BIO FINAL EXAM (Cumulative Portion)
5.0(3)
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes confirmed essay questions that will appear on the final, as well as questions answered from the outlines we were provided.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
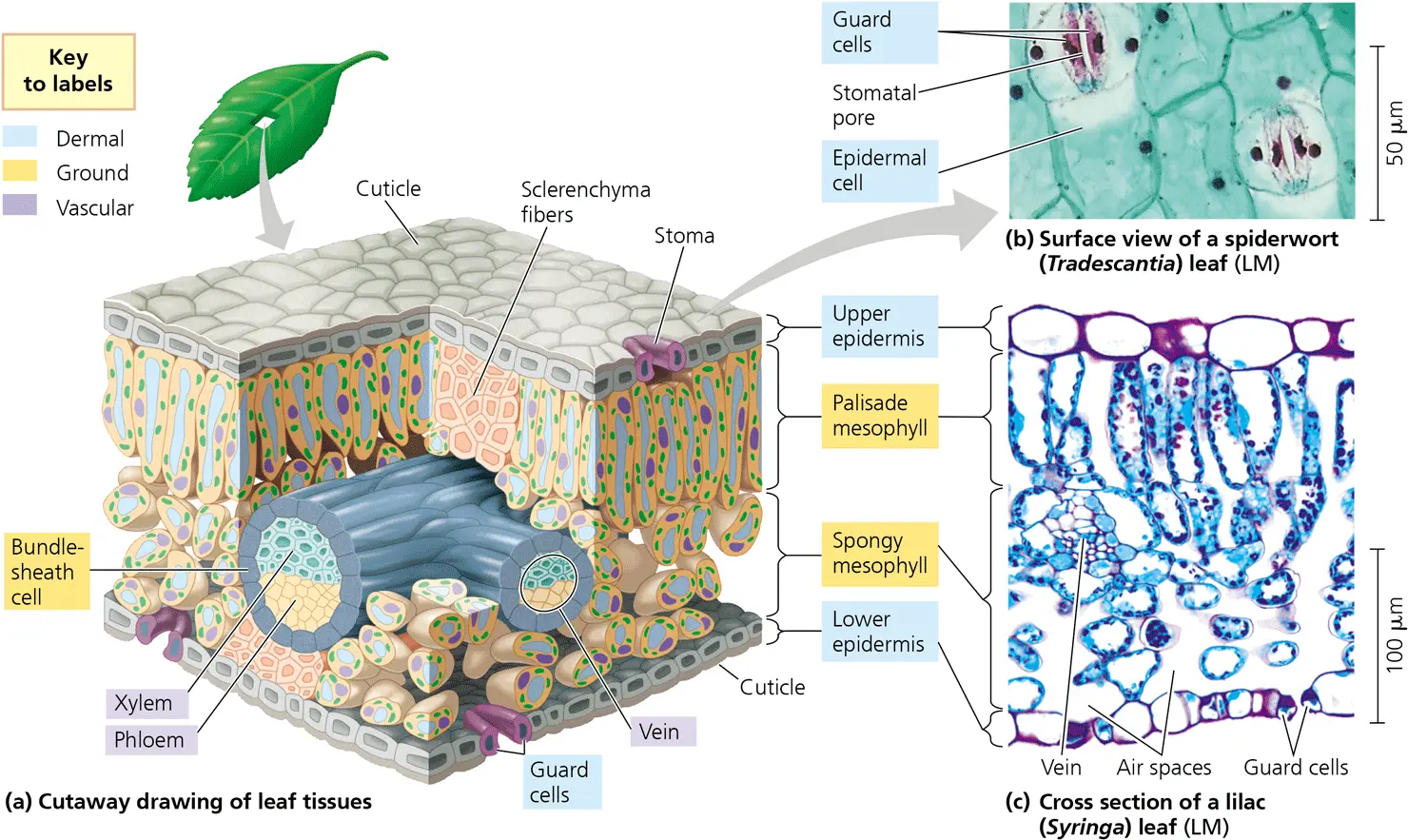
Describe the leaf and how it’s structure facilitates Photosynthesis. (35.18) GOOD ESSAY! (EDIT)
Dermal Tissue - Outer layer includes cuticle for protection, and guard-cell stomata combinations to selectively let certain nutrients and gases in including CO2 required for Photosynthesis to occur.
\
Ground Tissue - spongy level, thick collenchyma support in middle of structure, and parenchyma mesophyll in middle layer that has tightly packed chloroplasts that utilize a high SA:V ratio for efficient capturing of light for photosynthesis
\
Vascular Tissue - has xylem & phloem, xylem transports water required for photosynthesis and raw materials/nutrients around the plant, while phloem conducts sugars (products of photosynthesis), transports it throughout cell for an overall benefit
\
Ground Tissue - spongy level, thick collenchyma support in middle of structure, and parenchyma mesophyll in middle layer that has tightly packed chloroplasts that utilize a high SA:V ratio for efficient capturing of light for photosynthesis
\
Vascular Tissue - has xylem & phloem, xylem transports water required for photosynthesis and raw materials/nutrients around the plant, while phloem conducts sugars (products of photosynthesis), transports it throughout cell for an overall benefit
2
New cards
What are the key testable observations and two outcomes that comprise Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection? How do they relate to the concept of adaptation? Clearly state his theory. (ESSAY)
observations: traits are heritable, there is not enough resources to support population (competition is evident, not all will survive and reproduce), traits impact organism’s survival and reproduction. Relates to adaptation because only those with favored traits who adapted to their environment will be able to further survive, this is the theory of natural selection.
Outcomes: offspring act and or behave like parents (traits were passed), offspring better fit environment given respective pressures. Relates to adaptation because offpsring show evidence of having traits from parents that were better fit and adapted to their environment to survive.
Outcomes: offspring act and or behave like parents (traits were passed), offspring better fit environment given respective pressures. Relates to adaptation because offpsring show evidence of having traits from parents that were better fit and adapted to their environment to survive.
3
New cards
Define Natural Selection
those in an environment who are best fit given their environmental pressures are more likely to survive and reproduce
4
New cards
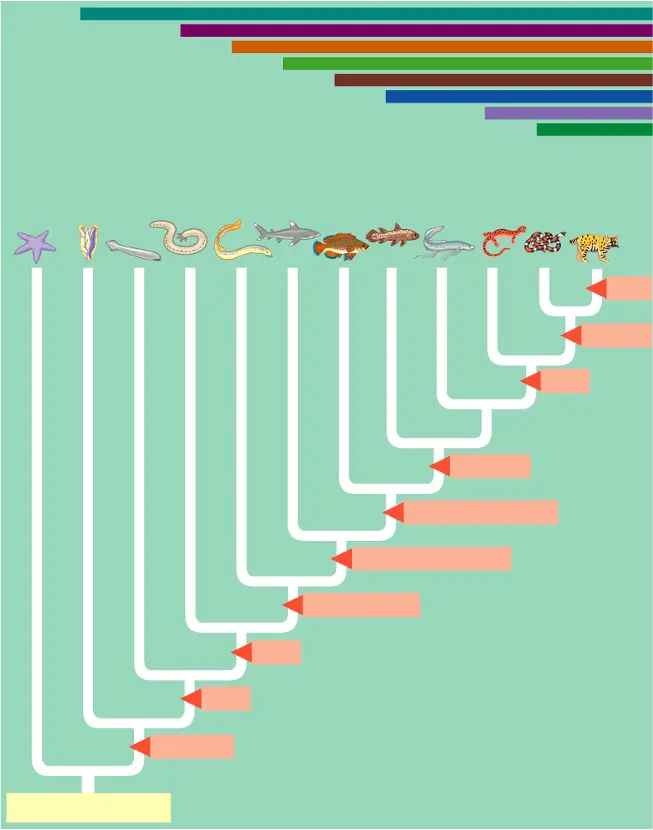
\
Fill in from bottom left to top right, then name species left to right
Fill in from bottom left to top right, then name species left to right
ancestral deuterostome, notochord, brain, head, vertebral column, jaws/mineralized skeleton, lung & lung derivatives, lobed fins, legs, amniotic egg, milk.
organisms: echinodermata, Urochordata, lancelets, hagfishes, lampreys, chondrichytes, ray-finned fishes, coelacanth, lungfishes, amphibians, reptiles, mammals
organisms: echinodermata, Urochordata, lancelets, hagfishes, lampreys, chondrichytes, ray-finned fishes, coelacanth, lungfishes, amphibians, reptiles, mammals
5
New cards
What are the major lines of support for evolution, before and after Darwin? (potential essay) (6 Before, 4 after)
Before: Malthus theory of overpopulation (Darwin used this to justify competition),
\
Lamarke Baptiste incorrect hypothesis that traits gained throughout life are directly passed to offspring (darwin used this to develop natural selection over time theory),
\
Linneaus Taxonomy and Aristotle Scala Naturai gave Darwin precedent to earth-being classifications,
\
Hutton Lyell also helped Darwin see through uniformitarianism that formation of earth’s geographical features is done in processes seen today,
\
artificial selection as humans could selectively pass down traits in an organism to future generations,
\
Galapagos Island Voyage showed adaptations amongst different islands
\
After: Drug Resistance by bacteria over time, and Guppies and finches adapting to their environments, molecular discovery, and homology.
\
Lamarke Baptiste incorrect hypothesis that traits gained throughout life are directly passed to offspring (darwin used this to develop natural selection over time theory),
\
Linneaus Taxonomy and Aristotle Scala Naturai gave Darwin precedent to earth-being classifications,
\
Hutton Lyell also helped Darwin see through uniformitarianism that formation of earth’s geographical features is done in processes seen today,
\
artificial selection as humans could selectively pass down traits in an organism to future generations,
\
Galapagos Island Voyage showed adaptations amongst different islands
\
After: Drug Resistance by bacteria over time, and Guppies and finches adapting to their environments, molecular discovery, and homology.
6
New cards
What are domains? How do they improve classification?
domains are the highest level of classification for living organisms, groups them based on cellular structures. Provides more accurate representation of life on earth by providing a more specific evolutionary relationship that was generalized in the 5 kingdom system.
7
New cards
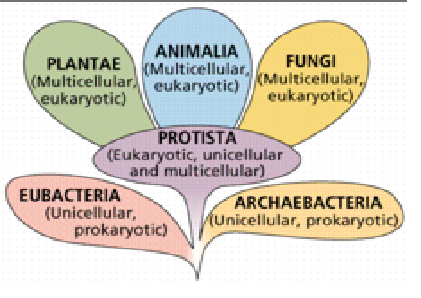
Relate Bacteria, Archea, Eukaryotes, and Protista, in the base of the tree of life.
\
early divergence of tree of life: Bacteria, archaea, and then eukaryotes branched from archae, includes: protists, plants, animals, fungi
early divergence of tree of life: Bacteria, archaea, and then eukaryotes branched from archae, includes: protists, plants, animals, fungi
8
New cards
Define Cladistics
\
classification of plants and animals depending on the amount of characteristics they share in common
classification of plants and animals depending on the amount of characteristics they share in common
9
New cards
What is the Biological Species concept?
(add what is a strength, and weakness of it?
\
\
define species on the criteria of whether or not they can breed with each other and produce fertile offpsring
\
strengths: defined, evolutionary base, gene pools and populations. Weaknesses: what is normal? This cannot be applied to asexual species (such as bacteria)
\
define species on the criteria of whether or not they can breed with each other and produce fertile offpsring
\
strengths: defined, evolutionary base, gene pools and populations. Weaknesses: what is normal? This cannot be applied to asexual species (such as bacteria)
10
New cards
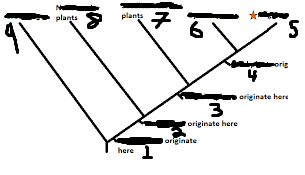
Name 1-9
\
1. green plants
2. land plants
3. vascular plants
4. seed plants
5. angiosperms
6. gymnosperms
7. seedless vascular plants
8. nonvascular plants
9. green algae
1. green plants
2. land plants
3. vascular plants
4. seed plants
5. angiosperms
6. gymnosperms
7. seedless vascular plants
8. nonvascular plants
9. green algae
11
New cards
Define Protostome
\
\
animals where mouth develops from the first opening in developing embryo (blastopore). includes; arthopods, mollusks, annelids
animals where mouth develops from the first opening in developing embryo (blastopore). includes; arthopods, mollusks, annelids
12
New cards
Define Deuterostome
anus develops from blastopore, mouth from second opening. ex: echinoderms, chordates, etc
13
New cards
what is and role of blastula in animal development
\
early stage in the development of animal embryo, divides fewer cells until gastrula is formed, hollow ball of cells
early stage in the development of animal embryo, divides fewer cells until gastrula is formed, hollow ball of cells
14
New cards
\
role of gastrula in animal development
role of gastrula in animal development
\
next stage after blastula, begins tissue layer, a ball within a ball
next stage after blastula, begins tissue layer, a ball within a ball
15
New cards
Define Coelom
fluid filled body cavity surrounded by mesoderm tissue, provides space for internal organs to develop and move independently of the body wall
16
New cards
Bacteria characteristics (domain 1)
prokaryotic, lack nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Diverse and widespread compared to archaebacteria, can inhabit multiple environments.
17
New cards
Archae characteristics (domain 2)
prokaryotic, lack nucleus and membrane bound organelles, found in extreme environments, like hotsprings, salt flats, etc.
18
New cards
Eukaryotes characteristics (domain 3)
contain nucleus and membrane bound organelles, have a cytoskeleton. include: animals, plants, fungi, protists.
19
New cards
Protista characteristics (domain 4)
do not fit neat into any other category. include unicellular organisms: amoebas, paramecia. also multicellular organisms like seaweed and kelp. most diverse eukaryotic group
20
New cards
Define Synapomorphy
\
shared derived characteristics
shared derived characteristics
21
New cards
Define monophyly
a group that shares an ancestor and all of its descendant species
22
New cards
\
5 synanyphmorphies/chordate characteristics (great essay)
5 synanyphmorphies/chordate characteristics (great essay)
\
notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits or clefts, muscular post anal tail, thyroid
notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits or clefts, muscular post anal tail, thyroid
23
New cards
function of notochord
\
basis for endoskeleton, flexible rod
basis for endoskeleton, flexible rod
24
New cards
function of dorsal hollow nerve cord
\
extends length of the body throughout embryonic development
extends length of the body throughout embryonic development
25
New cards
function of pharyngeal slits or clefts
\
originally for filter feeding, modified into gill slits for respiration, becomes structures of head and neck for many vertebrates
originally for filter feeding, modified into gill slits for respiration, becomes structures of head and neck for many vertebrates
26
New cards
function of muscular post anal tail
\
chordates have tail extending beyond anus, some lose tail during development (like frogs and humans)
chordates have tail extending beyond anus, some lose tail during development (like frogs and humans)
27
New cards
function of thyroid
found in neck of vertebrates, produces hormones for regulating metabolic processes in body
28
New cards
\
What is the difference between a regulator and a conformer, what is the advantage of each?
What is the difference between a regulator and a conformer, what is the advantage of each?
\
regulators control and maintain a constant internal temperature regardless of changing environment, while conformers allow internal body temperature to change in response to changing environment
\
ADVANTAGE: regulators can live in a wide range of environments, but have to use a lot of energy for homeostasis. Conformers are more energy efficient, but can only live in limited environments
regulators control and maintain a constant internal temperature regardless of changing environment, while conformers allow internal body temperature to change in response to changing environment
\
ADVANTAGE: regulators can live in a wide range of environments, but have to use a lot of energy for homeostasis. Conformers are more energy efficient, but can only live in limited environments
29
New cards
\
Define Endotherm/Ectotherm. Homeotherm/Poikilotherm
Define Endotherm/Ectotherm. Homeotherm/Poikilotherm
Endotherm - body heat derived from metabolism
Ectotherm - body heat derived from environment
Homeotherm - body temperature remains constant
Poiklotherm - body temperature fluctuates with environment
Ectotherm - body heat derived from environment
Homeotherm - body temperature remains constant
Poiklotherm - body temperature fluctuates with environment
30
New cards
\
Distinguish between hibernation and torpor and their role in Energy Management.
Distinguish between hibernation and torpor and their role in Energy Management.
\
Hibernation is a long-term state of reduced metabolism and lowered body temperature that some animals enter during the winter months when food is scarce. Torpor, on the other hand, is a short-term state of reduced metabolism and body temperature that some animals enter during times when food is temporarily scarce, such as during the night.
Hibernation is a long-term state of reduced metabolism and lowered body temperature that some animals enter during the winter months when food is scarce. Torpor, on the other hand, is a short-term state of reduced metabolism and body temperature that some animals enter during times when food is temporarily scarce, such as during the night.
31
New cards
\
What are the terms associated with describing locations with each symmetry?
What are the terms associated with describing locations with each symmetry?
bilateral: Cephalization, left and right mirror images, dorsal, ventral. anterior, posterior, proximal, distal
\
radial: oral, aboral, proximal, distal
\
radial: oral, aboral, proximal, distal
32
New cards
\
three tissue germ layers, and their organs
three tissue germ layers, and their organs
endoderm: gut, liver, lungs
mesoderm: skeleton, muscle, kidney, heart, blood
ectoderm: skin, nervous system
mesoderm: skeleton, muscle, kidney, heart, blood
ectoderm: skin, nervous system
33
New cards
\
What are the four major tissue types in animals?
What are the four major tissue types in animals?
\
epithelial tissue: surface of body
connective tissue: supports and connects tissues and organs in body (bone, cartilage, blood)
Muscular Tissue: movement and mechanical work
nervous tissue: communication and coordination in body
epithelial tissue: surface of body
connective tissue: supports and connects tissues and organs in body (bone, cartilage, blood)
Muscular Tissue: movement and mechanical work
nervous tissue: communication and coordination in body
34
New cards
\
What are the Ancestors of Plants
What are the Ancestors of Plants
\
ancestral green algae, land plants, vascular plants, extant seed plants
ancestral green algae, land plants, vascular plants, extant seed plants
35
New cards
3 major groups of bryophytes, what do they lack? and what is their significance?
\
liverworts, mosses, hornworts
\
lack true vascular tissues (depend on water) for reproduction, so they have a small size
\
colonize sterile soil, absorb water and nutrients, and contribute to new soils for ecosystems to begin on
liverworts, mosses, hornworts
\
lack true vascular tissues (depend on water) for reproduction, so they have a small size
\
colonize sterile soil, absorb water and nutrients, and contribute to new soils for ecosystems to begin on
36
New cards
\
Ferns are define by what they have (2)___________ and what they lack ___________ (1)
Ferns are define by what they have (2)___________ and what they lack ___________ (1)
\
vascular tissue and roots, seeds (use spores instead)
vascular tissue and roots, seeds (use spores instead)
37
New cards
\
What are the four groups of Fern like plants?
What are the four groups of Fern like plants?
\
Club Mosses, Ferns, Horsetails, Whisk Ferns
Club Mosses, Ferns, Horsetails, Whisk Ferns
38
New cards
What are the four Major groups of gymnosperms?
\
\
\
Cycadophyta, Gnetophyta, Ginkgophyta, coniferophyta
Cycadophyta, Gnetophyta, Ginkgophyta, coniferophyta
39
New cards
\
What are the traits gymnosperms have that previous plant groups lack, what plant characteristics do they lack?
What are the traits gymnosperms have that previous plant groups lack, what plant characteristics do they lack?
\
They produce seeds that are naked (no protective ovary wall), and they lack pistils and stamens
They produce seeds that are naked (no protective ovary wall), and they lack pistils and stamens
40
New cards
\
What is an Angiosperm?
What is an Angiosperm?
\
a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure- a fruiting plant
a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure- a fruiting plant
41
New cards
\
What Shared Derived traits define Angiosperm?
What Shared Derived traits define Angiosperm?
\
endosperm present within seeds, production of fruit that contains seeds
endosperm present within seeds, production of fruit that contains seeds
42
New cards
\
Besides some “primitive groups” what are the two major groups of angiosperms
Besides some “primitive groups” what are the two major groups of angiosperms
\
monocots and dicots
monocots and dicots
43
New cards
\
What are important animal milestones that are represented in the following groups, and what is common name: Porifera
\
parazoans, 1 phylum, sponges, filter feeding
parazoans, 1 phylum, sponges, filter feeding
44
New cards
\
What are important animal milestones that are represented in the following groups, and what is common name: cnidaria
What are important animal milestones that are represented in the following groups, and what is common name: cnidaria
\
eumetazoans, diploblastic, have forms of polyp and medusa, include medusazoans (jellyfish), and anthozoans (coral and sea anemones)
eumetazoans, diploblastic, have forms of polyp and medusa, include medusazoans (jellyfish), and anthozoans (coral and sea anemones)
45
New cards
\
lophotrochozoans significance + what is it named for?
\
most diverse animals, include: mollusks, segmented worms, flatworms, named from lophophore feeding structure, and trochophore larvae stage
most diverse animals, include: mollusks, segmented worms, flatworms, named from lophophore feeding structure, and trochophore larvae stage
46
New cards
\
ecdysozoans significance + what is it named for?
ecdysozoans significance + what is it named for?
\
external cuticle or exoskeleton, three major groups: Nematoda, arthropoda, other phyla, most species rich group: crustaceans and insects. Ecdysis named for molting
external cuticle or exoskeleton, three major groups: Nematoda, arthropoda, other phyla, most species rich group: crustaceans and insects. Ecdysis named for molting
47
New cards
\
echinodermata
echinodermata
\
spiny skin, 5 groups: sea stars (starfish), brittle stars, sea urchins/sand dollars, crinoids, sea cucumbers
spiny skin, 5 groups: sea stars (starfish), brittle stars, sea urchins/sand dollars, crinoids, sea cucumbers
48
New cards
Describe the basic relationship of the major invertebrate groups (Sponges, Cnidarians, Locotrocophores, Ecdysozoans and echinoderms) - what is the order of which they evolved (earliest to newest)?
sponges, cnidarians, locotrocophores, ecdysozoans, and echinoderms