B3 Enymes and digestion
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
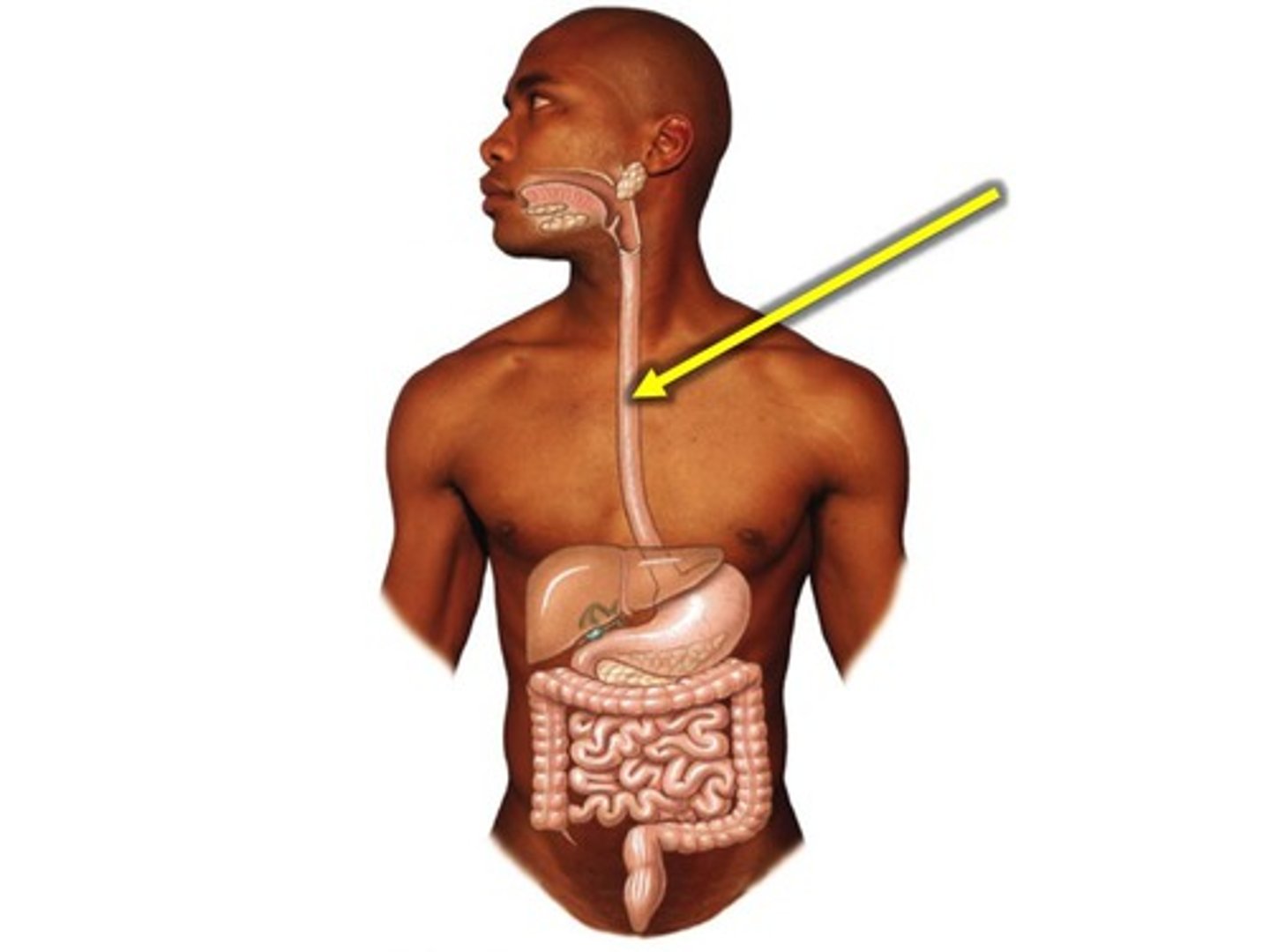
Oesophagus
Tube connecting the mouth to the stomach
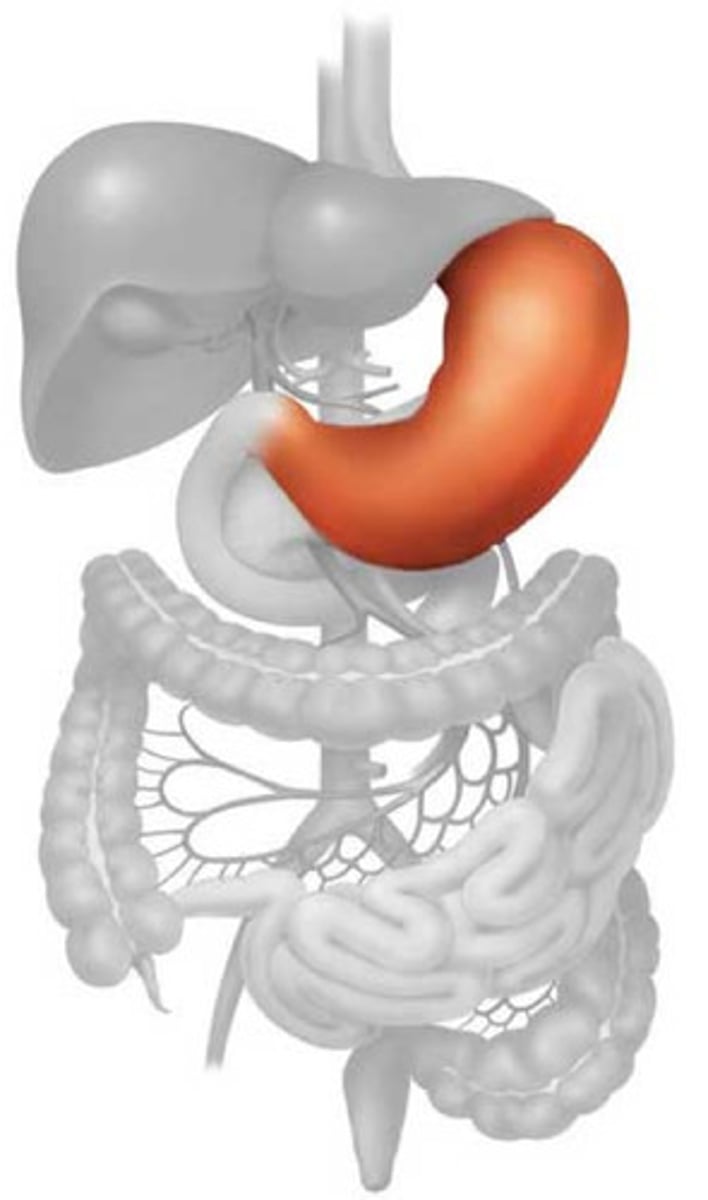
Stomach
A muscular and elastic sac that serves mainly to store food, break it up mechanically, and begin chemical digestion of proteins and fat.
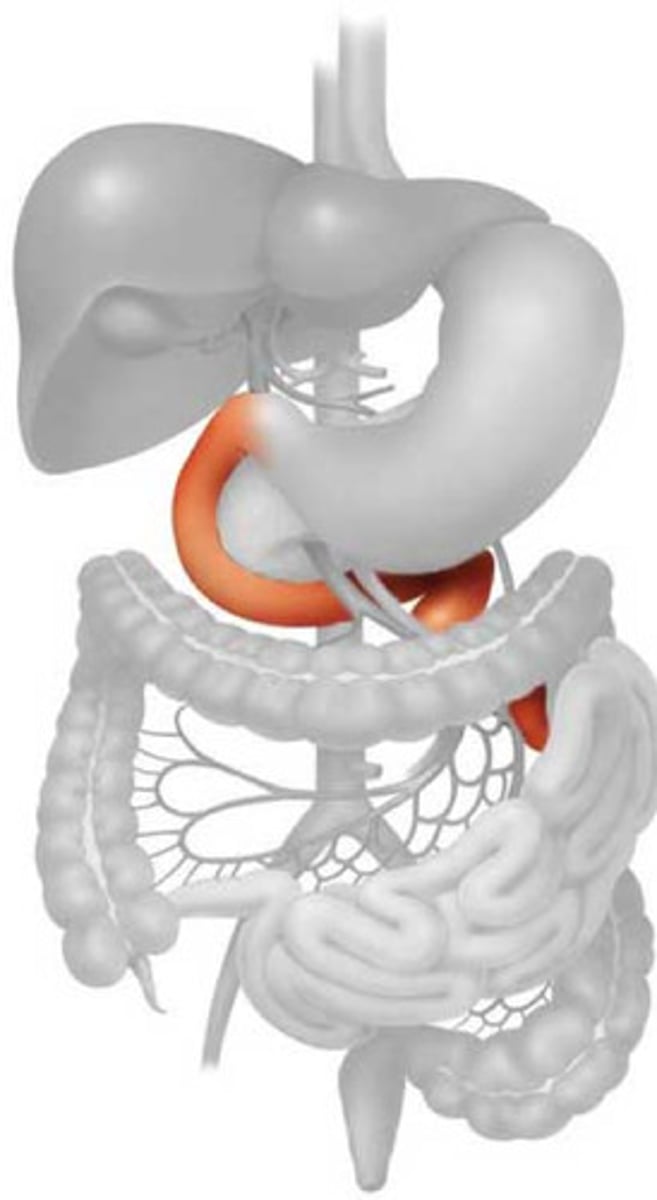
Duodenum
First section of the small intestine, where bile is added
Pancreas
Regulates the level of sugar in the blood and makes digestive enzymes
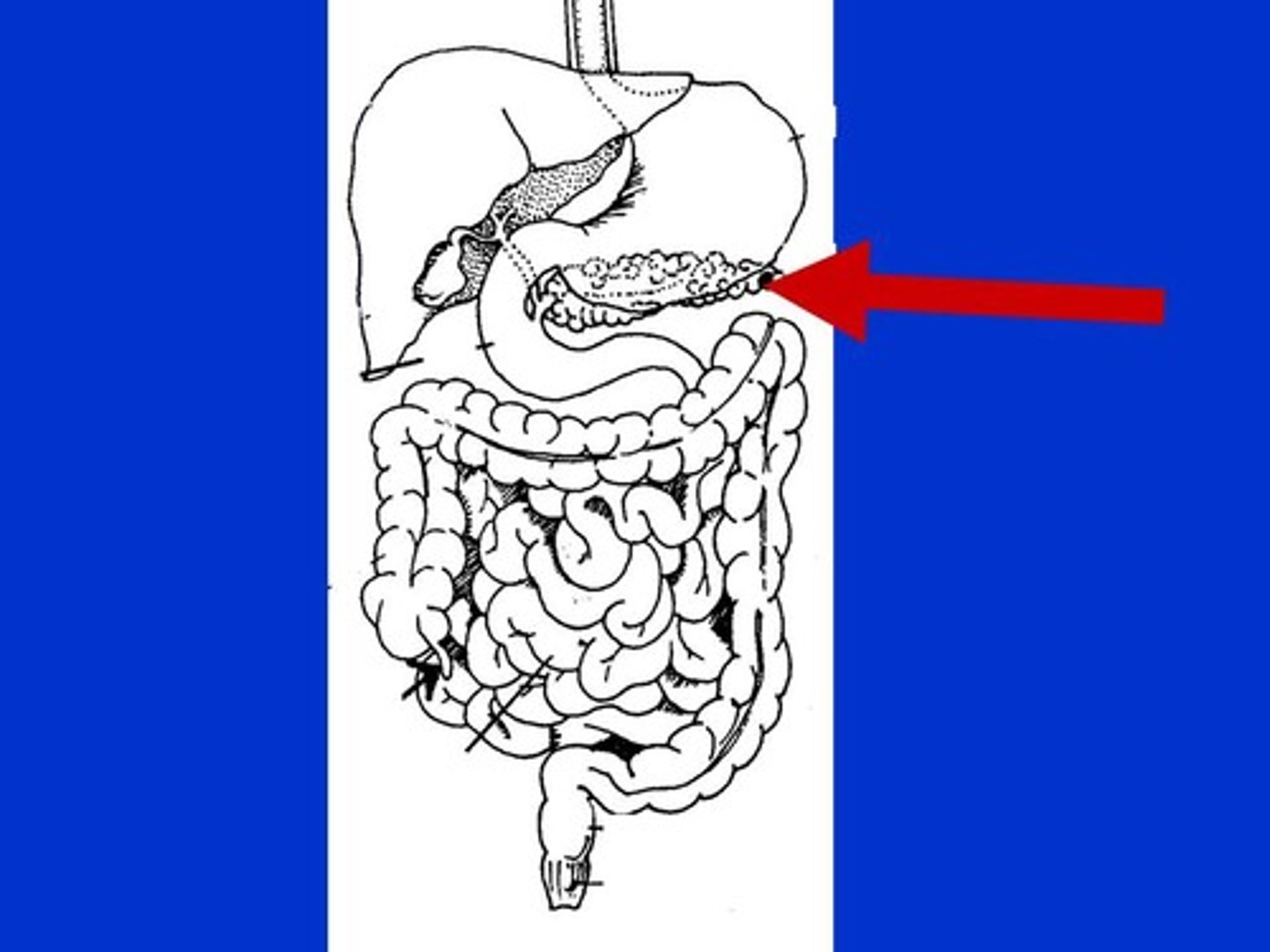
Liver
Produces bile
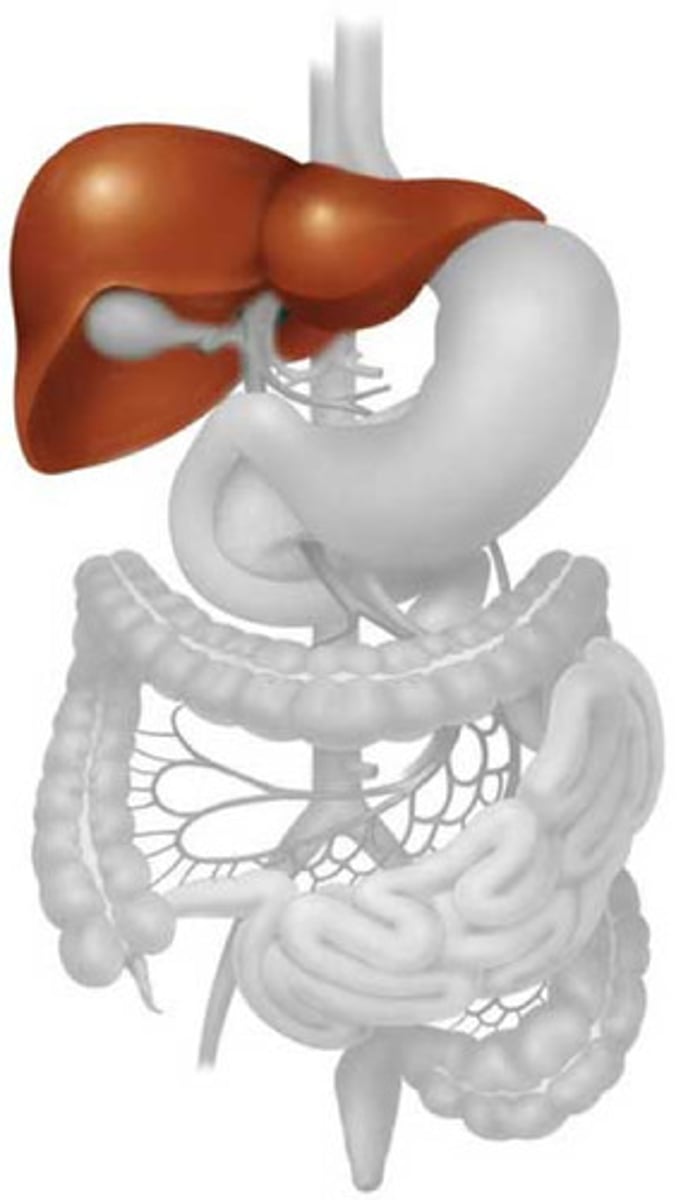
Gall bladder
Organ that stores bile
Bile
A substance produced by the liver that breaks up fat particles.

Small intestine
The part of the digestive system in which most chemical digestion takes place.
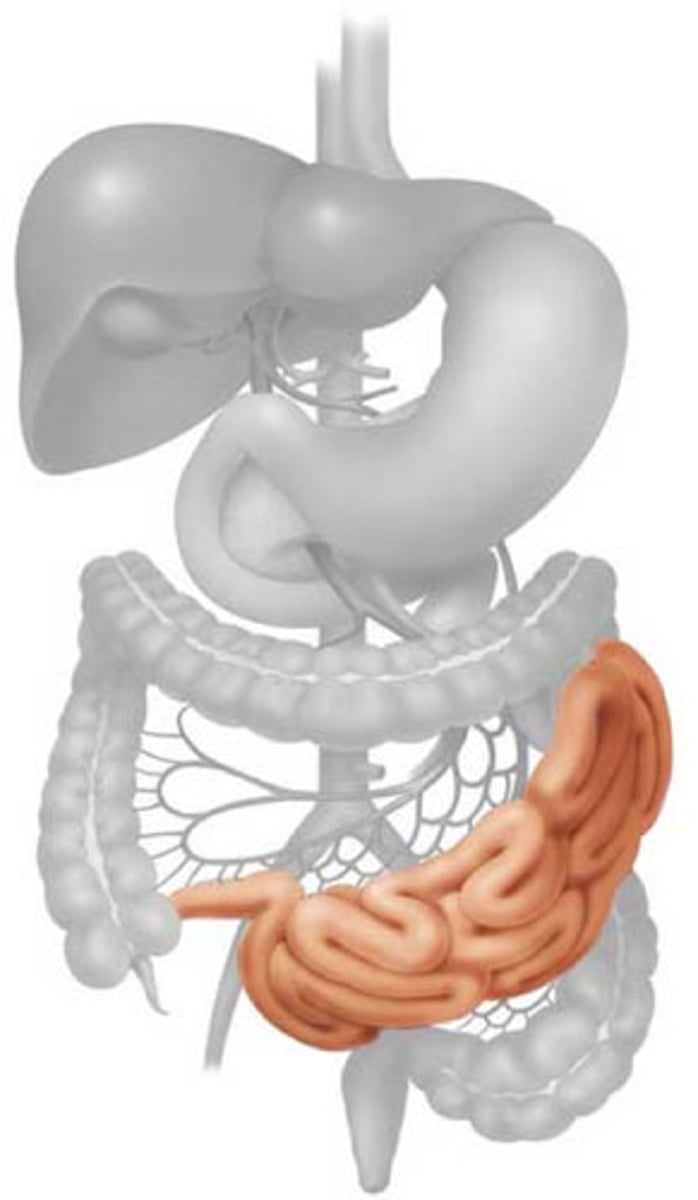
Large intestine
Absorbs water and forms feces
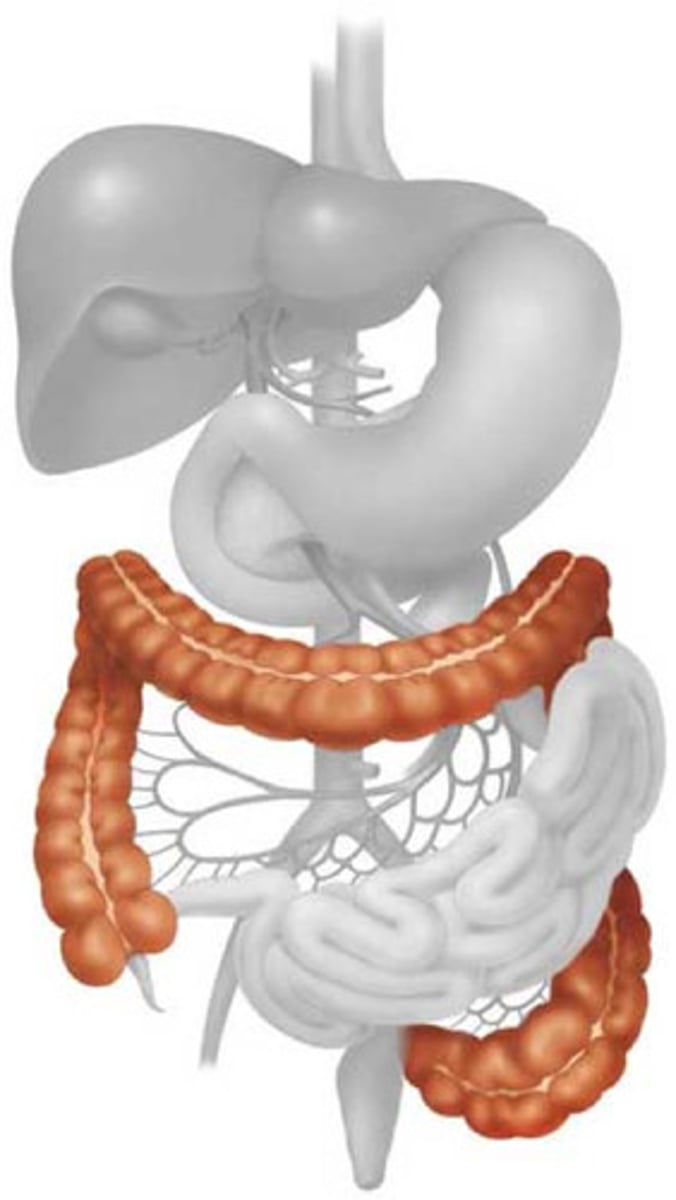
Rectum
A short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated
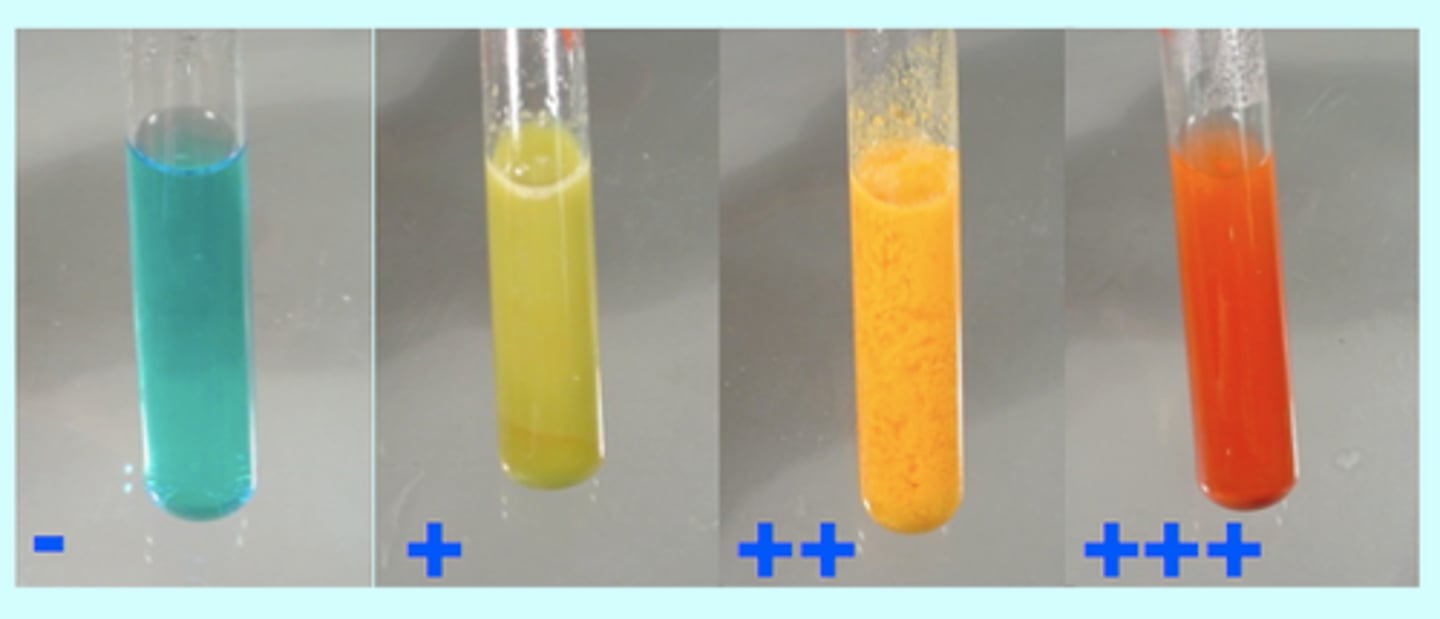
Iodine
Used to test for starch turns from brown to blue-black
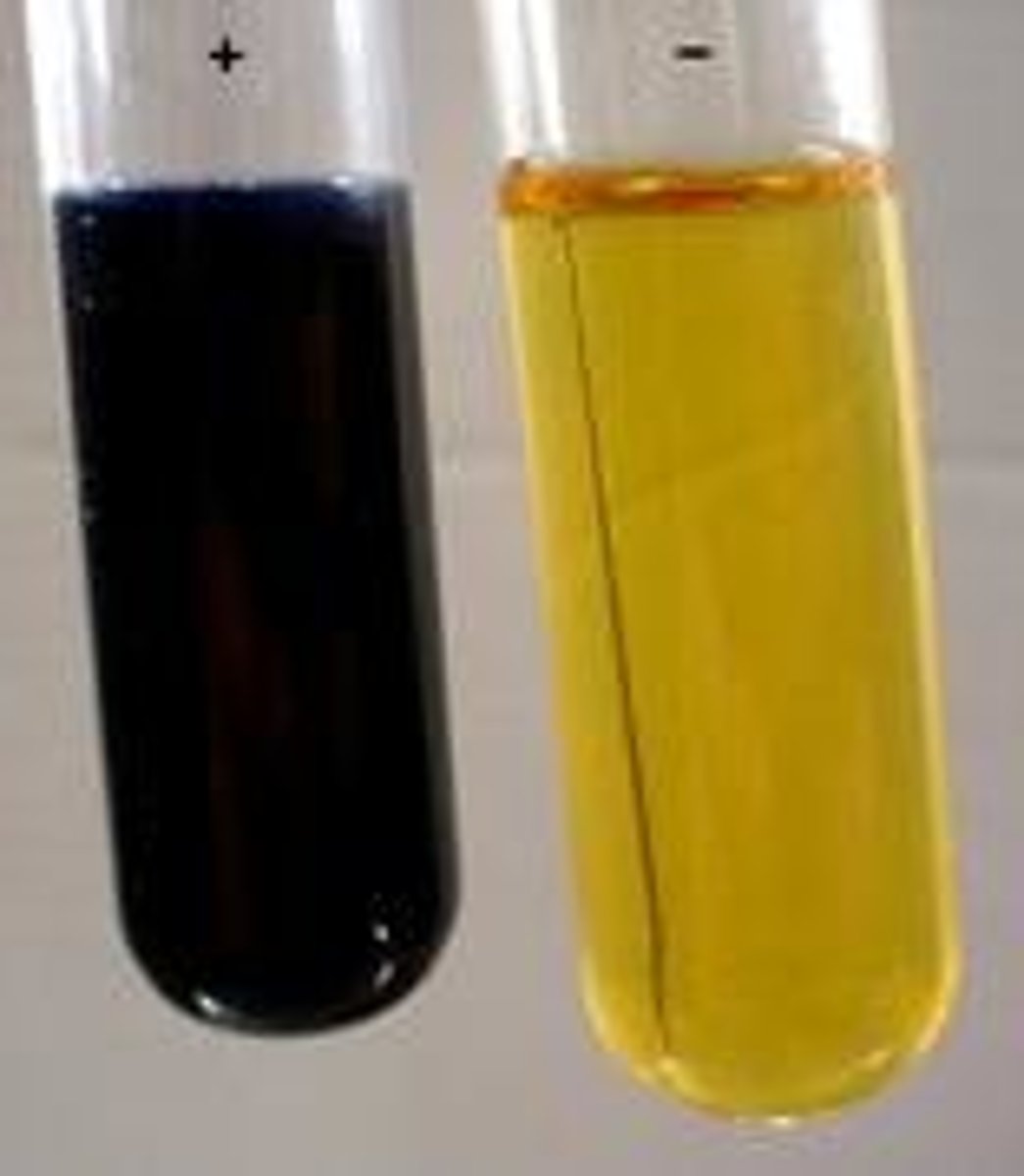

Benedicts solution
Used to test for Sugars - needs to beheated and turns brick red in colour
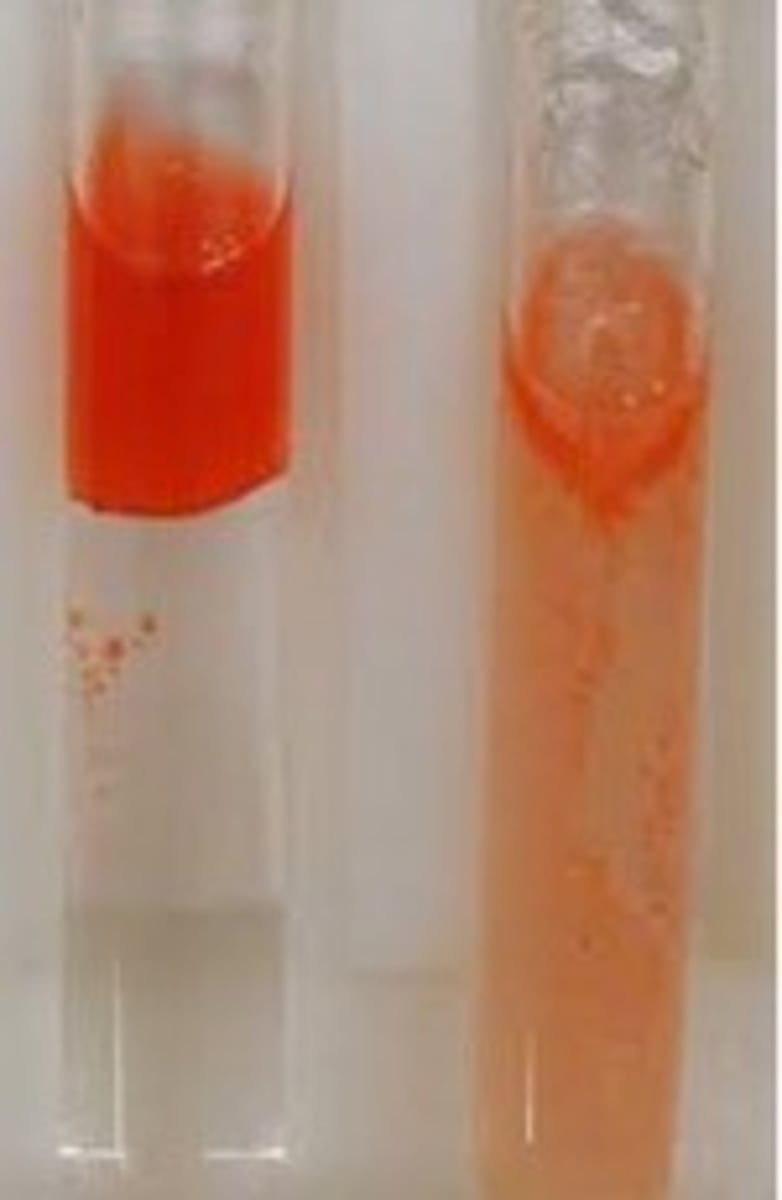
Sudan iii
Test for lipids - forms a red ring
Buiret solution
Test for proteins turns from blue to purple

Carbohydrate are
Made of sugars
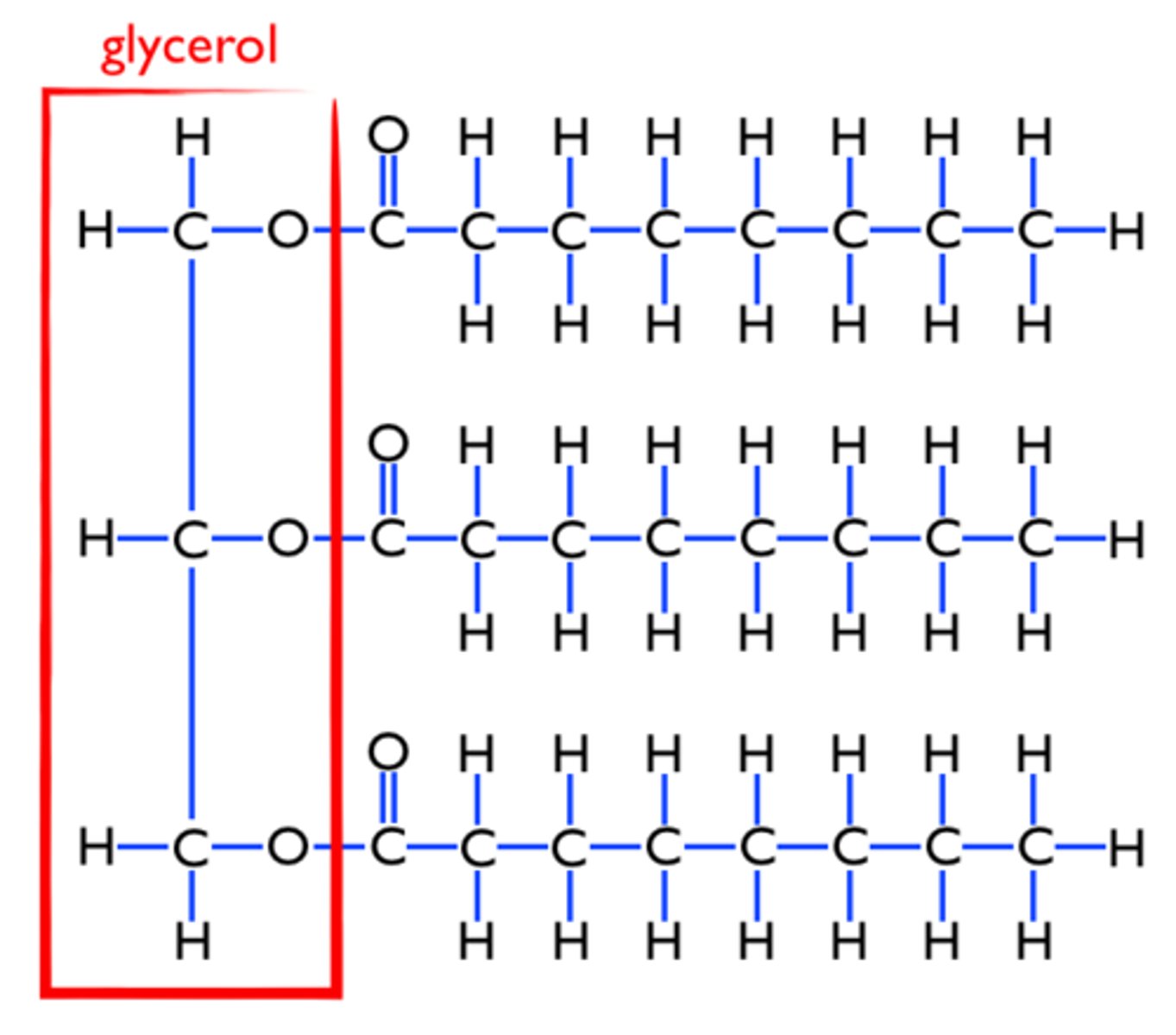
Lipids are
Made of glycerol and fatty acids
Proteins are
Made of amino acids
Enzymes are
Biological catalysts and protein molecules
Catalyst
Substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
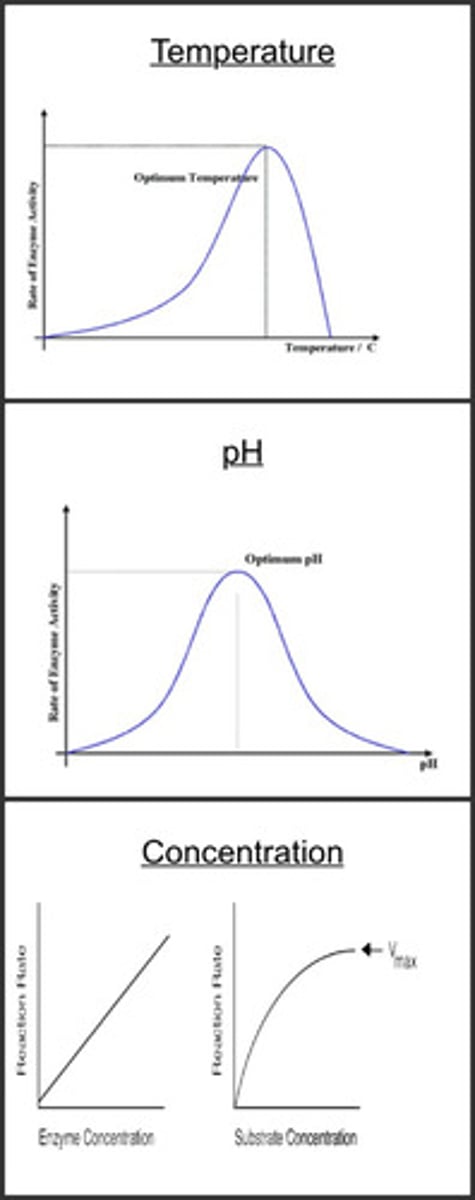
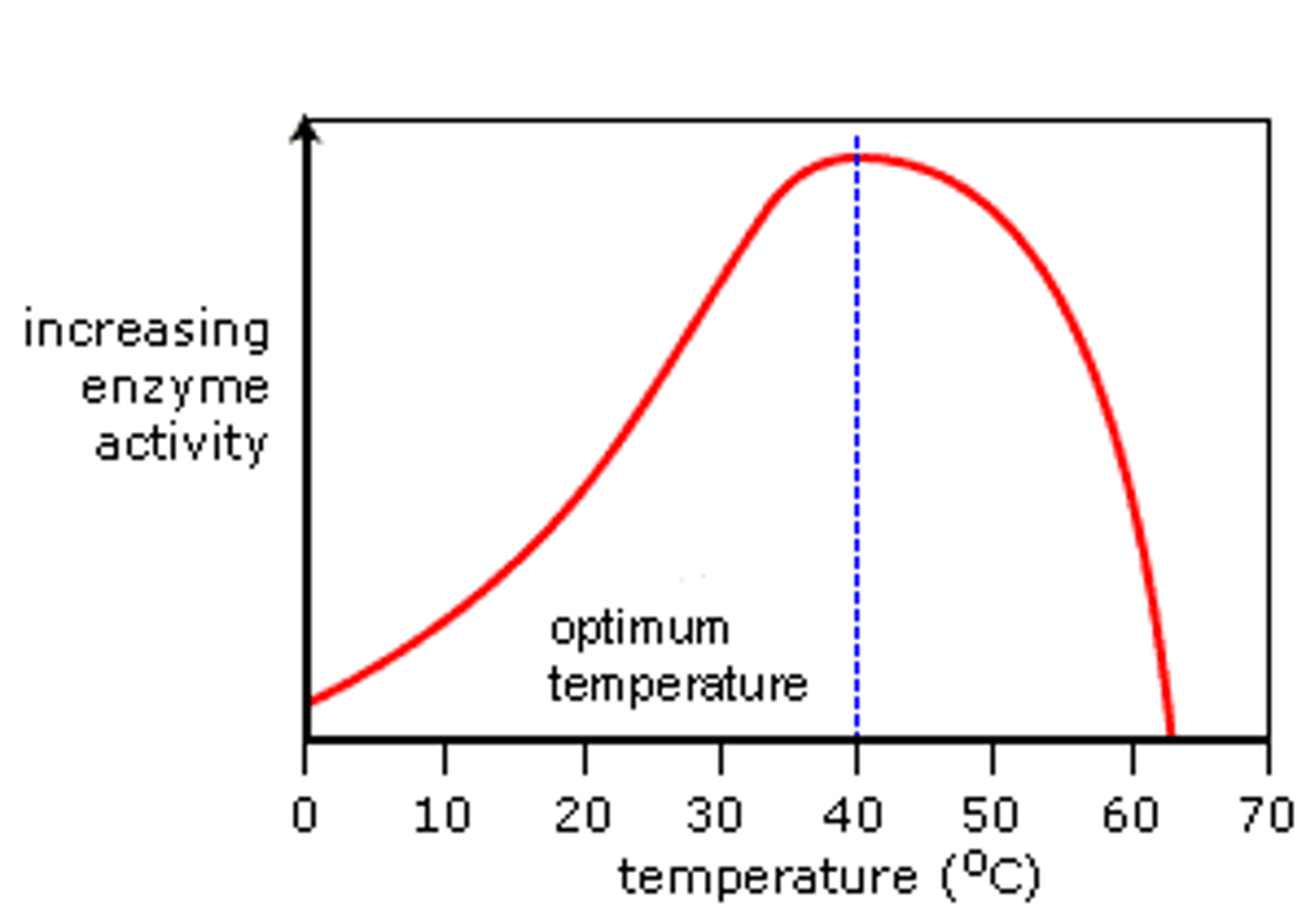
Factors that effect enzyme activity
PH, concentration, temperature
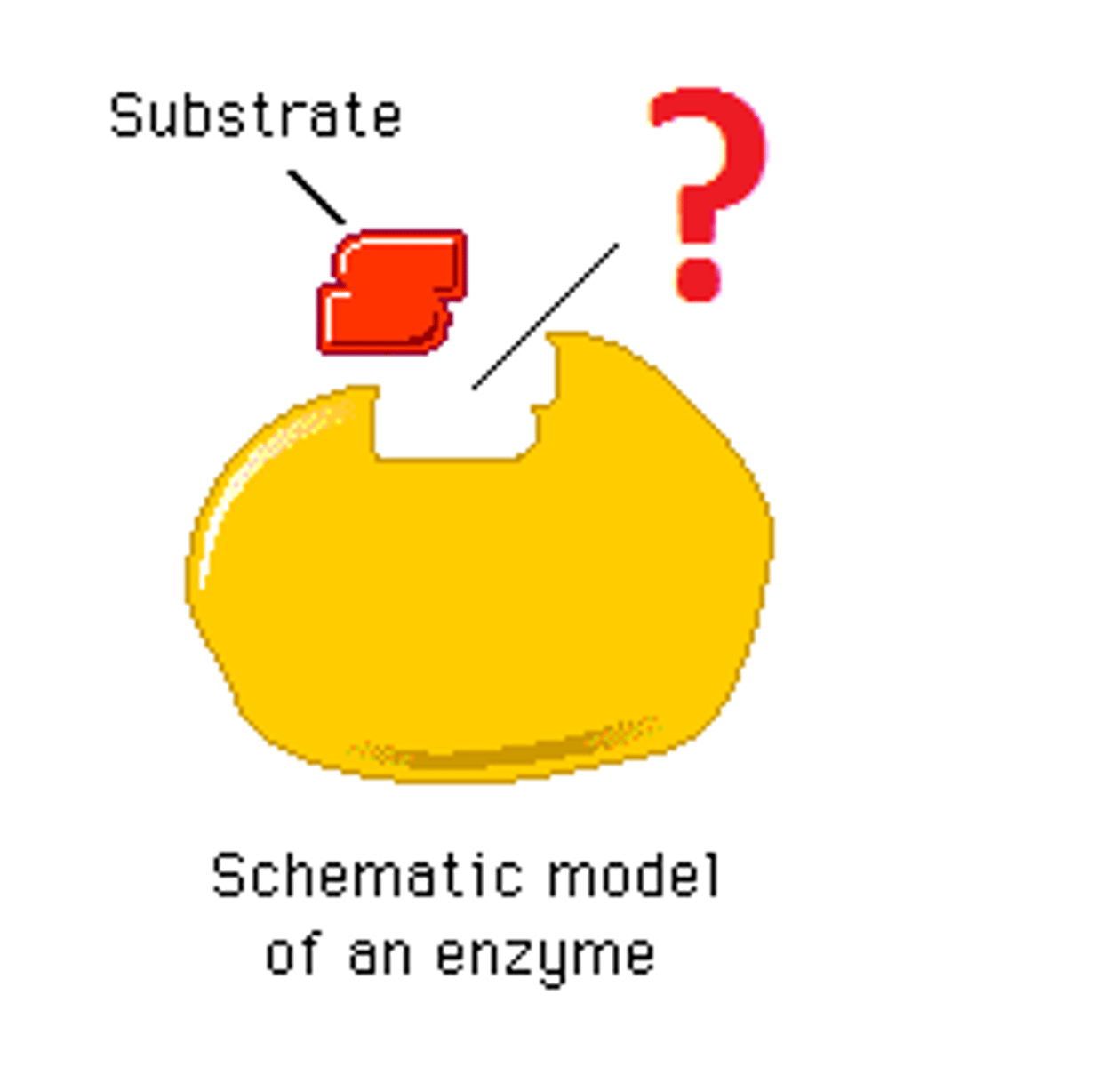
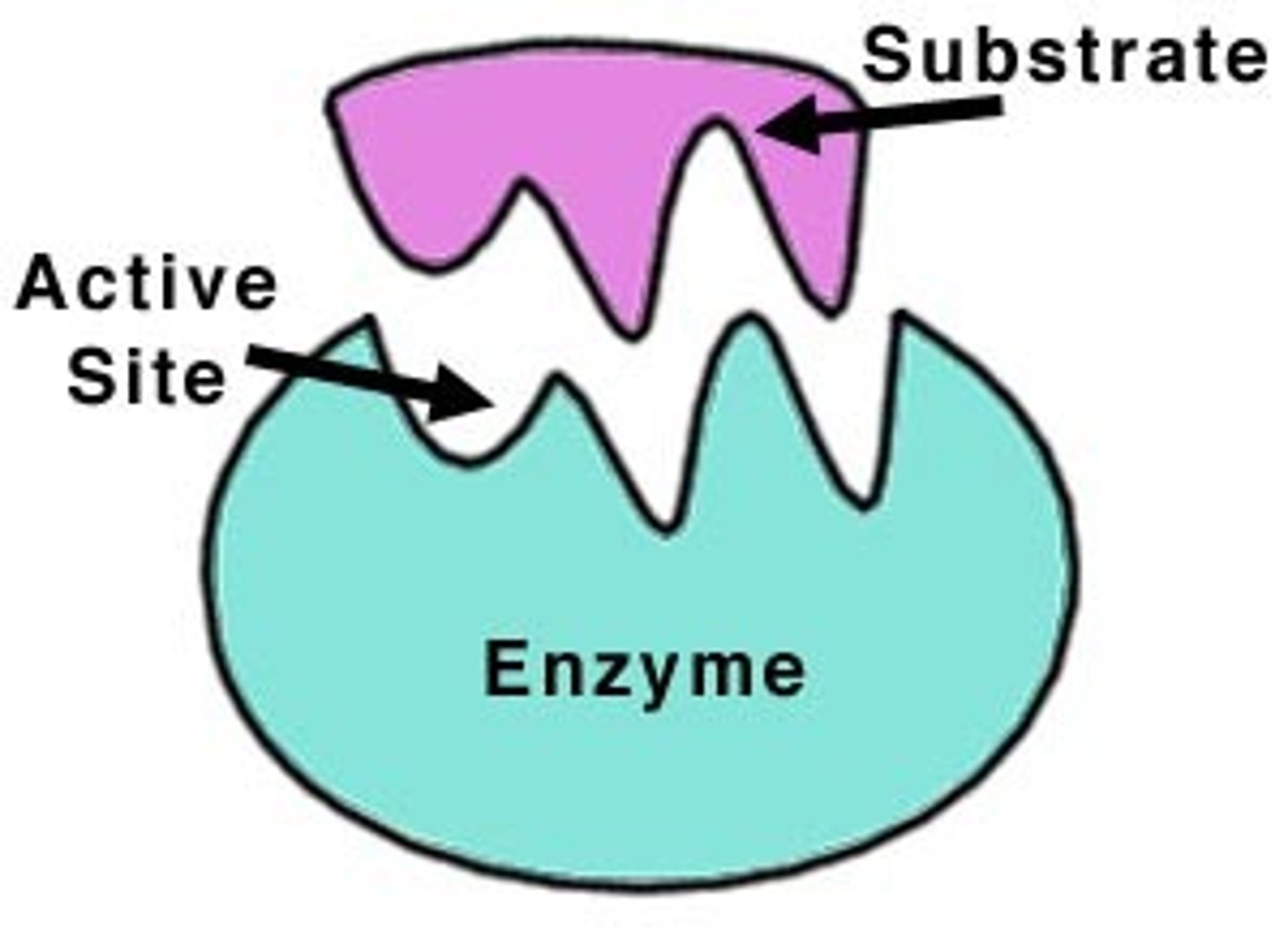
Active site
The part of an enzyme where the chemical reaction occurs.
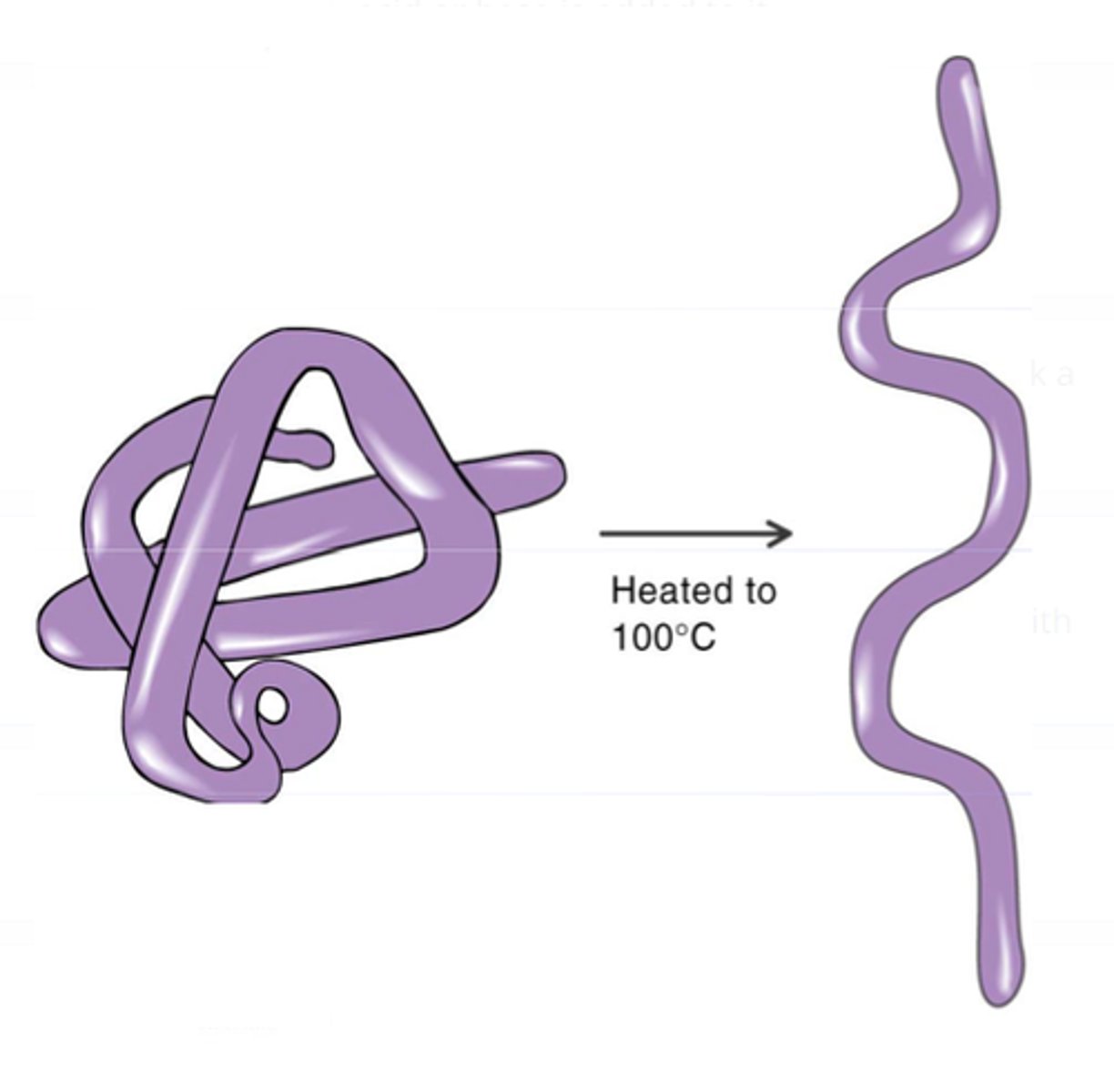
Denatured
Change the shape of an enzyme so that it can no longer speed up a reaction.
Substrate
A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme
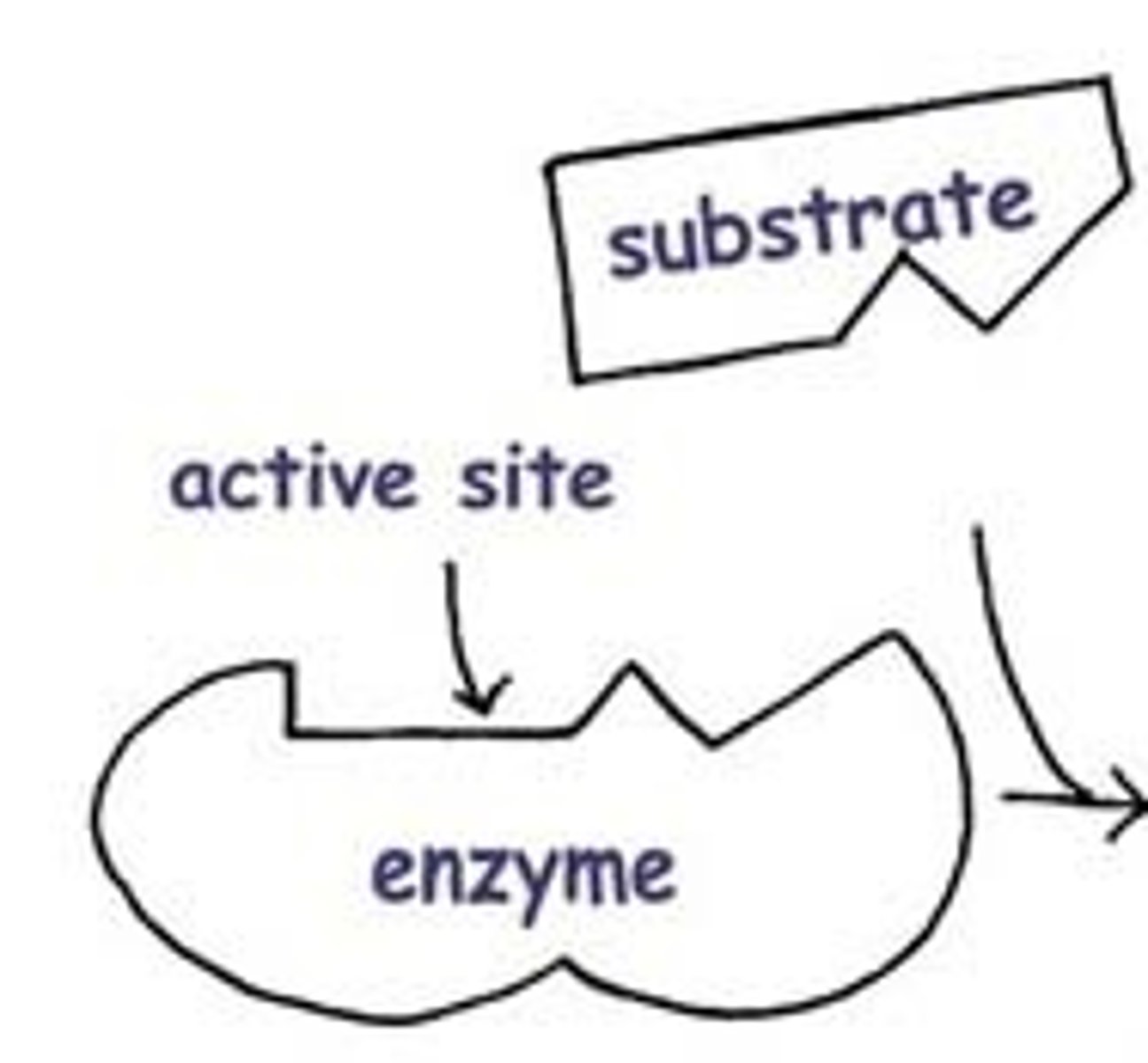
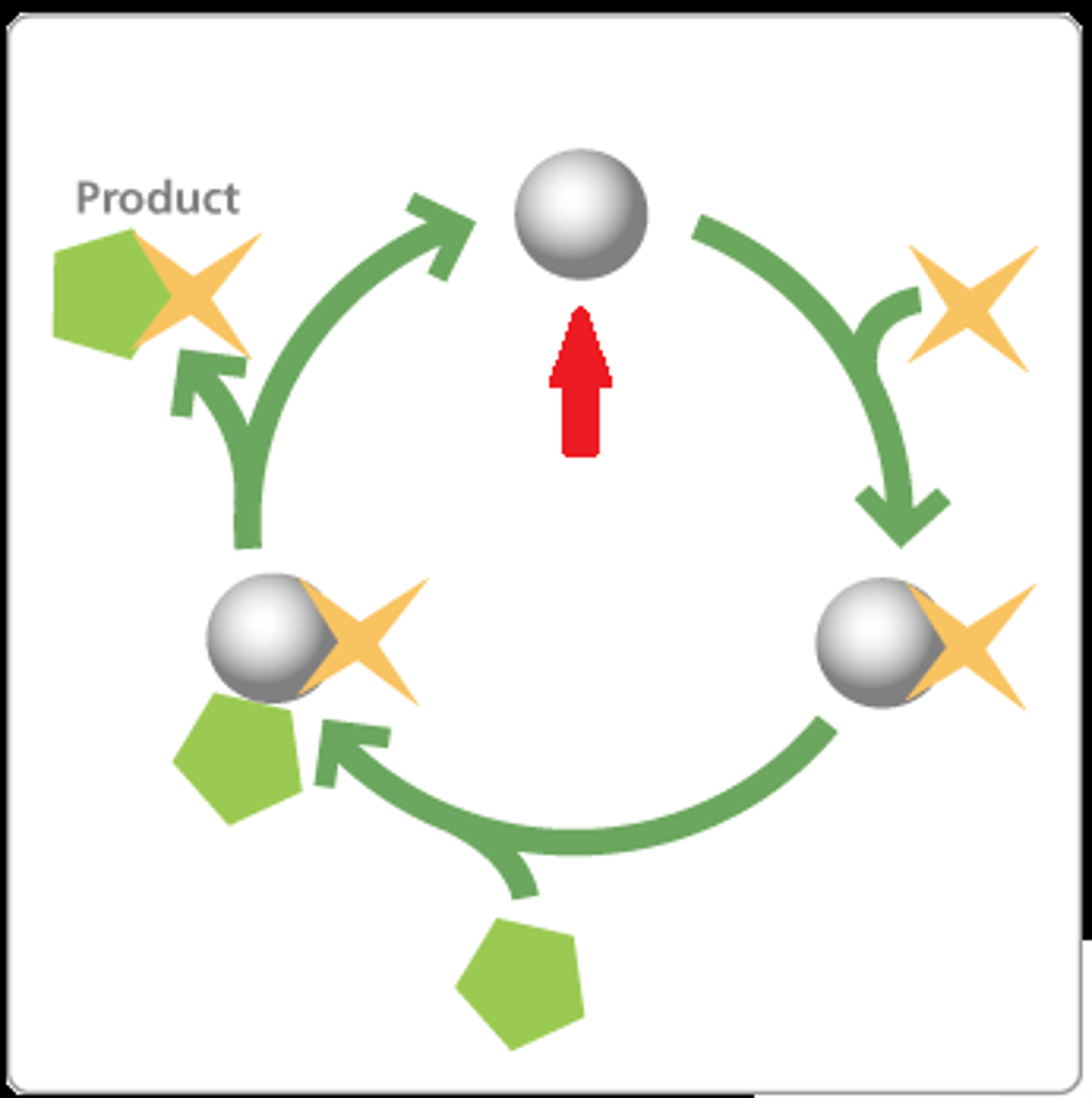
Lock and key model
Enzymes are specific. The only work on the substrate that they "fit."
Enzyme-substrate complex
When the substrate is attached to the enzymes

Optimum
The best conditions where enzymes work the best
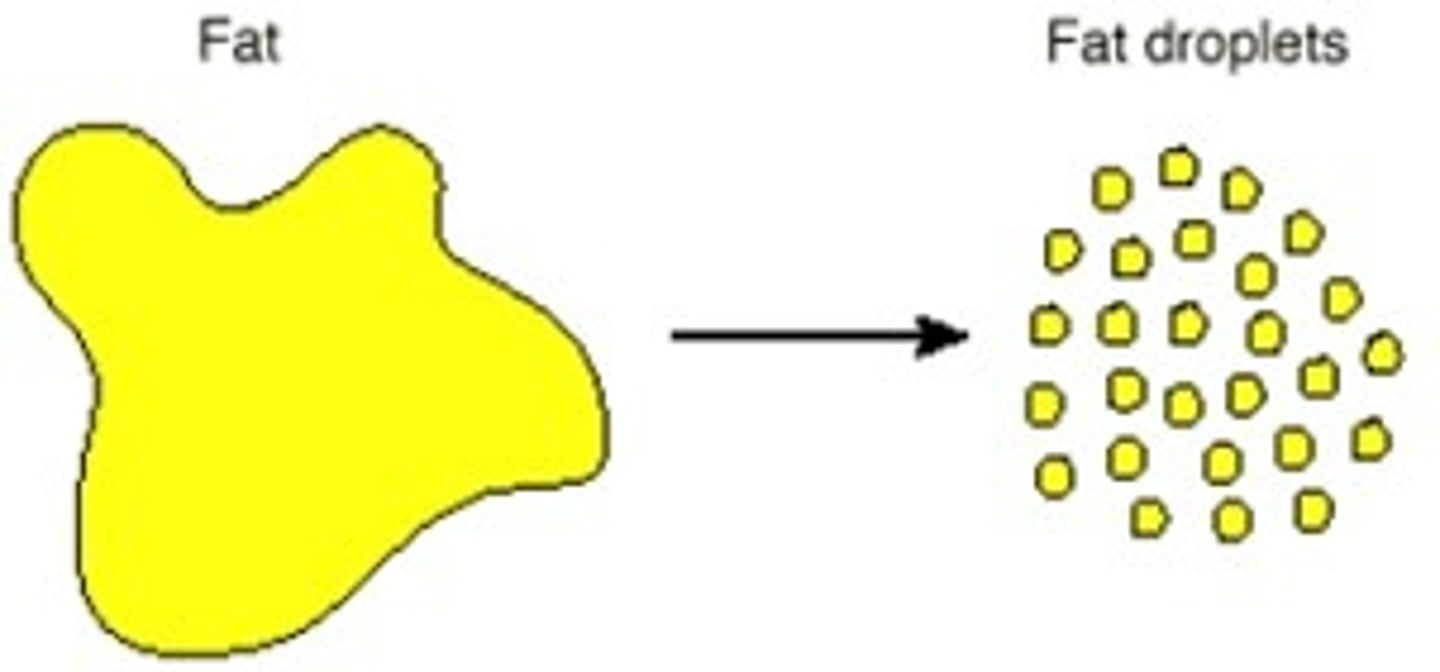
Emulsify fat
The function of bile, separating fats to give increased surface area
Saliva
Digestive juice produced by glands in your mouth

Hydrochloric acid
Substance produced by the stomach; used to create right stomach conditions for enzymes and kill bacteria
Amylase
Enzyme in saliva that breaks the chemical bonds in starches
Protease
Enzyme that digests protein
Lipase
Enzyme that breaks down fat

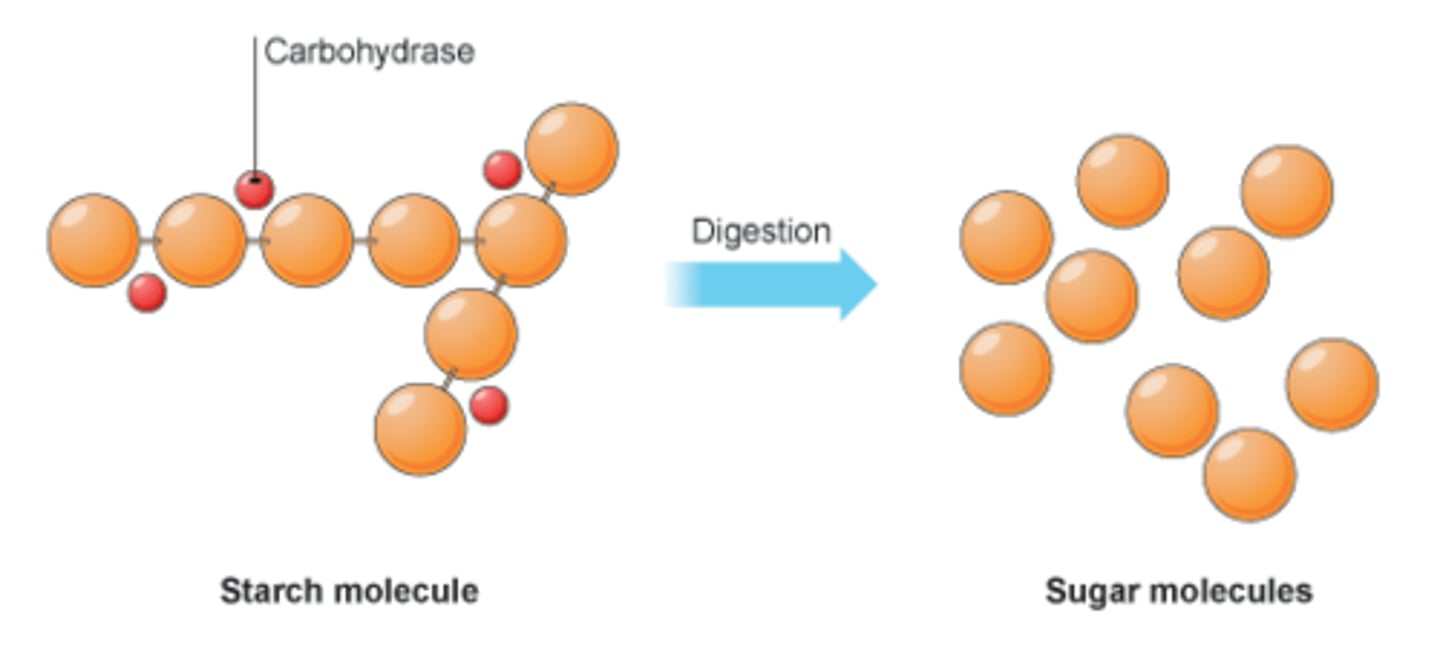
Carbohydrase
Enzyme that breaks down starches into sugars