Nomenclature Primer — Hydrocarbons
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary related to hydrocarbon nomenclature, including alkane naming conventions, IUPAC rules, branched alkanes, common prefixes, types of carbon atoms, and cyclic hydrocarbons.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Nomenclature
A system of naming chemical compounds, particularly in organic chemistry.
Alkanes
Hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2 and the suffix –ane, characterized by single bonds between carbon atoms.
Methane (CH4)
A linear alkane with 1 carbon atom.
Ethane
A linear alkane with 2 carbon atoms.

Propane
A linear alkane with 3 carbon atoms.
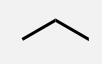
Butane
A linear alkane with 4 carbon atoms.
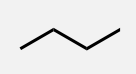
Pentane
A linear alkane with 5 carbon atoms.
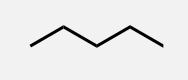
Hexane
A linear alkane with 6 carbon atoms.
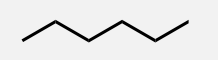
Heptane
A linear alkane with 7 carbon atoms.
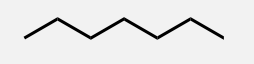
Octane
A linear alkane with 8 carbon atoms.
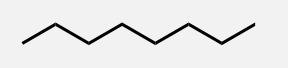
Nonane
A linear alkane with 9 carbon atoms.
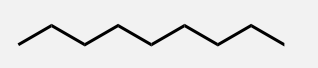
Decane
A linear alkane with 10 carbon atoms.
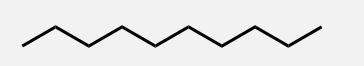
Greek prefixes (>5 carbons)
Used for alkanes with five or more carbon atoms (e.g., pent-, hex-, hept-).
IUPAC Rules
A systematic method for naming chemical compounds established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
Alkyl chain (substituent)
A branch off a main carbon chain; named by dropping the –ane suffix from the corresponding alkane and adding –yl (e.g., ethyl).
Ethyl group (CH3CH2–)
A substituent containing two carbon atoms, named by dropping the –ane suffix from ethane and adding –yl.
di-, tri-, tetra-
Prefixes used when the same substituent appears more than once on a carbon chain, indicating two, three, or four occurrences, respectively.
Alphabetical listing of substituents
Rule stating that when substituents are not identical, they are listed alphabetically in the compound's name, with hyphens separating different substituents.
n- (normal) prefix
A common naming convention used for straight-chain alkanes (e.g., n-propane, n-pentane).
iso- prefix
A common naming convention used for alkanes with one branching methyl group (e.g., isobutane, isopentane).
neo- prefix
A common naming convention used for alkanes with two branching methyl groups (e.g., neopentane, neohexane).
Primary carbon (1°)
A carbon atom attached to only one other carbon atom.
Secondary carbon (2°)
A carbon atom attached to two other carbon atoms.
Tertiary carbon (3°)
A carbon atom attached to three other carbon atoms.
Quaternary carbon (4°)
A carbon atom attached to four other carbon atoms.
Methyl carbon
A carbon atom attached to three hydrogen atoms (typically a 1° carbon in an end group).
Methylene carbon
A carbon atom attached to two hydrogen atoms (typically a 2° carbon in a chain).
Methine carbon
A carbon atom attached to one hydrogen atom (typically a 3° carbon at a branch point).
Cyclo- prefix
Used in naming rings, indicating a cyclic hydrocarbon structure (e.g., cyclopropane, cyclohexane).
Cycloalkane (CnH2n)
A class of cyclic hydrocarbons where carbon atoms are arranged in a ring, having the general formula CnH2n.
the–ane drop and add –yl
As with alkyl chains, rings may also be substituents off a carbon chain. We again drop the–ane and add –yl to get cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, etc.
Cyclopropane
A three-carbon cycloalkane with the chemical formula C3H6, known for its ring structure.

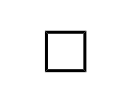
Cyclobutane
A four-carbon cycloalkane with the chemical formula C4H8, characterized by its square-shaped ring structure.
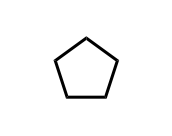
Cyclopentane
A five-carbon cycloalkane with the chemical formula C5H10, recognized for its pentagonal ring structure.
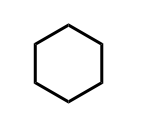
Cyclohexane
A six-carbon cycloalkane with the chemical formula C6H12, featuring a hexagonal ring structure.