Microscopy
1/36
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What type of image does a light microscope produce?
2D coloured image of whole cells or tissues;
limited resolution.
What type of image does a transmission electron microscope (TEM) produce?
High-resolution
2D
black and white image of internal ultrastructure.
What type of image does a scanning electron microscope (SEM) produce?
3D
black and white image of the cell surface.
Why does TEM have higher resolution than light microscopes?
Electrons have a shorter wavelength than visible light.
Why can’t living specimens be viewed with TEM or SEM?
Specimens must be placed in a vacuum and undergo complex preparation which kills them.
When would you use a light microscope instead of an electron microscope?
When observing living specimens, colour images, or needing simple preparation.
How do you prepare a wet mount slide?
Place drop of water on slide
add thin specimen
lower cover slip at angle to avoid air bubbles.
How do you prepare a dry mount slide?
Place solid specimen directly on slide
add cover slip; used for hair, pollen, insect parts.
What is the function of an eyepiece graticule?
Acts as a ruler in the eyepiece with graticule units; used to measure specimens.
What is the function of a stage micrometer?
A slide with a known scale (in µm) used to calibrate the eyepiece graticule.
How do you calibrate an eyepiece graticule with a stage micrometer?
Align scales
count how many graticule divisions = known micrometres
calculate value of one graticule division.
Why must calibration be repeated for each objective lens?
Because magnification changes the scale of the image.
What is staining in microscopy?
Adding coloured chemicals to specimens to increase contrast and highlight structures.
What is differential staining?
Using more than one stain to distinguish between different structures or cell types.
Why must specimens be thin for light microscopy?
So light can pass through for a clear image.
What is a photomicrograph?
A photograph taken through a microscope.
What is expected in biological drawings of cells under the light microscope?
Clear lines, no shading, proportionally accurate, labelled with annotated structures.
State the magnification formula.
Magnification = size of image ÷ size of real object.
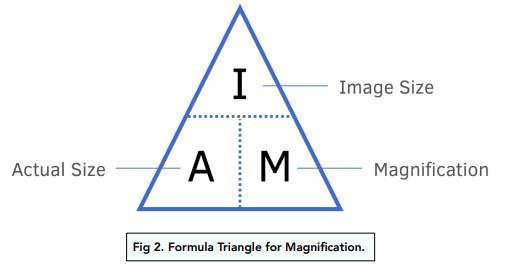
How do you convert millimetres (mm) to micrometres (µm)?
Multiply by 1000.
How do you convert micrometres (µm) to nanometres (nm)?
Multiply by 1000.
How do you convert micrometres (µm) to millimetres (mm)?
Divide by 1000.
How do you convert nanometres (nm) to micrometres (µm)?
Divide by 1000.
What is magnification?
How many times larger the image is compared to the actual specimen.
What is resolution?
The ability to distinguish two points as separate (level of detail).
What is the difference between magnification and resolution?
Magnification enlarges the image; resolution determines how clear and detailed it is.
Which has the lowest resolution: light, TEM, or SEM?
Light microscope.
Which two microscopes use electrons instead of light?
TEM and SEM.
Why are light microscopes still useful despite lower resolution?
They are quick, cheap, allow live specimens, and can show colour.
What is an artefact?
A structural detail or feature in an image that isn’t a true part of the specimen but instead results from the process of sample preparation
The resolving power of a microscope is a measure of its ability to distinguish between _____
Two adjacent objects as separate objects
What is the purpose of the coarse focus knob?
Rapidly moves the stage up and down
What is the purpose of the eyepiece in a microscope?
Magnify the image
What stains DNA/ RNA
Methylene blue
Whats stains cytoplasm into what colour
Eosin
pink
What stains starch into what colour
Iodine
blue-black
What stains bacterial walls?
Crystal Violet
lowest to highest resolution in microscopes?
Light microscope → scanning electron microscope → transmission electron microscope