Early Christian Art & Byzantine Art - Miscellaneous
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Catacomb
An underground cemetery consisting of a subterranean gallery with recesses for tombs, as constructed by the ancient Romans.
Syncretism
The amalgamation or attempted amalgamation of different religions, cultures, or schools of thought
Basilica
A large oblong hall or building with double colonnades and a semicircular apse, used in ancient Rome as a court of law or for public assemblies
Cross plan
This architectural style is the ideals of harmony and balance that were central to Renaissance art and architecture. The Greek often symbolizes the spiritual significance of Christianity, representing equality in the distribution of religious spaces.
Nave
The central part of a church, extending from the main entrance or rear wall to the transepts or chancel
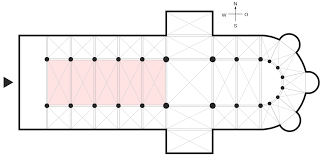
Transept
A transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building
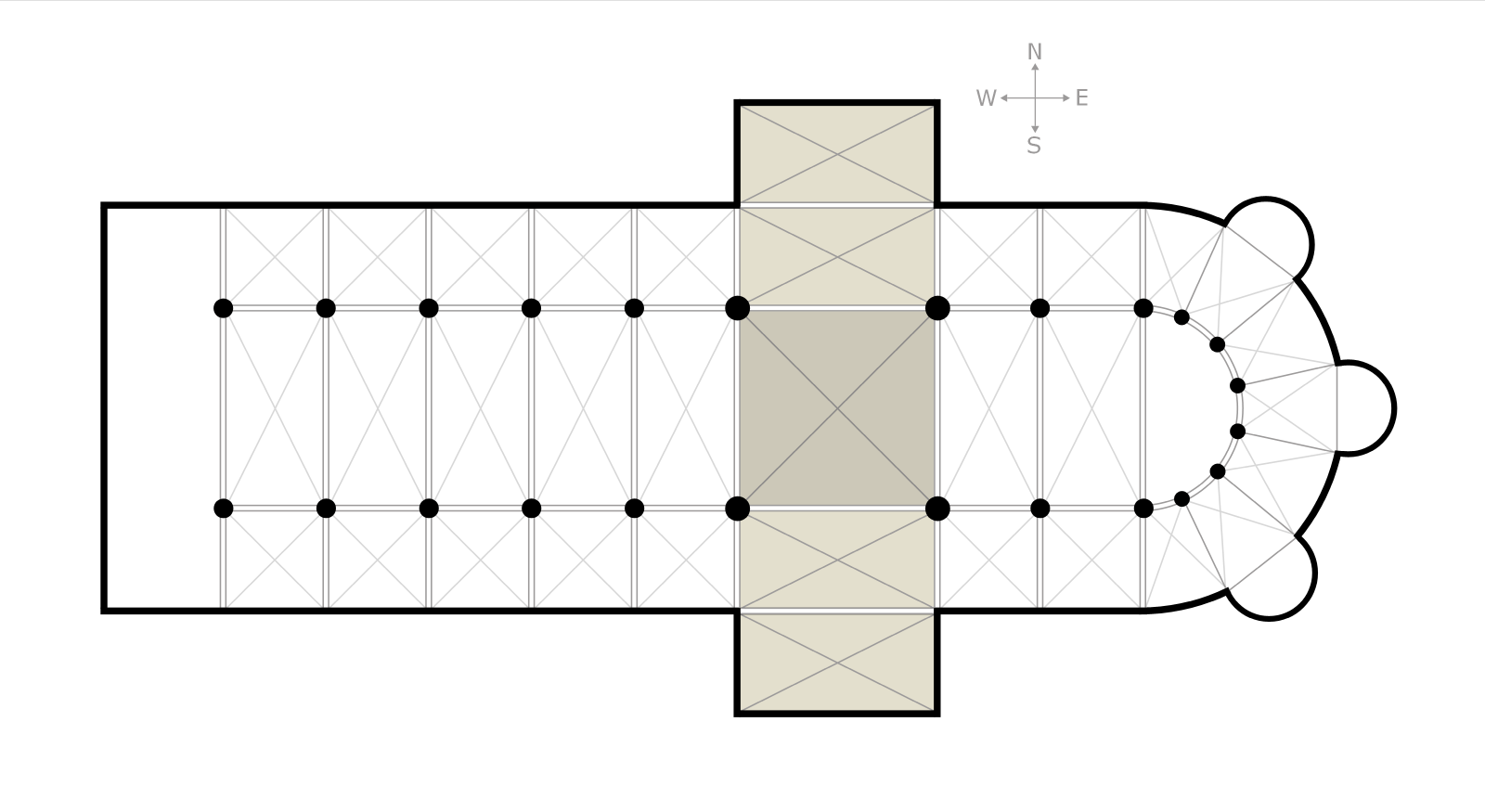
Crossing
It gives access to the nave on the west, the transept arms on the north and south, and the choir, as the first part of the chancel, on the east
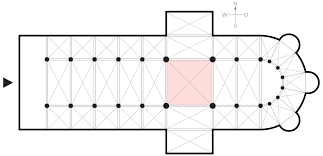
Apse
A semicircular recess, often covered with a hemispherical vault
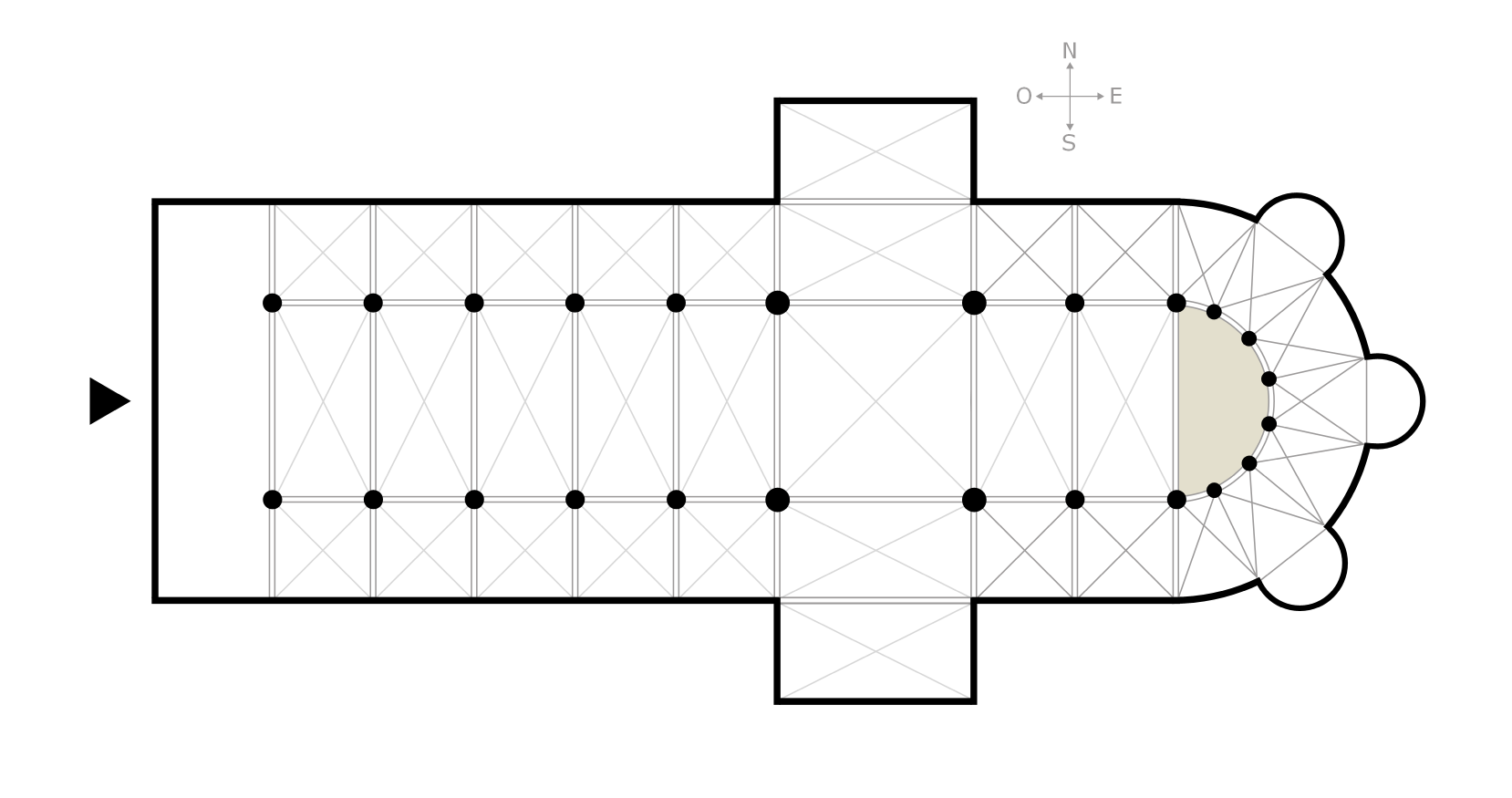
Clerestory
Any fenestrated (windowed) wall of a room that is carried higher than the surrounding roofs to light the interior space

476 AD
The fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided among several successor polities.
Constantinople
The capital of the Roman Empire during the reign of Constantine the Great in 330
Ravenna, Italy
By the fifth century, Rome lost its political, although not its spiritual, importance. The capital of the Western Roman Empire was moved to Milan in the late third century and then to _________, on the Adriatic coast, at the beginning of the fifth century.
Central plan
A collection of simple homogeneous, non-communicative agents that are managed by a single control center in a master–slave relationship
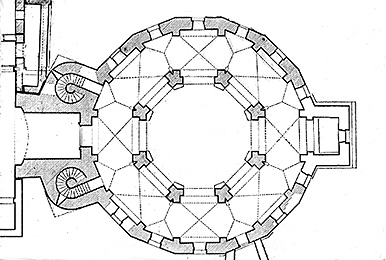
Ambulatory
The covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar
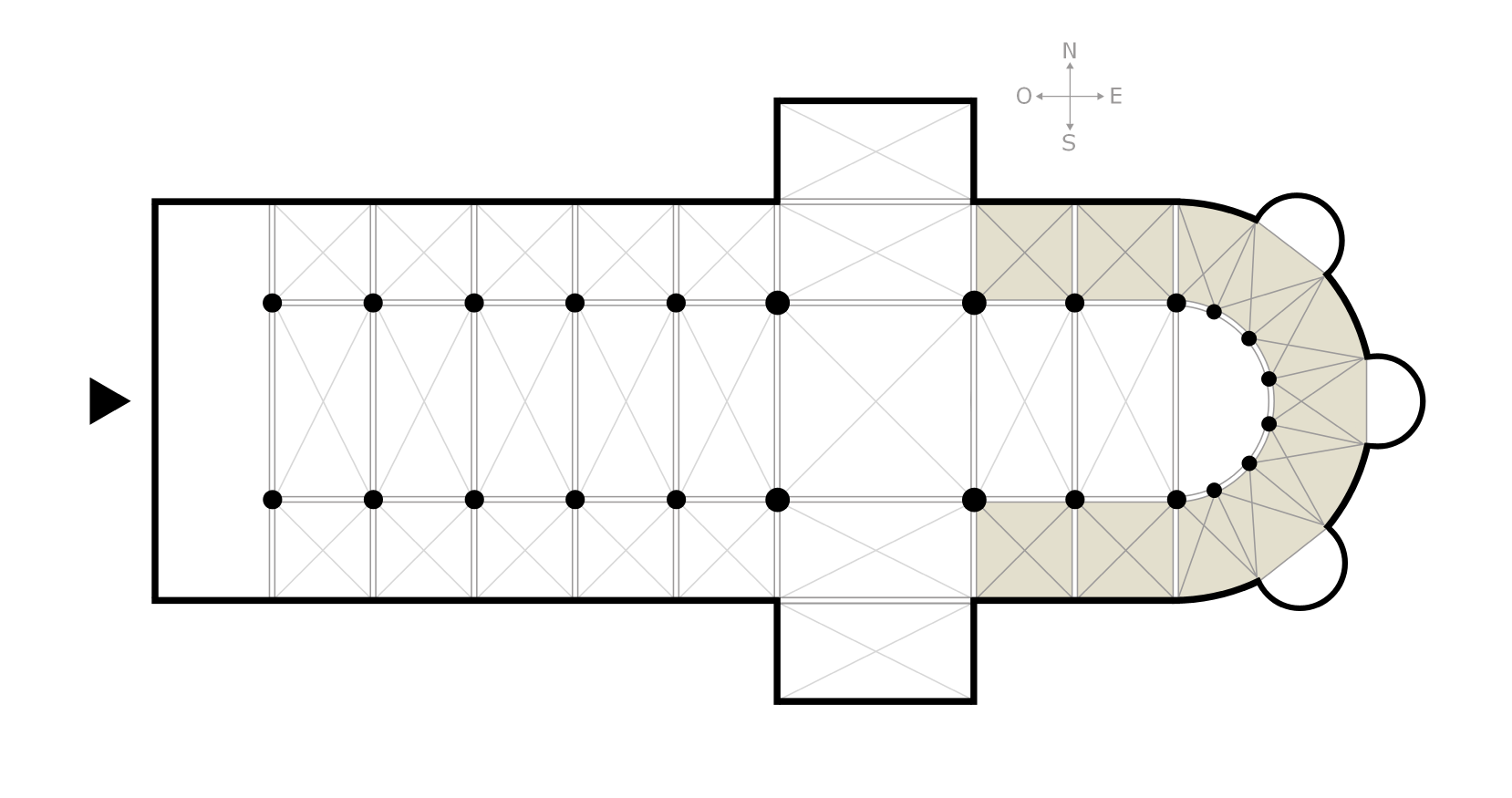
Icon
A building considered to be groundbreaking, or to claim uniqueness because of its design
Iconoclasm
The attempt to ban the veneration of icons (the representation of saintly or divine personages)
The Iconoclast Controversy (c. 726-843)
The Byzantine emperor, Leo III took a public stand against the perceived worship of icons, and in 730 their use was officially prohibited
Byzantium
An ancient Greek colony and transit point that became the location of the Byzantine Empire's capital city, Constantinople