P3 Particle Model of Matter
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Density
How closely packed the particles are in a solid, liquid or gas.
Density can also be described as…
The amount of particles per unit of volume.
What does all matter contain?
Particles
How are particles arranged in different states of matter?
Solid: tightly packed in a regular structure
Liquid: tightly packed but free to move past each other (irregular)
Gas: spread out and move randomly
Density of iron
7.8 g/cm³
Density of ice
0.98 g/cm³
Density of water
1 g/cm³
Density of air
0.00129 g/cm³
Density equation
Density = mass / volume

What are the units for density?
The standard unit is g/cm³, despite the standard unit for mass in physics to be kg and volume to be m².
What is the equation for the volume of a cone?
d = diameter
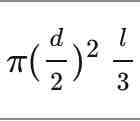
What is the equation for the volume of a sphere?
d = diameter
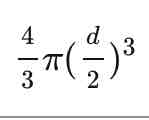
How can you measure the volume of the object if it is irregular?
You can use a displacement can.
What required practical is there to do with this topic?
Investigating density experiment
What are the 3 states of matter?
solid
liquid
gas
Solids - properties
Regular arrangement
Vibrate in a fixed position
Tightly packed together
Liquids - properties
Randomly arranged
Move around each other
Closely packed
Gases - properties
Randomly arranged
Move quickly in all directions
Far apart
What causes a material o change state?
Adding or removing energy from it.
Adding heat to a solid will cause it to…
…melt from a solid to liquid state.
Adding heat to a liquid will cause it to…
…evaporate to form a gas.
Adding heat to a solid cold also…
…cause it to become a gas without turning into a liquid. This is sublimation.
Cooling a gas causes it to…
…condense from a gas to a liquid.
Cooling a liquid causes it to…
…freeze from a liquid to a solid.
Boiling is a(n) ______ process. This is because….
active
People actively apply energy to a liquid to turn i into a gas using a heater such as a kettle.
Evaporation is a(n) ______ process. This is because…
Passive
The liquid slowly absorbs energy from the surrounding area so that some of its particles gain enough energy to escape the liquid.
What DOES NOT happen during changes of state?
changes in the number or particles
total mass
What DOES happen in changes of state?
changes in particles’ spacing
changes in particles’ arrangement
The changes caused by the changing of state are called ______ because…
physical
…the process can be reversed. This is different to changes caused by chemical reactions, which cannot be reversed so easily.
What happens to the particles when a material changes state?
chemical bonds between particles may form, break or stretch. There is a change in the chemical potential store of energy in the material.
The material will heat up of cool down as particles lose/gain speed. There is a change in the thermal store of energy within the material.
Internal energy
The total amount of kinetic energy and chemical potential energy of all the particles in the system.
What happens to the particles when energy is transferred to a material?
They speed up and gain kinetic energy.
What happens to the bonds when energy is transferred to a material?
Energy is put in to breaking the bonds holding the particles together, increasing the potential energy.
Conservation of energy
Any energy transferred to a material will be distributed between the chemical store and the thermal store, assuming none is dissipated to the environment.
In other words, energy can be transferred, dissipated or stored, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
Internal energy is a measure of…
…the total energy of all the particles in the object or substance - including kinetic energy of particles and chemical potential energy of bonds between them.
Temperature is a measure of…
…the average speed of the particles, this can be based on the kinetic energy of individual particles.
Why does it take a longer amount of time to raise the temperature of a large amount of water over a smaller amount?
Because more molecules need to have their speed changed.
Imagine a teaspoon of boiling water and a large bowl of water at room temperature.
Would it be able to melt an ice cube? Why/why not?
No
Even through the particles have lots of kinetic energy, there are very few of them.
Imagine a teaspoon of boiling water and a large bowl of water at room temperature.
Would the bowl of room temperature water be able to melt the ice cube?
Yes
Even through each individual particle has less kinetic energy, there are many more of them, making the total available energy much larger.
What is the freezing/melting point of water?
0°C
What is the boiling point of water?
100°C
What happens hen a solid is heated but it does not change state?
Its particles vibrate faster after being heated. This means that because it is a solid (with closely packed particles) and they are vibrating faster, its particles are more likely to hit each other and transfer the energy.
What does this transfer of energy between particles mean?
This means that energy spreads through the block quickly, and the temperature of the material goes up quickly - it takes less energy to raise the temperature of the material by 1°C.
A change in temperature in a system depends on:
the mass of the material
the substance of the material
the amount of energy put into the system
Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C.
What is the specific heat capacity of water?
4,200 J kg/°C
What is the specific heat capacity of brick?
840 J kg/°C
What is the specific heat capacity of copper?
385 J kg/°C
What is the specific heat capacity of lead?
129 J kg/°C
What are bricks often used for?
Why are they useful for this?
Often used in storage heaters, as they stay warm for a long time due to their high specific heat capacity.
What is water often used for?
Why is it useful for this?
Radiators in central heating systems use it as it has a high specific heat capacity, so it stays warm for longer, as it has a lot of energy to transfer to the environment.
What can be used instead of bricks in heaters?
They can be filler with oil, as it has a higher specific heat capacity (1,800 J kg/°C).
Change in thermal energy equation
change in thermal energy = mass x shc x temp change
(shc is specific heat capacity)
Latent heat of fusion
The amount of energy needed to melt or freeze the material at its melting point, with no change in temperature.
Latent heat of vaporisation
The amount of energy needed to boil or condense the material at its boiling point, with no change in temperature.
What is another way to calculate change in thermal energy?
change in thermal energy = mass x specific latent heat
How can latent heat be measured?
Using a heating or cooling graph; the larger the horizontal line (where change of state occurs its no change in temp), the more energy has been used to cause the change of state.
This means the amount of energy represented by these horizontal lines is equal to that latent heat.
Why does a material not change temperature while it is changing state?
All the thermal energy transferred to the material is being used to break the bonds between particles to change the state, rather than being stored as internal energy.
When can both equations for change in temperature be used?
When multiple changes occur, meaning when both temperature (specific heat capacity eq.) and state (specific latent heat eq.) change.
The particles in gases ON AVERGE move _____ than they do in solids of liquids. This means that…
quicker
…it does not take long for a gas to spread out to fill its entire container (and reach equilibrium).
What do particles moving around a container do to the container?
There is a force acting on the container due to the collisions acting on its walls by the particles. This force acts at right angles to the container.
pressure equation
Pressure = force / area

What are the particles in the air doing to a person standing in a room?
He is constantly being hit bu these particles as they are moving around rapidly.
What is the atmospheric pressure at sea level?
100,000 N/m²
Atmospheric pressure
The weight of air resting on the Earth’s surface.
When may the pressure of gas molecules increase?
If there are more molecules colliding each second
If the molecules are moving faster
If the volume of a container with a gas inside stays the same…
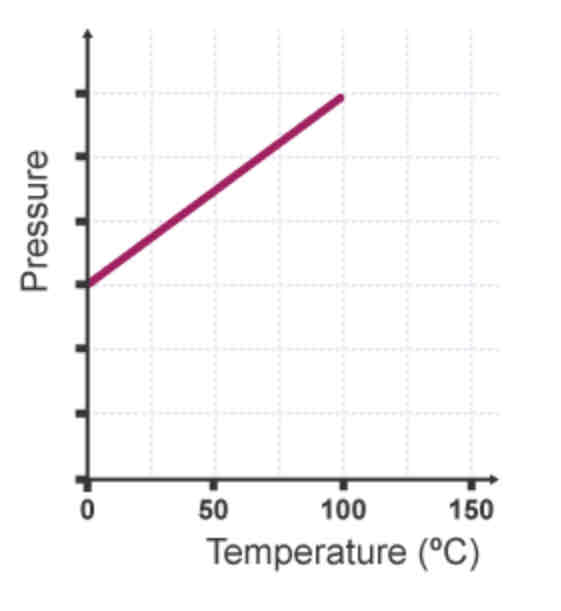
…the pressure of a gas increases as its temperature increases.
Why does an increased temperature cause the pressure in a container of gas to increase?
The gas particles move faster and therefore collide with the walls of the container more frequently and with more force, so more force is exerted on the walls of the container and he pressure increases.
What is the relationship between pressure and temperature?
Directly proportional
If a balloon is squeezed, it gets smaller.
What does this show us?
If the pressure is increased, the volume will decrease.
Who and when investigated the relationship between pressure and volume?
Robert Boyle, in the 17th century
What experiment did Boyle do to investigate the relationship between pressure and volume?
Poured mercury into a J-shaped tube sealed at one end, but trapping a bubble of air. Then pour some more mercury slowly and watch what will happen to the volume of the air bubble.
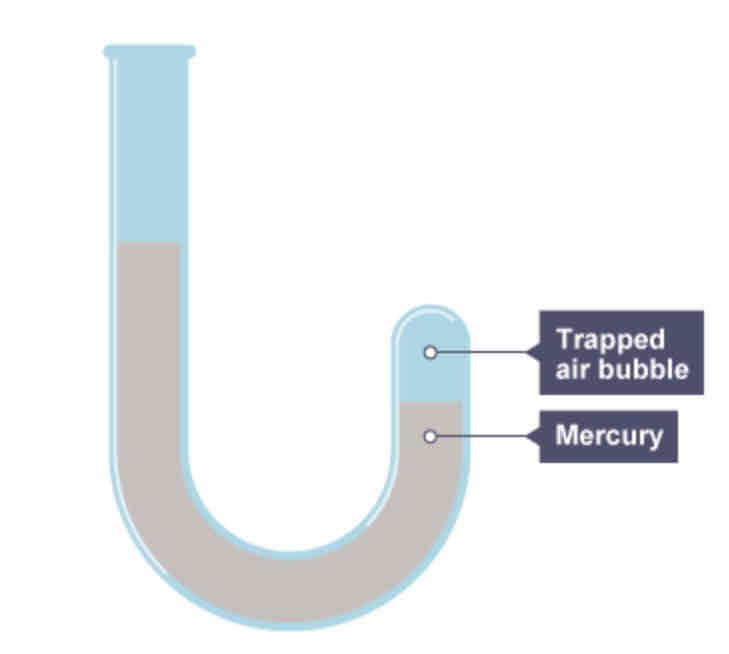
What were the results of Boyle’s experiment?
The higher the column of mercury in the left hand side of the tube, the greater the pressure the trapped air was experiencing and the smaller the bubble became.
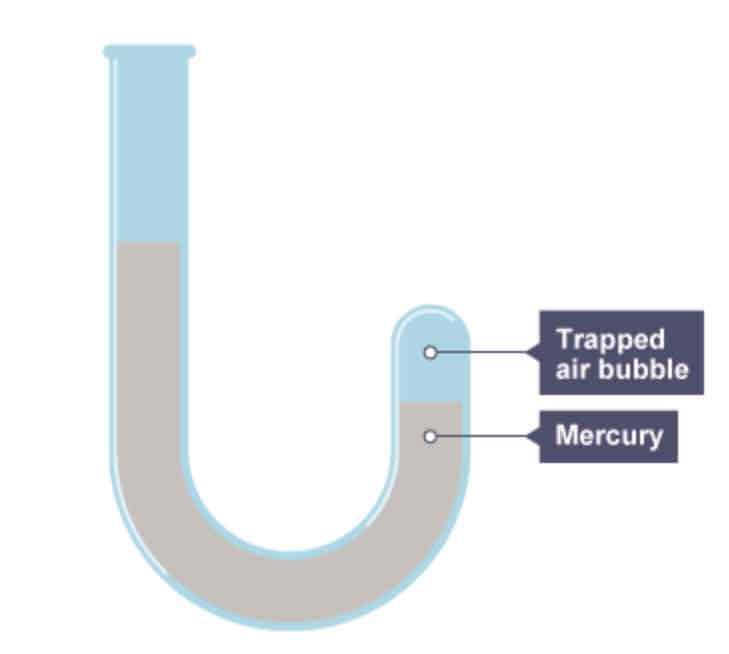
What was Boyle ale to show through his experiment?
That volume and pressure are inversely proportional.
For a fixed mass of gas at a constant temperature…
Pressure x volume = constant
p1 x V1 = p2 x V2

If the temperature of a gas stays the same, when the volume of its container decreases…
The pressure of the gas increases. This is becase the same number of particles collide with the walls of the container more frequently as there is less space. However, the particles sill collide its the same amount of force.
How can pressure be increased?
increasing the temperature - this increases the force of each collision
decreasing the volume - this increases the number of collisions per second
What was Boyle’s conclusion?
That volume could only be inversely proportional to pressure for a fixed mass of gas at a constant temperature.
Forces applied to the particles in a gas result in…
…a transfer of energy.
What happens when a person presses a piston down on a column of gas?
They apply a force that moves the piston a certain distance. They have done work on the gas by compressing it.
Work done equation
work done = force x distance
What does mechanical work do?
Transfers energy from the person or machine’s store of chemical energy to the internal energy store of gas.
What happens as the volume of a gas decreases?
The pressure increases because the particles are moving in less space and collide more often.
If the temperature of a gas is not fixed, what does an increase in pressure often lead to?
Why?
An increase in temperature
Because increased pressure causes particles to move more often (kinetic energy) so the gas has more internal energy, meaning the temperature must increase.
Why does a bicycle pump get warm when it is used to inflate a tire?
The gas in the pump is compressed and the pressure increases. As the temperature is not fixed, the increased pressure causes the particles to move more rapidly, and the gas has more energy in the internal store. This means its temperature also increases, and it gets warm.