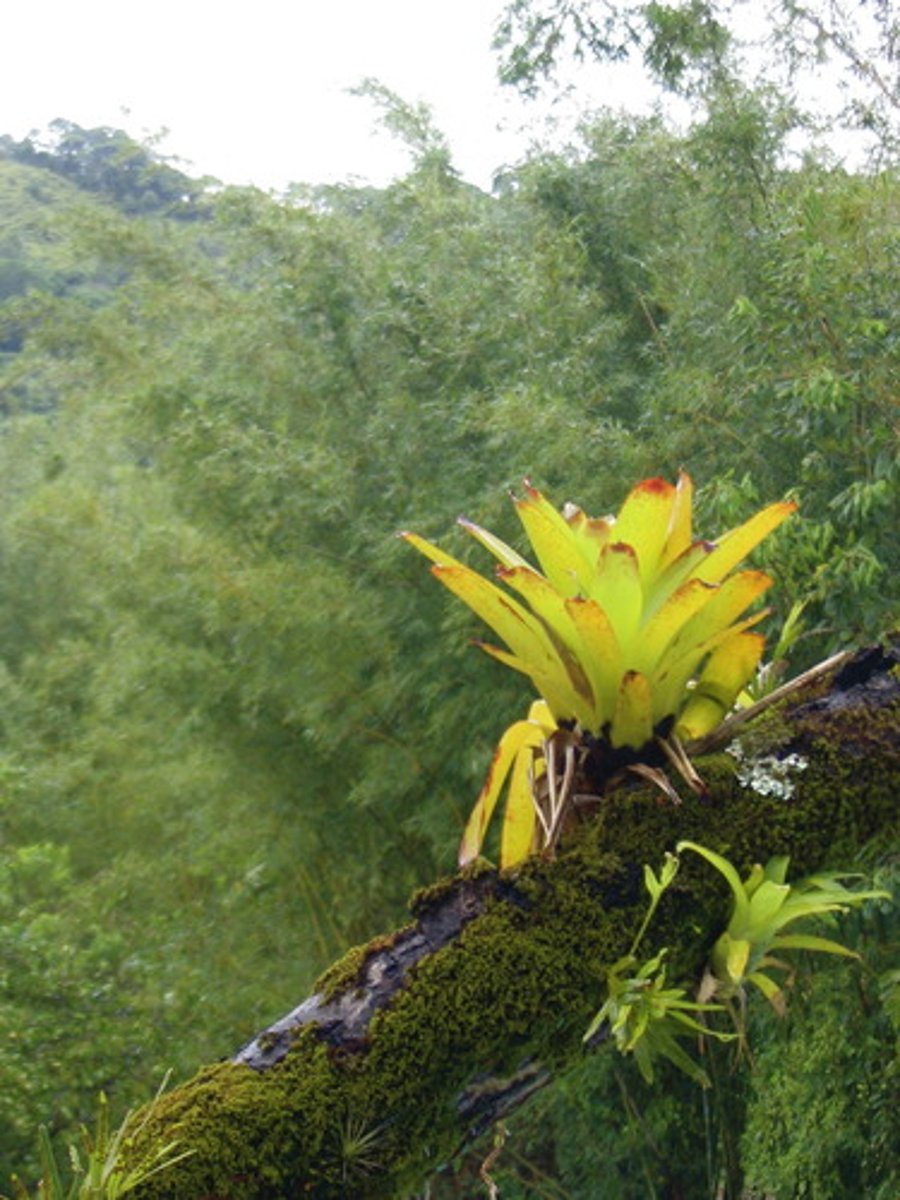
commensalism
a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and the other is unaffected

predation
any interaction (niche) in which one organism kills another for food.
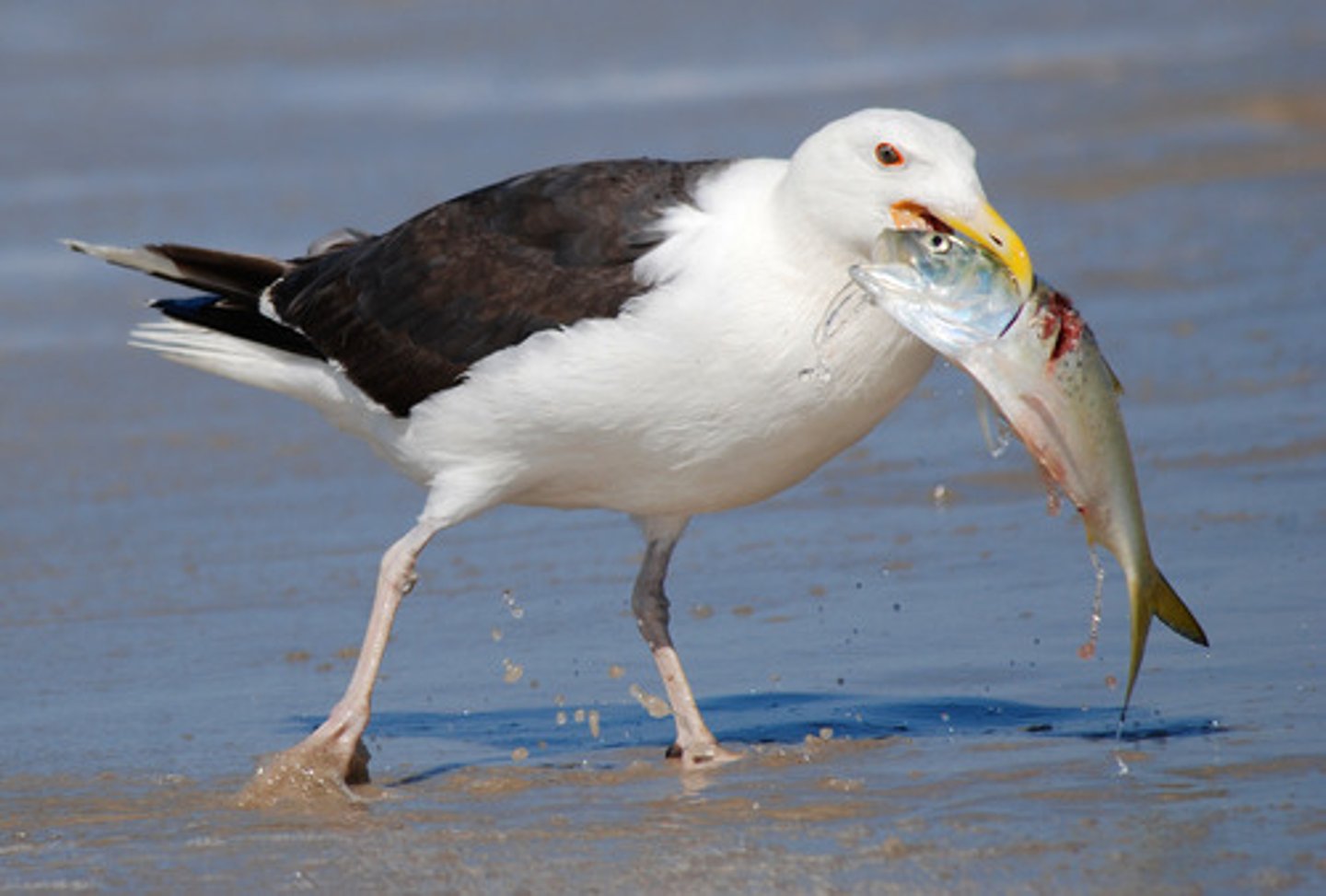

competition
any interaction (niche) involving the struggle between organisms over shared or limited resources
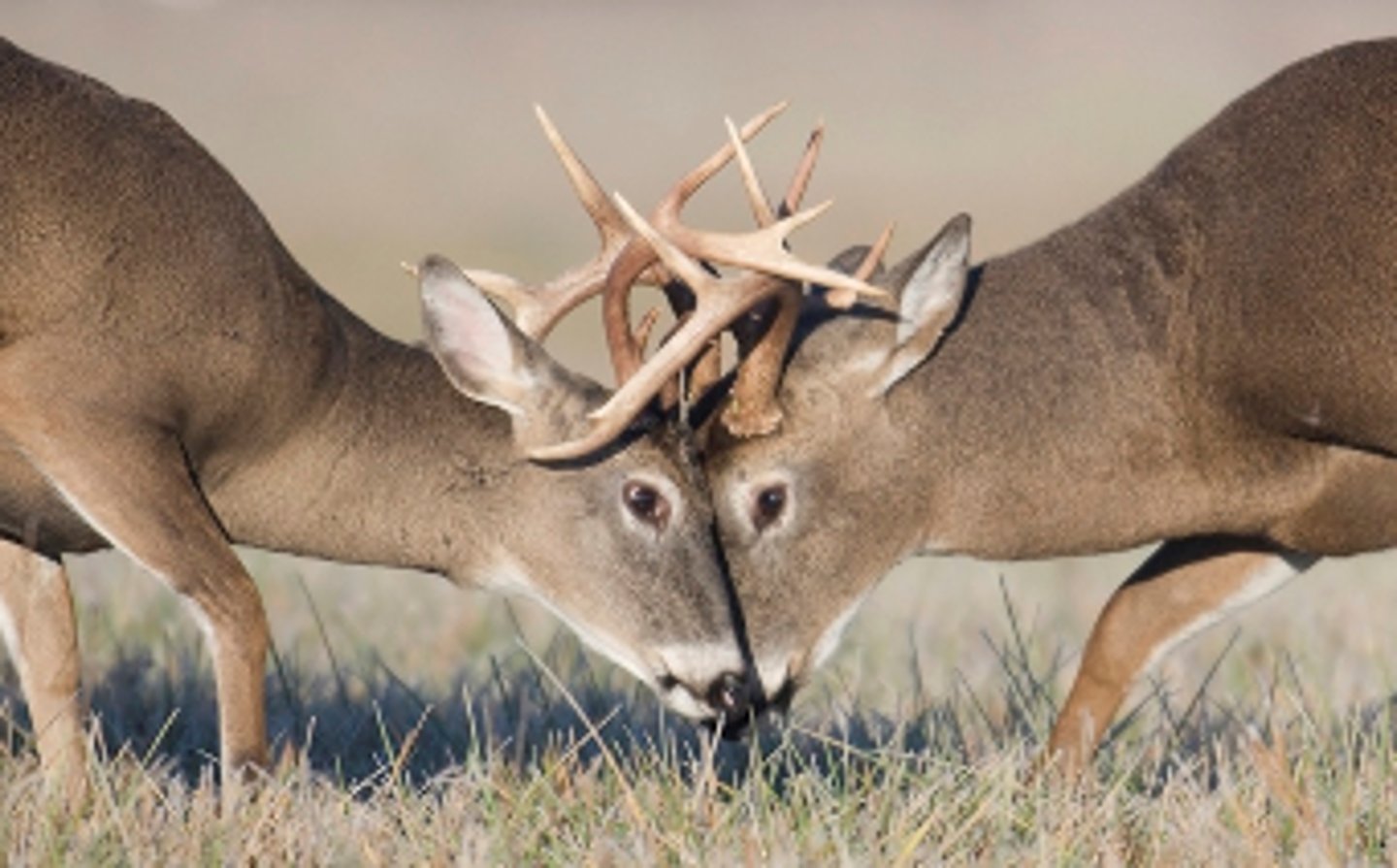

habitat
the biotic and abiotic environmental aspects of where an organism lives
2nd law of thermodynamics
principle which states that energy transfer between organisms increases entropy of the system; the free energy of the system also decreases and is therefore inefficient
1st law of thermodynamics
principle which states that as energy flows through ecosystems, it can be transformed from one form to another but cannot be created or destroyed.
biomagnification
the increase in chemical concentration in animal tissues as the toxin moves up the food chain
bioaccumulation
the increase in chemical concentration in animal tissues of a toxin over the course of an organism's lifetime
photosynthesis
process by which producers obtain energy
