Maternal/Peds Exam 3 study guide
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
The most common causes of subinvolution in the postpartum client are, select all that apply:
A. After birth hemorrhage
B. Multiple gestation
C. Uterine tetany
D. Retained placental fragments
E. Infection
D, E.
-Retained placental fragments.
-Infection
**Subinvolution is failure of the uterus to return to a nonpregnant state.
The most effective and least expensive treatment of puerperal infection is prevention. What is important in this strategy?
A. Large doses of vitamin C during pregnancy
B. Prophylactic antibiotics
C. Strict aseptic technique, including hand washing, by all health care personnel.
D. Limited protein and fat intake.
C. Strict aseptic technique, including hand washing, by all health care personnel.
What is considered the fourth (Puerperium) stage of pregnancy?
The interval between birth and return of reproductive organs to their nonpregnant state.
-Lasts about 6 weeks.
What is included in the postpartum assessment?
-B: Breasts
-U: Uterus (fundal height, uterine placement, consistency)
-B: Bowel and GI function
-B: Bladder function
-L: Lochia (Color, odor, consistency, and amount)
-E: Episiotomy (Edema, ecchymosis, approximation)
-H: Homan's sign (Discomfort in the calf muscles on forced dorsiflexion of the foot with the knee straight -- Determines signs of DVT)
-E: Emotional status
What are some postpartum complications that may occur?
-Hemorrhage
-Hemorrhagic (Hypovolemic) shock
-Venous thromboembolic disease
-Infections
-Psychotic disorders (Postpartum blues, Postpartum depression, Postpartum psychosis)
What would postpartum hemorrhage look like?
-1000 mL or more cumulative blood loss (500 vaginal birth, 1000 c-section)
-Bleeding with hypovolemia within 24 hours of birth:
-Uterine atony (Boggy uterus)
-Blood clots bigger than a quarter
-Perineal pad saturation in 15 mins or less
-Tachycardic
-Hypotension
-Pale
When would early, acute or primary hemorrhaging occur after birth?
Within 24 hours.
What could be the etiology (causes) of early, acute or primary hemorrhaging?
-Lacerations
-Placental separation
-Undue manipulation of the fundus
-Excessive traction on the umbilical cord
-Uterine atony (inadequate contraction of the uterus)
-Prolapse of the uterus into the vagina
When would late or secondary hemorrhaging occur after birth?
Over 24 hours after birth - 12 weeks postpartum.
What could be the etiology (causes) of late or secondary hemorrhaging?
-Subinvolution of the uterus (uterus does NOT return to normal size)
-Infection
-Retained placental fragments
-Coagulopathy (derangement of hemostasis, resulting in excessive bleeding or clotting)
What is the definition of Hemorrhagic (Hypovolemic) Shock?
An emergency in which the perfusion of body organs can become severely compromised, and death can occur.
What is the etiology (cause) of Hemorrhagic (Hypovolemic) shock?
Excess blood/fluid loss.
How would a venous thromboembolic disease occur?
Results from blood clots caused by inflammation or partial obstruction off vessels.
What would be defined as a postpartum infection?
Any infection of the genital tract occurring within 28 days of miscarriage, abortion or birth.
What is a good indication of infection postpartum?
Fever of 38*C (100.4*F) or more for two successive days of the first 10 postpartum days (not including the first 24 hours after birth).
What are examples of postpartum infections that may occur?
-UTI
-Respiratory Tract infection
-Mastitis
What is mastitis?
Inflammation of the mammary gland.
-Most common when a woman is breastfeeding
-Usually unilateral
-Can progress to abscess if not treated
-Occurs during the first 6 weeks of breast feeding
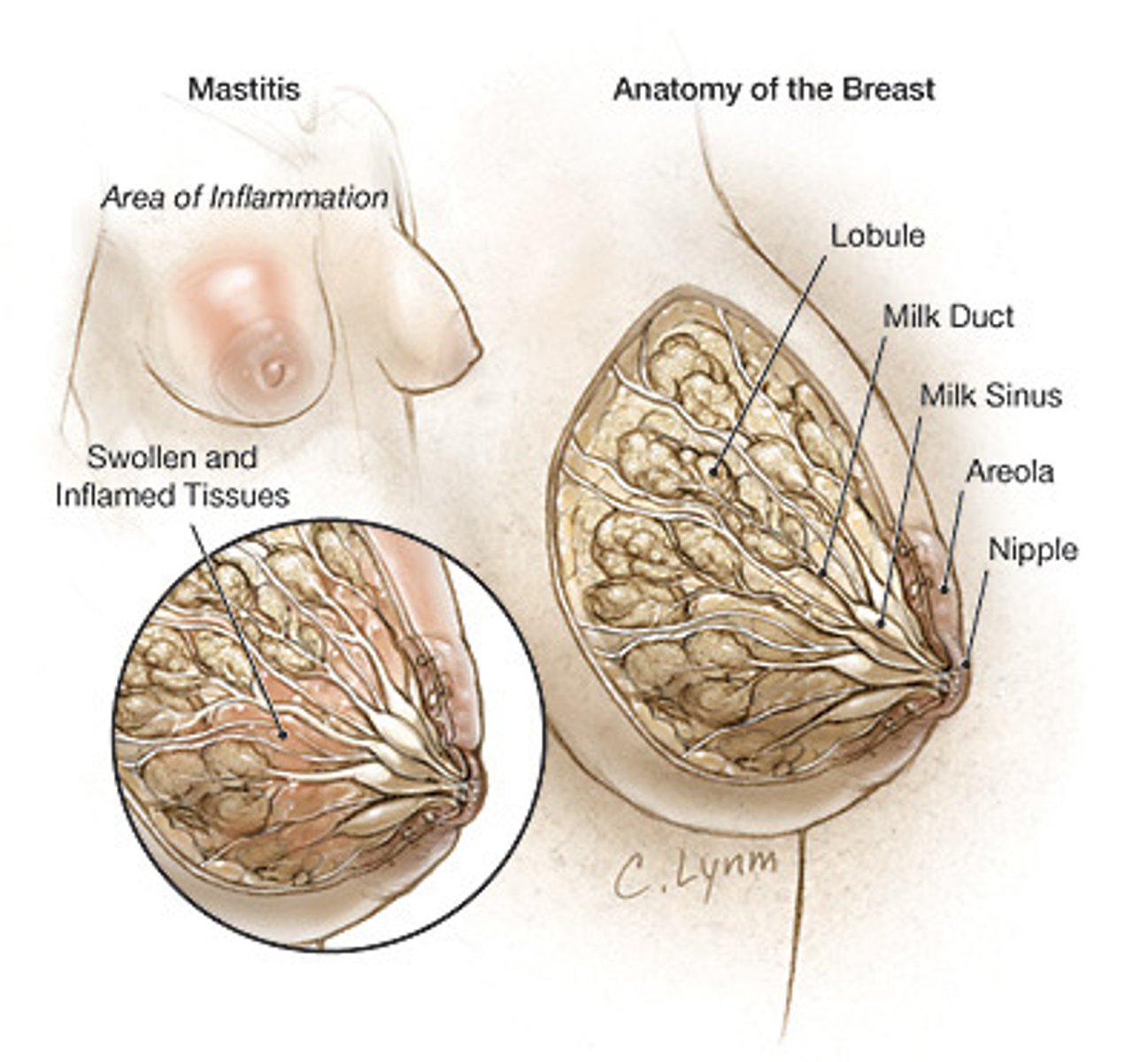
What is endometritis?
Inflammation of the endometrium.
-Caused by infiltration of bacteria into the inner lining of the womb.
-Starts 3 - 4 days postpartum
-Localized at placental attachment & spreads to entire uterine endometrium
What are some psychotic disorders that may occur postpartum?
-Postpartum blues
-Postpartum depression
-Postpartum psychosis
What are symptoms associated with Postpartum Blues?
-Feelings of sadness
-Lack of appetite
-Sleep pattern disturbances
-Feelings of inadequacies
-Crying easily for no apparent reason
-Restlessness
-Insomnia
-Fatigue
-Headache
-Anxiety
-Anger
-Sadness
What are symptoms associated with Postpartum Depression?
-Feelings of guilt and inadequacies
-Irritability
-Anxiety
-Persistent fatigue
-Feeling of loss
-Lack of appetite
-Persistent feelings of sadness
-Intense mood swings
-Flat affect
-Irritability
-Rejection of infant
-Severe anxiety and panic attacks
What are symptoms associated with Postpartum Psychosis?
-Pronounced sadness
-Disorientation
-Confusion
-Paranoia
What assessments should you look for in a mother who is showing signs of postpartum psychosis?
-Behaviors indicating hallucinations or delusional thoughts
-signs of self-harm or harming of infant
What is important when a patient is showing signs of hemorrhage in the postpartum period?
-Massage the fundus (to dispel blood clots & firm up the uterus)
-Elevate the patient's legs (get the circulation back to the organs)
What are some causes of MASTITIS?
-S. aureus
-Milk stasis (blocked duct)
-Poor breastfeeding technique (sore, cracked nipples leads to decrease in breastfeeding due to bottle feed supplementation)
-Contamination of breasts (poor hygiene)
What assessments factors would be an indication of postpartum depression?
-Crying
-Weight loss
-Flat affect
-Irritability
-Rejection of infant
-Severe anxiety and panic attack
What can be done to help a mother with postpartum psychotic disorders?
-Medications (antidepressants, antipsychotics, mood stabilizers for psychosis)
-Encourage rest (nap when baby naps)
-Time for self
-Follow up if at risk for developing depression
-Community resources
-Counseling
What is the definition of attachment in the postpartum period?
Parent and child come to love and accept each other.
What is the definition of mal attachment in the postpartum period?
The opposite of attachment, lack of interest in the newborn baby, difficulty accepting newborn baby.
What is included in the attachment theory?
-Attachment
-Bonding
-Proximity
-Acquaintance
-Claiming process
What does the Attachment portion look like in the attachment theory?
Parent and child come to love and accept each other.
What does the Bonding portion look like in the attachment theory?
The parent becomes acquainted with the infant, identifies the infant as an individual, and claims the infant as a member of the family.
What does the Proximity portion mean in the attachment theory?
Staying close to the infant.
What does the Claiming Process portion look like in the attachment theory?
The identification of the new baby.
Family makes comments like:
-"He looks just like Grandpa Ron."
-"He has the family nose."
-"Her toes are just like her dad's."
What does the Acquaintance portion look like in the attachment theory?
Eye contact, touch, talk, explore.
How would a nurse assess attachment behaviors between baby and family?
-When infant is brought to the parents, do they reach out for the infant and call the infant by name?
-Do the parents speak about the infant in terms of identification - Whom the infant resembles, and what appears special about their infant over other infants?
-When holding the baby, what kind of contact is seen (do parents feel at ease, do parents investigate or scrutinize certain parts of the body)?
-When the infant is awake, what type of stimulation do the parents provide (Do they talk to the infant, how do they look at the infant)?
-How comfortable do the parents appear in terms of caring for the infant?
-What type of affection do they demonstrate to the newborn (smiling, stroking, kissing, or rocking)?
-If the infant is fussy, what kinds of comforting techniques do the parents use (rocking, swaddling, talking, or stroking)?
How would a nurse help with the bonding process between baby and parents?
-Enhance parent-infant contact by increasing parent's awareness of infant responses.
-Rooming-in.
How is early parent to infant contact achieved and what are the benefits?
-Skin-to-skin immediately after birth
-May facilitate attachment process
How is extended parent to infant contact achieved and what are the benefits?
-Achieved through couplet care
-Family is encouraged to participate
-Optimizes family-centered care
What is the most common injury in children, but rare in infants?
Fractures.
-It warrants investigation if it is seen in an infant.
What bone is most frequently broken in childhood?
Distal forearm.
What is a simple or closed fracture?
Does not produce a break in the skin.
What is an open or compound fracture?
Fractured bone protrudes through the skin.
What is considered a complicated fracture?
Bone fragments that have damaged other organs or tissues.
What is considered a comminuted fracture?
Small fragments of bone are broken from fractured shaft and lie in surrounding tissue.
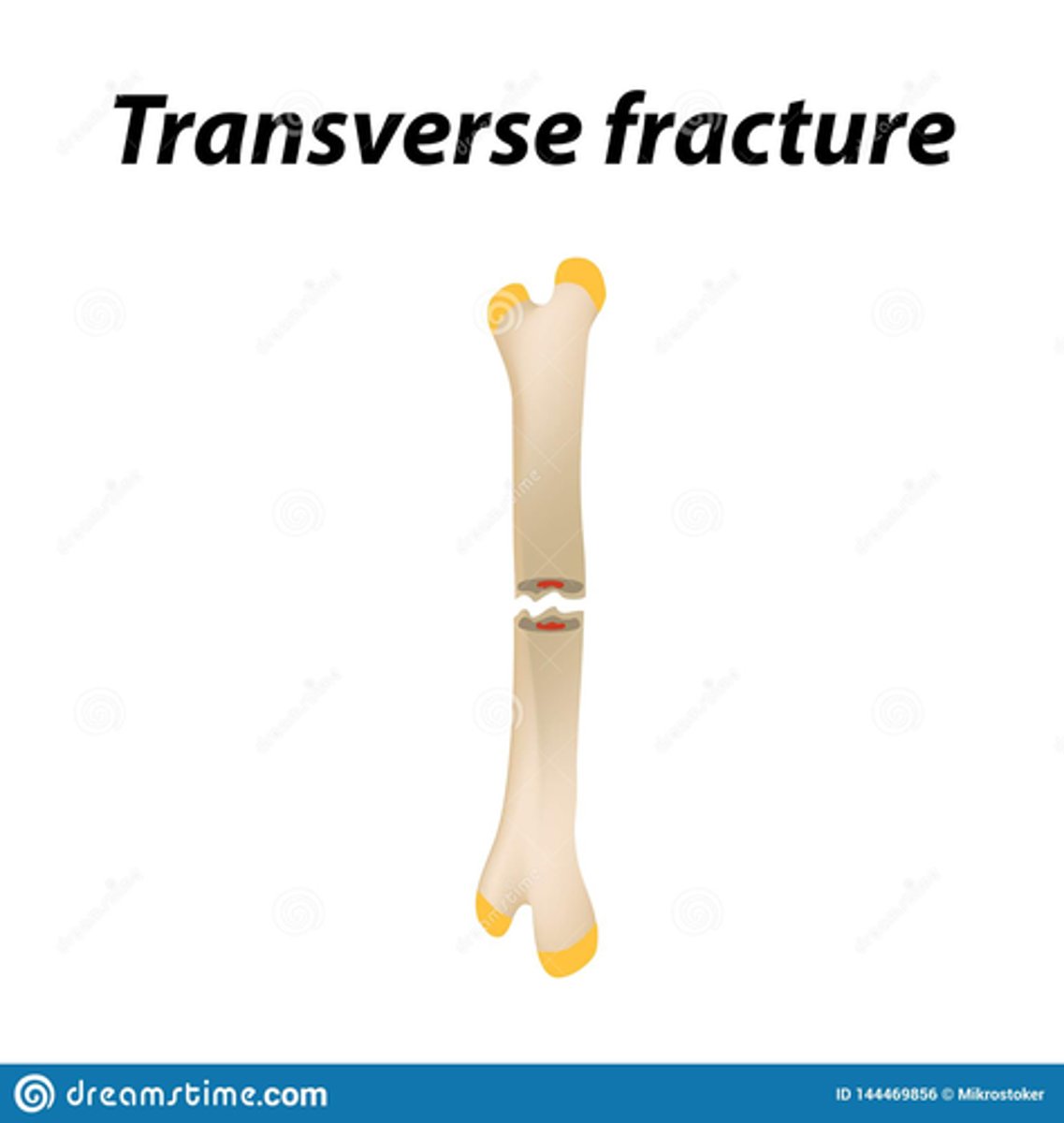
What is considered a transverse line fracture?
Crosswise at right angles to the long axis of the bone.
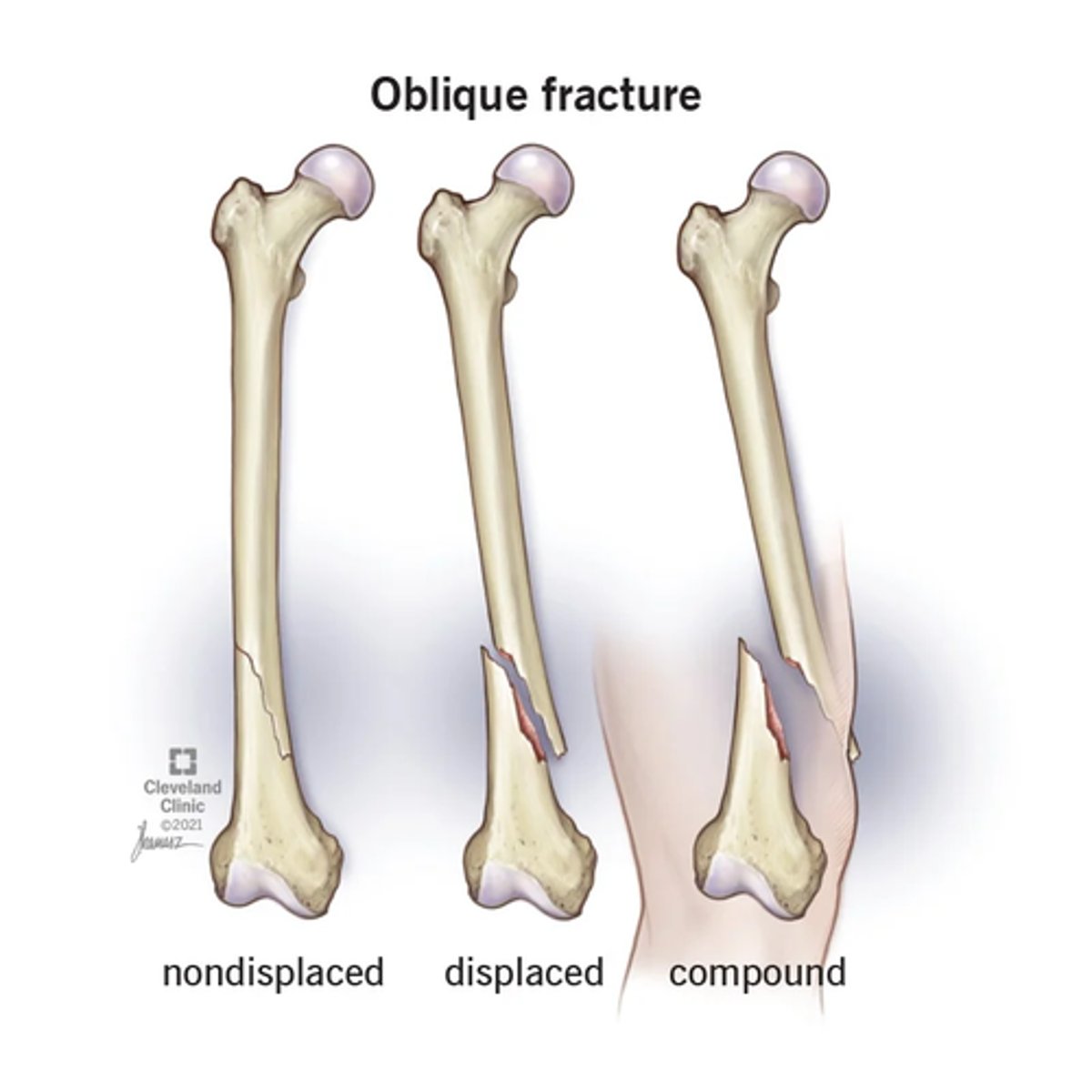
What is considered an oblique line fracture?
Slanting but straight between a horizontal and perpendicular direction.
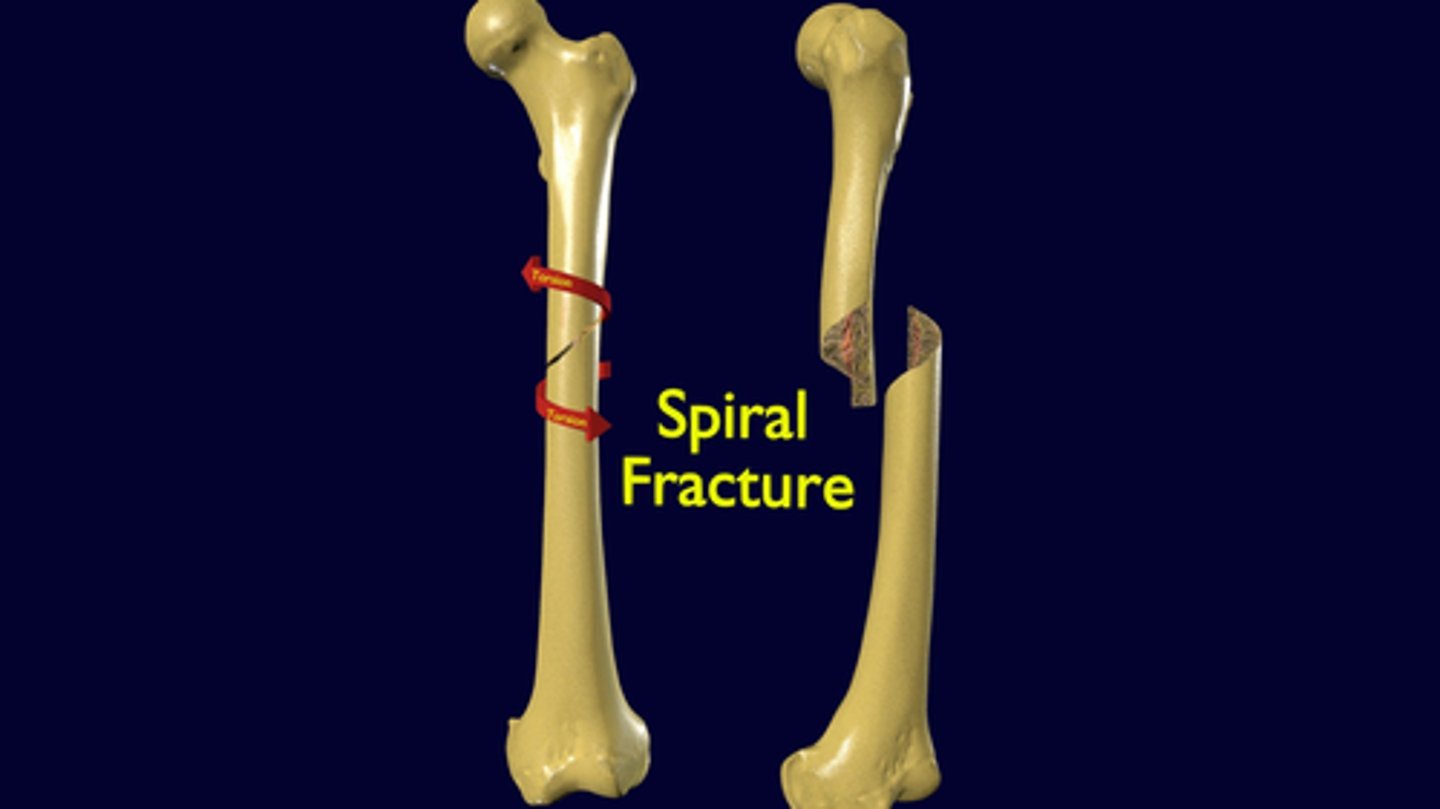
What is considered a spiral line fracture?
Slanting and circular, twisting around the bone shaft.
What are the goals of healing when it comes to fractures in children?
-Reduction and immobilization
-Restoring function
-Preventing deformity
What are the 6 P's in assessment when it comes to a fracture in children?
-Pain and point of tenderness
-Pallor
-Pulselessness
-Paresthesia (Sensation distal to the fracture site)
-Paralysis (Movement distal to the fracture site)
-Pressure
What is the purpose of tractions when it comes to fractures in children?
-Relieve fatigue in involved muscles
-Position distal and proximal bone ends
-Immobilize fracture site
-Prevent deformity
-Immobilize healing bone and prevent further injury
-Reduce muscle spasms
What are the three degrees of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hips (DDH)?
-First Degree (Acetabular Dysplasia)
-Second Degree (Subluxation)
-Third Degree (Dislocation)
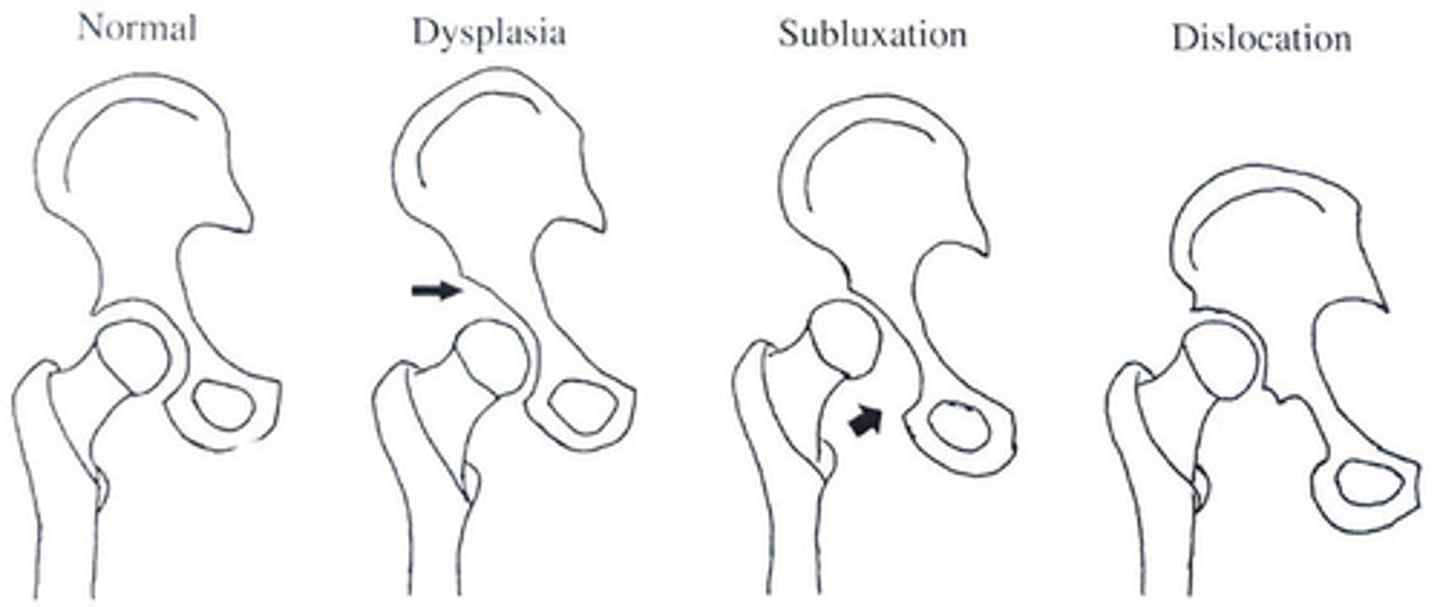
What does 1st degree ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA look like?
-Mildest form of DDH
-Delay in acetabular development (The acetabular roof is shallow and oblique)
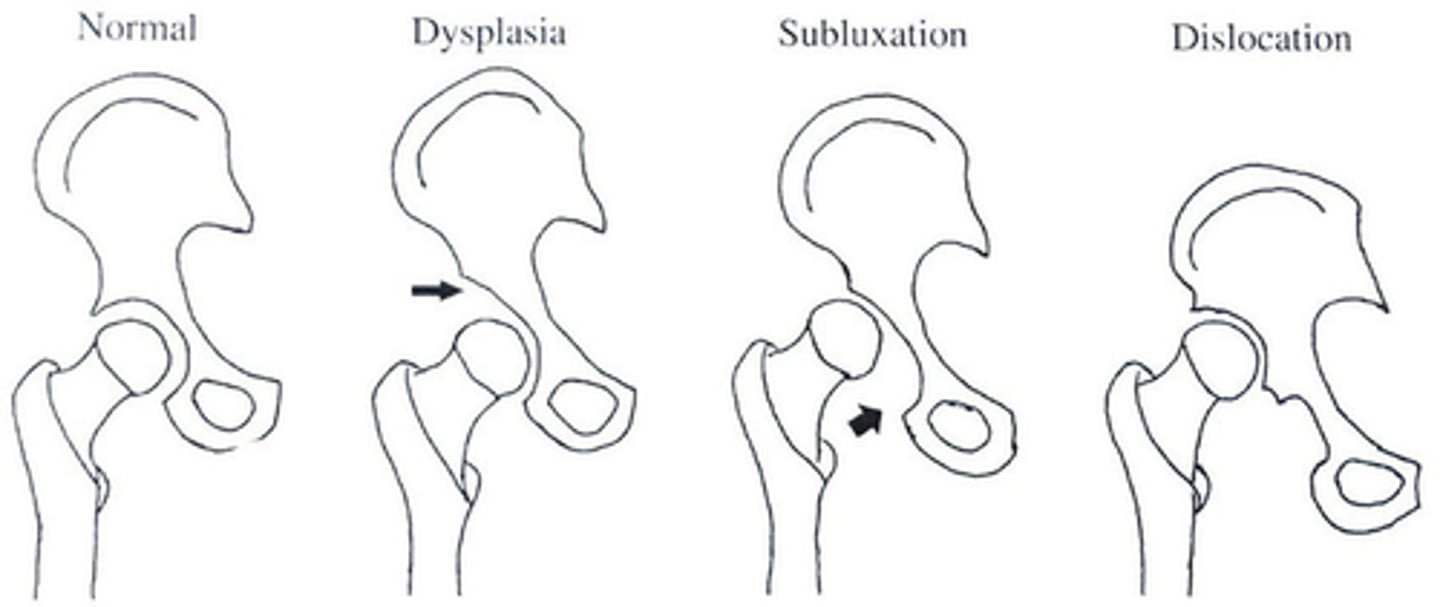
What does 2nd degree SUBLUXATION look like?
-Incomplete dislocation of the hip
-Femoral head remains in contact with the acetabulum
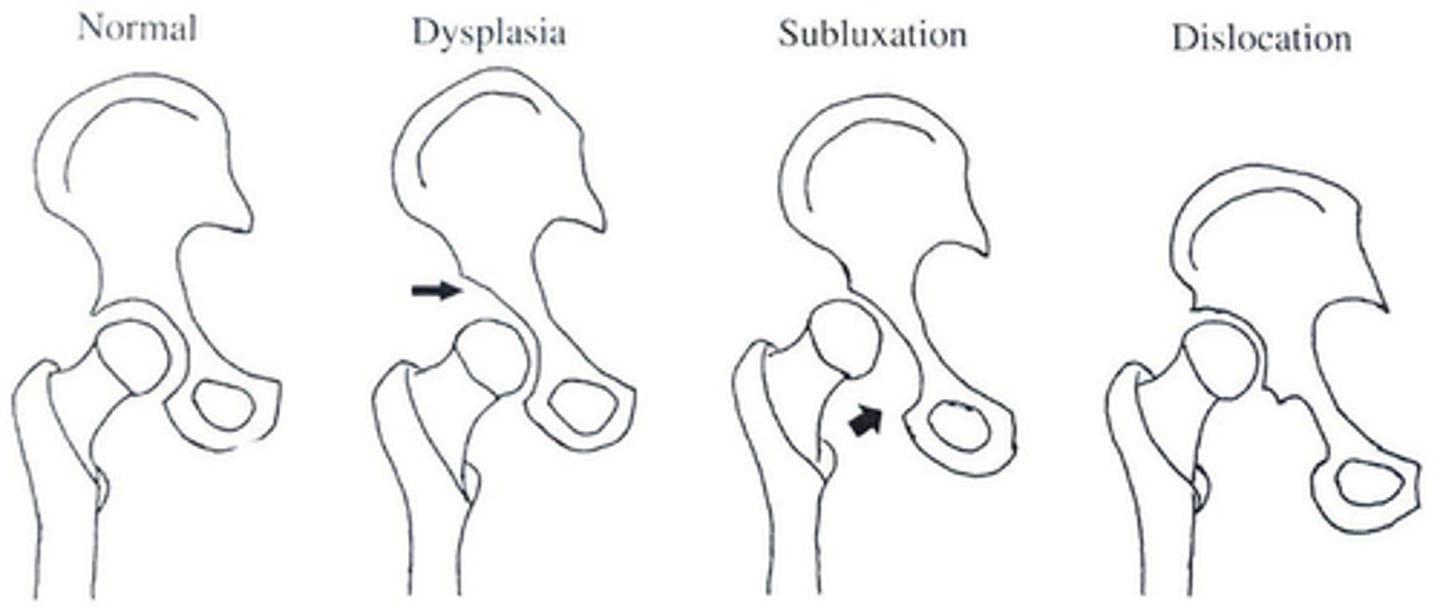
What does 3rd degree DISLOCATION look like?
Femoral head doesn't have contact with the acetabulum.
What are the clinical manifestations of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hips (DDH) in younger infants?
-Asymmetric gluteal and thigh skin folds
-Uneven knee levels
-A positive Ortolani test (Hip is reduced by abduction)
-A positive Barlow test (Hip is dislocated by adduction)
-Shortening of the femur
-Widened perineum
-Limited hip abduction
What are the clinical manifestations of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hips (DDH) in older infants and children?
-One leg is shorter
-Walking on toes
-Walks with a limp
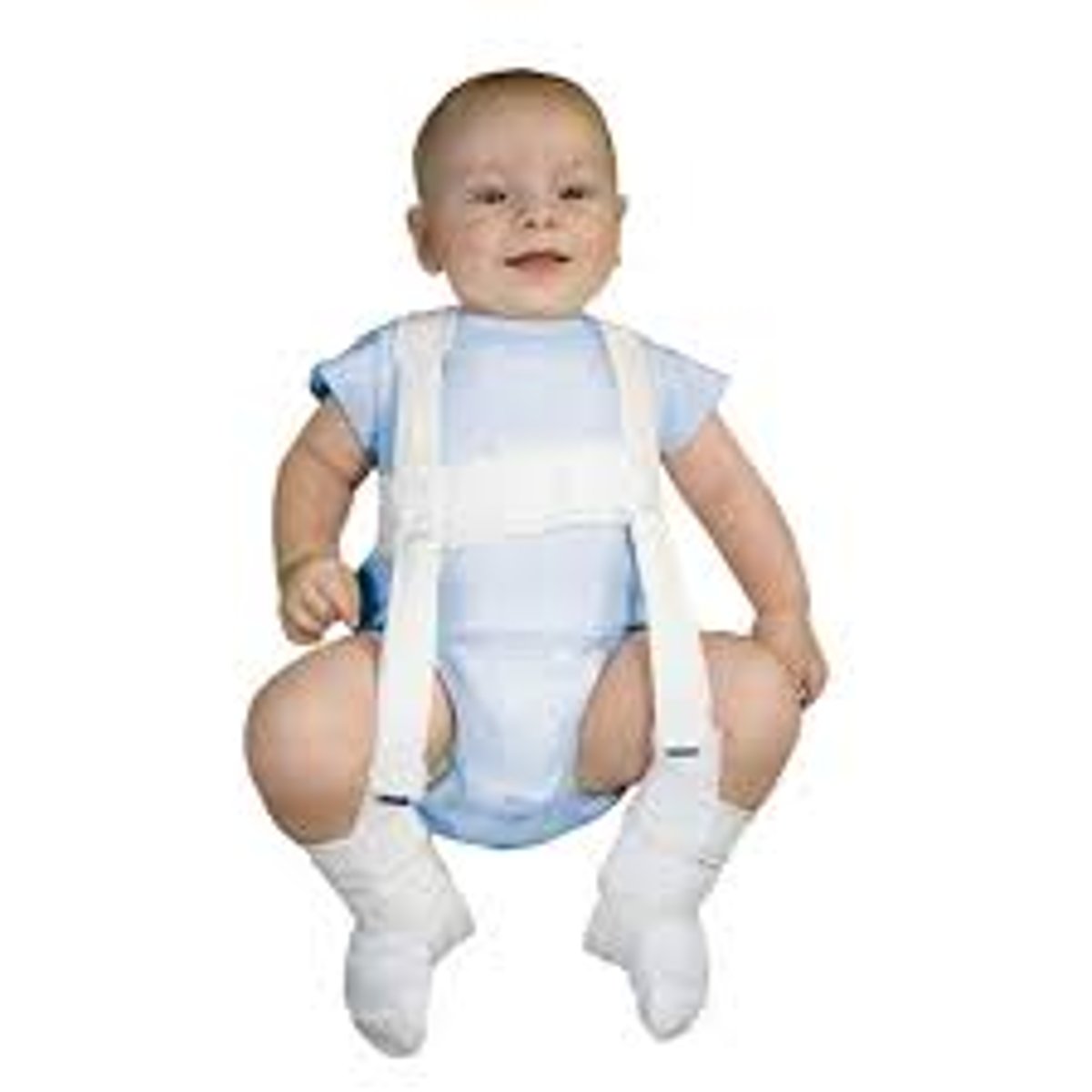
What is the therapeutic management for an infant newborn to 6 months with DDH?
Pavlic Harness
-Check straps every 1-2 weeks
-Will be in harness for 12 weeks
-Perform skin/neuro checks
-Place the diaper under the straps

What is the therapeutic management for a child 6 months - 2 years with DDH?
Surgical closed reduction with placement of hip spica cast.
-Needs adjusted to accommodate growth
-Prepare for surgery
-Neuro checks
-Assess post op pain
-Skin/cast care
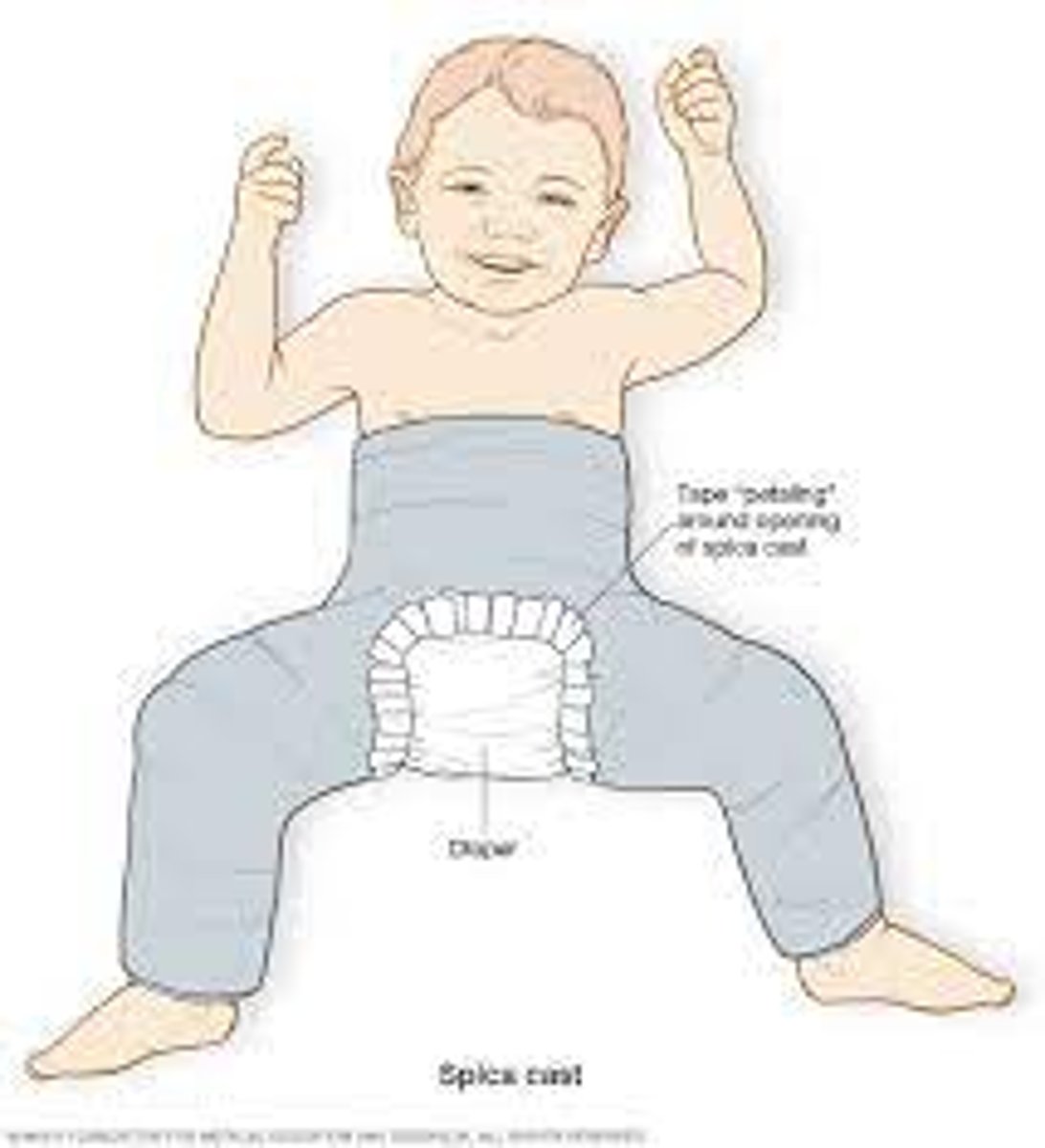
What is the therapeutic management for older children with DDH?
-Surgical reduction with pre-surgical traction.
-Femoral osteotomy reconstruction
-Tenotomy are often needed
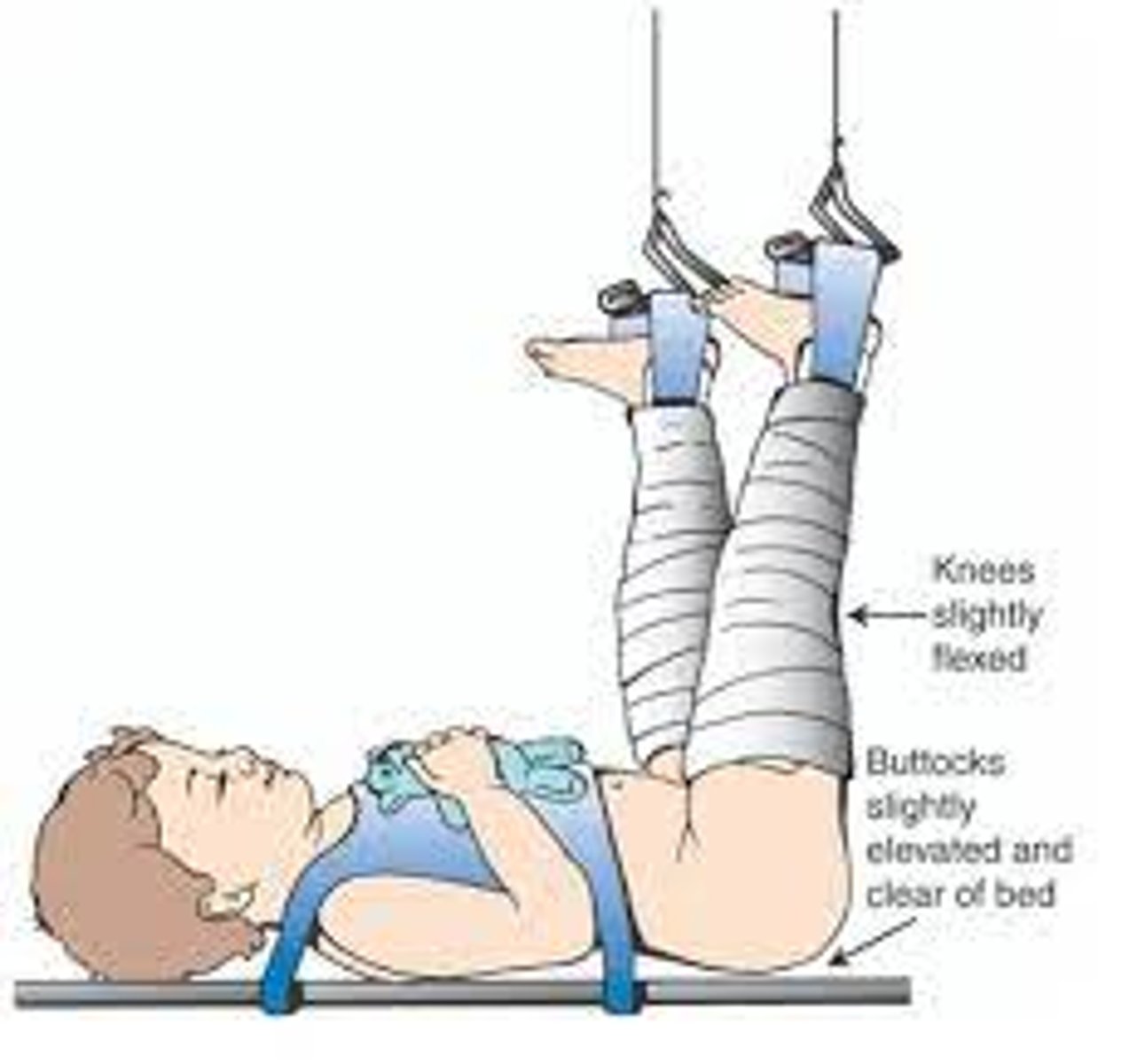
What is needed when there is an adduction contracture present?
Bryant traction is likely used.
-Hips are flexed at a 90-degree angle with buttocks off bed.
-Ensure the client maintains alignment.
What is the major intervention to alleviate uterine atony and restore uterine muscle tone?
Fundal massage.
What is the term if there is a failure of the uterine muscle to contact firmly?
Uterine atony.
-It is the most frequent cause for excessive bleeding following childbirth.
What is a perineal treatment that involves sitting in warm water for approximately 20 minutes to soothe and cleanse the site and to increase blood flow, enhancing healing?
Sitz bath.
What is the term for swelling of the breast tissue caused by increased blood and lymph supply to the breasts as the body begins the process of lactation?
Engorgement.
What is the blood product that is administered to Rh-negative, antibody (Coombs)-negative women who give birth to Rh-positive newborns?
RhoGam (Rh immune globulin).
-It is administered at 28 weeks of gestation and again within 72 hours after birth.
When would the RhoGam (Rh immune globulin) shot be administered to an expecting mother that requires the shots?
-28 weeks of gestation
-72 hours after giving birth
What is the process by which a parent comes to love and accept a child and a child comes to love and accept a parent?
Attachment.
What is the term that is often used to refer to the process of attachment (a parent comes to love and accept a child and a child comes to love and accept a parent)?
Bonding.
What is the term for loss of 500 mL or more of blood after vaginal birth or 1000 mL or more after cesarean birth?
Postpartum hemorrhage.
What is considered excessive blood loss that occurs within 24 hours after birth, most often caused by marked uterine hypotonia?
Early (Acute, primary) blood loss.
What is considered blood loss that occurs more than 24 hours after birth but less than 6 weeks after birth?
Late (secondary) blood loss.
A nurse is preparing to administer RhoGAM to a postpartum woman. Before implementing this care measure the nurse should:
A. Ensure that medication is given at least 24 hours after birth.
B. Verify that the Coombs test results are negative.
C. Make sure that the newborn is Rh negative.
D. Cancel the administration of the RhoGAM if it was given to the woman during her pregnancy at 28 weeks of gestation.
B. Verify that the Coombs test results are negative.
-The Coombs test results must be negative, indicating that antibodies have not been formed before RhoGAM can be given.
-The newborn needs to be Rh positive.
When assessing postpartum women during the first 24 hours after birth, the nurse must be alert for signs that could indicate the development of postpartum physiologic complications. Which of the following signs would be of concern to the nurse? Select all that apply.
A. Temperature - 38*C
B. Fundus - Midline, boggy
C. Heart rate of 88 beats per minute
D. Anorexia
E. Fatigue
F. Voids approximately 150 - 200 mL of urine for each of the first three voiding's after birth.
G. Saturated perineal pad in 10 minutes.
H. Sore nipples after 3 breastfeeding sessions.
B, D, G, H.
-Fundus - Midline, boggy
-Anorexia
-Saturated perineal pad in 10 minutes.
-Sore nipples after 3 breastfeeding sessions.
During maternal attachment and bonding with the newborn, which of the following might a mother say?
A. "She has her grandfather's nose."
B. "His ears lay nice and flat against his head, not like mine and his sister's, which stick out."
C. "She gave me nothing but trouble during pregnancy, and now she is so stubborn she won't wake up to breastfeed."
D. "He has such a sweet disposition and pleasant expression. I have never seen a baby quite like him before."
D. "He has such a sweet disposition and pleasant expression. I have never seen a baby quite like him before."
-Choice A reflects the first phase of identifying likeness
-Choice B reflects the second phase of identifying differences
-Choice C reflects a negative reaction of claiming the infant in terms of pain and discomfort.
Which of the following nursing actions would be least effective in facilitating parent attachment to their new infant?
A. Referring the couple to a lactation consultant to ensure continuing success with breastfeeding.
B. Keeping the baby in the nursery as much as possible for the first 24 hours after birth so the mother can rest.
C. Extending visiting hours for the woman's partner or significant other as desired.
D. Providing guidance and support as the parents care for their baby's nutrition and hygiene needs.
B. Keeping the baby in the nursery as much as possible for the first 24 hours after birth so the mother can rest.
-Early close contact is recommended to initiate and enhance the attachment process.
Which of the following would be a priority question to ask a woman experiencing postpartum depression?
A. Have you thought about hurting yourself?
B. Does it seem like your mind is filled with cobwebs?
C. Have you been feeling insecure, fragile, or vulnerable?
D. Does the responsibility of motherhood seem overwhelming?
A. Have you thought about hurting yourself?
-The potential for harming herself and the baby is the most serious.
What is an upper airway infection characterized by hoarseness and a "barking" cough?
Croup.
In order to prevent bladder dysfunction in older children with spina bifida, the child and parents are taught what?
A. Clean intermittent catheterization
B. Foley catheter care
C. Oral fluid challenge
D. Bladder irrigations
A. Clean intermittent catheterization
The nurse is planning care for a 4-year-old child admitted with bacterial meningitis. Which of the following would be the most appropriate intervention to include in the plan of care?
A. Keep environmental stimuli to a minimum.
B. Encourage active range of motion by the child every 2-4 hours and prn.
C. Administer pain medication cautiously as it could dull the sensorium.
D. Measure head circumference to assess developing complications.
A. Keep environmental stimuli to a minimum.
An 8-year-old child diagnosed with asthma is being taught how to use a spacer with an albuterol inhaler. What is the best way for the nurse to evaluate the child's understanding of how to use the spacer?
A. Guide the child step by step through the process.
B. Have the child attach the spacer to the inhaler and use it.
C. Have the child verbalize how to use the spacer.
D. Attach the spacer to the inhaler, then have the child to use it.
B. Have the child attach the spacer to the inhaler and use it.
What drug is usually given first in the emergency treatment of an acute, severe asthma episode in a young child?
A. Magnesium sulfate
B. Theophylline
C. Atrovent
D. Albuterol
D. Albuterol
An 18-month-old is admitted with acute laryngotracheobronchitis (LTB). The child will most likely be treated with which of the following?
A. Racemic epinephrine nebulized treatments and corticosteroids.
B. Intravenous (IV) and oxygen.
C. Antibiotics and albuterol
D. Chest physiotherapy (CPT) and oxygen.
A. Racemic epinephrine nebulized treatments and corticosteroids.
An 8-year-old female presents to the clinic with complaints of a sore throat and fever. A throat culture is obtained, and the diagnosis of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS) pharyngitis is confirmed. Which of the following would be appropriate health teaching for the parents and child?
(Use an X for health teaching below that is indicated, contraindicated, or non-essential regarding treatment of GABHS pharyngitis).
A. In certain strains of this disease, a characteristic erythematous sandpaper-like rash; known as scarlet fever may develop.
B. A follow-up throat culture is recommended after completion of antibiotic therapy.
C. Children who experience a GABHS infection are at increased risk for the development of acute rheumatic fever and acute glomerulonephritis, thus it is imperative to complete the antibiotic therapy prescribed.
D. Application of a warm or cold compress to the neck area may provide pain relief, antipyretics may also be administered for throat pain and to decrease fevers.
E. Children should discard their toothbrush after completion of antibiotic therapy.
F. Children are considered contagious until they have received antibiotic therapy for a full 48-hour period of time.
Indicated:
A, C, D.
-In certain strains of this disease, a characteristic erythematous sandpaper-like rash; known as scarlet fever may develop.
-Children who experience a GABHS infection are at increased risk for the development of acute rheumatic fever and acute glomerulonephritis, thus it is imperative to complete the antibiotic therapy prescribed.
-Application of a warm or cold compress to the neck area may provide pain relief, antipyretics may also be administered for throat pain and to decrease fevers.
Contraindicated:
E, F.
-Children should discard their toothbrush after completion of antibiotic therapy.
-Children are considered contagious until they have received antibiotic therapy for a full 48-hour period of time.
Non-Essential:
B
-A follow-up throat culture is recommended after completion of antibiotic therapy.
What comes out of the breasts before lactation occurs, and how long does it take for milk to come in after birth?
-Colostrum (yellowish fluid), comes out first.
-Milk comes 72 - 96 hours after birth.
-Breasts will become heavier and fuller.
How long will it take for engorgement to resolve if a mother is choosing not to breastfeed?
24 - 36 hours.
What is the definition of involution of the uterus?
Return of the uterus to nonpregnant state following birth.
-It is quick
-The fundus descents 1-2 cm every 24 hours
-The uterus is not palpable 2 weeks after childbirth
-Officially back to nonpregnant state by 6 weeks.
How long does the lochia rubra (red) stage last and what does it include?
-3 to 4 days.
-Blood and decidual and trophoblastic debris
How long does the Lochia Serosa (pinkish brown) stage last and what does it include?
-22 to 27 days
-Old blood, serum, leukocytes, and debris.
How long does the Lochia Alba (Whitish/yellow) stage last and what does it include?
-2 to 6 weeks after birth
-Leukocytes, decidua, epithelial cells, mucus, serum, and bacteria.
How long does it take for Episiotomies to heal?
2 - 3 weeks.
-Could take up to 4-6 weeks.
At what day postpartum should the fundus by halfway between the symphysis pubis and the umbilicus?
The 6th postpartum day.
What are the three stages of lochia?
-Lochia Rubra
-Lochia Serosa
-Lochia Alba
What is the benefit of colostrum?
It provides Immunoglobulin A (IgA), which provides passive immunity to the newborn.
-Lysozymes
-Leukocytes
-Macrophages
-Lactoferrin
What are nursing interventions that can help a new parent be successful in breastfeeding?
-Provision of adequate calories and fluids to support breastfeeding.
-Practice of rooming-in (staying together in the same room) as part of baby-friendly initiatives.
-Lactation consultants
-Encourage breastfeeding through the first months of life
What are the four basic breastfeeding positions?
-Football hold (under the arm)
-Cradle (most common)
-Modified cradle (Across the lap)
-Side-lying
How often should a parent feed the newborn until they can start feeding the infant on an on-demand schedule?
Every 3-4 hours.
-3 hours during the day
-4 hours during the night
What is clubfoot?
Complex deformity of the foot and ankle.
-Occurs as an isolated defect
-Or may be associated with other disorders (cerebral palsy, spina bifida)
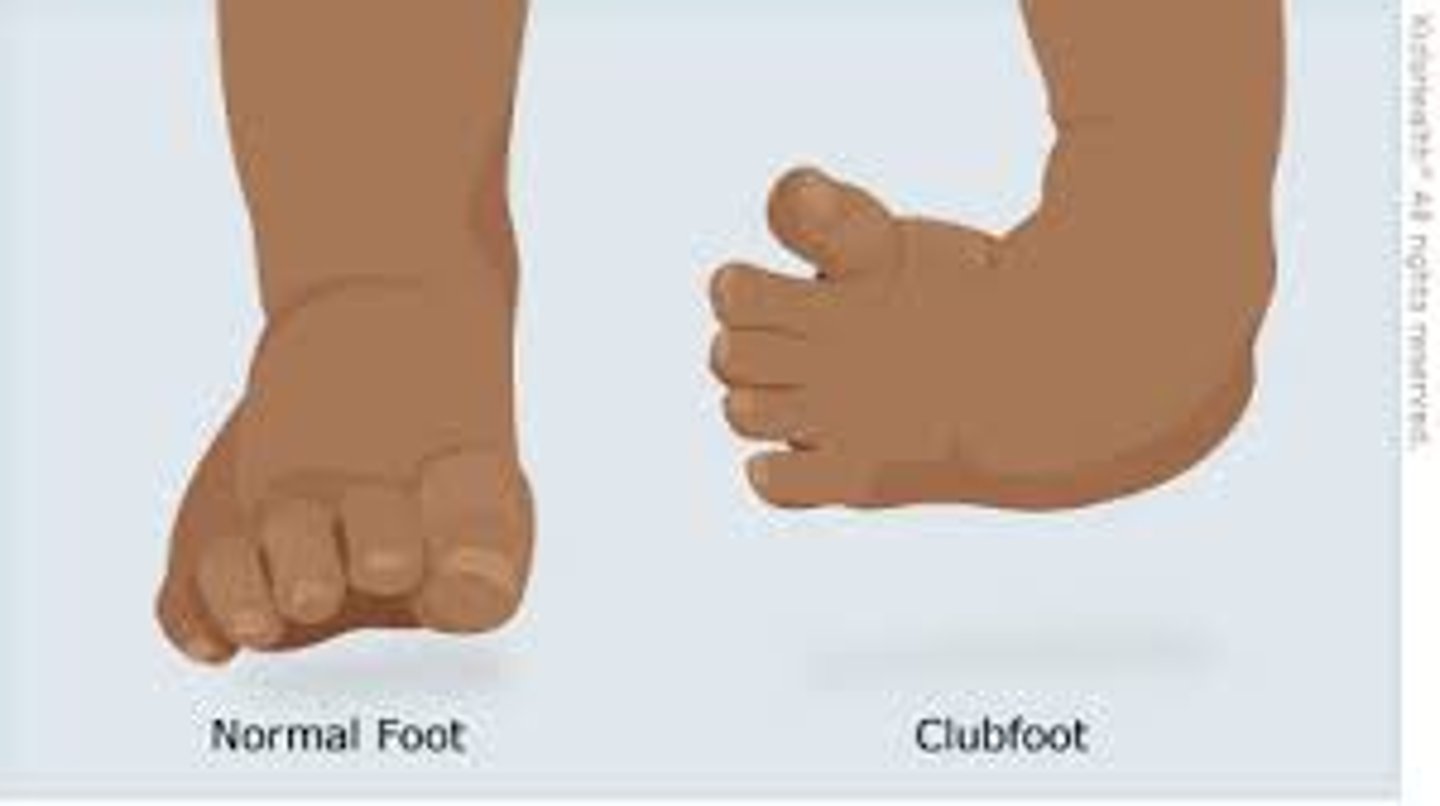
What are some diagnostic evaluations when it comes to clubfoot in infants?
-Prenatal ultrasound can identify the deformity.
-A thorough hip exam is necessary with all infants with clubfoot due to increased risk of hip dysplasia associated with clubfoot deformities.
What are the 3 stages of clubfoot treatment?
1. Correction of the deformity
2. Maintenance of the correction until normal muscle balance is gained
3. Follow-up observation to avert possible recurrence of the deformity