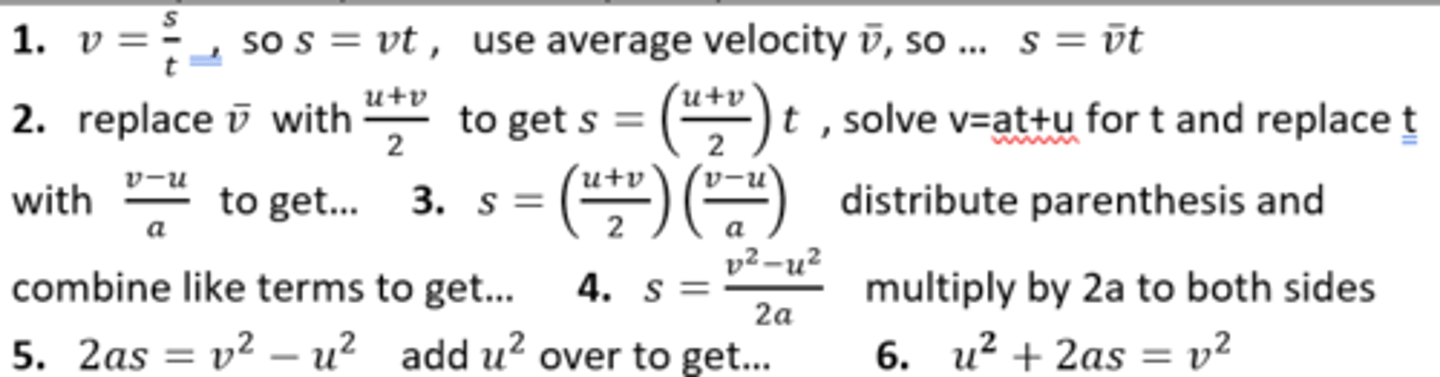Ch.1 and 2 Kinematics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
1
New cards
Displacement
Distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point.
2
New cards
Velocity
Rate of change of displacement
3
New cards
Acceleration
Rate of change of velocity
4
New cards
Gradient of a displacement-time graph
Velocity
5
New cards
Gradient of a velocity-time graph
Acceleration
6
New cards
Area under velocity-time graph
Displacement
7
New cards
Kinematic Equations
v = at + u
v^2 = u^2 + 2as on formula sheet
s = ut + 1/2 at^2 on formula sheet
s = (u +v)t/2
8
New cards
Projectile motion
Vertical acceleration is -g or g (9.81)
Horizontal acceleration = 0
9
New cards
Terminal velocity
The greatest velocity a falling object can achieve.
Acceleration = 0
10
New cards
Derive v = at + u
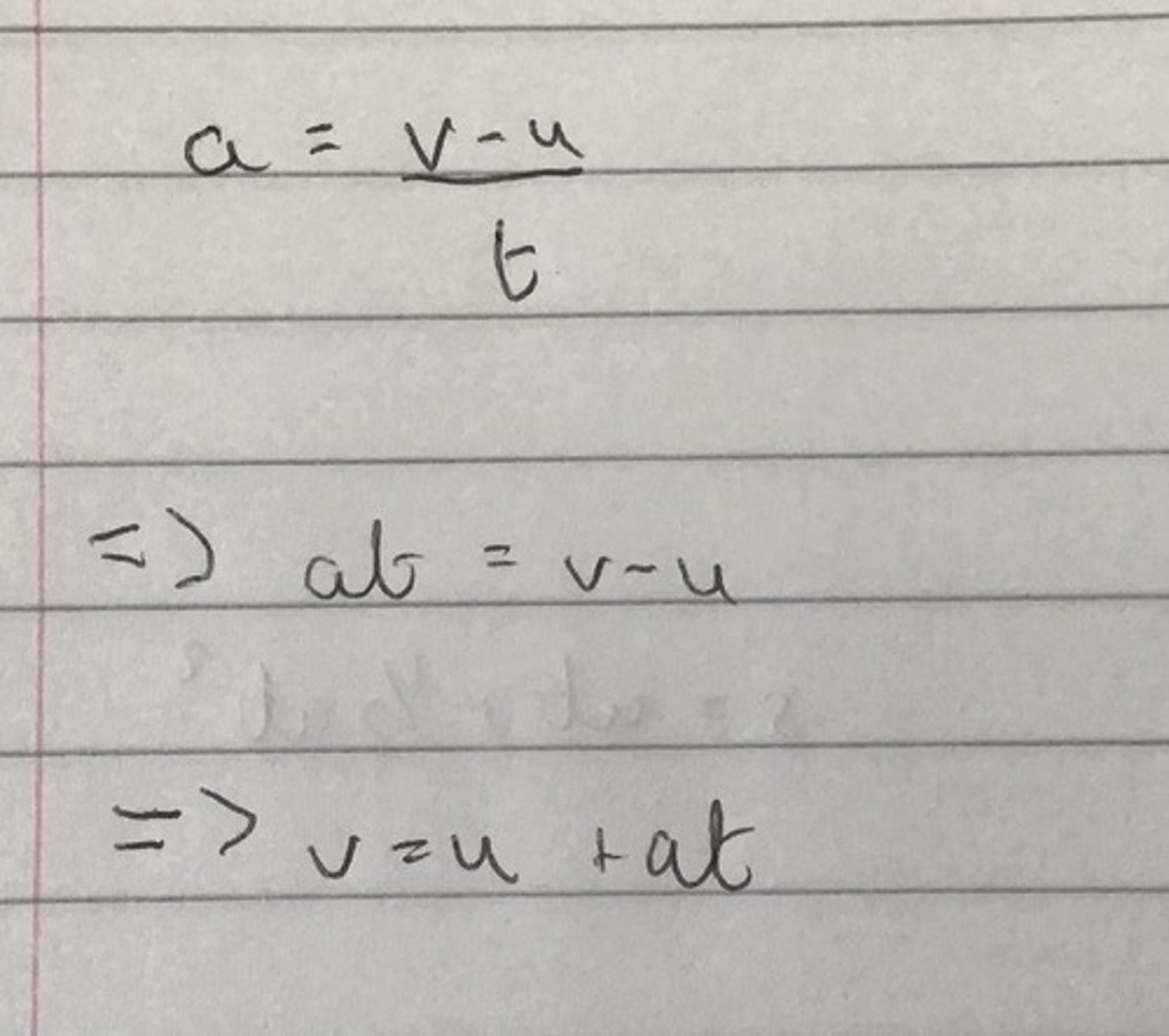
11
New cards
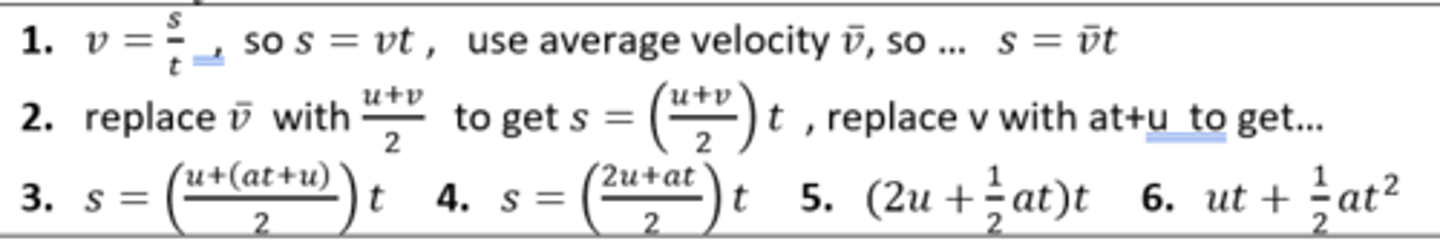
Derive: s = ut + 1/2 at^2
12
New cards
Derive: v^2 = u^2 + 2as