The Respiratory System (Slides 24-45)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is the cartilage and adventitia?
C-shaped hyaline cartilages closed
by fibroelastic membrane
posteriorly (includes the trachealis
muscle)
What is the cartilage?
1. Some cartilages anastomose
2. All have perichondrium
3. Some may be replaced by bone tissue
with age
What is the adventitia?
1. Dense CT
2. Surrounds cartilages and trachealis
muscle
3. Binds trachea to adjacent structures
4. Larger blood and lymphatic vessels,
and nerves
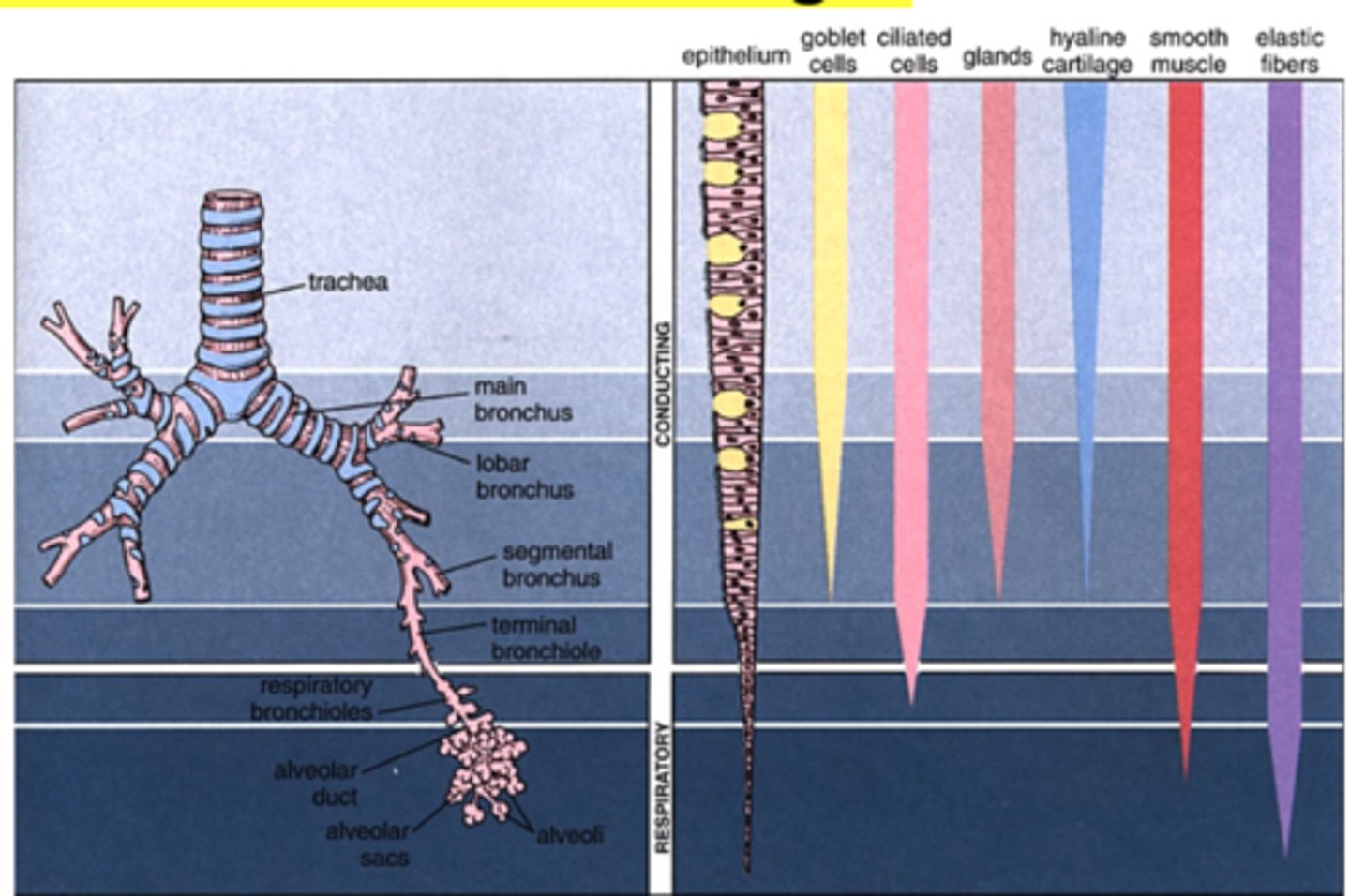
What is the branching pattern of the bronchial tree?
Bronchi branch off repeatedly
Resulting bronchi have smaller diameter
Bronchioles diameter is less than 1 mm
What are the bronchioles?
Each enters a
pulmonary lobule.
Each delineated with
CT, pyramidal shape,
and the apex aimed
at the hilum
What is the tertiary bronchi?
Together with its
branches form a
bronchopulmonary
segment, each w/
CT capsule and
blood supply
What is the secondary bronchi?
each supply a pulmonary lobe
What is the primary bronchi?
each supply a lung
What are the five layers of the bronchi?
1. Mucosa
2. Muscularis (smooth muscle)
3. Submucosa (loose CT)
4. Cartilage layer
5. Adventitia
What does the mucosa contain?
1. Respiratory epithelium
2. Bronchioles
3. Epithelium
The main, secondary, and tertiary bronchi have what?
respiratory epithelium
What is the respiratory epithelium?
1. Cellular height decreases gradually
2. Initial thick basement membrane becomes very
discrete in secondary bronchi
3. Lamina propria similar to trachea
What is the epithelium of the mucosa?
gradual changes from larger
bronchioles to terminal bronchioles
What does the epithelium contain?
1. Pseudostratified (with fewer goblet cells)
2. Ciliated simple columnar (much less goblet cells)
3. Ciliated simple cuboidal (no goblet cells)
The mucosa becomes _______ as bronchial diameter ___________.
thinner, decreases
What does the muscularis ( Smooth Muscle) contain?
1. bronchi
2. bronchioles
3. Terminal bronchioles
What is the bronchi of the muscularis
prominent spiral bands of smooth muscle crisscrossing with elastic fibers of deeper lamina
propria
What is the bronchiles of the muscularis?
prominent circular band of smooth muscle
What are the terminal bronchioles of the muscularis?
thinner, incomplete circular layer of smooth muscle
What is the submucosa ( Loose CT)?
1. Glands and adipose tissue in larger bronchi
2. Bronchioles do not have glands
What is the cartilage layer?
1. Main bronchi have circular rings of cartilage
2. Intrapulmonary bronchi have plates instead of rings and they become smaller in smaller bronchi
3. No cartilage at all starting in bronchioles (replaced by a complete smooth muscle layer)
What is the adventitia of the bronchi?
1. Dense connective tissue
2. Continuous with adjacent structure
What are the main changes of the main (extrapulmonary) bronchi?
Same structure as trachea except
cartilage form a circular ring
What are the cartilage changes in the intrapulmonary bronchi?
1. Cartilage rings replaced by cartilage
plates
2. Plates become gradually smaller and less
numerous
3. Bronchioles (≤ 1 mm), no cartilage plates
How is the muscular layer of the bronchi added?
1. Smooth muscle forming a
complete circular layer
2. As bronchi branch off and
become smaller
3. Smooth muscle becomes an
increasingly conspicuous
layer
4. Amount of cartilage
decreases (disappear
completely in bronchioles)
5. Smaller bronchi have
discontinuous muscle layer
Cartilage plates and smooth muscle in intrapulmonary bronchi
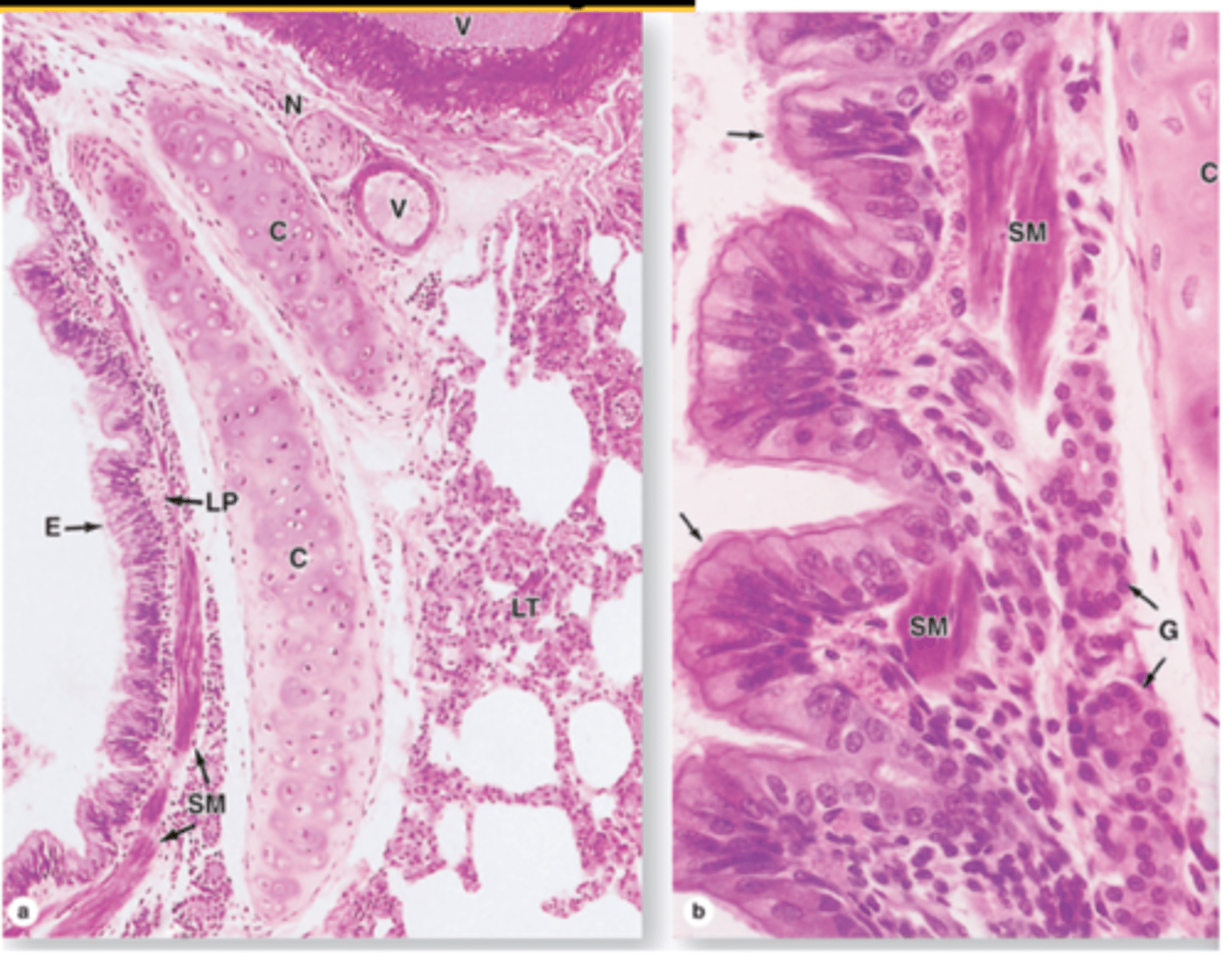
What do the bronchioles contain?
1. No mucosal glands nor cartilage
2. Thicker smooth muscle layer
3. Mucociliary escalator
4. Epithelium
What is the epithelium of the bronchioles?
1. gradual changes from larger
bronchioles to terminal bronchioles
2. Pseudostratified (with goblet cells)
3. Ciliated simple columnar (much less goblet
cells)
4. Ciliated simple cuboidal (no goblet cells)
What gives rise to respiratory bronchioles?
the branches of segmental bronchi
What are mid-sized bronchioles?
1. Ciliated columnar epithelium
2. Smooth muscle associated with
abundant elastic fibers
3. Connective tissue
4. Abundant lymphocytes of MALT
5. numerous lymphoid nodules
What are smaller bronchioles?
1. Ciliated simple cuboidal epithelium
2. Prominent layers of smooth muscle
3. Abundant MALT
What are the simple cuboidal epithelium of the terminal bronchioles?
1. Club cells with exocrine functions
2. Apical domain is dome-shaped
3. Abundant secretory granules
What are the functions of bronchial exocrine (club) cells of the simple cuboidal epithelium of the terminal bronchioles?
1. Secretion of surfactant lipoproteins and
mucins
2. Detoxification of inhaled xenobiotic
compounds by enzymes of the SER
3. Secretion of antimicrobial peptides and
cytokines
What are the other epithelial cells of the simple cuboidal epithelium of the terminal bronchioles?
1. Brush cells
2. DNES small granular cells
3. Stem cells
What are is the lamina propria of the simple cuboidal epithelium of the terminal bronchioles?
1. Elastic fibers
2. Smooth muscle
What are the respiratory bronchioles?
1. Alveoli present in their walls
2. First part of respiratory portion
3. Mucosa similar to that of terminal
bronchioles
4. Have few openings to alveoli
5. Epithelium has Club cells and squamous
cells at alveolar openings
6. Club cells become more numerous
distally as ciliated cells number
decreases
7. Lamina propria of loose CT
8. Smooth muscle
9. Elastic CT
What are the alveolar ducts?
1. After distal respiratory bronchioles
2. Lined by the openings of alveoli
3. Squamous epithelium in both the
alveolar ducts and alveoli
4. Thin lamina propria with a strand of
smooth muscle around the opening
of alveoli
5. Elastic and collagen fibers network
supports each ducts and its alveoli
What are the alveolar sacs?
1. End of alveolar ducts
2. Spaces surrounded by alveoli
opening into this space
3. Lined by a thin simple
squamous epithelium
4. Supported by very thin lamina
propria with elastic and
reticular fibers
5. abundant capillaries surround
each alveolus
What is alveoli?
1. Sack-like invaginations
2. About 200 nm diameter
3. About 200 million alveoli in each lung
4. Total internal surface 75 m2
5. Separated by interalveolar septa: Scattered fibroblasts and Sparse ECM of CT
6. Richest capillary network
What is the sparse ECM of CT?
Elastic and reticular fibers
Blood-air barrier (respiratory membrane)
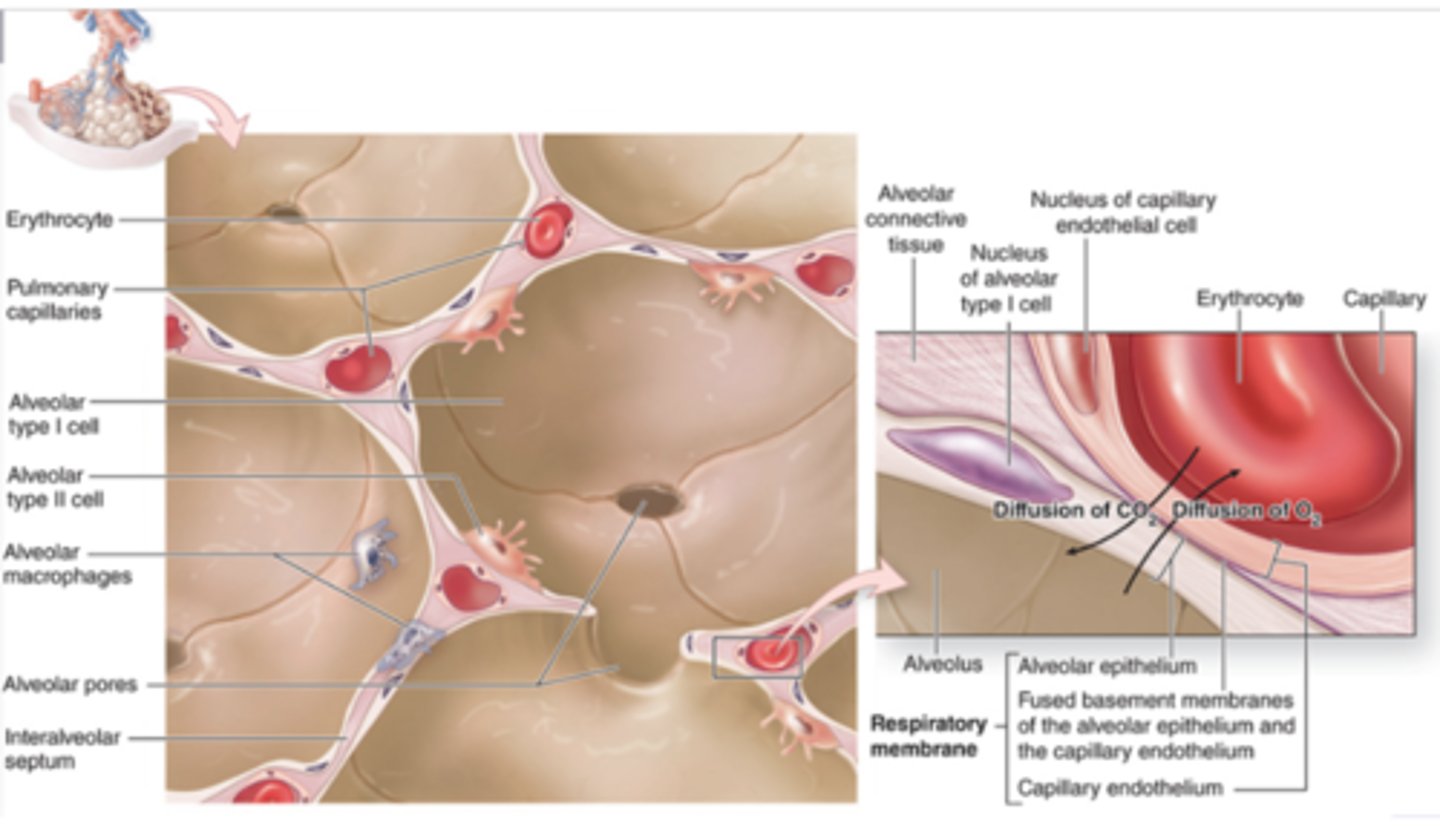
In the alveolar epithelium, what are the type 1 alveolar cells (type 1 pneumocytes)?
1. 95% of alveolar lining
2. Very thin squamous epithelial
cells
3. Perinuclear organelles
4. Cytoplasm committed to blood-air
barrier only 25 nm thick with
pinocytic vesicles
5. Joint by desmosomes
6. Tight junctions prevent leakage of
interstitial fluid into alveolar
lumen
In the alveolar epithelium, what are the type 2 alveolar cells (type 2 pneumocytes) or septal cells?
1. 5% of alveolar lining
2. Cuboidal cells
3. Interspersed among type I pneumocytes
4. Tight junctions and desmosomes
5. Large, euchromatic, round nucleus with
nucleoli
6. Lightly stained cytoplasm with many
vesicles
7. contains Lamellar bodies
8. Release pulmonary surfactant
What are the lamellar bodies?
1. vesicles with stacked
parallel membrane lamellae
2. Lipids, phospholipids, and proteins
How does the type 2 alveolar cells or septal cells release the pulmonary surfactant?
Continuously removed by type I and type II
pneumocytes, and macrophages
What are dust cells?
1. Alveolar macrophages
2. In alveoli and interalveolar
septum
3. Slightly darker than type II
pneumocytes
What does the pleural membrane contain?
1. Serous membranes
2. Visceral pleura
3. Parietal pleura
4. Mesothelium
5. Pleural cavity
6. Loose connective (supporting) tissue
7. Collagen and elastic fibers (continuous
with those of the lung tissue)
What is the visceral pleura of the pleural membrane?
attached to lung tissue
What is the parietal pleura of the pleural membrane?
lines the thoracic wall
What is the mesothelium of the pleural membrane?
special simple squamous epithelium
What is the pleural cavity of the pleural membrane?
space between visceral
and parietal layers