Developmental Psyc Exam 1
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is development
Pattern of movement or change that begins at conception and continues through the life span
Includes growth, decline, dying
What is the average and maximum life span in US
79/122
What are Paul Baltes Characteristics of Development
Lifelong
Multidimensional
Multidirectional
Plastic
Constantly able to change
Contextual
All develop occurs within a context
Families, neighborhoods, schools, workplace
Multidisciplinary
Involves growth, maintenance, regulation of loss
Biological sociocultural, and individual factors working together
What are the periods of development
Prenatal period
Conception to birth
Infancy
Birth to 18-24 months
Early Childhood
3-5 years
Middle and late childhood
6-10/11 years
Adolescence
10-12 to 18-21 years
Early adulthood
20s-30s
Middle adulthood
40s-50s
Late adulthood
50s-70s to death
How can we conceptualize age?
Chronological age
Number of years since birth
Biological age
Age in terms of biological heath
Psychological age
Adaptive capacities compared with others of the same chronological age
Social age
Connections with others and the social roles that individuals adopt
What are the patterns of aging
Normal
Pathological - greater than average decline
Successful - later decline in health than average
theory
An interrelated, coherent set of ideas that helps to explain phenomena and make predictions
Hypothesis
Specific assertions and predictions that can be tested
Freud’s psychoanalytic theory
Describe development as primarily as unconscious and heavily influenced by emotions
Early experiences with parents shape development
Stress the importance of the unconscious
What is Erikson’s Theory?
Primary motivation for human behavior is social -> reflects a desire to affiliate with other people
What is Skinner’s Operant Conditioning
Consequences of a behavior produce changes in the probability of a behaviors occurrence
Rewards and punishments shape behavior
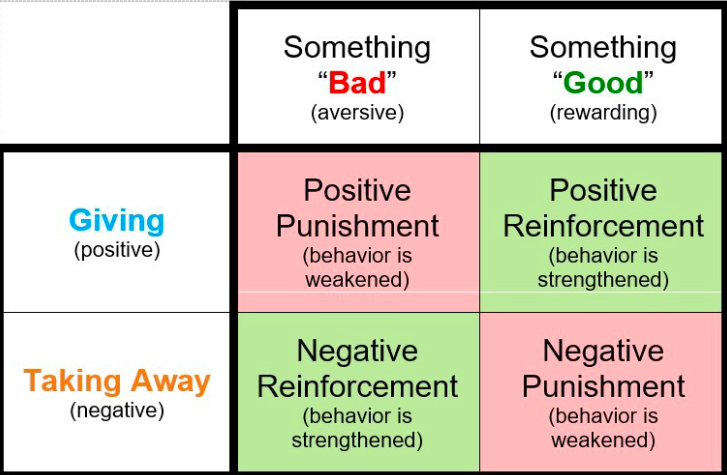
Ethological Theory
behavior is strongly influenced by biology, tied to evolution, and characterized by critical or sensitive periods
Attachment during first year of the life has a consequences throughout the life span
Secure attachment predicts optimal development
Ecological Theory
Emphasizes environmental factors in development
Development reflects the influence of several environmental systems
Microsystem
Where individual lives, friends, church group etc.
Mesosystem
Relationships between microsystems
Exosystemic
Experiences in other social settings
Mass media, online
Legal services
Friends of family
Neighbors
Macrosystem
General culture where individual lives
USA -> Texas -> Ft. Worth
Chronosystem
Time
What is the difference between correlational and experimental research design?
Correlation research
Describe the strength and direction of the relationship
Correlation coefficient: a number used to describe the degree of association between two variables (+1.00 to -1.00)
Correlation does NOT equal causation
Experimental research
Determine if one factor causes another
IV: factor manipulated
DV: factor that may change; measured by the researcher
Experiment group: Group who is being tested
Control group: group that is not manipulated
Random assignment: determines which group participants will be placed in
What is Natural Selection
Individuals best adapted to their environment are most likely to survive and reproduce
Their characteristics are passed onto the next generation
Over generations, organisms with the characteristics best suited for survival make up an increased percentage of the population
Emphasizes adaptation, reproduction, and survival of the fittest in shaping behavior
Chromosomes
Threadlike Structures made up of DNA
DNA
Complex molecule that contains genetic information
Genes
The basic unit of hereditary information
methylation
turns genes off
Mitosis vs Meiosis
Body cells reproduce through mitosis
The nucleus duplicate itself and divides (two identical cells)
The new cells each contain the same DNA as the original
Sperm and egg cells are formed through Meiosis
A cell of the testes or ovaries duplicates chromosomes but divides twice, forming four cells
Each has half the genetic material of the original

Sources of Variability
Genotype
All of a persons actual genetic materials
genes
Dominant Gene
Overrides expression of the recessive gene
Always going to express itself when present
Phenotype
Observable and measurable characteristics of an individual
Expression of genes ex: blue eyes
Recessive gene
Only exerts influence if both genes in the pair are recessive
What are down syndrome, Fragile X syndrome, and Turner syndrome?
Down syndrome
Extra chromosome causing intellectual disability
Fragile X
Abnormality in X chromosome, causes intellectual disability, short attention span
Turner Syndrome
Missing X chromosome in females, intellectual disability, sexual underdevelopment
Compare passive, evocative, and active/niche-picking genotype-environment correlations.
Passive genotype-environment correlations
Occur because biological parents provide the rearing environment
Evocative genotype-environment correlations
Occur because a child's genetically influenced characteristics elicit certain types of environments
Active (niche-picking) genotype-environment correlations
Occur when children seek out environments they find compatible and stimulating
What are the periods of prenatal development and their key characteristics?
Conception: when a single sperm cell unites with an ovum in a process called fertilization
Germinal period
First 2 weeks after conception
Creation of fertilized egg; cell division; attachment of zygote to uterine wall (implantation)
Embryonic period
2-3 weeks after conception
Cell differentiation massively increases; support systems for cell form
Organogenesis
Building of certain organs
Fetal period
Lasts about 7 months
Fetus is viable about 6 months after conception
Average birth weight is 8 lbs.
Neural Tube
The structure that forms from the ectoderm during embryonic development, which later develops into the brain and spinal cord.
Neural Migration
Neurons move to their destination in the brain, then a mature into a more complex structures
Neurogenisis
Massive proliferation of new neurons.
At the peak, roughly 200,000 neurons are created per minute
What are the stages of birth and their key characteristics?
First stage: uterine Contractions
15-20 min apart
Cervix stretches and opens to 10cm
For a fist child, average of 6-12 hours
Second Stage
Begins when baby's head moves through cervix until baby's body emerges
45 mins - 1 hour
Contractions almost every minute
Third Stage: Afterbirth
Placenta, umbilical cord, and other membranes are detached and expelled
A few Minutes
Cephalocaudal pattern of growth
Growth sequence that gradually works from top to bottom of the body
Typically, sensory and motor development proceeds according to this pattern
Proximodistal Pattern of growth
Growth sequence in which growth starts at the center of the body and moves toward the extremities
Menarche
a girl’s first menstruation occurring late in the pubertal cycle
Puberty
Brain neuroendocrine process that stimulates rapid physical changes, primarily in adolescence
Gonadotropins
Hormones that stimulate the testes or ovaries
Promotes changes in sperm production, menstruation, release of eggs
Testosterone
a hormone associated in boys with the development of genitals, increased height, and deepening of the voice
Estradiol
a type of the hormone estrogen associated in girls with breast, uterine, and skeletal development
Climacteric
Midlife transition in which fertility declines
Menopause
End of menstrual periods, usually late 40s-50s
Lobes of the brain
frontal
occipital - vision
temporal - hearing, language
parietal - attention, motor control, spatial location
What are the parts of a neuron
1. Cell body + Nucleus
2. Axon
3. Dendrite
4. Myeline Sheath
5. Node of Ranvier
6. Axon Terminal
7. Synapse
Myelination
The process of encasing axons with a myelin sheath, improving the speed and efficiency of information processing
Lateralization
Specialization of function in one hemisphere
Acetylcholine
memory loss (Alzheimer's disease)
Dopamine
Decreased motor control (Parkinson's disease)
How much REM sleep do infants get
about half of their sleep is REM, compared to 1/5 for adults
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
SIDS occurs when infants stop breathing, usually during the night, and die without apparent cause
Infants should be placed to sleep on their backs
Evolutionary theory of aging
Natural Selection is linked with reproductive fitness
Hormonal Stress theory of aging
body has lower resistance to stress and disease
What are the leading causes of death for each developmental period?
Children: Malnutrition
Adolescent: Health Compromising Behaviors
Young adults: Chronic Health Problems
Adults: Cancer
Compare adolescent and emerging adulthood health.
Adolescent's health
Adolescents is a critical juncture for adopting behaviors that affect health
Social contexts influence adolescent health
Families, peers, schools, neighbors, and culture
Making adolescents have a limited capacity to resist peer pressure and risk taking
Emerging and Young adults health
Emerging adults have more than twice the mortality rates of adolescents
Many know how to be healthy but don’t apply the information to their own behavior
Dementia
Neurological disorder in which the primary symptoms involve deterioration of mental function
Alzheimer Disease
A progressive, irreversible brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and physical function
What is Parkinson disease?
Chronic, progressive disease characterized by muscle tremors, slowed movements, and partial facial paralysis
Triggered by degeneration of dopamine producing neurons in the brain
Anorexia Nervosa
Eating disorder that involves a relentless pursuit of thinness through starvation
Weight loss due to food intake restriction
Bulimia Nervosa
An eating disorder that involves a consistent binge-and-purge eating
Define binge drinking.
Emerging adults are MOST likely to engage in Binge-drinking
Binge drinking is 5+ drinks in a row
rooting reflex
When an infants cheek is stroked or the side of mouth is touched, the infant turns its head and tries to find something to suck
Sucking reflex
Occurs when infants suck an object placed in their mouth
Enables infant to get nourishment before it associates a nipple with food
Moro Reflex
A startle response to sudden intense noise or movement
Newborns arch their back, through back their head, fling out limbs then close them
Coughing, sneezing, blinking, shivering, yawning
Grasping reflex
Infants tightly grasp an object placed in their palm
What are the motor develop milestones?
1. Prone, lift head
2. Prone, chest up, use arms for support
3. Roll over
4. Support some weight with legs
5. Sit without support
6. Stand with support
7. Pull self to stand
8. Walk using furniture for support
9. Stand alone easily
Walk alone easily
How does motor development change over the lifespan?
Motor development improves until around age 30, than it begins to decrease
Fine motor skills
Finely tuned movements, such as any task requiring finger dexterity
Infants have hardly any control over fine motor skills at birth
Gross Motor Skills
Those that involved large activities, such as ones arms or walking
Gross motor skills development requires postural control
Dynamic process linked with
Sensory information in skin, joints, and muscles
Vestibular organs in the inner ears that regulate balance and equilibrium
Vision and hearing
Sensation
A reaction that occurs when information interacts with sensory receptors
Presbyopia
Difficulty viewing close objects, and an increased blind spot
Cataracts
A thickening of the lens of the eye
Causes vision to become cloudy, opaque, and distorted
Results in partial loss of vision by 70 for 30% of people
Macular Degeneration
Causes deterioration of the macular of the retina, which corresponds to the focal center of the visual field
Normal peripheral vision, unable to see right in front of them
Glaucoma
Damage to the optic nerve due to pressure created by fluid buildup in the eye
When do infants/fetuses develop smell and taste?
Smell
Newborns can differentiate odors (ex: breast pads)
Taste
Sensitivity to taste is present even before birth
Intermodal Perception
The ability to integrate information about 2 or more sensory modalities such as vision or hearing
Palmer Grasp
Grasp with whole hand
Pincer Grasp
Grasp small objects with finger and thumb
perception
The interpretation of what is sensed
Accommodation of the eye
The eyes ability to focus and maintain an image on the retina
Declines most sharply at 40-59 years of age
Outcomes of Breastfeeding (for the child)
Lower likely-hood of SIDS
No evidence that it protects against allergies
osteoporosis
Extensive loss of bone tissue