River landscapes in the uk
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
course
the path of a river as it flows downhill
describe the course of a river
A steep upper course
A gently sloping middle course
An almost flat lower course
what does the long profile of a river show
how the gradient changes
what do rivers form as they flow downhill
Channels and valleys
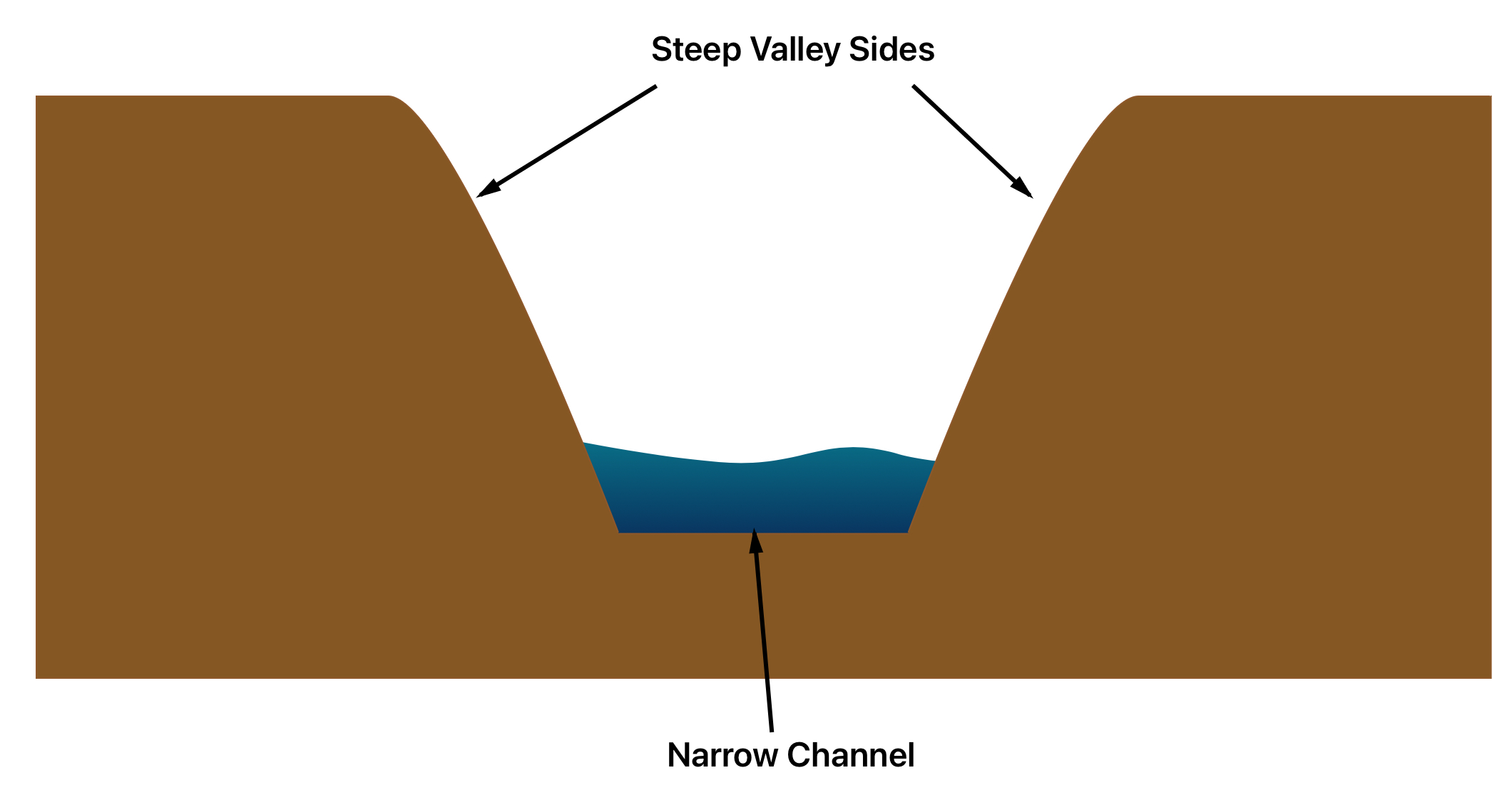
Upper course of a river:
steep gradient
V shaped valley
Narrow, shallow channel
Steep sides
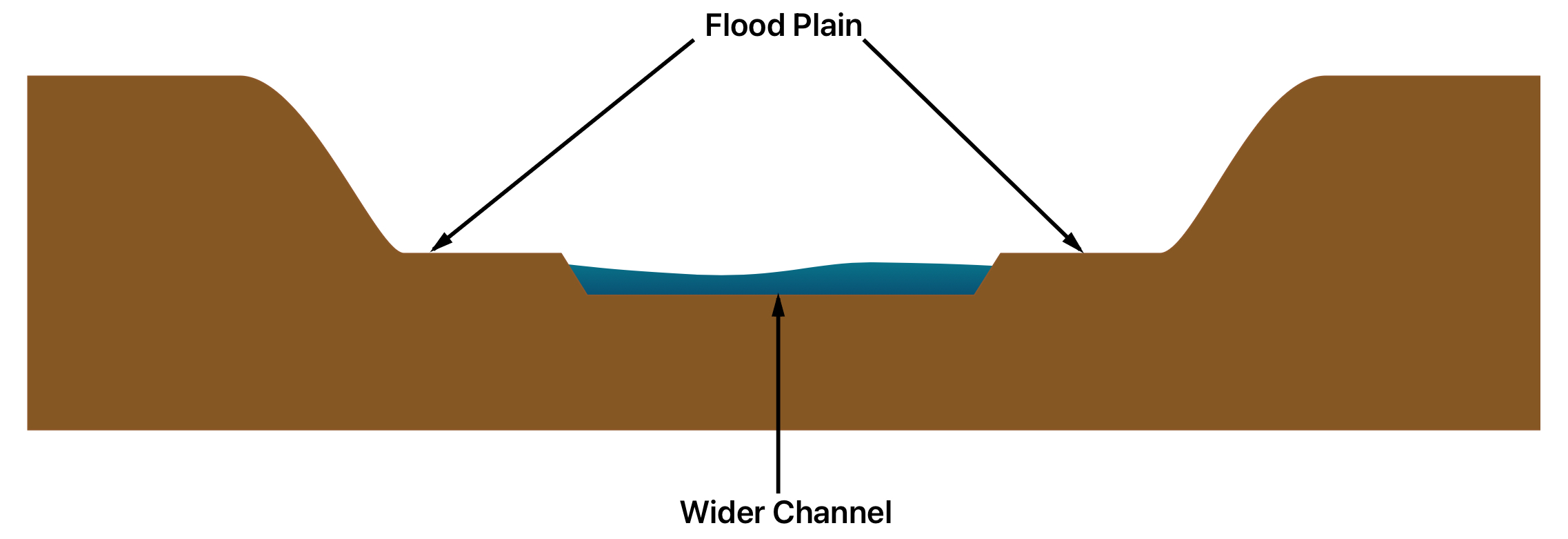
middle course of a river:
medium gradient
Gently sloping valley sides
Wider, deeper channel
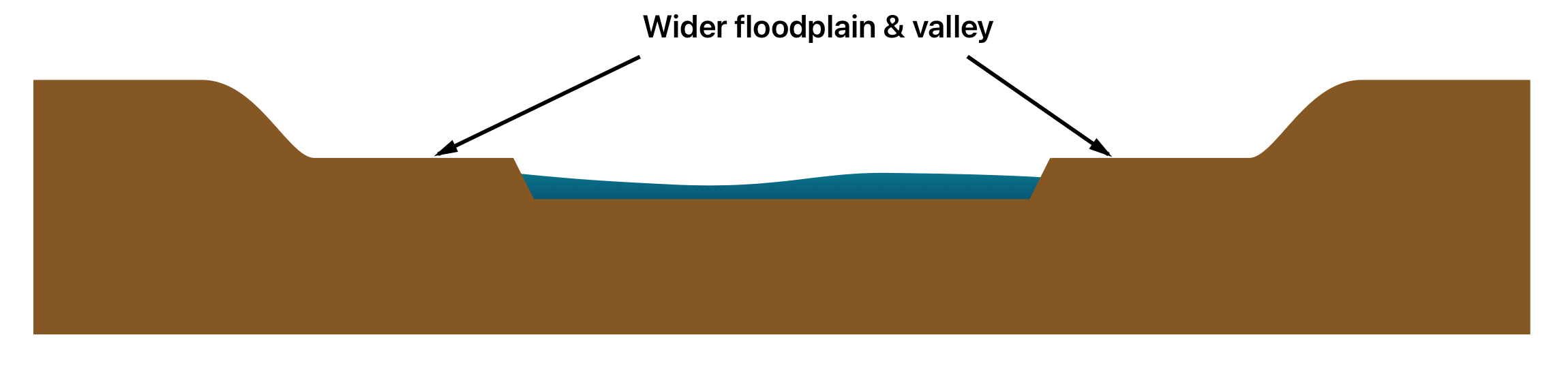
lower course of a river:
gentle gradient
Very wide, almost flat valley
Very wide, very deep channel
Source of a river
Where the river begins
Mouth of a river
where the river flows into a larger body of water
Vertical erosion
deepens the river valley and channel making it v - shaped
Dominant in the upper course of a river
High turbulence causes the rough, angular particles to be scraped along the river bed - causes intense downward motion
lateral erosion
widens the river valley and channel during the formation of meanders
Dominant in the middle and lower courses of the river
hydraulic action
the force of the river water colliding with rocks breaks rock particles away from the river channel
abrasion
eroded rocks picked up by the river, scrape and rub against the channel - wearing it away
attrition
eroded rocks picked up by the river crash into one another and break into smaller pieces
Solution
river water dissolves some types of rock - e.g. chalk and limestone
In what course is erosion dominant in
Upper course
transportation
the movement of eroded material
what does how material is eroded depend on
velocity of the water, size of particles
Traction
Large particles like borders are pushed along the river bed by the force of the water
suspension
small particles like silt and clay are carried along by the water
Saltation
pebble sized particles are bounced along the river bed by the force of the water
solution
Soluble materials e.g. limestone dissolve in the water and are carried along
deposition
when the river drops a material its transporting
when does deposition occur
when the river loses its velocity and energy
reasons why rivers slow down and drop material
the volume of the water falls
The amount of eroded material increases
The water is shallower e.g.the inside of a bend
The river reaches its mouth
where are waterfalls and gorges found?
in the upper course of a river
how are waterfalls and gorges formed?
A layer of hard rock and soft rock are together
Water erodes the soft rock by hydraulic action because it is less resistant
The water makes a plunge pool and an undercut is formed
The hard rock is no longer supported by the soft rock eventually collapsing
( gorge ) - the waterfall retreats overtime and a gorge is formed
Interlocking spurs
hillsides that interlock with each other ( like a zigzag if you looked from above) as the river winds around them
how are interlocking spurs formed
Vertical erosion deepens the river channel
Water can’t cut through hard rock because it is too resistant so it winds around the hills
how are meanders formed?
the current is faster on the outside of the bend because the river channel is less deeper - less friction to slow the water down
More erosion takes place (via abrasion and hydraulic action) on the outside bend, forming river cliffs
The current is slower on the inside of the bend because the river channel is shallower - there’s more friction
Eroded material is deposited on the inside of the bend forming slip off slopes
aerial view of a meander
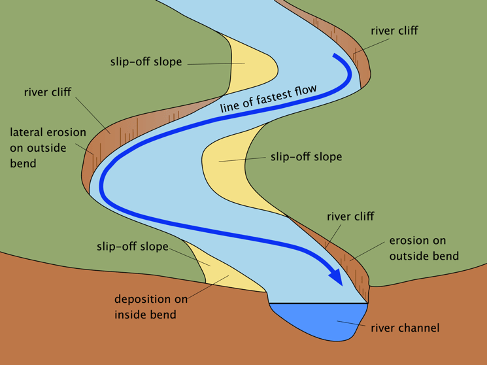
Cross section of a meander

How are ox bow lakes formed?
erosion causes the outside bends to get closer until theres only a small bit of land left - the neck
The river breaks through the neck - usually during a flood
The river flows along the shortest route
Deposition cuts off the meander
An oxbow lake is formed
River that flooded in the Banbury flooding:
River Cherwell
date of Banbury flooding
Easter 1998
cost of damages of Banbury flooding
£12.5 million
lives lost in Banbury flooding
0
people forced to evacuate in Banbury flooding
350
What have the government done to manage the risk of flooding?
roads have been built higher up - so flooding wont disrupt traffic
Embankments and flood walls have been constructed outside businesses and houses of importance
A pumping station to pump any flood water out of the town
Flood water storage - gates can be closed if weather reports show a risk of high rainfall, water will be gradually released downstream to avoid sudden flooding
social effects from the flooding
uninsured houses are at risk because homeowners lose everything and must pay for repairs themselves
Environmental effects from the flooding
During construction of the flood water storage, heavy machinery damaged the nearby vegetation
Soil was removed from areas surrounding Banbury to make enbankments - disrupts habitats and wildlife
(Positive) New biodiversity plan increases vegetation to reduce risk of flooding - will improve the environment
economic effects from the flooding
construction work cost £18.5 million
Construction jobs were created in the process, as well as some jobs to maintain biodiversity plan
Storage scheme has saved £100 million in avoiding damages
river discharge
volume of water flowing in a river per second - measured in cumecs (cubic metres per second - m³/s)
What do hydrographs show
how the discharge at a certain point in a river changes over time in relation to rainfall
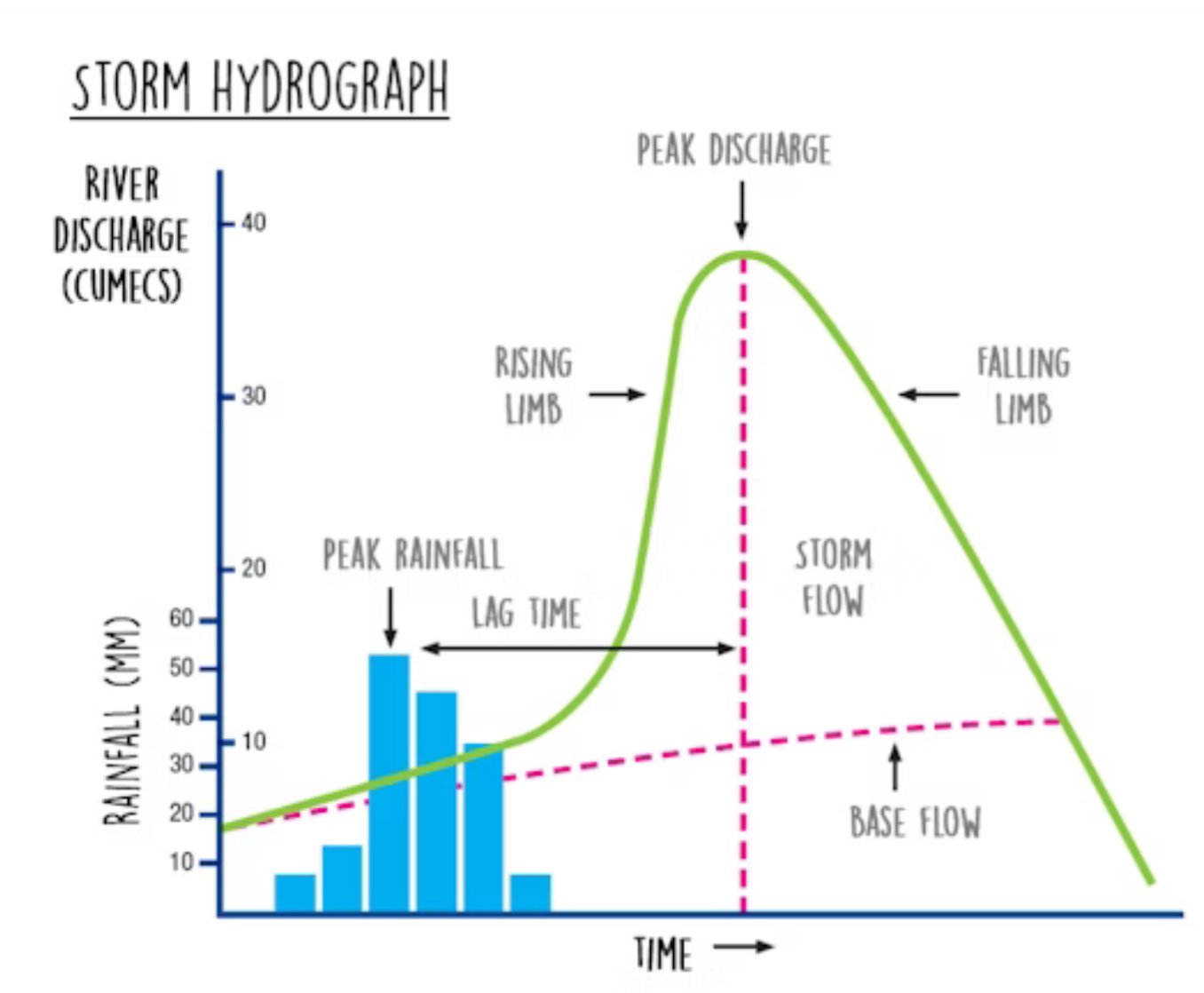
peak discharge : the highest discharge in the period of time you’re looking at
Lag time : the delay between peak rainfall and peak discharge
Rising limb : increase in river discharge as rainwater flows into the river
Falling limb : decrease in river discharge as the river returns to its normal level
how does heavy rainfall affect flood risk
Heavy water means that the water arrives too quickly to infiltrate - a lot of surface runoff which increases discharge
how does rock type affect flood risk?
clay soils and some rocks e.g. granite is impermeable - surface runoff is increasd
How does prolonged rainfall affect flood risk
prolonged rainfall can’t saturate the soil - further rainfall can’t saturate, runoff is increased
how does relief (changes in land height) affect flood risk
if a river is in a steep sided valley water will reach the river channel quicker because it will travel down the steeper slopes faster - rapidly increases discharge
Engineering
reduce the risk of flooding or its effects
hard engineering
Man made structures built to control the flow of rivers and reduce flooding
Dams and reservoirs
dams are barriers built across the river - usually in the upper course
A reservoir (Artificial lake) is formed behind the dam
benefits of dams and reservoirs
reservoirs store water (e.g. after heavy rain), control water flow, and prevent floods downstream
Can be used to generate hydroelectric power
Disadvantages of dams and reservoirs
very expensive
Can flood existing settlements
Material is deposited in the reservoir - farmland downstream can become less fertile
channel straightening
meanders are removed by building straighter, artificial channels
benefits of channel straightening
water leaves the area faster rather than building up so flood risk is lower
disadvantages of channel straightening
Flooding may happen downstream instead
Faster moving water may cause more erosion downstream
Embankments
Raised walls are built along river banks
Benefits of embankments
river can hold more water - floods are less frequent
disadvantages of embankments
expensive
Risk of severe flooding if water rises above level of embankments or if they break
Flood relief channels
channels are built to divert water around built up areas e.g infrastructure or to divert excess water from a river if the levels get too high
benefits of flood relief channels
gates on the channels mean that the release of water can be controlled - reduces flood risk
disadvantages of flood relief channels
increases discharge where the relief channels rejoins the river or another river - will cause flooding
soft engineering
schemes set up using knowledge of a river and its processes to reduce the effects of flooding
flood warnings and preparation
Environmental agency issues flood warnings through media
Buildings are modified to minimise flood damage
Residents can prepare sandbags and flood boards prior to floods
advantages of flood warnings and preparation
warnings give people time to move possessions or evacuate - reduces the impact of flooding
disadvantages of flood warning and preparation
doesnt prevent floods
Some people may not have access to the warnings
Modifying buildings is expensive
Doesn’t guarantee safety from a flood
Flood plain zoning
restrictions prevent buildings on a parts of a flood plain that are likely to be affected by a flood
Advantages of flood plain zoning
flood risk is reduced - fewer impermeable surfaces are created
impact of floodings are reduces - no buildings at risk of damage
Disadvantages of flood plain zoning
cant help in an area with existing buildings
Planting trees
increases interception of rain water (and lag time)
adv of planting trees
discharge and flood risk decrease
vegetation reduces soil erosion in the valley
provides better habitats for wildlife
Disadvantages of planting trees
less land is available for farming
river restoration
making the rive rmore natural - e.g. removing man made levees so that the flood plain can flood naturally
adv of river restoration
discharge is reduced - less risk of flooding downstream
little maintenance needed
better habitats for wildlife
disadvantages of river restoration
local flood risk can increase