EXERCISE 1: INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Microscopy
technical field of using microscopes to view samples and objects that cannot be seen with the unaided eye
Microscope
optical instrument used to view or magnify minute specimens
Microscope
an instrument that produces enlarged images of small objects
Illumination of the Specimen
a light source (LED, halogen bulb, natural light) is directed towards the specimen light passes through a condenser lens (directs light onto the specimen)
Passage of Light through the Specimen
light can be absorbed, transmitted, or refracted, creating an initial image
Objective Lens Magnification
light passes through the specimen and enters the objective lens (responsible for the initial magnification of the image)
Formation of the Real Image
objective lens produces a real, inverted image of the specimen, which is then projected into the body tube of the microscope
Ocular Lens (Eyepiece) Magnification
real image formed by the objective lens is further magnified by the eyepiece, which is another convex lens
Formation of the Virtual Image
eyepiece magnifies the real image into a larger virtual image that appears to be located at some distance away from the eyepiece
Magnification
degree to which an object is enlarged when viewed through a microscope
1,000 times the actual size of the specimen
how many times can a light microscope magnify?
Resolution
degree of clarity of an image when viewed through a microscope
Contrast
distinction between the light intensity of the specimen image and the adjacent background relative to the overall background intensity
Robert Hooke
first to identify and name a cell through a study of cork under a microscope
Cells
coined this term because they resembled the small rooms occupied by monks
Simple Microscope (Magnifier)
Light Illuminated, Single lens system, The image appears in 3D, Individual cells cannot be seen due to its low magnification, Enlarges objects without inverting it
Compound Microscope
Light Illuminated, The image appears in 2D, The most commonly used microscope, Individual cells, even living cells, can be viewed, Has high magnification but low resolution
Stereoscopic/Dissecting Microscope
Consists of 2 microscopes mounted in one body, Each ocular (eyepiece) can be adjusted, Low magnification, Has a 3D perspective, Used to view live specimen
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Electron Illuminated, Image is seen in 2D, but its picture appears in Black & White, Has high magnification and resolution
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Electron Illuminated, Image is seen in 3D, Has high magnification and resolution, but the image appears in Black & White, Specimen is coated in gold, and the electron bounces off to give you an exterior view of the specimen
Base, Pillar, Arm, Inclination Joint, Stage, Stage Clip, Body Tube, Draw Tube, Dust Shield, Revolving Nosepiece, Adjustment Knob, Coarse Adjustment Knob, Coarse Adjustment Knob, Fine Adjustment Knob
Mechanical Parts
Base
V or U-shaped structure that supports the whole instrument
Pillar
vertical extension of the base to which the arm is attached
Arm
curved basic part of the microscope to which the base, body, and stage are attached
Inclination Joint
Moveable part that facilitates the tilting of the microscope
Stage
platform upon which the slide containing the specimen is placed
Stage Clip
pair of metal parts that holds the slide in place
Body Tube
hollow cylinder in front of the upper part of the arm that serves as a housing for the lens; Serves as a passageway of light from the objectives to the eyepiece
Draw Tube
smaller cylinder attached to the base of the body tube that holds the ocular
Dust Sheild
fixed plate attached to the base of the body tube & situated above the revolving nosepiece; Protects objectives from dust and dirt
Revolving Nosepiece
rotary head is attached to the base of the body tube and holds the objective; facilitates the shifting of the objective
Adjustment Knob
used to adjust the objective when focusing, which, when turned clockwise or counter-clockwise, lowers or raises the body tube
Coarse Adjustment Knob
upper, larger knobs used for faster movement of the body tube when focusing on the lower power objective
Fine Adjustment Knob
lower, smaller knobs used for final focusing under high power objectives and in viewing at different levels
Abbe Condenser (Illuminator), Iris Diaphragm, Mirror
illuminating parts
Abbe Condenser (Illuminator)
lowers or raises the intensity of light
Iris Diaphragm
plate that regulates the amount of light that enters the condenser
Mirror
Usually 2 faces where one surface is Plane (for a very bright source of light) and the other is Concave (for low intensity of light). Used to reflect light through the objective lens and into the eyes
Eyepiece/Ocular, Objectives (Scanner, LPO, HPO, Oil Immersion Objective)
Magnifying Parts
Eyepiece/Ocular
detachable tube on top of the draw tube. May be provided with a pointer, which is used to point to a part of the specimen
Scanner (Red)
shortest cylinder with the widest opening; lowest magnification; used to observe a wider field of objects (4x-5x)
Low Power Objective/ LPO (Yellow)
smaller lens opening; observing the general outline of the object under study and locating various parts of the specimen (10x)
High Power Objective/HPO (Blue)
longer tube with smaller lens compared to LPO (40x-50x)
Oil Immersion Objective (White)
longest tube with the smallest opening (90x-100x)
Eyepiece/Ocular
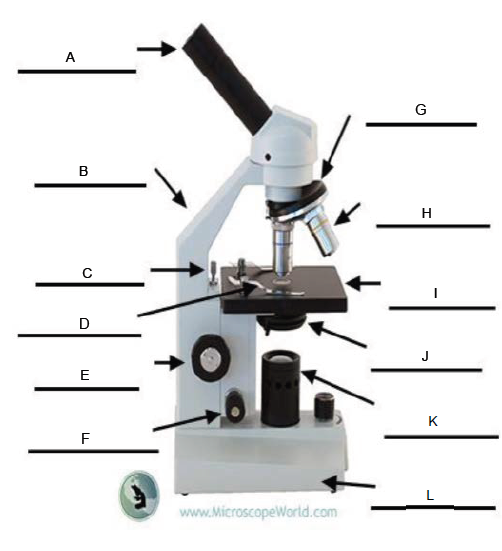
A.
Arm
B.
Rack Stop
C.
Stage Clip
D.
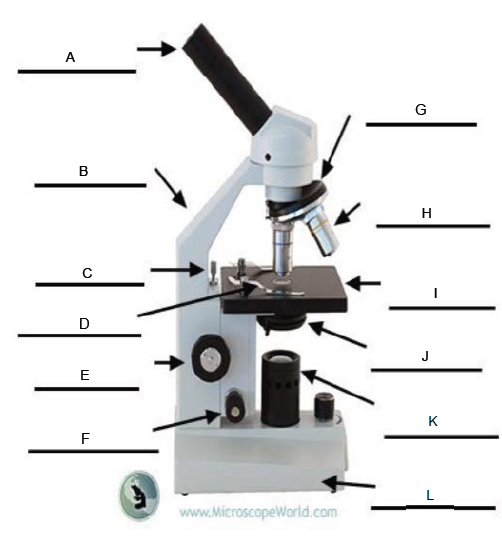
Coarse Adjustment Knob
E.
Fine Adjustment Knob
F.
Revolving Nosepiece
G.
Objective Lens
H.
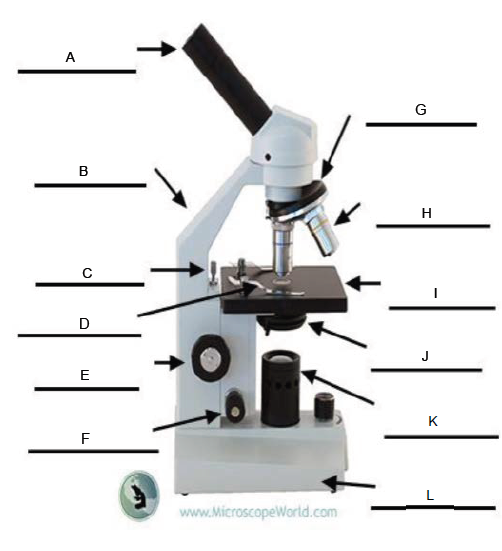
Stage
I.
Condenser
J.
Illuminator
K.
Base
L.