Chemistry - Isotopes and Mass Spectrometry
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different atomic mass
Isotopes properties
-Same atomic number (same element)
-Different mass numbers
-Chemically similar, but may have different physical properties
Isotopes types
-Stable isotopes: Do not decay (e.g., Carbon-12)
-Radioactive isotopes: Unstable, emit radiation (e.g., Carbon-14)
Why sometimes radioactive?
-combination of P+and No does not provide sufficient strong nuclear force to hold the nucleus together indefinitely.
-Eventually it will rearrange itself and emit a particle and radiation as it becomes stable.
Mass spectrometry
-Technique which measures atomic and molecular mass
-Also can be used to find isotopic abundance
Mass Spectrometry allows for:
-Separation of individual isotopes of an element sample
-Determination of the mass of each isotope, relative to C-12
-Calculation of the relative abundances of the isotopes in the sample
Mass spectrometry process
-The sample is vaporised and ionised (allows them to be manipulated by electric and magnetic fields.)
-Ions are accelerated by an electric field and then separated based on their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) using a magnetic or electric field.
-A detector records the number of ions for each mass-to-charge ratio, generating a mass spectrum.
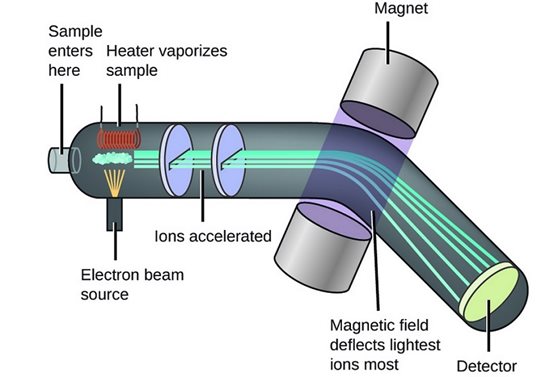
Size of the charge’s impact on deflection
Greater the charge the larger the deflection
mass of particle’s impact on the degree of deflection
Larger the mass the less the deflection
Mass spectra graphs
Output of mass spectrum, peaks for each of the ions that are detected for each ratio
if no scale %abundance
Peak height/total peak heights x 100