Neuropharmacology Drugs
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Parasympathetic nervous system
Slows heart rate, gastric secretion, empties bowel and bladder, focuses eye for near vision, constrict pupil, and contract bronchial smooth muscle.

Sympathetic nervous system
Regulates cardiovascular system by maintaining blood flow, vasoconstriction, promotes secretion of sweat, goosebumps, increase heart rate and blood pressure, dilates bronchi to improve oxygenation, and dilates pupils.

Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction. When things play a role on acetylcholine to inhibit them, they are called anticholinergics.
Acetylcholinesterase
the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. Without this enzyme, ACH floods the body and overstimulates the nerves in those areas.
Cholinesterase inhibitors
Anticholinesterase agents (it is an ANTI cholinergic-enzyme) allow for more acetylcholine to be present.
Atropine
Antidote for cholinesterase inhibitors.
Myasthenia Gravis
An autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction characterized by fluctuating weakness of certain muscle groups. Affects eye muscles and eye lids, chewing, shallowing, speaking, and breathing.
Highly variable course of the disease, affected by stress levels. Muscular atrophy is rare.

Pyridostigmine drug card
Major function: Cholinesterase inhibitor. Increases muscle strength by mild stimulation of the CNS.
Adverse effects: Excessive muscarinic stimulation, respiratory depression, neuromuscular blockade (paraylsis), nausea/vomiting in an overdose, and seizures.
Pyridostigmine precautions/contraindications
Obstruction of GI/urinary tract, peptic ulcer disease, asthma, coronary insufficient, and hyperthyroidism.
Pyridostigmine nursing implications
Assess vitals and swallowing ability prior to administration. Take in the morning, don't 2x or skip doses, may need extra for physical activity, and is used as a life-long treatment.
Parkinson's disease
A chronic, progressive, degenerative disorder that produces characteristic motor symptoms: tremor at rest, rigidity, postural instability, and bradykinesia. Medications are aimed at balancing the dopamine and acetylcholine in the brain.
Levodopa/carbidopa (kinda like dopamine)
Major function: Provide exogenous source of dopamine and enhances the neurons that are still producing domaine, relieving tremors and rigidity in the brain. Combination of levodopa and carbidopa helps control side effects like dyskinesia and psychosis experienced with Levodopa alone.
Adverse effects: Nausea and vomiting, irregular heart issues, psychosis, nightmares, agranulocytosis, orthostatic hypotension, dark sweat and urine. May affect (or activate) skin cancer.
Levodopa/carbidopa nursing considerations
Get vitals, asses for orthostatic hypotension, give with food to minimize GI irritation (no high protein diets, it will cause an on/off effect). May take several months to see results.
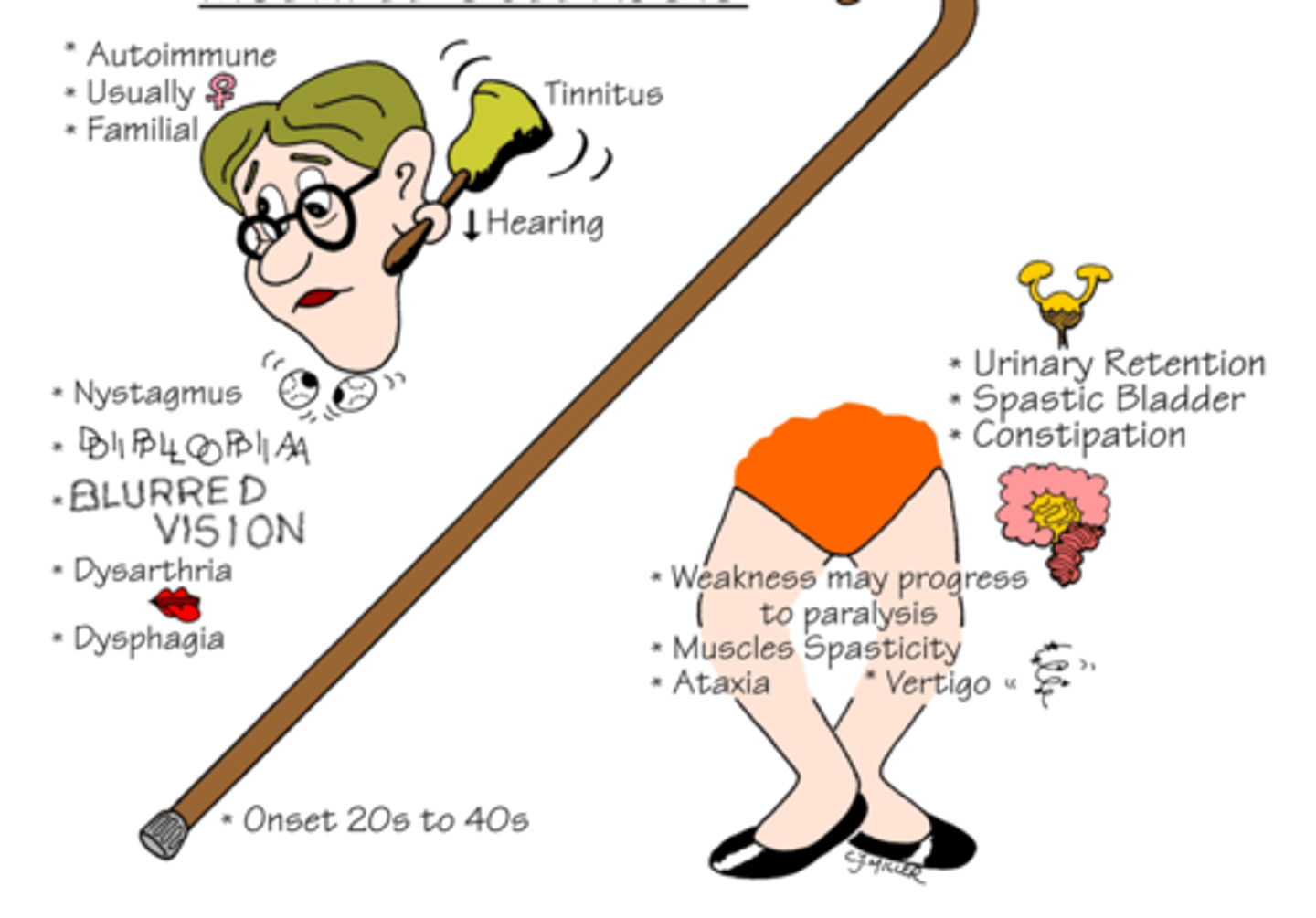
Multiple scleorsis
Chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder that damages the myelin sheath of neurons in the CNS. Demyelination resulting in delayed motor response from neurons. Exact cause is unknown. Causes a wide variety of wide variety of sensory and motor deficits.
S/S: Tinnitus, decreased hearing, usually women diagnosed, nystagmus, blurred vision, diplopia, dysphagia, urinary retention, spastic bladder, constipation, paralysis.
Glatiramer acetate
Major function: Used for long-term therapy of relapsing-remitting MS. Protects myelin by inhibiting immune response that creates inflammatory cells.
Generally tolerated very well. Your patients might feel anxiety, palpations, flushing right after injection. This usually goes away in 15-20 minutes.
Natalizumab
Major function: Used for MS and Crohn's disease. Prevents circulating leukocytes from leaving vasculature. Second-line treatment for MS when Glatiramer acetate doesn't work.
Also generally tolerated well. Monitor LFTs, and WBC's because overtime it will suppress immune function in general.
Interferon beta
Major function: Reduces the frequency and severity of attacks. Also delays progression of disability of MS.
Give at night. Rotate sites.
Adverse effects: Seizures, depression, insomnia, neutropenia anemia, TTP, flu-like symptoms, and liver inflammation.
Baclofen
Major function: Treats muscle spasticity by mimicking the inhibitory actions of GABA in the CNS.Used for MS, spinal cord injury, and cerebral palsy. NOT FOR STROKE.
Adverse effects: No antidote. Gradual withdraw over 1 to 2 weeks (TAPER). CNS depressant, GI symptoms, urinary retention, and hyperglycemia.
Epilepsy
Group of neurologic disorders characterized by recurrent episodes of convulsive seizures, sensory disturbance, abnormal behavior, LOC, or any combination of these.
Meds that work on seizures work by altering electrolyte movement. The goal in treating epilepsy is to reduce seizures to an extent that enables the patient to live a normal or near normal life. Complete elimination of seizures may not be possible without causing intolerable side effects

Phenytoin (Traditional anti-seizure drug)
Major function: Suppresses neuronal discharge. Narrow therapeutic index. Absorption and metabolism can vary.
Adverse effects: Visual disturbances, ataxia, vertigo, hyperplasia of gums (in 20% of patients), hirsutism, teratogenic, rash, dysrhythmia and hypotension.
Phenytoin nursing considerations.
Monitor LFTs, electrolytes, phenytoin levels (normally 10-20 mcg/mL) This drug inactivates oral birth control, reduces warfarin and glucocorticoid efficacy, and alcohol reduces levels.
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
Major function: Suppresses neuronal discharge. Usually preferred because it is better tolerated than phenytoin.
Adverse effects: Leukopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia—and, very rarely, fatal aplastic anemia.
Carbamazepine (Tegretol) nursing considerations
Monitor LFTs, CBS, BUN/Creatinine, electrolytes, tegretol levels (Normally 4-12 mcg/mL). Also interacts with oral birth control, reduces warfarin efficacy, and no grapefruit juice.
Valproic acid (Valproate)
Major function: Suppression of seizure through Na+ channels.
Adverse effects: Gi issues, liver failure, pancreatitis, Teratogenic effects, and thrombocytopenia.
Valproic acid nursing considerations
Monitor LFTs, CBS, electrolytes, and glucose levels. Give at bedtime if possible, give with food, no abrupt withdraw, and avoid alcohol.
Valproic acid should not be used during pregnancy, unless it is the only anti-seizure drug that works because of it's teratogenic effects.
Gabapentin
Major function: Anti-seizure medication. Unknown MOA, effects GABA (of course). Sometimes given for PVD (peripheral vascular disease) pain.
Adverse effects: Fatigue, somnolence (strong desire to sleep), dizziness, leukopenia.
Gabapentin nursing considerations
Monitor BUN/creatinine, CBC, and monitor V/S, avoid alcohol, and taper.
A baclofen overdose would cause
hypotension, dizziness, and nausea.
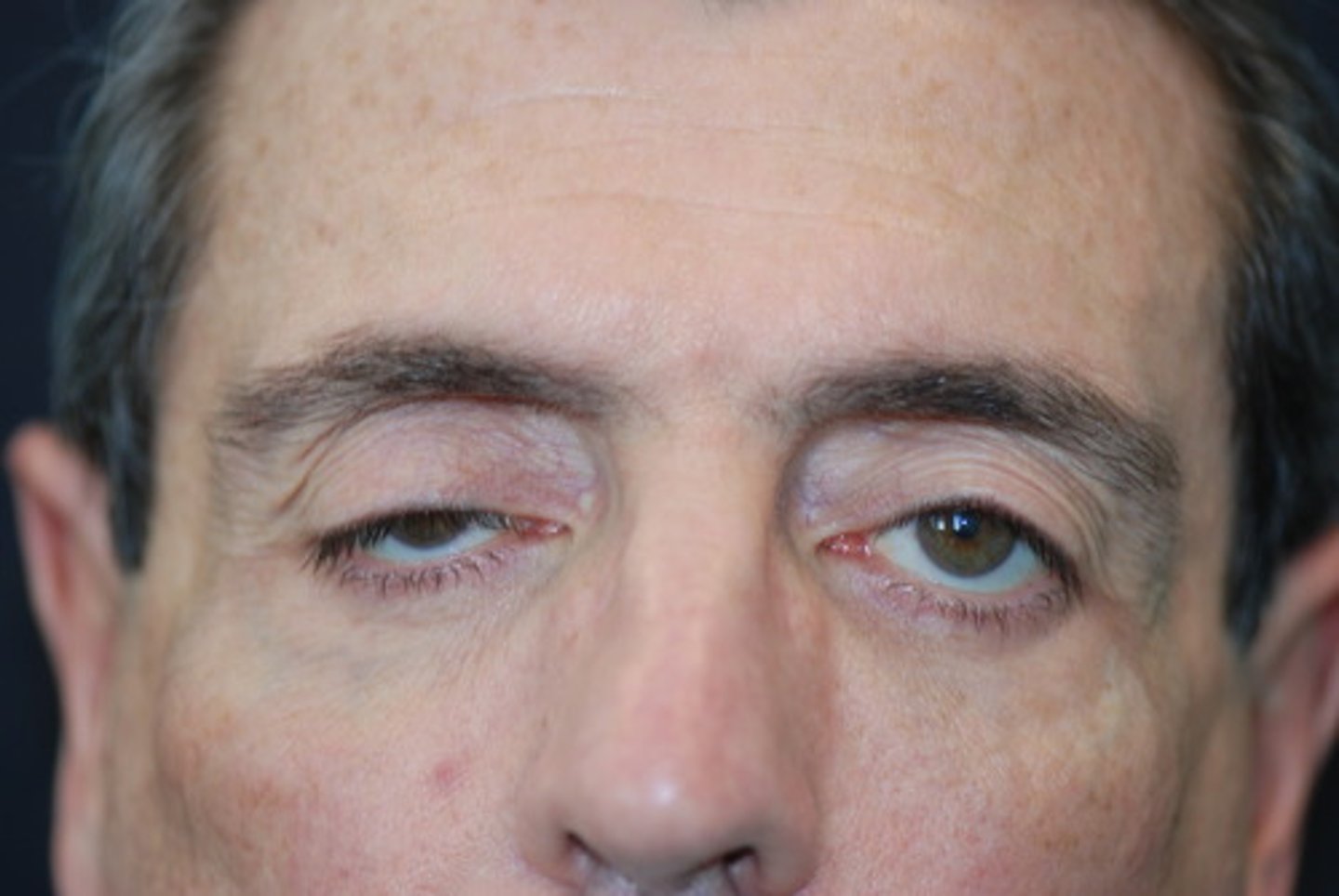
ptosis
drooping
Which statement would a nurse include in the teaching plan for a patient with a new prescription for phenytoin?
A. "It is very important to have good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly."
B. "You may continue to have wine with your evening meals but only in moderation."
C. "This drug may cause easy bruising. If you notice this, call your clinic immediately."
D. "Be sure to call the clinic if you or your family notice that you are experiencing increased anxiety or agitation."
E. "You may have some mild sedation. Do not drive until you know how this drug will affect you."
A, D, and E
Why might a nurse want to tell a young woman who is on phenytoin, to also take birth control?
Because of the fetal risks associated with phenytoin during pregnancy, you want to use birth control.
Phenytoin normal levels
10-20 mcg/mL
A client with myasthenia gravis has difficulty chewing and has received a prescription for pyridostigmine. The nurse would check to see that the client takes the medication at what time?
30 minutes before meals. You want the medication to be able to kick in to allow for easier swallowing in the patient by the time they need to eat.
Levodopa/carbidopa adverse effects
Nausea and vomiting, hypotension, psychosis, nightmares, agranulocytosis, orthostatic hypotension, dark sweat and urine. May affect (or activate) skin cancer.