Brain and Cranial Nerves
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
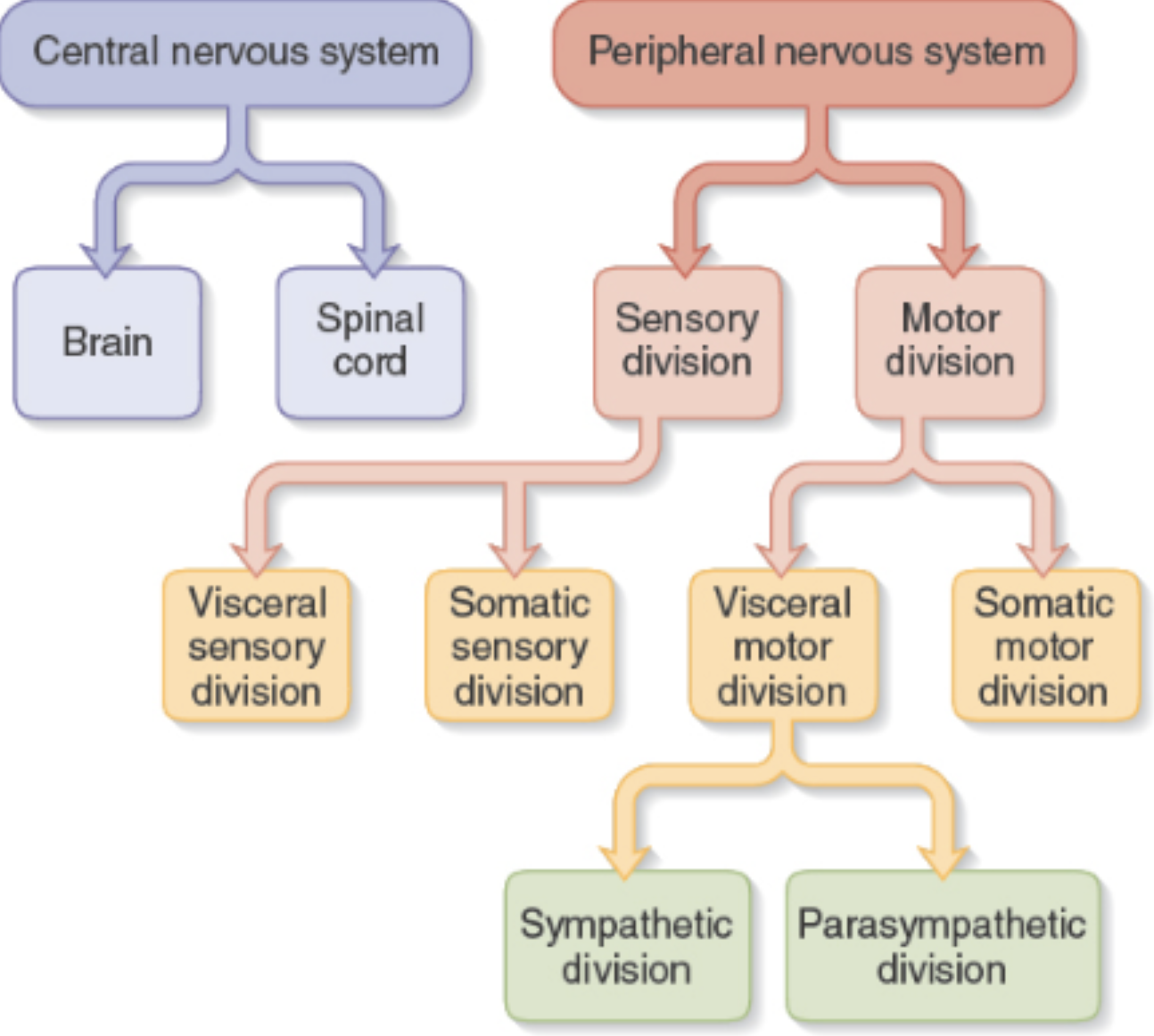
composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
composed of any nerve or ganglia outside of the CNS.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
carries signals from skin, muscles, bones, and joints.
Somatic Sensory Division (ANS)
carries signals to glands, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle; responsible for visceral reflexes.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
arouses the body for action; “fight or flight”.
Sympathetic Division (ANS)
has calming effect; “rest and digest” or “feed and breed”.
Parasympathetic Division (ANS)
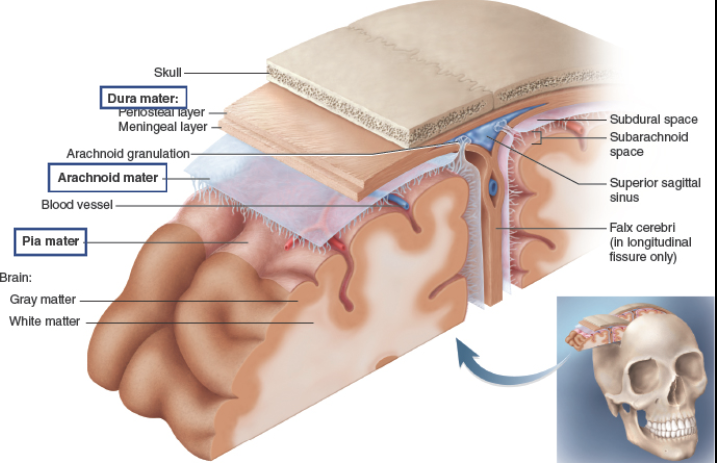
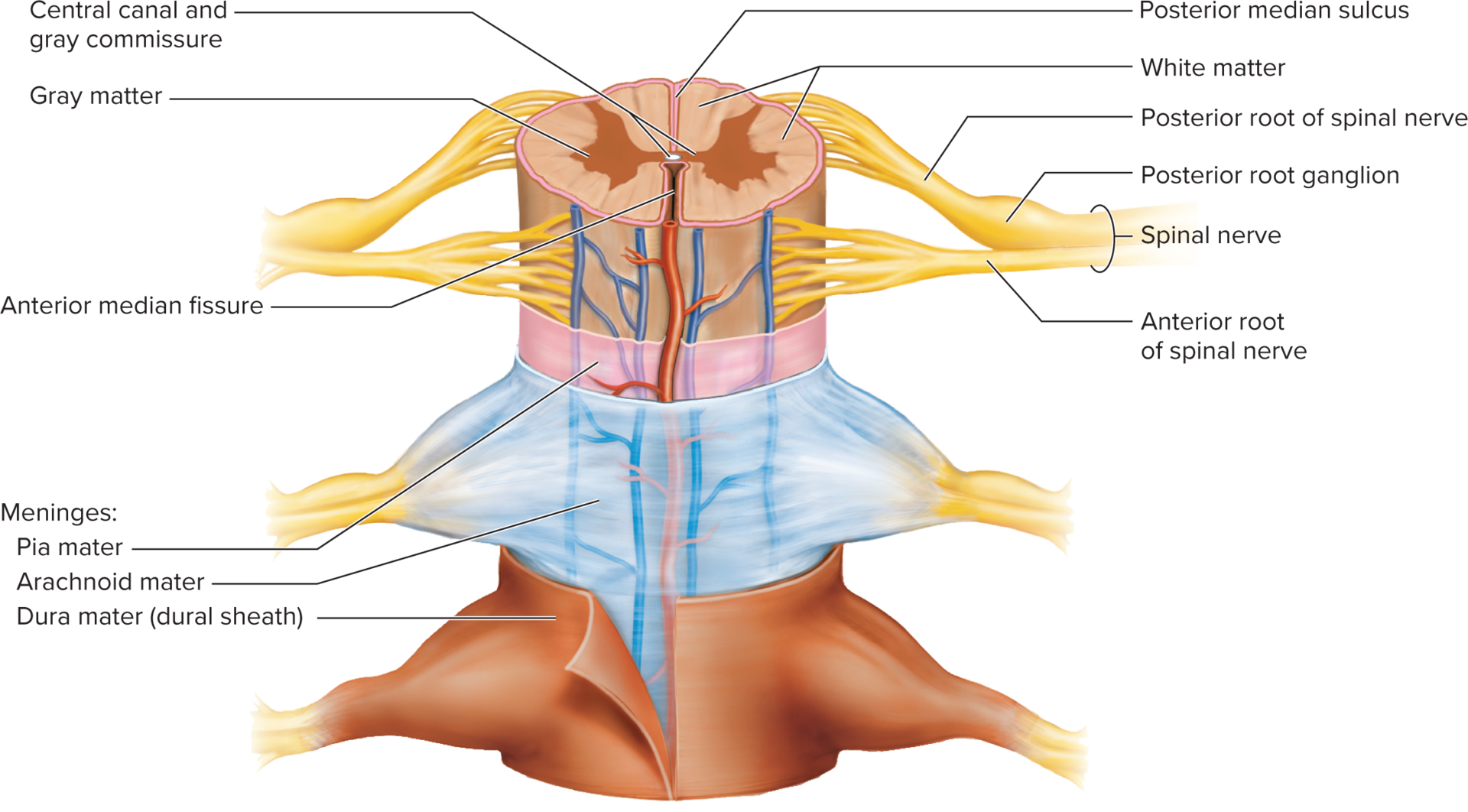
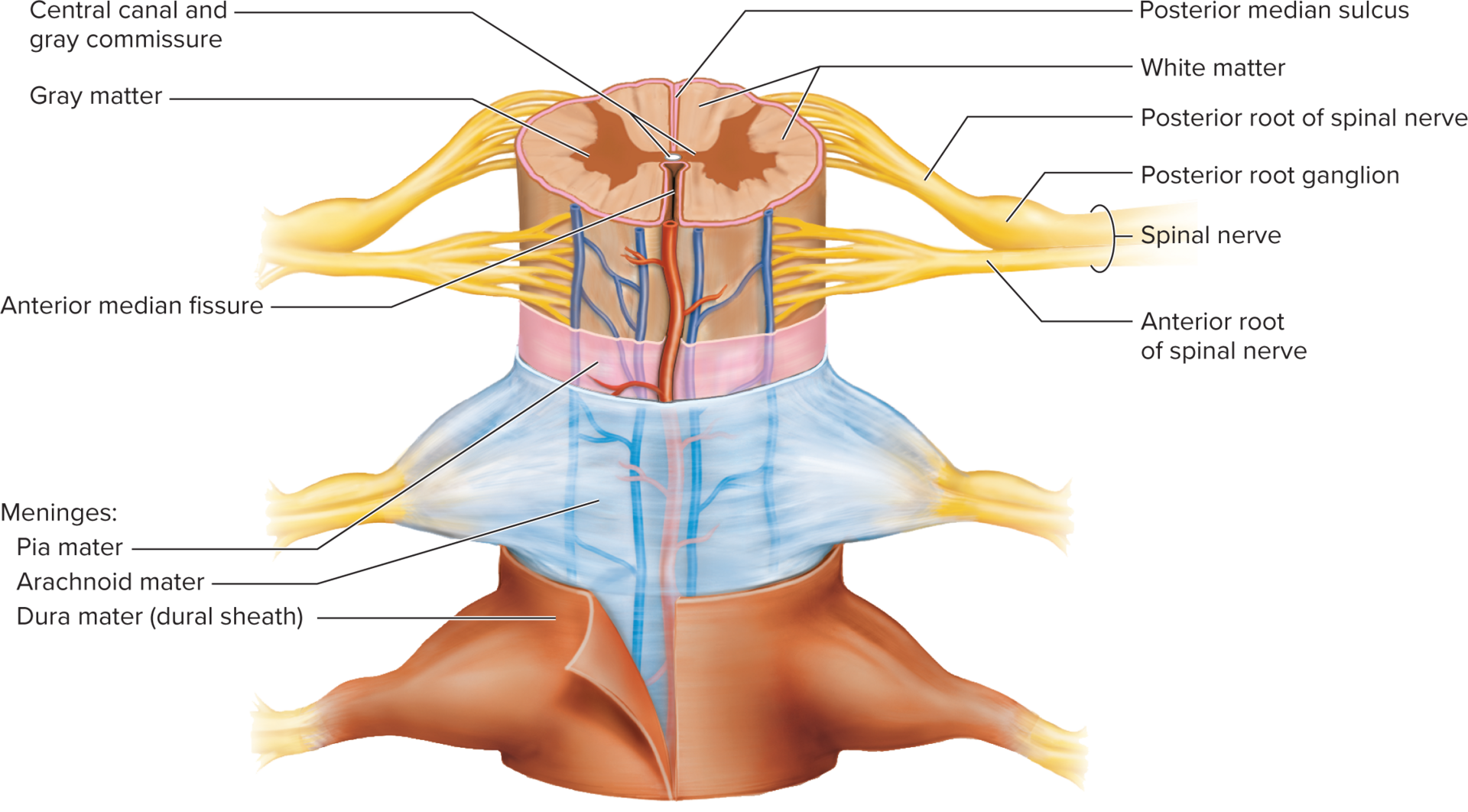
CT layers which protect the brain and provide a structural framework.
Meninges
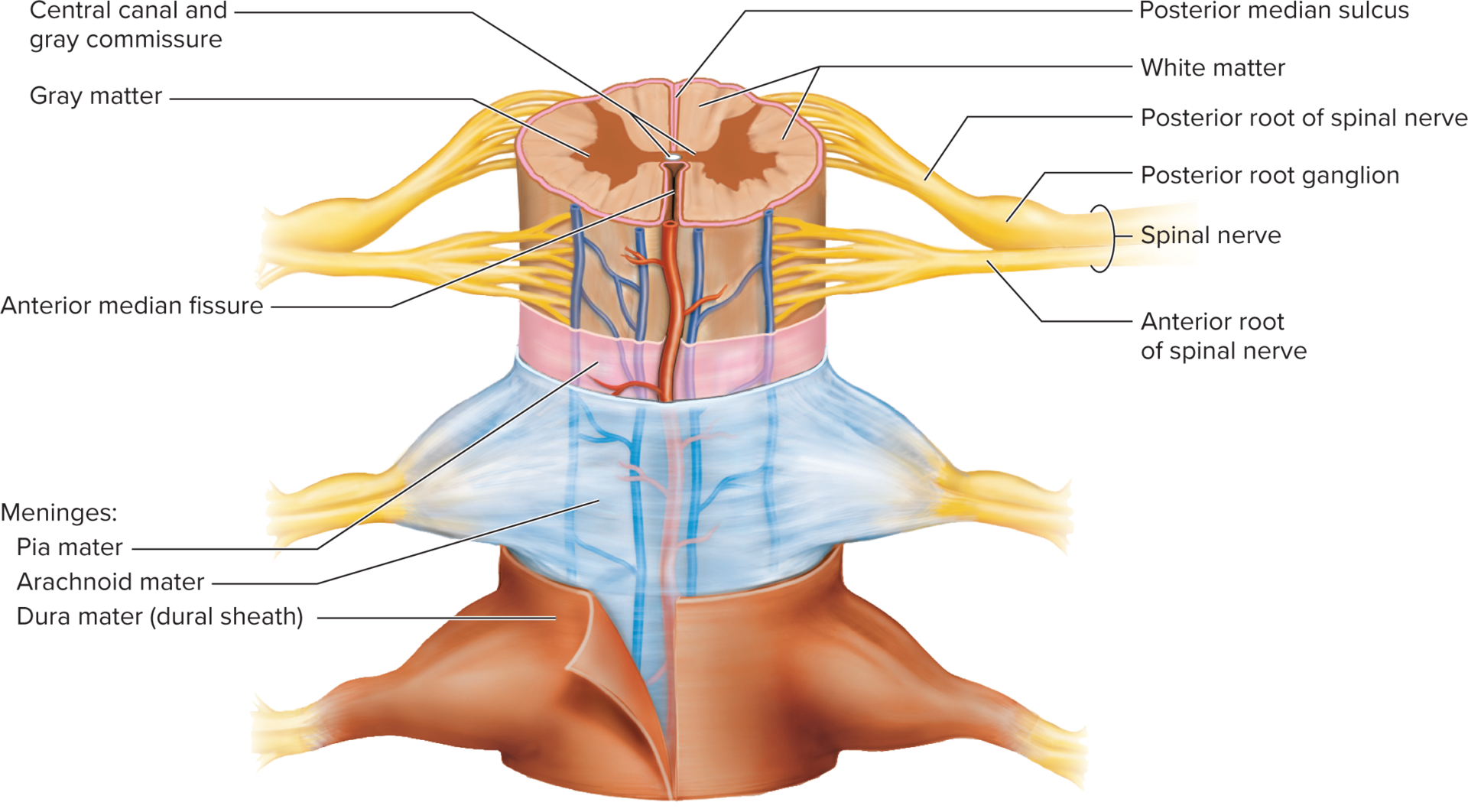
tough, two-layered sheet of fibrous CT.
Dura mater
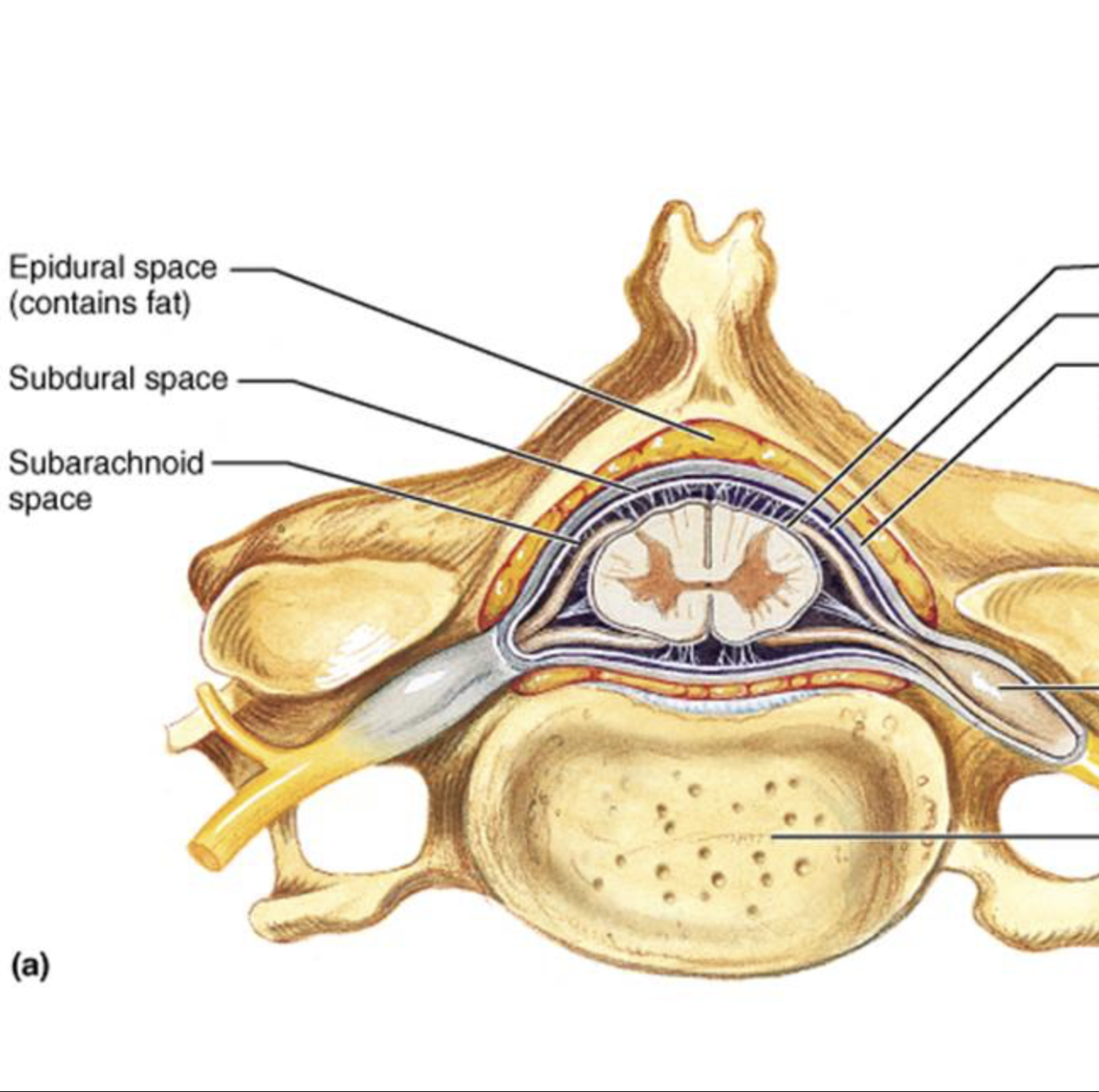
allows movement between dura mater and arachnoid mater and has CSF, i.e. cushioning and protection for brain.
Subdural space
web-like structure that secures blood vessels.
Arachnoid mater
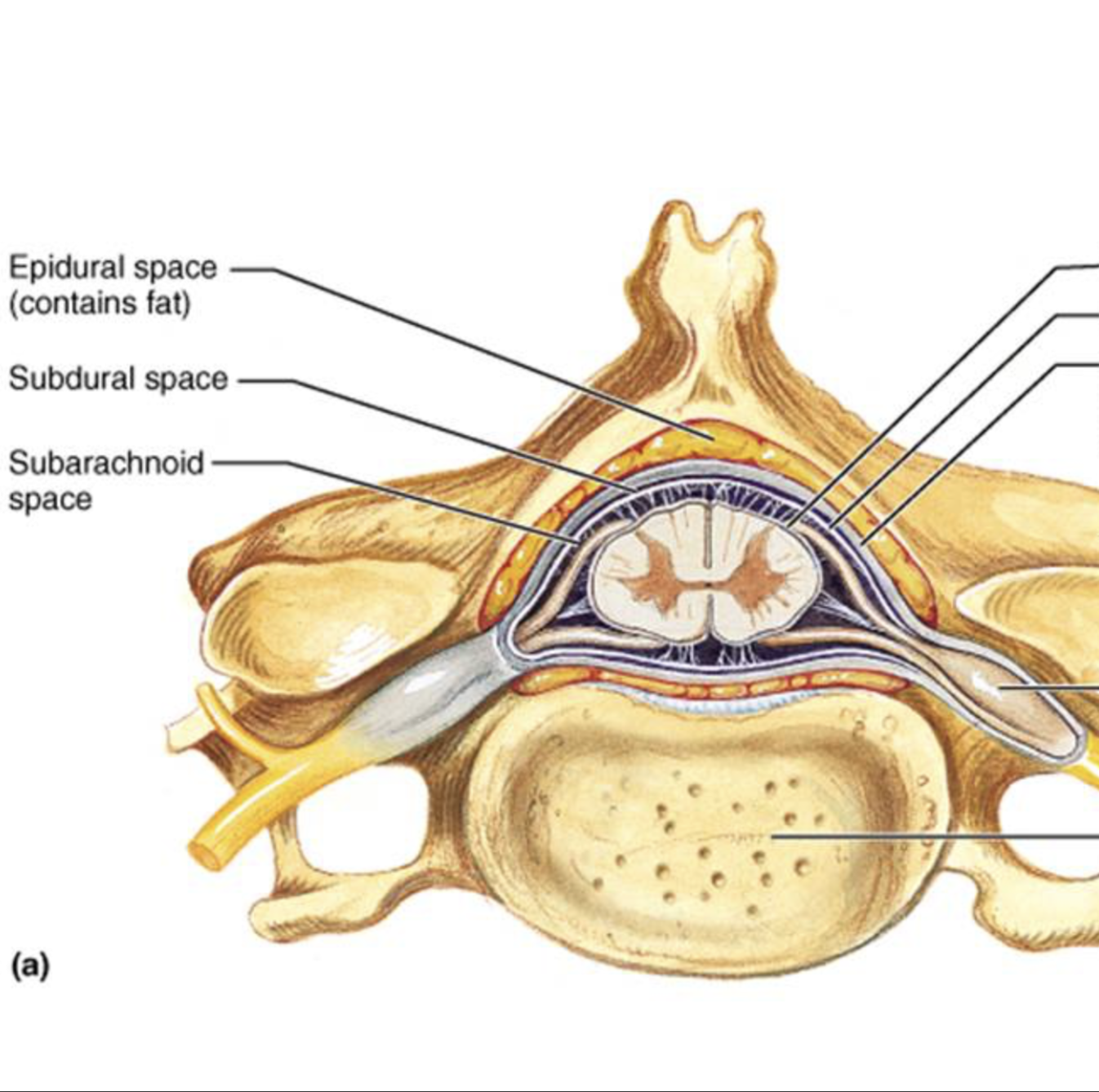
CSF-filled area between arachnoid and pia mater; cushions and protects the brain and spinal cord.
Subarachoid space
thin, shiny layer that adheres to the contours of the brain.
Pia mater
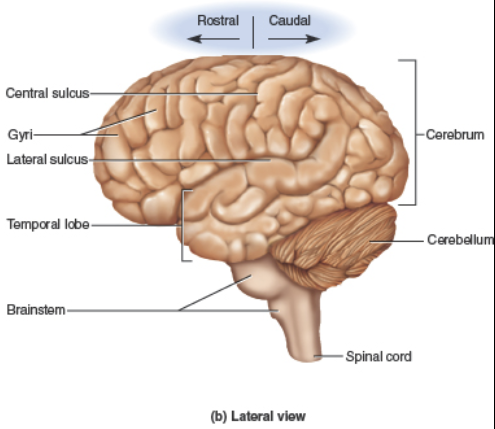
shallow grooves.
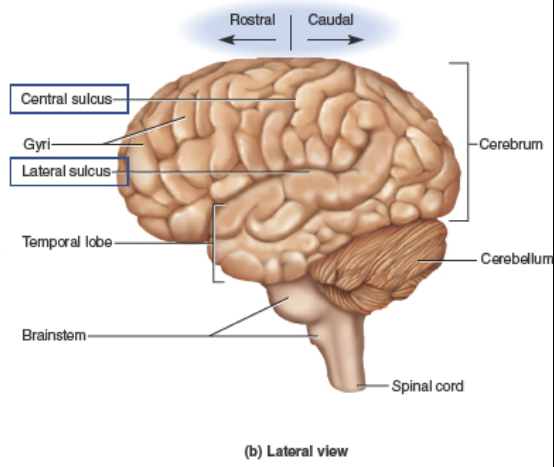
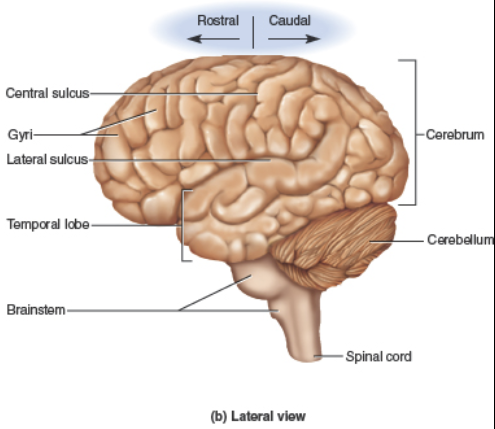
Sulci
deep grooves that separate brain structures.
Fissures
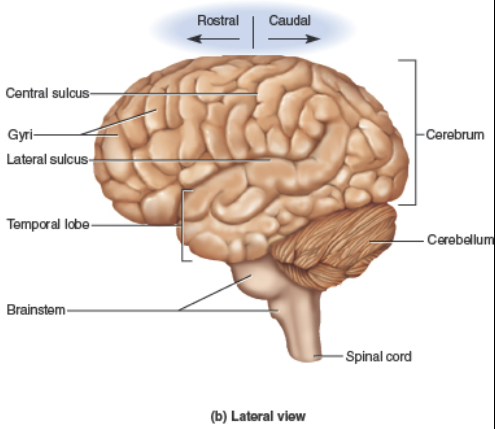
thick, rounded folds.
Gyri
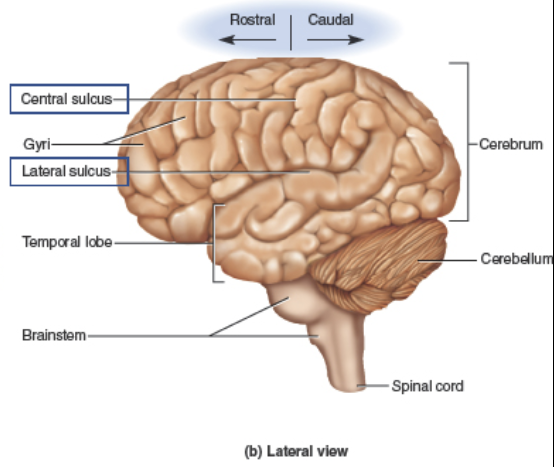
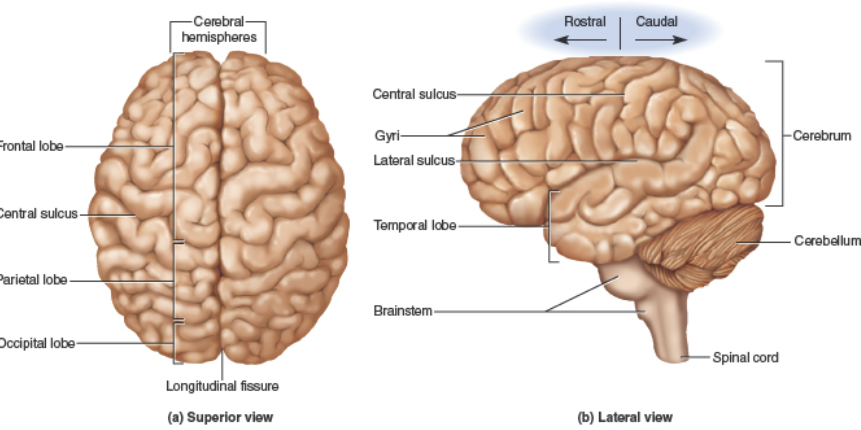
divides the Frontal and Parietal lobes.
Central sulcus
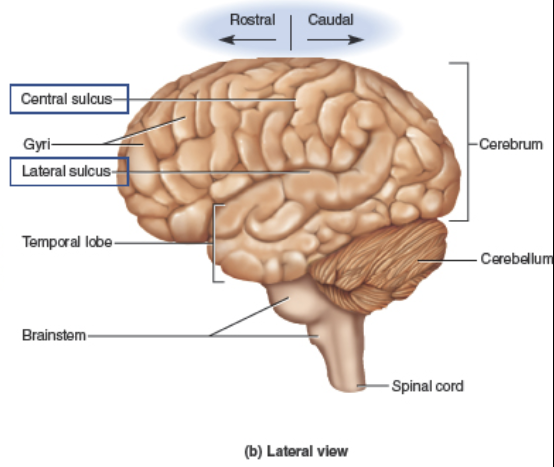
separates the Temporal and Parietal lobes.
Lateral sulcus
separates the right and left hemispheres.
Longitudinal fissure
separates the Cerebellum and the Occipital lobe.
Transverse fissure
connects the right and left hemispheres.
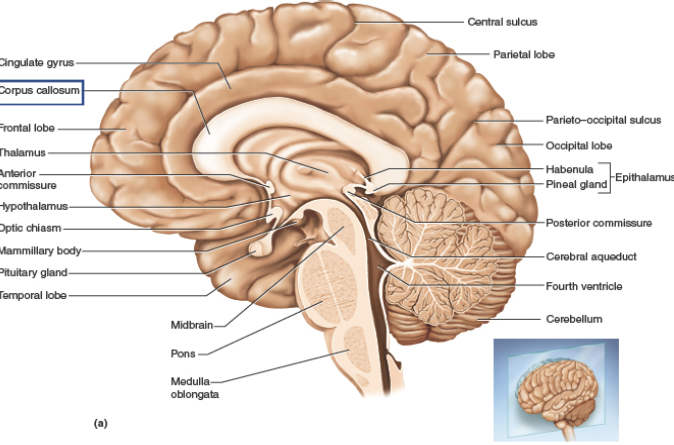
Corpus callosum
surface layer over the cerebrum and Cerebellum.
Cerebral cortex
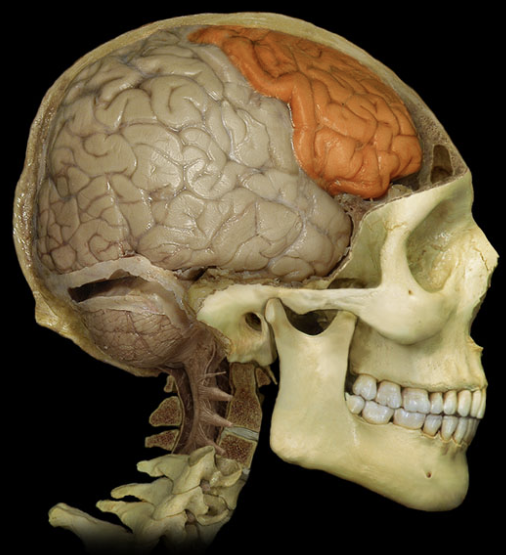
responsible for voluntary motor functions, motivation, foresight, planning, memory, mood, emotion, social judgment, and aggression.
Frontal lobes (CC)
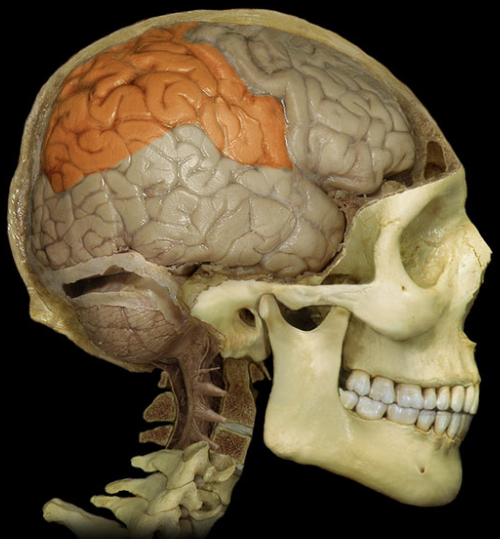
primary site for receiving and interpreting signals of the general senses and taste.
Parietal lobes (CC)
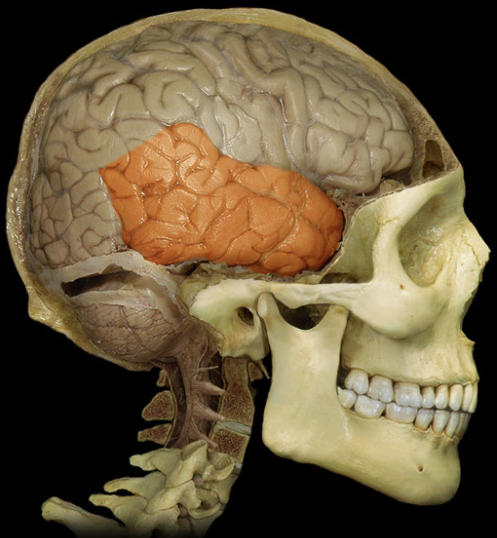
responsible for hearing, equilibrium, smell, learning, memory, and some aspects of emotion.
Temporal lobes (CC)
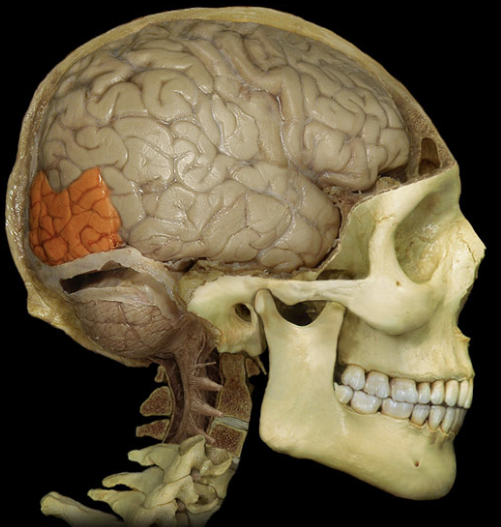
visual center of the brain.
Occipital lobes (CC)
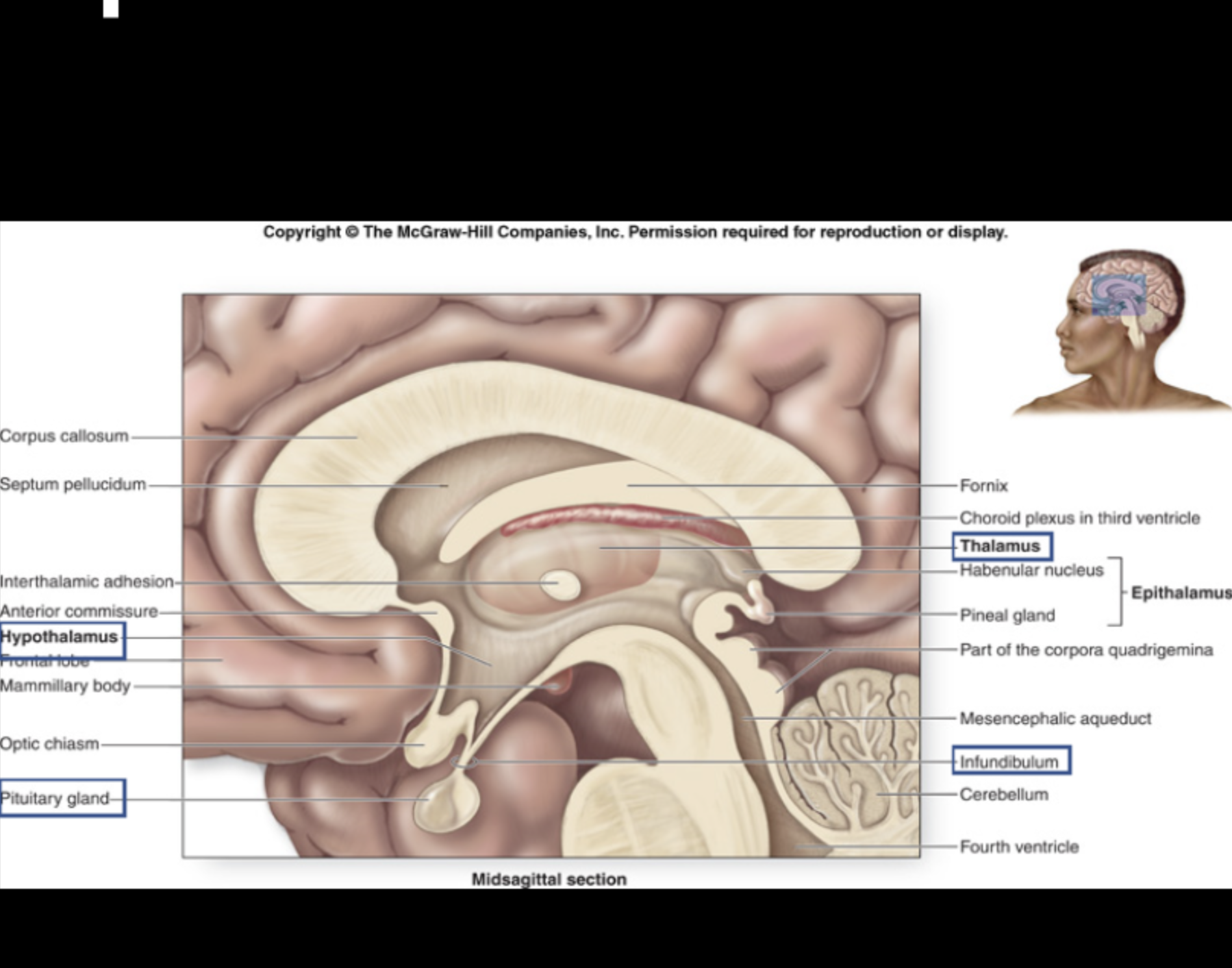
relay center for sensory information.
Thalamus
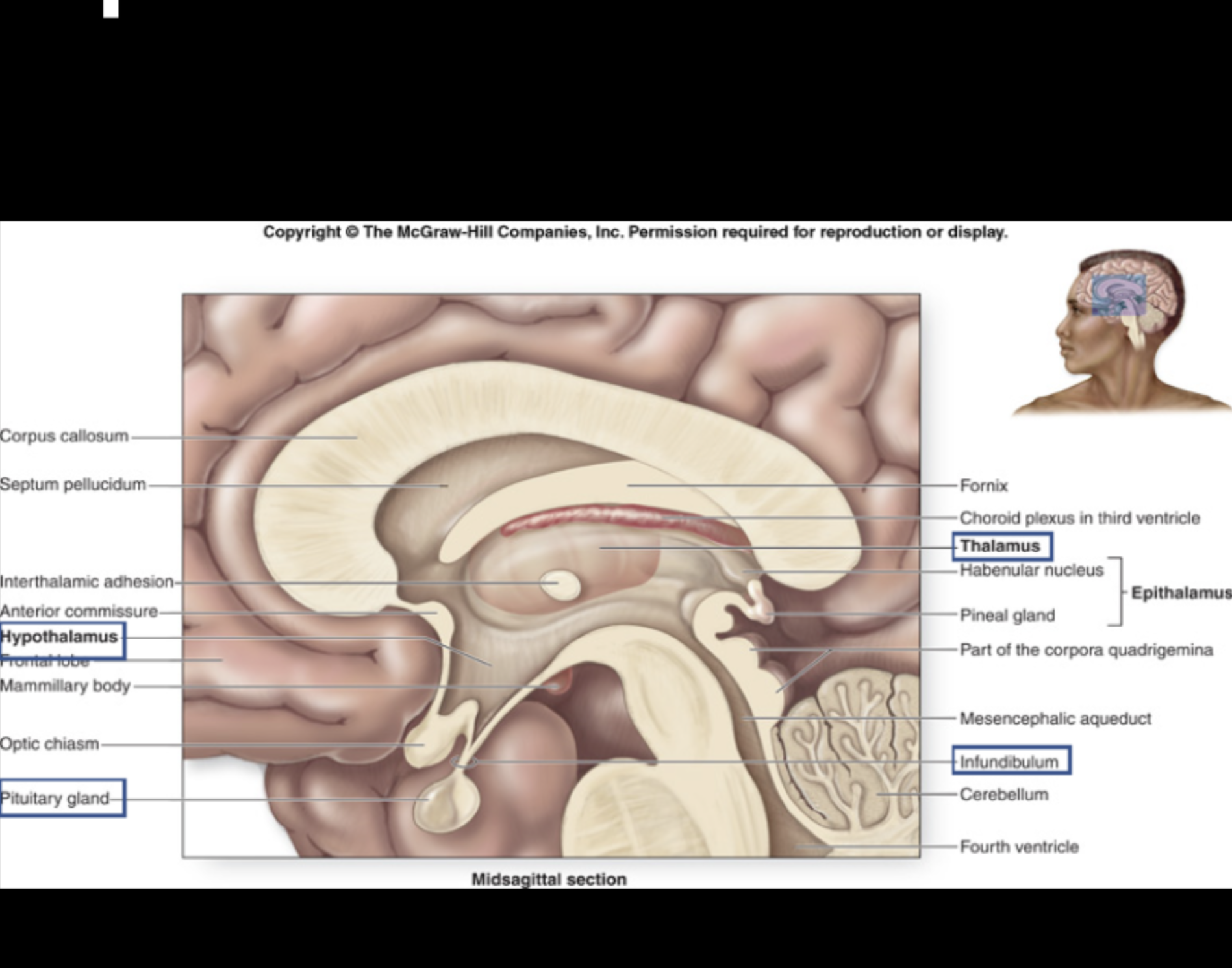
major control center for regulation of homeostatic responses such as hormone secretion, autonomic effects, thermoregulation, and food/water intake.
Hypothalamus

connects the Hypothalamus to the Pituitary Gland.
Infundibulum
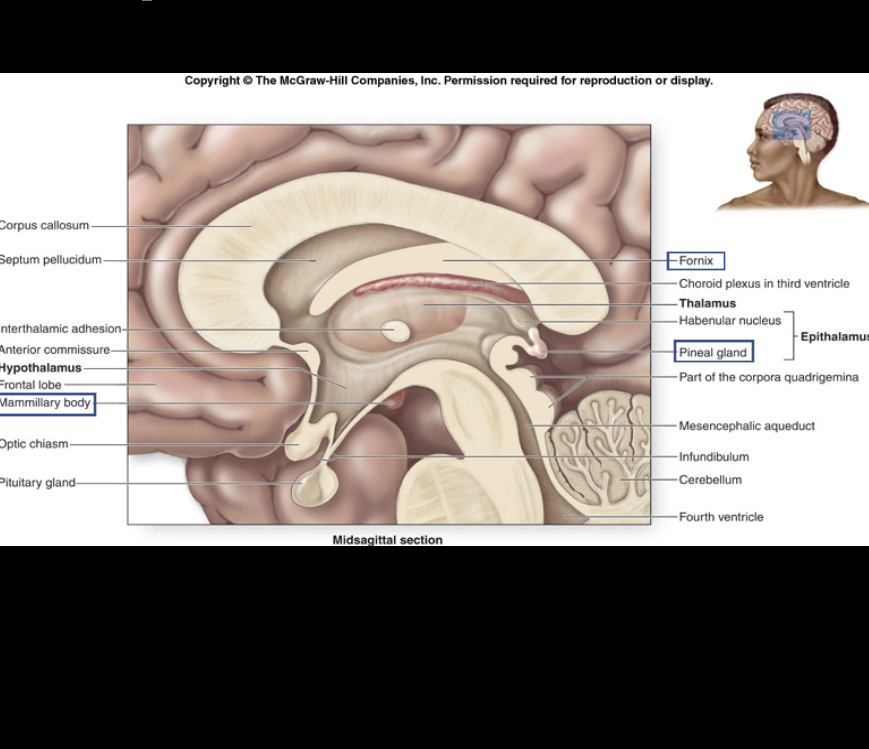
relay center for long-term memory.
Mammillary body
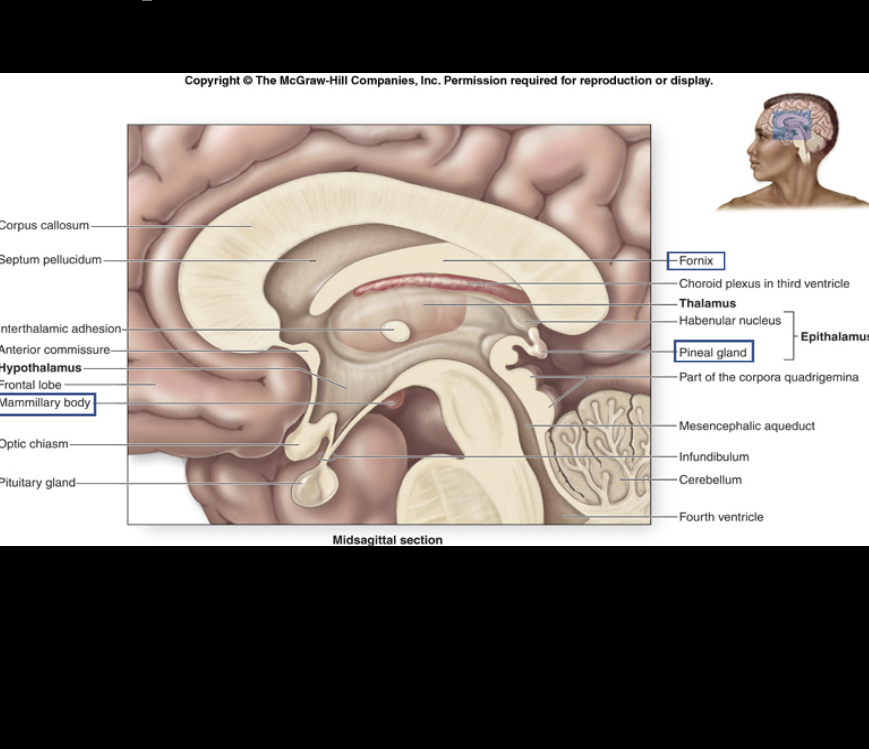
regulates circadian rhythms; produces melatonin (night time hormone) from serotonin (day time hormone).
Pineal gland
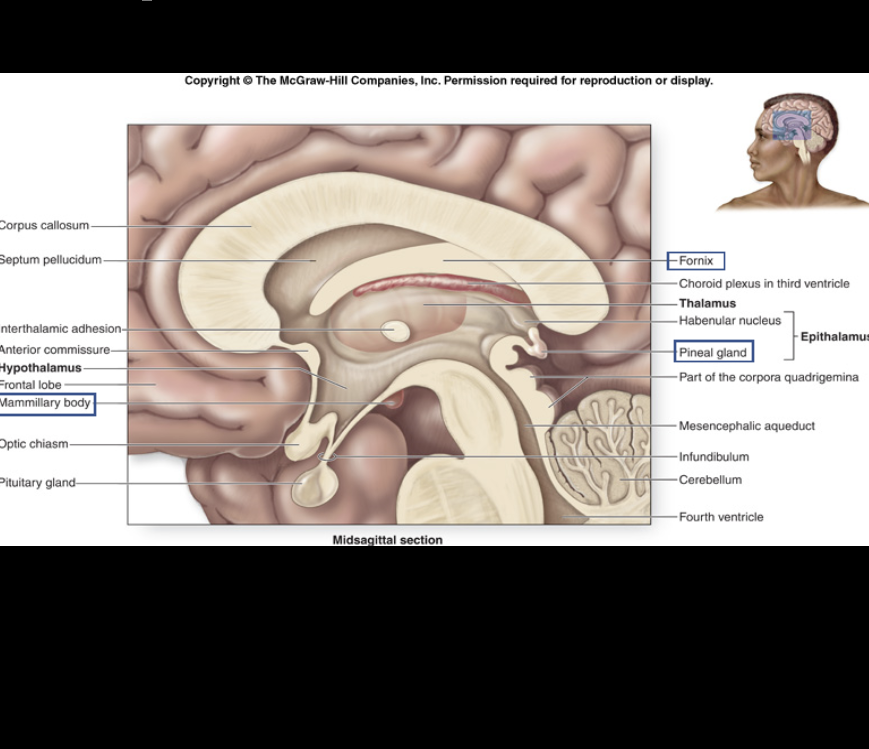
works in conjunction with the Hypothalamus to release/secrete hormones.
Pituitary gland
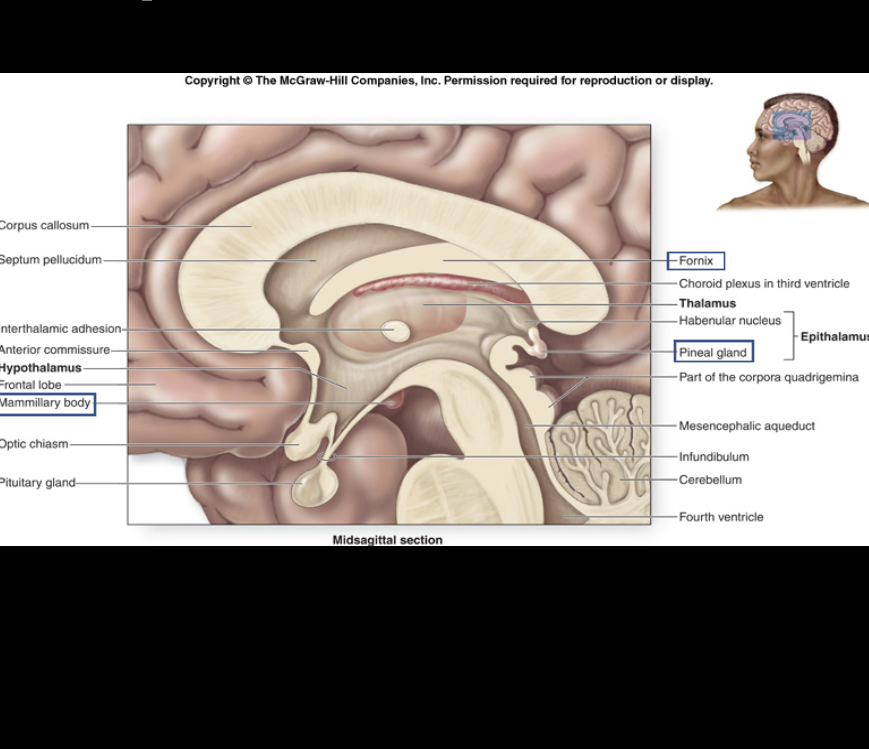
connects Hippocampus to mammillary body.
Fornix
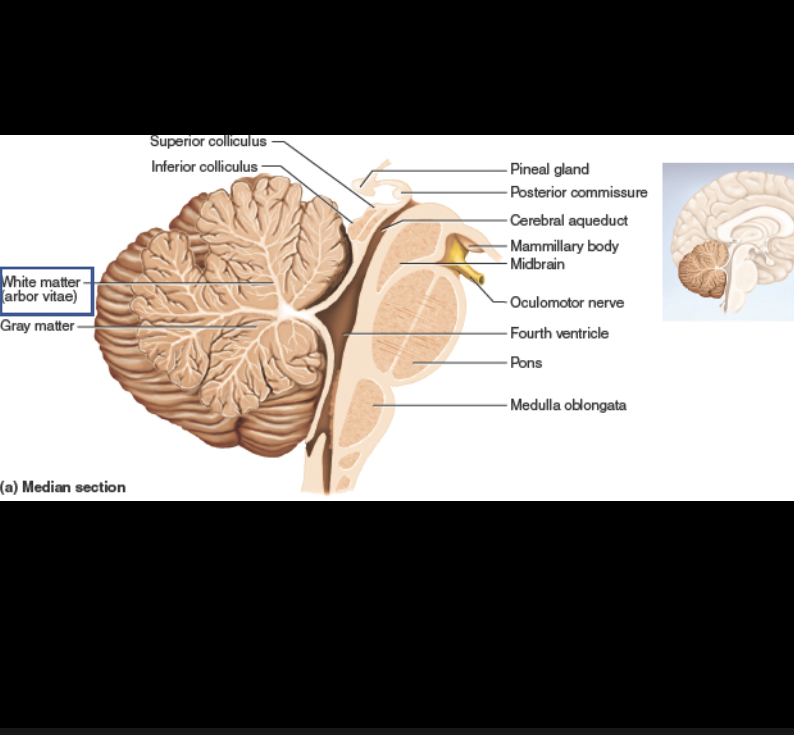
“tree of life”; brings sensory motor info to and from the Cerebellum.
Arbor vitae (cerebellum)
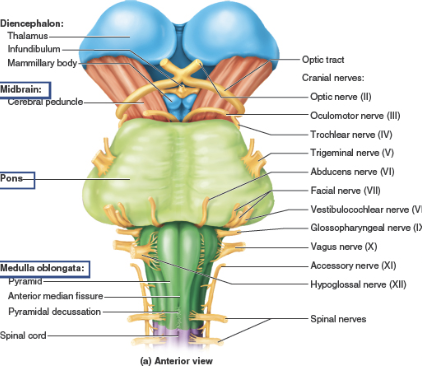
connects the Diencephalon to the Pons.
Midbrain
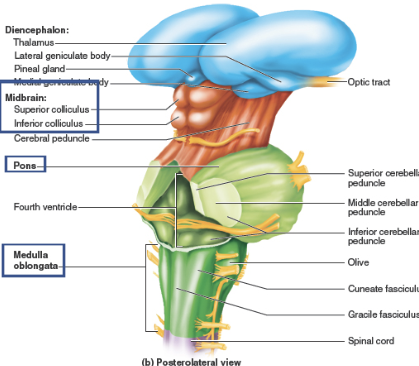
formed from Superior and Inferior Colliculi.
Superior Colliculi: controls visual reflexes.
Inferior Colliculi: controls auditory reflexes.
Corpora quadrigemina
connects Brain Stem to Cerebellum; contains ascending sensory tracts and descending motor tracts.
Pons
connects spinal cord to Pons.
Cardiac Center: regulates rate and force of heart beat.
Vasomotor Center: regulates blood pressure and flow.
Respiratory Centers: regulate rhythm and depth of breathing.
Reflex Center: sneezing and gagging.
Medulla oblongata
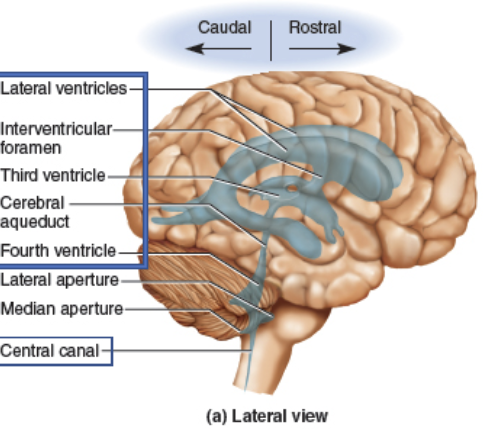
spaces in the brain w/CSF, allows flow of CSF through CNS.
Lateral, Third, Fourth Ventricles; Cerebral aqueduct and Central canal
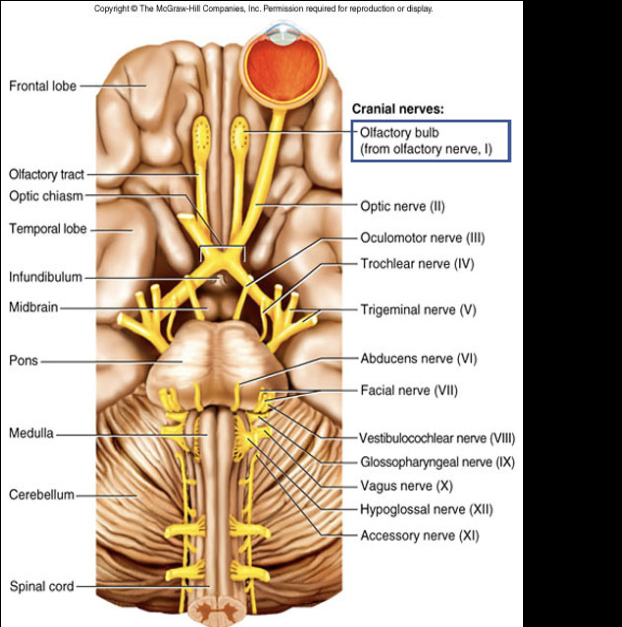
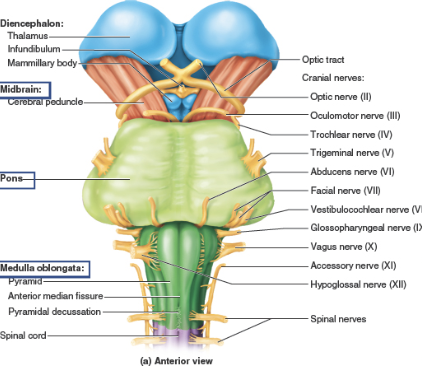
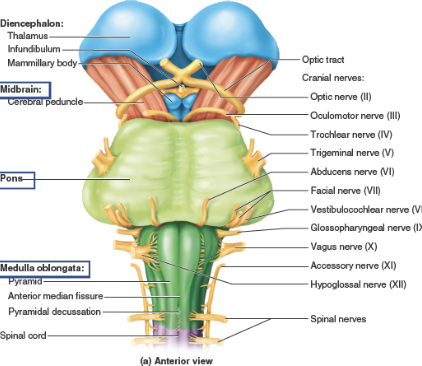
Cranial Nerve I
Composition: sensory
Function: smell
Damaged: impaired smell
Olfactory nerve (I)
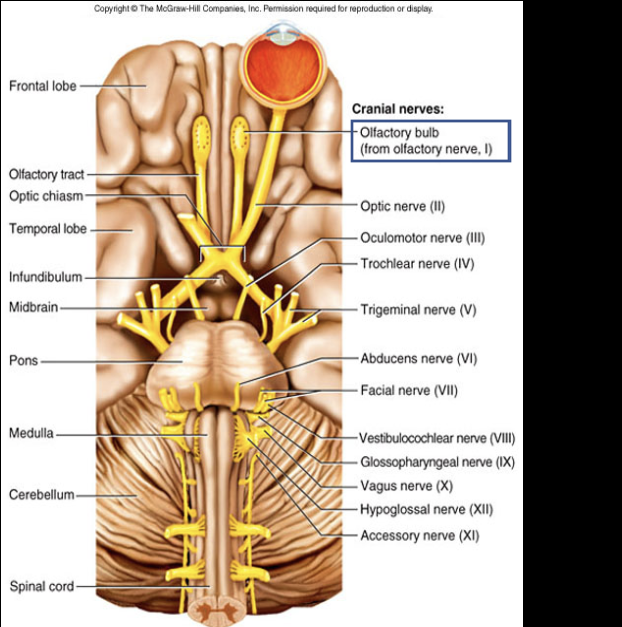
receive info about smells from nose and sends it to brain via olfactory tracts.
Olfactory bulb
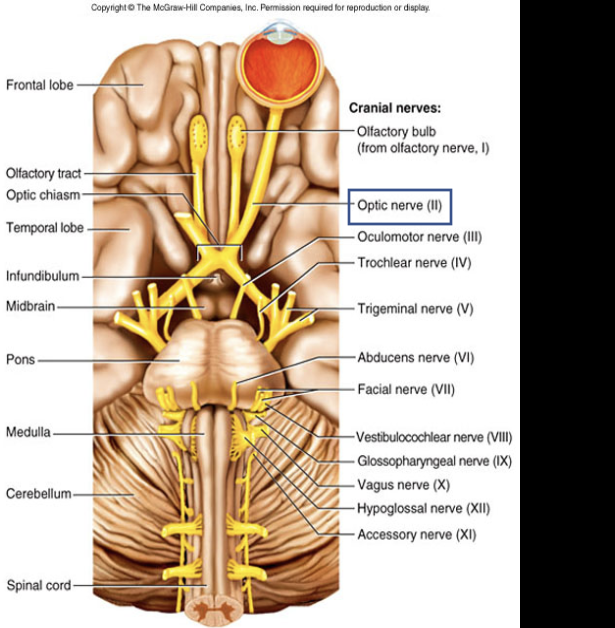
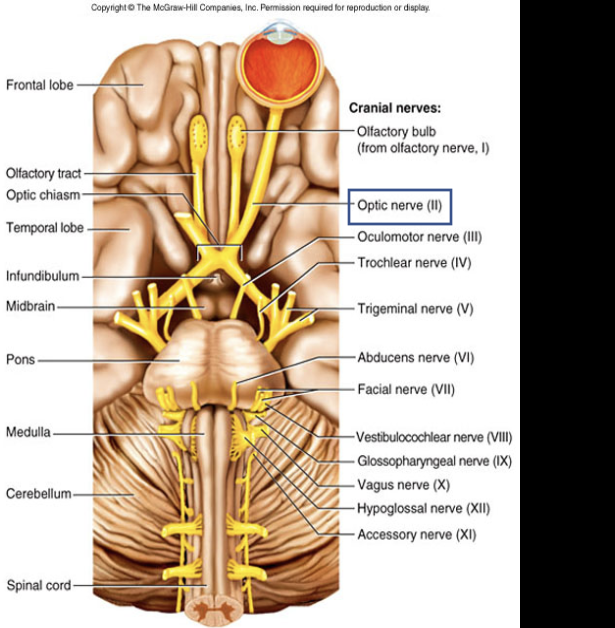
Cranial Nerve II
Composition: sensory
Function: vision
Damage: blindness
Ipsilateral and contralateral nerve fibers
Optic nerve (II)
Optic chiasm
allows crossing of fibers from nasal retina to the optic tract on the other side, enables vision from one side of both the eyes to be appreciated on opposite side.
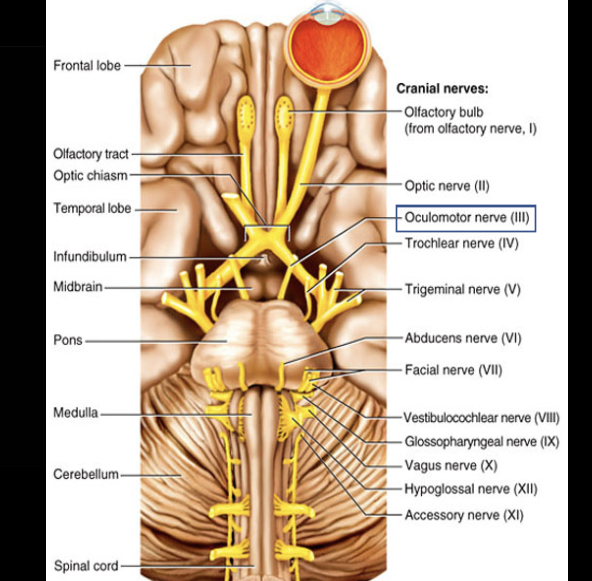
Cranial Nerve III
Composition: motor
Function: eye movement, opening of eyelid, and pupil constriction.
Damage: drooping eyelid, dilated pupil, inability to move eye in some directions.
Oculomotor nerve (III)
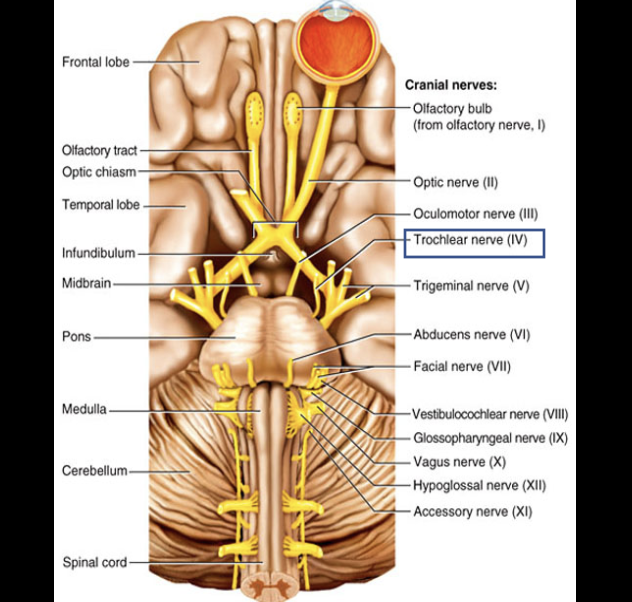
Cranial Nerve IV
Composition: Motor
Function: eye movement (superior oblique muscle).
Damage: weakened ability to look downward.
Trochlear nerve (IV)
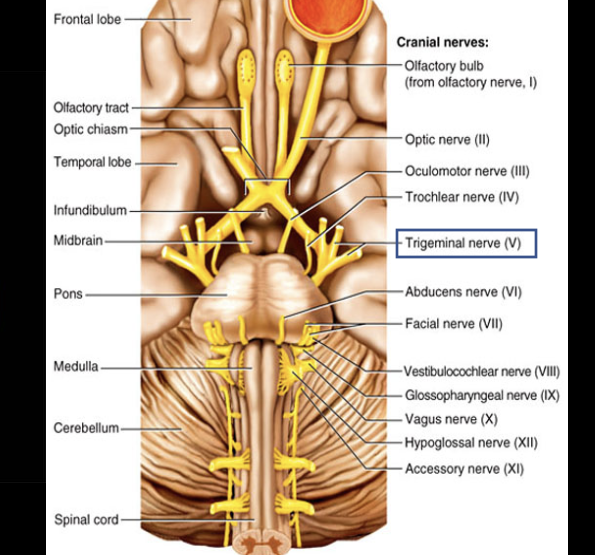
Cranial Nerve V
Composition: mixed
Function: sensory- face; motor- muscles of mastication.
Damage: loss of facial sensation; impaired chewing.
Trigeminal nerve (V)
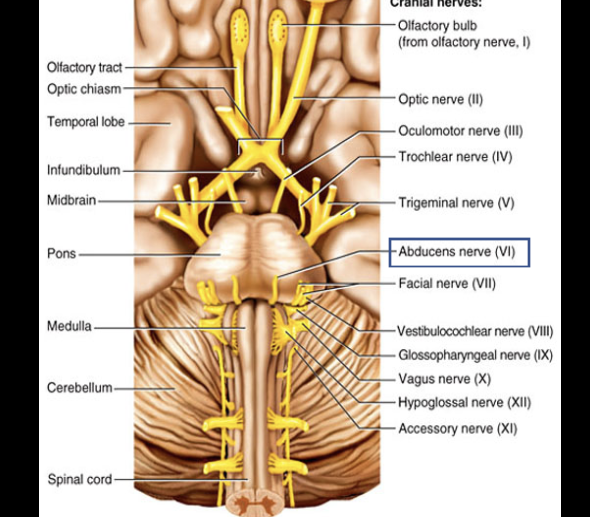
Cranial Nerve VI
Composition: motor
Function: lateral movement of eye (Lateral Rectus muscle).
Damage: inability to turn eye laterally.
Abducens nerve (VI)
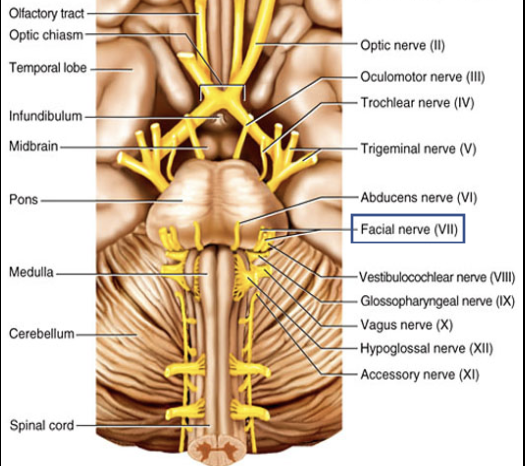
Cranial Nerve VII
Composition: mixed
Function: sensory- taste on anterior 2/3’s of tongue; motor- various facial/neck muscles and glands.
Damage: inability to control facial muscles, impaired sense of taste.
Facial nerve (VII)
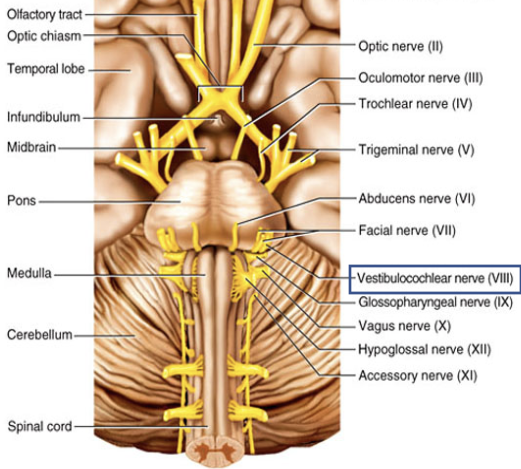
Cranial Nerve VIII
Composition: sensory.
Function: hearing and balance.
Damage: deafness and impaired balance.
Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
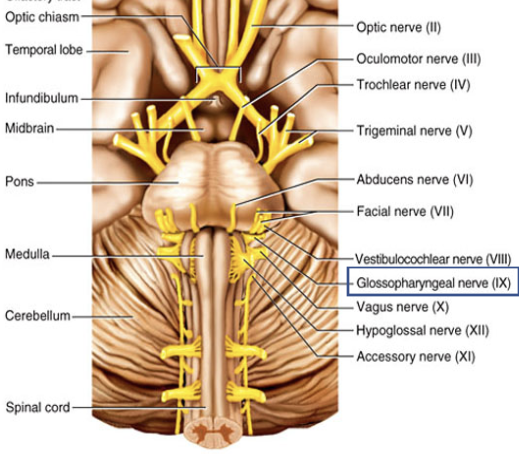
Cranial Nerve IX
Composition: mixed
Function: sensory- taste, touch, pressure, pain, and temperature on posterior 1/3 of tongue; Motor- salivation, swallowing, and gagging.
Damage: loss of taste, impaired swallowing.
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
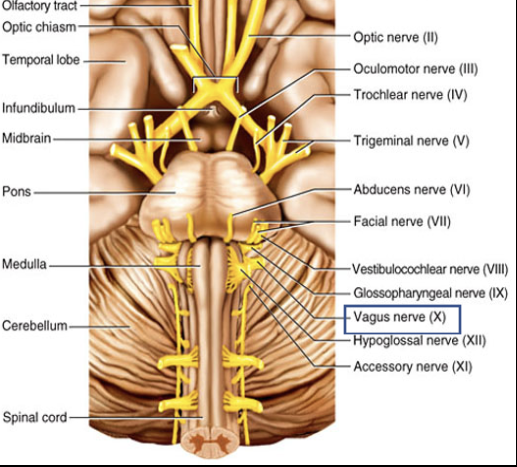
Cranial Nerve X
Composition: mixed
Function: sensory- taste, hunger, and fullness; Motor- swallowing, speech, and regulation of heart and GI tract.
Damage: impaired swallowing and GI motility; fatal if both Vagus nerves damaged.
Vagus (X)
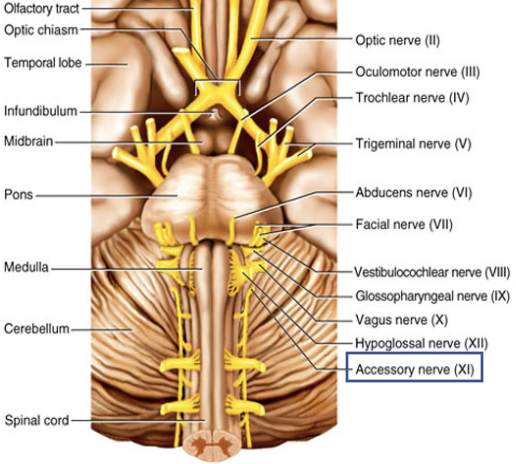
Cranial Nerve XI
Composition: motor
Function: swallowing; head, neck, and shoulder movements.
Damage: impaired movement of head, neck, and shoulders.
Accessory nerve (XI)
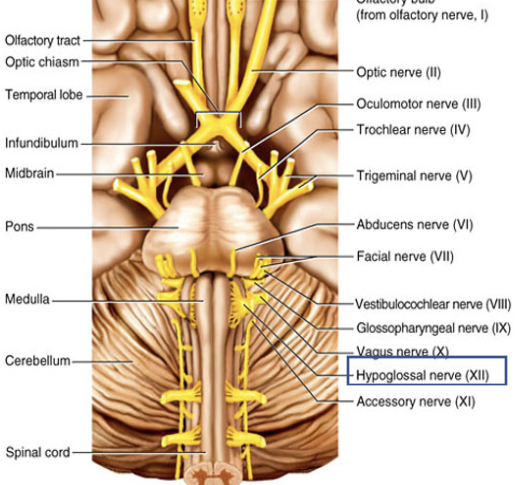
Cranial Nerve XII
Composition: motor
Function: tongue movements for speech, food manipulation, and swallowing.
Damage: impaired tongue movements for speech and swallowing.
Hypoglossal nerve (XII)