the global economy (4.6, 4.7, 4.8, 4.9, 4.10)
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
balance of trade
net exports = exports - imports
(New Zealand shows a trade deficit of $14.81 billion, slightly better than the previous $15.41 billion. It highlights an increase in exports to $5.40 billion and a decrease in imports to $7.11 billion)
trade surplus
exporting more than is imported
trade deficit
exporting less than is imported
trade gap
credit items
payments received from consumers, firms or governments located outside of the economy
debit items
payments made to consumers, firms or governments outside of the economy
balance of trade
includes only goods & services
balance of payments
summary of a country’s international trade
considers all international transactions
current account
capital account
financial account
current account
a record of trade flows, income flows and income transfers across borders
all exports & imports of g&s +net investment income (from overseas assets) + net balance (of transfers made between countries by individuals, firms and governments)
balance of trade in goods- all imports & exports of physical goods between a country and the rest of the world
balance of trade in services- all imports & exports of services between a country and the rest of the world
income- income receipts (inflows or credit items) earned from foreign investments - income payments (outflows or debit items) of factor incomes paid to foreign investors (essentially inflows & outflows of payments to the factors of production)
current transfers- inflows & outflows of money that are not made in exchange for trade or output
(india deficit at $9.2 billion down by $17.9 billion from the same quarter in the previous year, due to marginally higher trade deficit in merchandise and marginally lower surplus in invisibles)
capital account
records the different forms of capital inflows & outflows of a country during a given time period
capital transfers- forms of capital inflows & outflows of a country
transactions in non-produced- non-financial assets are the legal property rights to natural resources and intellectual property rights to intangible assets (they produce income for the country)
financial account
record of the transactions that relate to the change in ownership of assets (cross-border investments)
foreign direct investment
portfolio investment
reserve assets- stocks of foreign currencies & liquid assets held by central banks used to balance international transactions & payments
official borrowing- government borrowing
interdependence between accounts
the overall balance of payments must balance because in the long term, a country can only spend as much as it earns
sum of credits = sum of debits
current account = capital account + financial account (+ errors & omissions)
errors and omissions
represent statistical discrepancies when compiling the account
sustainable development
economic development that meets the needs of the present generations without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
social sustainability
the ability of an economy to develop social processes & structures that enable its current population to live optimally and to support the ability of future generations to do the same
economic sustainability
the optimal use of scare resources in such a way as to ensure future generations are not disadvantaged
environmental sustainability
the responsible use of the planet’s natural resources so that future generations are not compromised
multidimensional nature of sustainable development
development includes more than just growth but also indicators such as reduction in poverty, income inequality, gender inequality, political oppressions and unemployment
mercantilism
political & economic policy that focused on wealth creation through international trade
single indicator
statistical measure of economic development through focus on one indicator
GDP/GNI per capita at PPP
the average income in an economy divided by poopulation size
purchasing power parity
(PPP)
exchange rate that enables residents to purchase a common basket of goods and services in different countries
health indicators
use of health-related determinants of quality of life
life expectancy
under 5 mortality rates
education indicators
use of education-related determinants of quality of life
literacy rates
mean years of schooling
economic/social inequality indicators
societal indicators use measures that determine the extent to which social factors contribute to development
health & education indicators
shelter & housing
crime & homicide rates
safety & degree of trust
energy indicators
use of factors that create affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all citizens
environmental indicators
use of environmental issues that influence or determine the quality of life
global warming & climate change
desertification
deforestation
waste disposal management systems
loss of biodiversity and ecosystems
composite indicators of measuring development
statistical method that combines single indicators into a combined index
human development index
measure of economic development comprising
real income
life expectancy
educational attainment
(China has new long-term development strategies that will improve the HDI, environment, and human development, HDI is about 0.768. Life expectancy rose by 17 places, education rose by 29 places and income index rose by 38 places)
gender inequality index
calculates gender disparities through reproductive health, empowerment and labor market participation
inequality-adjusted human development index
average level of human development by accounting for inequalities in society
happy planet index
a measure of sustainable human wellbeing
how individuals & countries are able to achieve long, happy and sustainable lives
well being
life expectancy
inequality of outcomes
ecological footprint
strengths and limitations of approaches to measuring economic development
fail to consider qualitative factors
different members of society need to measure development differently
measuring economic well-being is a multilayered, complex process that changes over time
some indicators better portray a strength of a country (not full picture)
economic growth
increase in GDP per capita or other measure of aggregate income, typically reported as an annual change in real GDP
driven by improvements in productivity (producing more goods/services with the same inputs of capital, labor, energy and materials
increase in quantitative output
economic development
increase in standard of living in a nation’s population with sustained growth from a simple low-income economy to a modern high income economy
involves the processes by which a nation improves the economic, politic and social well-being of people
a qualitative measurement
poverty trap
when an economic system requires a significant amount of capital in order to earn enough to escape poverty
not having capital makes it difficult to acquire capital, creating a cycle of greater poverty and deprivation from one generation to the next
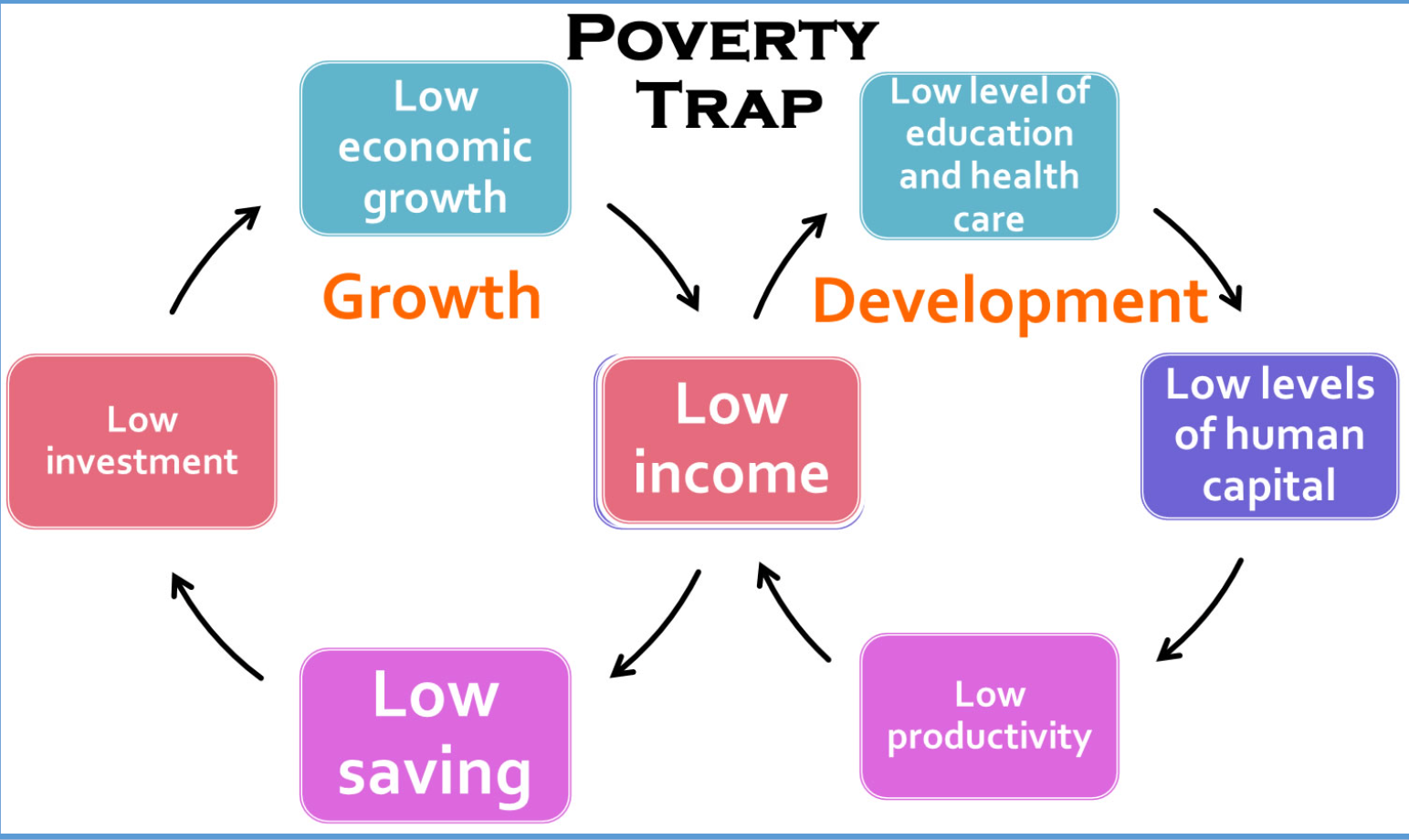
economic barriers to economic growth/development
rising economic inequality
lack of access to infrastructure &technology
low levels of human capital
low access to education & healthcare
dependence on primary sector production
lack of access to international markets
informal economy
capital flight
indebtedness
geography
tropical climates & endemic diseases
informal economy
economic activities that are not officially part of a country's GDP
capital flight
withdrawal of money, resources and assets from a country due to economic/political uncertainties
thus hindering investor confidence
indebtedness
condition of owing money
overall debts to creditors by individuals, businesses and government of the country
political/social barriers to economic growth/development
weak institutional framework
legal system
taxation structures
banking system
protection of property rights
gender inequality
unequal political power & status
lack of good governance → corruption
institutional framework
established systems, contexts and structures that shape economic behavior in a country
micro-credit
loans of exceedingly small amounts to individuals on low income for self-employment projects that generate revenue so that they can become self-reliant
property rights
entitlement to tangible & intangible assets owned by individuals, organizations or governments
measures of good governance
voice & accountability
political stability
absence of violence
govt. effectiveness
regulatory quality
rule of law
control of corruption
significance of barriers
resource endowment
history
political systems & stability
climate
population
factors of ELDC development
education and health
use of technology
women’s empowerment
access to credit/micro-credit
income distribution
all have positive externalities of production & consumption
trade strategies
potential net gains for countries engaged in international trade
import substitution- encourages domestic production & consumption through protectionist policies
export promotion- focus on greater international trade
economic integration- process of countries becoming more interdependent and economically unified
import substitution
advantages:
increase in domestic production
increase in domestic employment
less dependence on imports (resilience from external shocks)
reduced transport costs
disadvantages:
detrimental to economic efficiency (distorts market forces of d&s for imports & exports)
consumers pay higher prices & have less choice
reduced competitiveness thus reducing attractiveness of exports
export promotion
advantages:
use of international specialization & export-led growth strategies increases productive capacity of country
domestic firms can access larger markets (greater economies of scale and larger profits)
efficiency (transfer of skills & tech → productive gains)
disadvantages:
ELDC exporters face stiff competition & struggle to compete against larger corporations
other countries’ protectionist policies discourage export promotion from ELDCs
opportunity cost of G to support strategy
economic integration
advantages:
greater flows of g&s between countries → economic benefits for trading partners
increased choice & higher quality (bc of international specialization & competition)
lower/removing trade barriers → reduction in prices, gain in productivity (bc of competition & efficiency)
disadvantages:
compromise/adjust internal policies
have to impose common trade restrictions
diversification
countries broadening their supply of g&s in export markets
advantages:
helps ELDCs overcome over-specialization → create new employment opportunities
reduce vulnerability to fluctuating prices in primary sector output
disadvantages:
risk of failure → ELDCs lack experience & expertise
higher costs → broader range of products produced
requires long-term plans → time consuming & expensive
(Malaysia wants to advance in the manufacturing sector, aiming to invest more in the high-tech industry in goods such as chips and electric vehicles)
social enterprise
organization that focuses on meeting specific social objectives
advantages:
encourages volunteerism & civic commitment
receive govt. support (tax incentives & preferential support programs) to encourage participation
attracts attention from news & media
disadvantages:
small bc of low funding
profit generated goes to funding ongoing expenditures → less funds to invest in country
fall short of expectations (lack of commitment)
market based policies
dynamic, outward-looking macroeconomic strategies using free market forces (liberating industries & improving market incentives)
trade liberalization- reduction/ removal of trade barriers to increase competition, productivity & efficiency
privatization- transfer of ownership of govt. assets from public sector to owners in private sector
deregulation- reduction/removal of govt. rules in an industry
trade liberalization
advantages:
encourages free & fair trade → reduction in costs of conducting international trade
reduction in regulatory costs → overall reduction in prices
increased competition, productivity & efficiency
disadvantages:
intense competition → no longer profitable for domestic firms
dumping on ELDCs
cheaper flow of g&s → producers lack environmental & ethical compliance to cut costs
privatization
advantages:
cuts G on maintaining assets & raises one-time revenue
private sector achieves more optimal allocation of scarce resources (bc of incentive to work & invest)
private sector fosters competition → reduced prices, improved quality and more choice
disadvantages:
privates cut jobs to remove inefficiencies → unemployment
rising price (profit motive)
deregulation
advantages:
limits inefficiencies brought about by excessive govt. control & administrative processes
allows market forces to allocate resources → quicker decision-making
disadvantages:
market exposed to uncertainties & fluctuations
increase in deceptive schemes & corruption
interventionist policies
tax policies- used to redistribute wealth to protect & support poorest members of society
transfer payments- financial assistance made to less fortunate members of society (including state pensions, child allowance and unemployment benefits)
minimum wage policies- lowest amount of money employers are legally obliged to pay their workers
(Malta’s child allowance is set to rise by 250 euros per child in order to alleviate the rising levels of poverty)
provision of merit goods
education programs- allocate a portion of govts budget to education & training
health programs- preventative healthcare system prevents spread of disease
infrastructure- physical structures & facilities required for efficient running of a country
(UK is investing 600 million GBP to improve education, where every student will have to mandatorily study some sort of maths and english until the age of 18.)
inward foreign direct investment
direct investment into production in a country by a MNC in another country
(focuses on enhancing Tajikistan's economic potential through better investment and business environments: reforms in investment law and tax codes, and modernizing investment promotion strategies, strengthening sectors like mining, manufacturing, and agriculture)
foreign aid
the international transfer of capital, g&s from a country or org. for the benefit of the recipient country
advantages:
helps escape poverty cycle (humanitarian, economic and political benefits)
increases production & productivity in ELDCs
injection into circular flow of income → help reduce inequalities & unemployment in ELDCs
disadvantages:
economic dependence
corrupt govts misuse aid
if concessionary loan → interest repayments (financial burden)
(UK government committed to raising £11.6 billion, half of which will be spent aiding foreign countries that aren’t as developed to adapt to the impacts of climate change)
humanitarian/development aid
helps recipient countries achieve economic development & improve quality of life
provided by individual countries, NGOs, multilateral org
grants- non-repayable financial assistance
concessional long-term loans- loans w/ highly favorable terms & conditions
project aid- helps specific developmental projects
program aid- support a specific industry
conditional aid- capital, grants or loans on condition it is used for policy reforms and structural adjustments
tied aid- spend foreign aid on buying products from donor
debt relief
partial or total remission of foreign debts
heavily indebted poor country- nation w/ huge outstanding debt
debt rescheduling- renegotiating length of time to repay loans
official development assistance
foreign aid from donor govts rather than NGOs or non-proft orgs
bilateral aid- govt → govt
multilateral aid- govt → international org → reducing poverty in developing nations
non-government organizations
(NGOs) agents in provision of foreign aid
multilateral development assistance
financial support delivered through international institutions
(The Health Impact Investment Platform is providing an initial €1.5 billion in concessional loans and grants to strengthen primary health care services in low- and low-to-middle-income countries, aiming to strengthen health systems in countries like Angola, Ethiopia, and Rwanda)
institutional change
improved access to banking
increasing women’s empowerment
reducing corruption
extending & protecting property rights
uploading land rights
(432 million women of working age in India, out of which 343 million are employed in the unorganised sector → estimated that just by offering equal opportunities to women, India could add US$ 770 billion to its GDP by 2025. At present the contribution of women to the GDP remains at 18%)
improved access to banking
enables more individuals to have access to credit
ELDCs don't have necessary funds to invest, hindering innovation & skills development of the workforce
used for investment to increase production & productive capacity
more employment, less inequality in income, less poverty
microfinance- small sums borrowed by individuals for self-employment
mobile banking- allows conduction of financial transfers remotely
increasing women’s empowerment
ignoring gender disparities is detrimental
gender equality helps end social & cultural discrimination against females
huge impact on their self-esteem and mental wellbeing
in long-term → positive effects on maternal health and reduces child mortality
reducing corruption
corruption is fraudery & dishonesty by people in power/authority
well-structured/enforced legal systems & good governance are essential to creating an institutional framework and an environment conducive to national and international trade
land rights
ability of individuals to obtain, use & hold land
land ownership is an important source of security, income and wealth
property rights
entitlement to tanglible & intangible assets
property rights of an economic good or service:
the right to use the asset
the right to earn income from the asset
the right to transfer the good or service to others
the right to enforce property rights of the asset
strengths and limitations of strategies for promoting economic growth and economic development
dependent on different factors, including the context of the country, budgetary constraints, political and social influences, and the degree of good governance
government intervention to achieving economic growth/development
strengths:
provision of essential infrastructure
investment in human capital
establishment of a stable economy
provision of a social safety net
weaknesses:
excessive bureaucracy
poor planning
corruption
market-oriented policies to achieve economic growth/development
strengths:
efficiency
competitiveness
economic growth
benefits of free trade
investment opportunities
weaknesses:
market failures
development of a dual economy- when two distinct economic sectors exist within a country, with different levels of development
income and wealth inequalities