IB SL Psych Paper 1 Part A (SAQs) Practice
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Explain the Localization of Behavior with reference to one relevant study
Concept:
Localization of behavior/function is the theory that specific parts of the brain are responsible for certain behaviors and cognitive processes. There are three types:
Strict - clear correspondence between function and brain area
Weak - Area may be responsible, but not exclusively, to a function
Widely Distributed Function - Functions that are distributed throughout the brain
Evidence: HM Milner - investigates the role of the hippocampus in memory formation and consolidation
Tested his ability to recall information and form new long-term memories, Conducting a variety of memory tasks, such as word recall and learning new motor tasks, to assess his short-term and long-term memory abilities, Observing his behavior over time to assess his ability to retain new information.
HM retained short term memory, could not form new long-term memories, and could occasionally recall memories from before the surgery
Link: Hippocampus/Middle temporal lobe’s localized function is memory formation/short to long term memory conversion
Explain the effect of one neurotransmitter on human behaviour, with reference to one relevant study
Concept:
Neurotransmitters: chemicals passed between neurons to communicate with each other and the body
This process can be interrupted by antagonists who block receptor sites
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin
Acetylcholine: responsible for the consolidation of memory in the hippocampus
An action potential travels down the axon and releases neurotransmitters in the axon terminal
Neurotransmitters are then released into the synapse from the terminal buttons
The neurotransmitters cross the synapse and fit into receptor sites on another neuron
The neurotransmitters are finally broken down by enzymes or are reabsorbed into the axon terminal by the process of reuptake
Evidence: Antonova - investigates the effect of scopolamine and acetylcholine on spatial memory in the hippocampus
Participants were injected with either scopolamine or a placebo in separate sessions then asked to navigate a VR arena while their brain activity was measured using fMRI. The task required them to learn and remember the layout of the arena. After the task, participants were required to recall the layout of the arena, and they came back to do it again a few weeks later with the opposite condition.
Found significant reduction in hippocampus activation when given scopolamine
Link: Since scopolamine is an antagonist to acetylcholine and we saw a decreased amount of hippocampus activity when it was introduced, acetylcholine may play a part in encoding spatial memories.
Explain the use of one research method in one study of hormones or pheromones.
Concept:
Hormones are a class of chemicals that affect behavior and is secreted by glands in the endocrine system
Hormones: Adrenaline, cortisol, melatonin, neuropeptide Y, oxytocin, testosterone
Oxytocin: from the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary gland, acts as a neurotransmitter to affect mother-child attachment, social bonding, and trust
fMRIs: measure changes in blood flow in the active brain, creates a film to show changes over time
Evidence: Baumgartner - investigate the role of oxytocin in promoting trust during a trust game.
Participants were administered either oxytocin or a placebo via nasal spray then asked to play a game where they decided whether to trust another player with money. The decision involved transferring money to the other player, who could either return some of it or keep it. Brain activity was measured using fMRI to track how oxytocin affected the amygdala
fMRI showed lower activity in the amygdala when participants were administered oxytocin, participants affected by oxytocin continued to invest even if trust was broken
Link: The use of a true experiment where an IV (oxytocin amount) was established and its effects were measured by observation of behavior and of amygdala activity through fMRI
Explain one model of memory with reference to one relevant study.
Concept:
Models of memory: Ways to conceptualize the processes of memory; a hypothesized representation of how memory works with available evidence
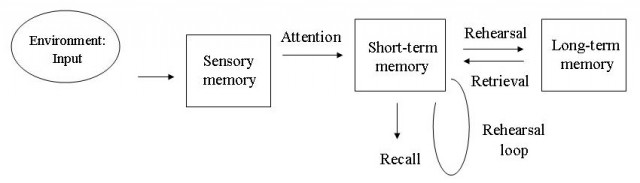
Multi-Store Memory Model: (image), inspired by computer science models
Evidence: HM Milner - investigates the role of the hippocampus in memory formation and consolidation
Tested his ability to recall information and form new long-term memories, Conducting a variety of memory tasks, such as word recall and learning new motor tasks, to assess his short-term and long-term memory abilities, Observing his behavior over time to assess his ability to retain new information.
HM retained short term memory, could not form new long-term memories, and could occasionally recall memories from before the surgery
Link: The ability for HM Milner to retain short term memory but not form long term memory supports the fact that short and long term are separate stores and that information must travel between them
Explain one bias in thinking and decision making with reference to one relevant study.
Concept:
Cognitive Biases: systematic errors in thinking that impacts our choices and judgements
System 1 Thinking: intuitive, automatic, requires limited effort and is influenced by cognitive biases
System 2 Thinking: rational, goal directed, requires effort and controls for cognitive biases
Evidence: Englich & Mussweiller - tests effects of Anchoring Bias
After they had formed an opinion about the case (about 15 minutes), trial judges were given a questionnaire. Half of the participants were told that the prosecutor demanded a 34-month sentence, while the other half were told he demanded a 2-month sentence, then they were asked what sentence they recommended based on the information they had.
When presented with a low anchor of two months, the average sentence was 18.78 months. In the high anchor condition of 34 months, the average sentence was 28.70 months.
Link: This study shows how Anchoring Bias occurs when we rely too heavily on an initial piece of info offered to make decisions and how not even experts are immune to it.
Explain the use of one research method in one study of the reliability of cognitive processes.
Concept:
Cognitive processes can be unreliable due to reconstructive memory, emotions, and cognitive biases
Reconstructive Memory: Suggests that memories are not exact replicas of what happened but are actively reconstructed during recall, often influenced by our existing knowledge, expectations, and other cognitive factors
Evidence: Yuille & Cutshall - investigates whether leading questions would affect the memories of eyewitnesses
4 months after a robbery, eyewitnesses were interviewed and asked two leading questions: whether they saw A broken headlight or if they saw THE broken headlight/A yellow panel or THE yellow panel, then asked to rate their stress the day of the event on a 7pt scale. Their accounts were compared to the original police reports.
Their accounts recalled a lot of detail seen in the police reports and were 79%-84% accurate. Participants also did not see or did not recall the items mentioned in the leading questions.
Link: The research method used in this study was a true experiment, where leading questions was the IV, and interviews were held to attain answers. This directly measures reconstructive memory, with the added benefit of the scenario being naturalistic, and also having police reports to compare their accounts to.
Explain one cultural dimension with reference to one relevant study.
Concept:
Cultural Dimensions: The trends of behavior in a given culture that reflect the values of that culture
Hofstede’s 6 cultural dimensions: Power Distance Index, Individualism/Collectivism, Uncertainty Avoidance Index, Masculinity/Femininity, Long-term/Short-term orientation, Indulgence/Restraint
Correlational, but good for discussing cultural differences and challenging ethnocentrism
Individualism vs. collectivism: the degree to which people are integrated into groups
Evidence: Berry - measuring the level of conformity in individualistic vs. collectivistic cultures
Used the Asch paradigm line test on the collectivistic rice farming Temnes, the individualistic Inuits, and the Scots as a control. For some of the trials, they misled the participants into thinking people of their culture thought a certain line was longest, even if it wasn’t.
They found that the Temnes (collectivistic) had a higher rate of conformity than the Inuits, who were even lower than the Scots. It also did not matter if the natives were westernized or not.
Link: Individualism vs. Collectivism can help explain behaviors like conformity and how even when acculturation occurs, the intrinsic cultural dimensions of one’s native culture can affect behavior.
Explain one effect of enculturation on human cognition and/or behaviour, with reference to one relevant study.
Concept:
Enculturation: the process of adopting/internalizing the schemas of one’s own culture
A constant process that reinforces your identity as a member of your culture throughout life
Can be caused by direct tuition, social cognitive theory, or participatory learning
Evidence: Odden & Rochat - aimed to see the role of social cognitive theory in cultural norm development
Longitudinal observation of society’s children, then a basic knowledge test about their societies systems
There is hardly any direct instruction in Samoan culture, but by 10 years old children began learning how to fish without instruction, and by 12 they were proficient in it. When given tests about their chief system, they showed a broad understanding of it despite it not being taught until high school.
Link: Enculturation, especially through the ideas of social cognitive theory, affect how children learn the skills that their society deems important and how they learn the social hierarchy.
Explain one study of acculturation.
Concept:
The process of cultural/psychological change as a result of contact between 2 or more cultural groups
4 strategies for acculturation: Integration, Marginalization, Separation, Assimilation
The 4 strategies can be visualized using Berry’s model
Acculturative stress: A reduction in the mental health and well-being of ethnic minorities that occurs during the process of adaptation to a new culture, aka culture shock
Acculturation Gaps: generational differences in acculturation that may cause family conflict
Evidence: Lueck & Wilson - investigates variables that may predict acculturative stress in Asian Americans
Large sample comprised of adult 1st gen immigrants, US Born Asian Americans, and the children of 1st gen immigrants
Semi-structured interviews with interviewers of similar background to participants, measured acculturative stress, language proficiency, discrimination, social networks, family cohesion, socioeconomic status
Found that 70% of the sample experienced acculturative stress and that certain protective factors decreased acc. stress: Bilingualism, sharing family values, and being satisfied with economic opportunities
Speaking only English and experiencing negative treatment caused more acc. stress