OT503: Biomechanic Basics
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Force
A push or pull of matter
Tensile force
pulling
Compressive force
pushing
Moment
Turning effect of force (torque)
Action
Specific motion a muscle can generate at a joint
Another term for lever arm
Moment arm
Moment arm
Distance from the joint axis to the muscle
Mechanical advantage
leverage
The moment arm is perpendicular to _____
the line of pull of the muscle
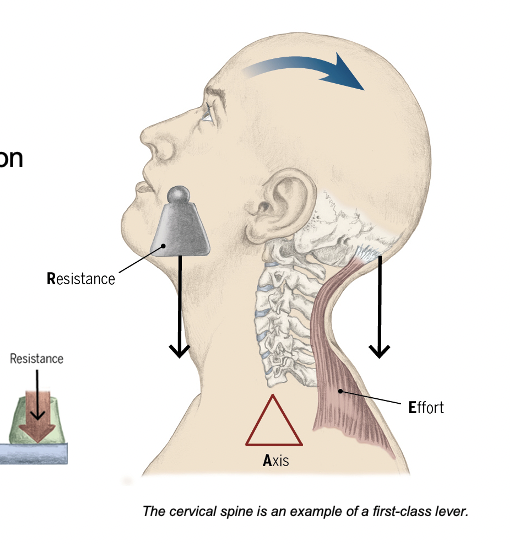
What is the order of the forces and axes of a first-class lever?
EAR
What is an example of a first-class lever on the human body?
Human neck
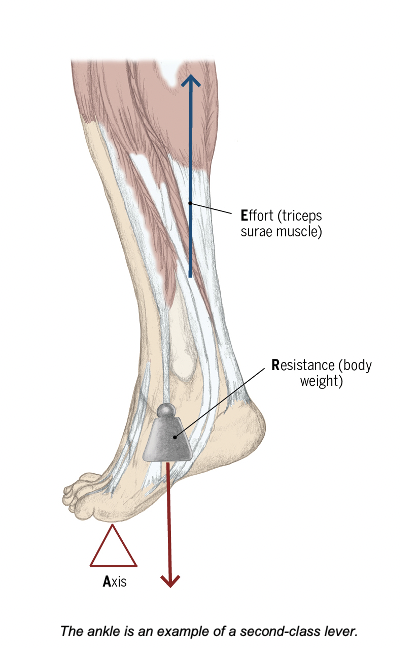
What is the order of the forces and axes of a second-class lever?
ARE
What is an example of a second-class lever in the human body?
The ankle
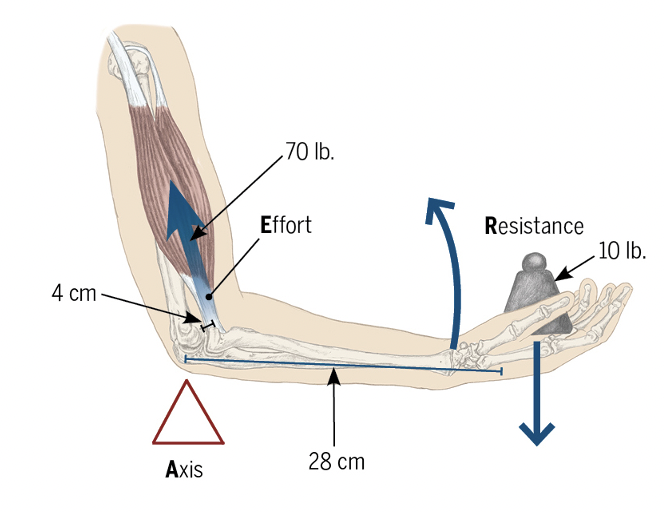
What is the order of the forces and axes of a third-class lever?
AER
What is an example of a third class lever in the human body?
Elbow
What is the most common lever in the human body?
Third-class lever
Joint reaction force
force generated within the joint in response to external forces acting upon it
Stress
Amount of applied force per area
Strain
Amount of material displacement under a specific amount of stress
Elasticity
The ability to stretch and return to the original shape
Elastic deformation
Ability to return to normal shape after strain
Yield point
The maximum amount of stress that can be sustained before tissue failure
Plastic deformation
Permanent deformation of tissue but retains continuity
What two things are bones mostly made from?
Collagen and calcium
Cortical/cancellous bone has greater mineral content?
Cortical
Cortical/cancellous bone makes up the shaft of long bones
Cortical
Cortical/cancellous bones have higher collagen content
Cancellous
Cortical/cancellous bones are found in the marrow cavity and at the end of long bones
Cancellous
What covers the ends of long bone along with the cancellous bone?
Articular cartilage
Articular cartilage is mostly ______
hyaline
What is the purpose of articular cartilage on the bone?
Absorbs forces between bones
True/False: Articular cartilage is one layer of CT on the ends of long bones
False; it’s multilayered
Osteoarthritis
Degeneration of cartilage within a joint
What do ligaments connect?
Bone to bone
What do tendons connect?
Muscle to bone
Ligaments/tendons contribute to joint stability
Ligaments
Ligaments/tendons help transfer forces
tendons
Joint capsule
Dense fibrous sleeve around the synovial joint
The joint capsule offers active/passive stability
passive
Aponeurosis
Fibrous insertion that connects adjacent muscles
The aponeurosis of the abdonimal muscles forms which structure?
Rectus sheath
What provides force for a fucntional movement?
Muscle
Myofibrils
Long cylindrical strands of contractile proteins
Sarcomere
Contractile units of a muscle
The thin filaments of a muscle are ____
actin
The thick filaments of a muscle are
myosin
Actin/myosin forms the central shaft of each sarcomere
Myosin
Motor Unit
A single motor neuron and the muscle fiber it innervates
The muscle is strongest in ______ position
midrange
True/false: The commands of a motor neuron are all-or- none
True
Fascia
Noncontractile tissues within the muscle
Flaccid muscle
Floppy results from loss of innervation to a muscle
Hypertonia
Muscle with increased tone
Muscle spindles
Elongated and encapsulated structures within muscle fibers that signal changes in muscle length and protect muscles
Which type of muscle fibers have a low force over a long period of time
Slow-twitch
Which muscles fibers allow for a powerful contraction
Fast-twitch
Type 1 fibers are _____
Slow-twitch
Type 2 are _____ fibers
Fast-twitch
_______ are located at the junction of muscle and tendon and are more sensitive than spindles
Golgi Tendon Organs
What does the GTO do?
Senses how much tension a muscle is exerting and causes the muscle to relax when necessary
The GTO is the opposite of the ______ ______
muscle spindle
Resistive force
resistance, usually from the weight of body or from carrying an object
Exerted force
The effort or internal force from muscles
The farther the muscle position and its generated force from the axis/joint, the smaller/larger the mechanical advantage and the faster/slower the speed of motion
Larger; slower
Adaptive shortening occurs when the muscles increase/decrease in length because of a/no force
decrease; no