Week 3 Progressive Waves
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
progressive wave
a type of wave that transfers energy without transfering matter (only disturbs), can be longitudinal or transverse waves
what are the two types of waves
mechanical and electromagnetic waves
mechanical waves
needs material or medium to travel through (cannot exist in vacuum), can be transverse or longitudinal (ex. voice [needs air], instrument sounds[needs air], ocean waves [needs water])
electromagnetic waves
do not need medium (can exist in vacuum), always are transverse (ex. radio frequency, visible colors)
what is being disturbed in the air that allows sound to transfer (ex.voice)
pressure in the air
transverse wave
disturbances (or vibrations) are perpendicular to the direction of the wave
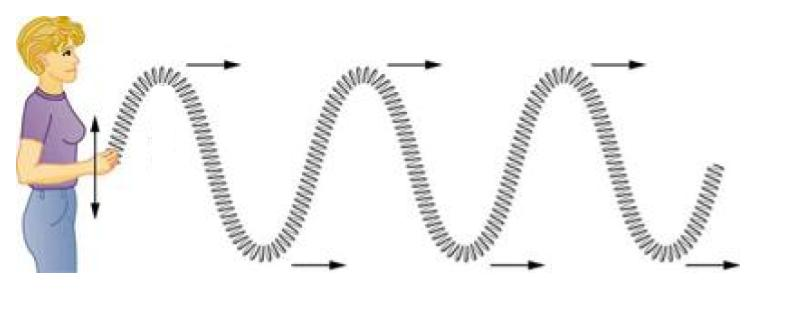
longitudinal wave
disturbance (or vibrations) are parallel to the direction of the wave

wave frequency
the number of waves that pass a fixed point in a given amount of time
what is the SI unit for wave frequency
Hertz (Hz)
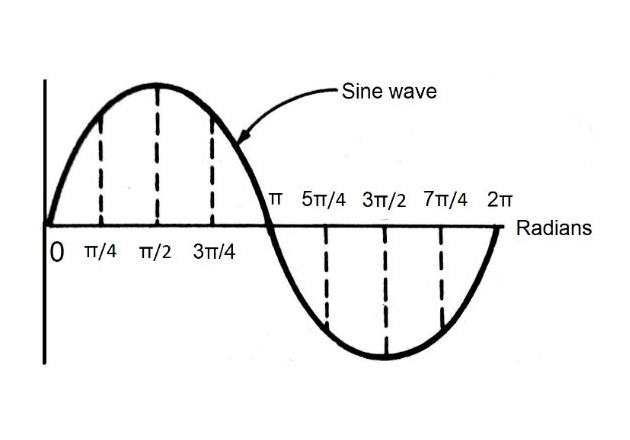
radian
SI unit of angular measurement (rad); an arc of a circle with the same length as the radius of that circle, like degrees
what are the 2 features common to all waves
a wave is a travelling disturbance and carries energy from place to place
what is the SI unit for wavelength
meters (m)
what is the equation to find frequency of a wave?
f=1/T, where f=frequency(Hz) and T=period (seconds)
how do you convert radians to degrees and vice versa?
degrees x π/180 = radian
radian x 180/π = degrees
1 cycle/wavelength is equal to how many radians?
2π
what is the equation used to find wave speed?
v=fλ, where v=speed(m/s), f=frequency(Hz), and λ=wavelength(m)
or
v=1/T(λ), where T=period(seconds)
periodic waves
consist of cycles or patterns that are reproduced over and over again by the source
what are the 4 different wave interactions?
reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference
constructive interference
A crest / trough or condensation / rarefaction of one wave is positioned with the crest / trough or condensation / rarefaction of the other wave (in phase). results in amplitude of the wave thats the sum of the two waves.
deconstructive interference
A crest / condensation of one wave is positioned with the trough / rarefaction of the other wave and vice versa (out of phase). results in the waves canceling each other out leaving only a constant air pressure
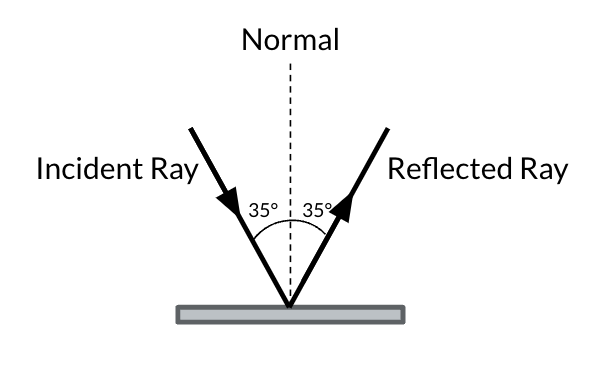
reflection wave
when a wave bounces off a surface, staying in its original medium
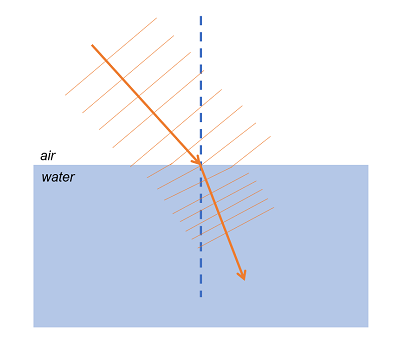
refraction wave
the change in direction of a wave, such as light or water waves, as it passes from one medium to another, happens because the wave's speed changes at the boundary between the two materials
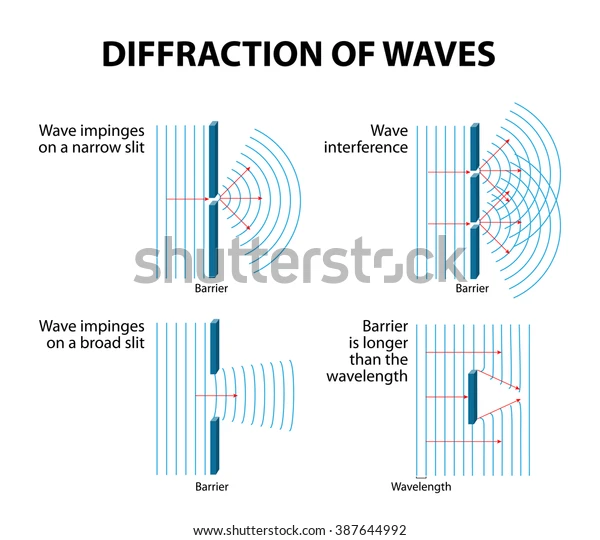
diffraction wave
the spreading out of waves as they pass through a gap or around an obstacle
water wave
not transverse or longitudinal, instead combines both and move on nearly circular paths
what determines the speed of the wave travelliing
the properties of the medium/material that a wave travels through (tension and mass [mass per unit length])
except for electromagnetic waves which don’t need a medium
net force
overall, single force that combines all individual forces acting on an object
linear density
mass per unit length m/L
equation to find speed of wave calculating the tension and mass of the material it travels through
v = sqrtF/(m/L), F= tension
sound waves are
mechanical and longitudinal waves
phase difference
measure of difference between two waves; measured in rad/deg
path difference
measure of difference between two waves; measured in meters or a fraction of wavelength