RAD 113: Bony Thorax
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
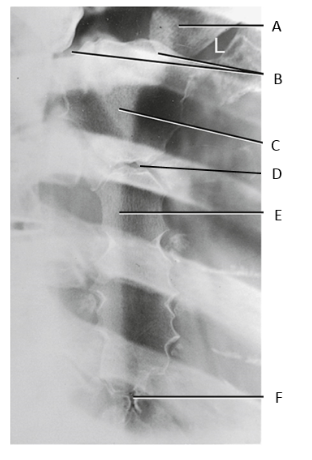
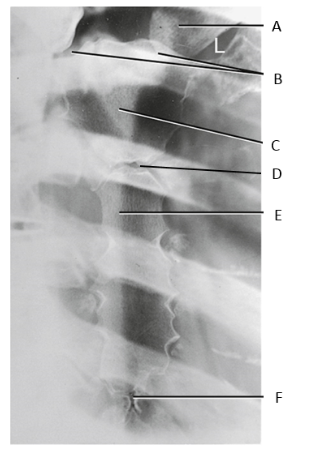
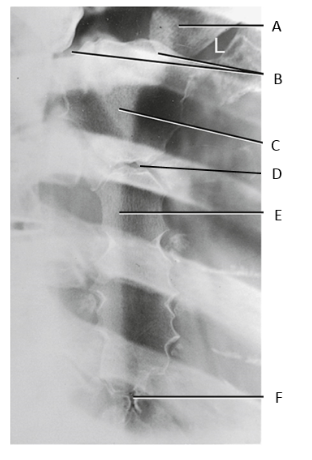
A
clavicle
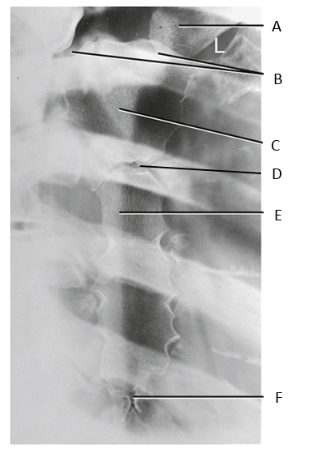
B
SC joints
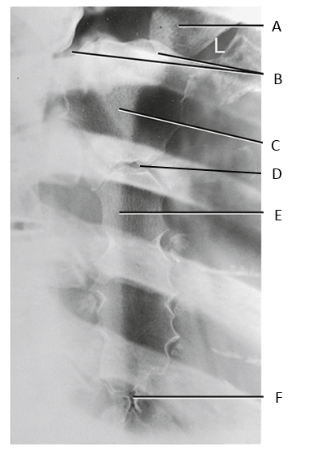
C
manubrium
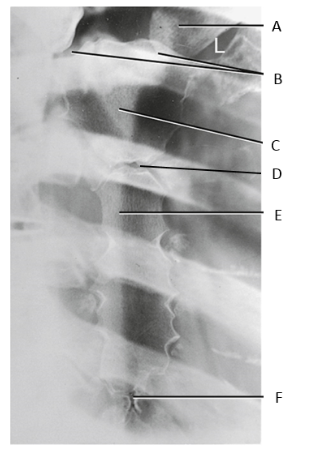
D
sternal angle
E
body of sternum
F
xiphoid process
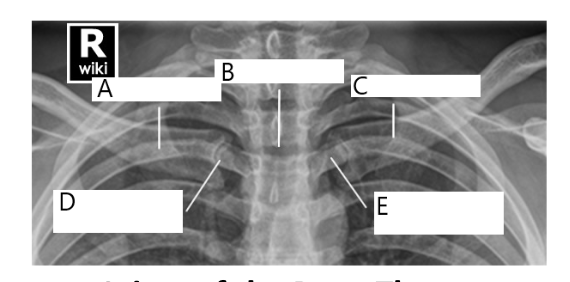
A
right clavicle
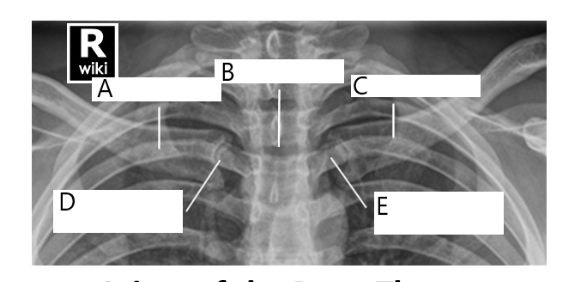
B
sternum
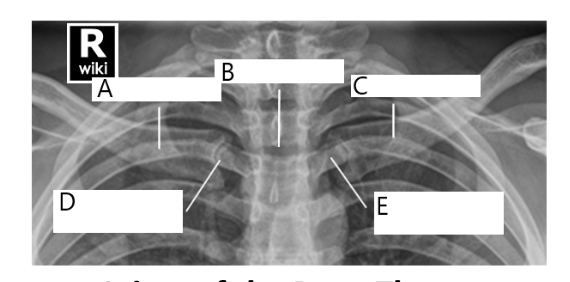
C
left clavicle
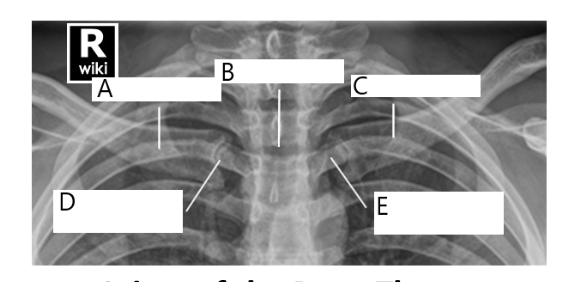
D
right SC joint
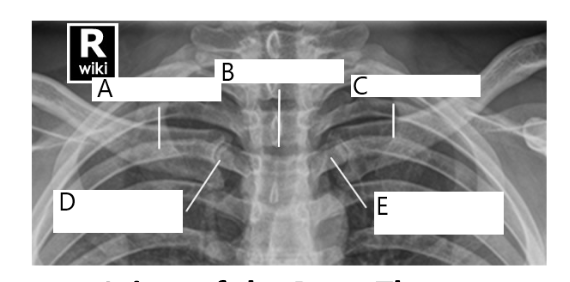
E
left SC joint
costochondral unions
synarthrodial (immovable)
1st sternocostal joint
cartilaginous
synarthrodial
2nd-7th sternocostal joints
synovial
diathrodial
plane/gliding
sternoclavicular joints (SC)
synovial
diathrodial
plane/gliding
6th-9th interchondral joints
synovial
diathrodial
plane/gliding
1st-10th costotransverse joint
synovial
diathrodial
plane/gliding
1st-12th costovertebral joints
synovial
diathrodial
plane/gliding
1st rib fracture
may cause injury to lungs/ cardiovascular structure
associated with underlying arteries or veins
lower rib fractures
may be associated with injury to the spleen, liver, or kidney
flail chest
A portion of the ribs are broken when the patient breathes, the lungs collapses & then reexpands
Multiple adjacent ribs are broken in multiple places
sternal fracture
caused by blunt trauma
associated with underlying cardiac injury
pectus carinatum
congenital deformity where the sternum & xiphoid process protrudes outward
AKA: pigeon breast
pectus excavatum
congenital deformity where the sternum caves inward
AKA: funnel chest
metastases
malignant rib lesions
osteolytic, osteoblastic, combo
nuclear medicine
osteolytic metastases
destructive lesions
osteoblastic metastases
increased bony density
combo metastases
osteolytic & osteoblastic
moth-eaten appearance of bone resulting from a mix of destructive & blastic lesions
osteomyelitis
localized or generalized infection of bone & marrow
bacterial infection is most common cause
RAO sternum
patient erect facing Bucky & rotate 15-20° RAO
IR = 1.5” above jugular notch
perpendicular to mid sternum & to left of MSP
orthostatic breathing
evaluation
sternum superimposed on heart shadow
left clavicle & jugular notch
entire sternum
RAO sternum rotation
large chest = 15°
thinner chest = 20 °
why is the sternum done RAO?
to shift the sternum to the left of the vertebral column & superimpose it with the heart shadow
What if the patient cannot be prone? (RAO sternum)
LPO sternum
RAO sternum trauma modification
angle the tube 15-20° across the right side of the patient (right to left)
Lateral Sternum
true lateral, hands clasped behind back with shoulders relaxed, MCP to IR
perpendicular to mid sternum & anterior to MCP
60-72” SID
full inspiration
evaluation:
entire sternum
Lateral Sternum Trauma Modification
horizontal beam lateral done instead
PA SC joints
patient prone with head & chin straight resting on sponge
CR perpendicular to MSP & T2-T3
expiration
evaluation
bilateral left & right SC joints equal distance from the spine
lateral manibrium
medial clavicles
SC joint obliques (RAO/LAO)
prone/erect with 10-15° rotation toward the side of interest, SC joints centered to IR
side closest to IR is shown best
CR perpendicular to T2-T3 & 1-2” lateral of MSP
expiration
evaluation
SC joint open & shifted away from
what if the patient cannot lie prone? (SC joint obliques)
can be done as an RPO/LPO with 10-15° rotation away from the side of interest with the CR 1-2” lateral to MSP
Why are PA CXRs included in a rib series?
To rule out pneumothorax & hemothorax or other internal injuries
Upper Ribs bilateral
CR
perpendicular to T7 & MSP
14×17 portrait
40 SID
IR = 1.5 above shoulders
full inspiration
evaluation
posterior ribs 1-9 above the diaphragm
How to tell if the patient is rotated on the lateral sternum?
ribs projected anteriorly past sternum
posterior pain ribs
AP projection
anterior pain ribs
PA projection
Lower Ribs bilateral
CR
side of interest centered on IR midway between MSP & lateral margin of thorax
expiration
evaluation
ribs 10-12
Axillary Ribs (Obliques)
patient erect rotated 45°
Above diaphragm
CR to T7
full inspiration
Below diaphragm
CR to midway between the xiphoid process & the lower rib margin
expiration
Axillary Ribs posterior pain
LPO
left posterior rib pain
RPO
right posterior rib pain
Upper Ribs unilateral
CR
perpendicular to T7 & midway between MSP & outer margin of thorax
14×17 landscape
72 SID
full inspiration
14×17
evaluation
posterior ribs 1-9 above the diaphragm
Lower Ribs Unilateral
CR
side of interest centered on IR midway between MSP & lateral margin of thorax
expiration
evaluation
ribs 10-12 below diaphragm
Axillary Ribs, anterior ribs
LAO
right anterior rib pain
RAO
left anterior rib pain
what 4 views would you do for a patient complaining of right, anterior rib pain?
PA upper ribs
PA lower ribs
LAO
CXR
what 4 views would you do for a patient complaining of left posterior rib pain
AP upper ribs
AP lower ribs
LPO
CXR
what 4 views would you do for a patient complaining of right posterior rib pain
AP upper ribs
AP lower ribs
RPO
CXR
what 4 views would you do for a patient complaining of left anterior rib pain
PA upper ribs
PA lower ribs
RAO
CXR
posterior obliques axillary ribs
RPO/LPO
elongates ribs closest to IR
anterior obliques axillary ribs
RAO/LAO
elongates side furthest away from IR
where does the 2nd costocartilage attach?
sternal angle
Why are 1-7 true ribs?
they attach to the sternum
Why are 8-10 ribs false ribs
they do not attach to the sternum
floating ribs (11-12)
no anterior attachment
Where is the widest part of the thorax
between 8th & 9th rib
posterior end of rib sits ___ to the anterior portion
3-5” superior
posterior obliques (RPO/LPO)
elongates closest to the IR
anterior obliques (RAO/LAO)
elongates side furthest away from IR