5. hemorrhage, thrombosis, and infarction
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
hemorrhage
escape of blood from circulatory system
petechia
very small, pinpoint superficial hemorrhage (1-2 mm diameter)
ecchymosis
larger superficial hemorrhages (2-3 cm diameter); essentially a bruise
hematoma
hemorrhage in a confined space (e.g. spleen and ear) secondary to trauma
primary hemostasis disorders
↓ vascular integrity — trauma/inflammation
↓ platelet concentration/function
↓ vwF
mucosal/skin bleeds
secondary hemostasis disorder
↓ coagulation factor concentration/function
big bleeds
thrombosis
too much clotting
arterial thrombi
firm clot attached to vessel wall (not easily removed)
dull red, pink, tan, gray color
coronary, cerebral, femoral arteries
meshwork of fibrin, platelets, RBCs, degenerating leukocytes
venous thrombi
gelatinous, soft, glistening red clot
loosely adhered to vessel wall
meshwork of mostly RBCs (red thrombi) — venous circulation is more sluggish
forms a long luminal cast
embolus
detached piece of a thrombus (clot)
thromboemoblism
process of detachment from main thrombus
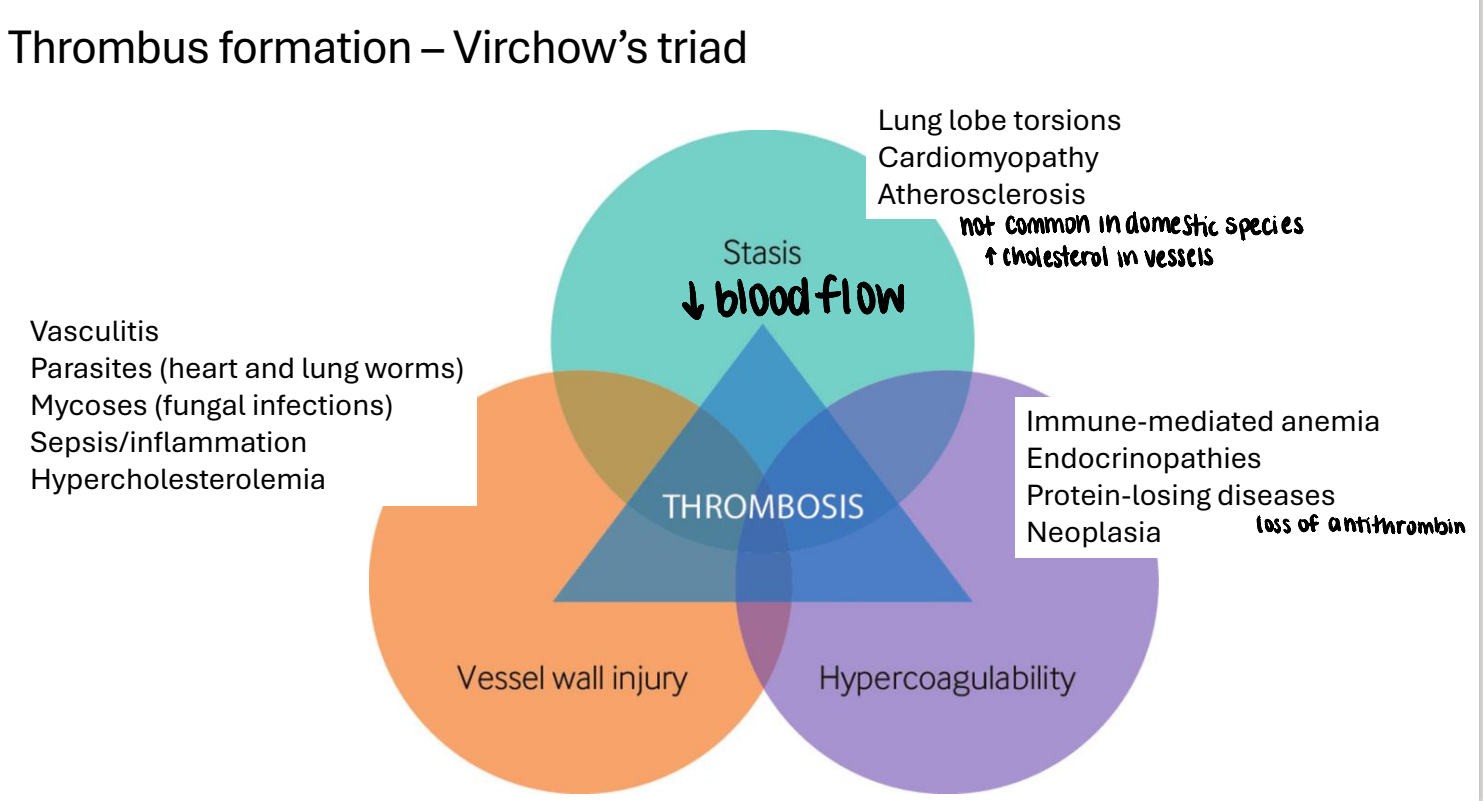
what are the 3 components of thrombus formation (Virchow’s triad)?
stasis
vessel wall injury
hyper-coagulability
procoagulant effects of endothelial cells
decrease expression of thrombomodulin, protein C, TFPI
antifibrinolytic effects of endothelial cells
secretion of plasminogen activator inhibitors → downregulation of t-PA
resolution of thrombi
small thrombi: removed via fibrinolysis
larger thrombi: removed by macrophages and repaired by fibrosis
very large (occlusive or mural) thrombi: organized into new vascular channels = recanalization
infarction
local area of peracute (very fast) ischemia that undergoes necrosis
most commonly secondary to thromobsis or thromboembolism
can also occur with external obstruction of blood supply
arterial obstruction (infarction)
loss of blood flow to downstream tissue → abrupt necrosis; immediate infarction
venous obstruction (infarction)
stagnation of blood flow and reduction/loss of venous return → progressive ischemia and eventual necrosis