Neuro 28: UMN & LMN
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
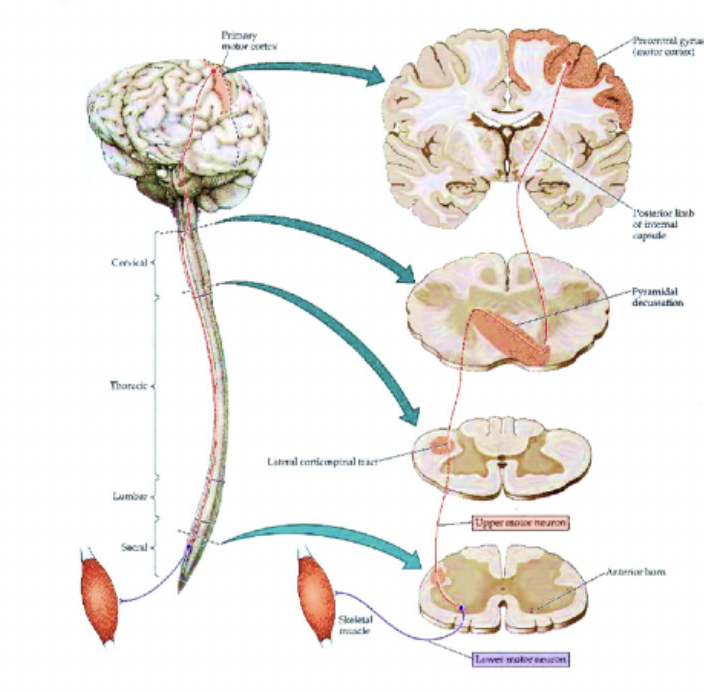
brain to spinal cord
UMNs transmit info from where to where?
spinal cord to skeletal muscle
LMNs transmit info from where to where?
ventral horn
where are LMNs located
skeletal muscle
what will UMN or LMN lesions generally affect?
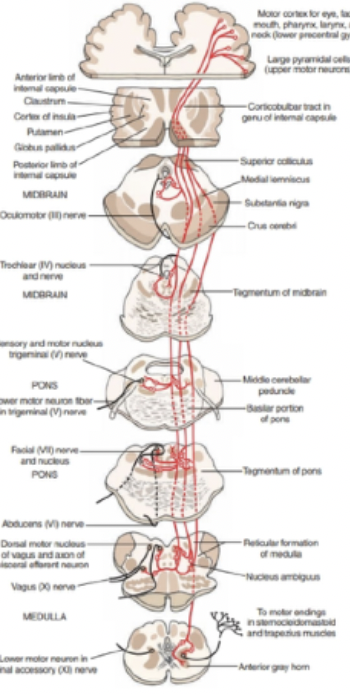
corticobulbar tract
volitional movement of the skeletal muscles in oral cavity, larynx, and face; terminate in motor nuclei of cranial nerves
V, VII, XI, XII
what cranial nerves does the corticobulbar tract go to?
medullary pyramids
where does the lateral corticospinal tract cross over?
corticospinal
which tract?
corticobulbar
which tract?
spinal cord level
where does the anterior corticospinal tract cross over?
sign
objective evidence of disease
symptom
patient reporting subjective evidence of disease
facial (lower muscles of facial expression)
hypoglossal (genioglossus muscle)
LMNs of the brainstem receive bilateral innervation except?
left (towards the lesion)
lesion in right motor cortex or internal capsule affecting the hypoglossal nerve will cause the tongue to deviate ?
UMN
UMN or LMN lesion?
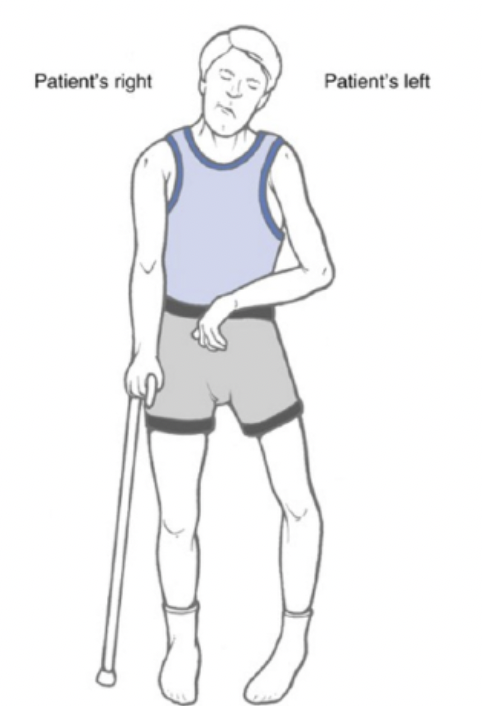
weakness (partial paralysis)
-presia
no movement
-plegia
no movement
paralysis
weakness/no movement (imprecise term)
palsy
both LEs
para-
paraparesis
weakness of both LEs
monoparesis
weakness of one limb
facial diplegia
symmetrical facial weakness
quadriplegia
paralysis of all 4 limbs
UMN
UMN vs. LMN lesion: increased reflexes
LMN
UMN vs. LMN lesion: atrophy
both
UMN vs. LMN lesion: muscle weakness
LMN
UMN vs. LMN lesion: fasciculations/fibrillation
UMN
UMN vs. LMN lesion: increased tone
both
UMN vs. LMN lesion: sensation intact
UMN
UMN vs. LMN lesion: + Babinski sign
loss of sensation in peripheral neuropathy but not LMN lesion
how to distinguish between peripheral neuropathy and LMN lesion?
stroke
infection
tumor
TBI
multiple sclerosis
cerebral palsy
huntington’s disease
causes of UMN lesion (7)
MCA
arterial supply to the internal capsule
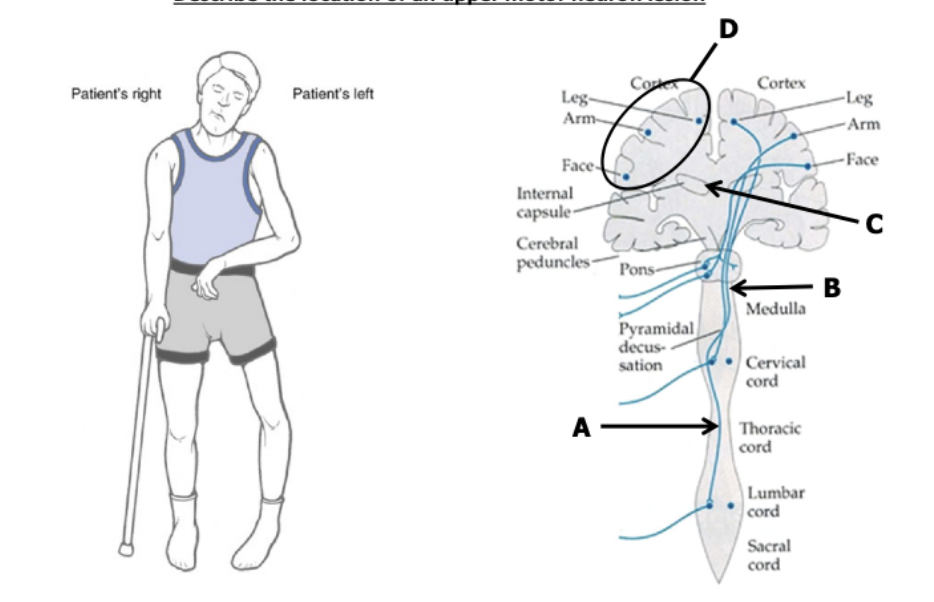
cortex or internal capsule
location of UMN lesion: results in weakness in the contralateral LE, UE, face, or combination
below pons
location of UMN lesion: face spared of weakness
below C5
location of UMN lesion: UE spared of weakness
above pyramidal decussation (90%)
location of UMN lesion: contralateral weakness
below pyramidal decussation (90%)
location of UMN lesion: ipsilateral weakness
UMN
UMN vs. LMN lesion to VII: forehead spared
LMN
UMN vs. LMN lesion to VII: whole side of face involved
~posterior limb to genu of internal capsule
location of UMN lesion: right face and UE weakness/paralysis
below pons
location of UMN lesion: right UE and LE weakness/paralysis
C - internal capsule
no aphasia or speech dysfunction = not cortex (D)
face involvement = above pons (A/B)
where is the lesion most likely?
note: patient has no aphasia or speech dysfunction
LMN
UMN vs. LMN lesion: hyporeflexia or areflexia
poliomyelitis
infection of anterior horn cells with variable anatomic pattern depending on how many spinal nerve root levels are affect and where
LMN
UMN vs. LMN lesion: flaccid paralysis
injury to ventral horn cells or axons leaving spinal cord
trauma to peripheral nerve
infections
botulism (botox)
poliomyelitis
cauda equina syndrome
causes of LMN lesion (6)
myelin in the CNS
what does multiple sclerosis affect?
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
“no muscle nourishment”
ALS
progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects UMNs and LMNs
onset 50-60 years
men > women
military veterans
initially: painful muscle cramping and fasciculations, dysarthria, dysphagia, and respiratory difficulties
exam: weakness, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, atrophy, fasciculations, head droop
none
what are the effects of ALS on mental status?
respiratory failure
most common COD for ALS
imaging (CT, MRI, dopplers, MRA)
blood work (enzymes)
muscle biopsy
EMG (insertional activity)
MNCV
methods of dx for UMN or LMN lesions
motor nerve conduction velocity (MNCV)
nerve stimulation with electrodes and action potentials measured to determine nerve function; helps diagnose LMN lesion or peripheral neuropathy