2. Surfactants and self-assembly
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Surfactant
Molecules that interact with surfaces or interfaces . Surfactants are usually amphiphilic organic compounds, that have hydrophobic part (tail) and hydrophilic part (head). Surfactant= surface active agents
Example: sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) or fatty acid salts in common hand soap
Anionic polar head groups
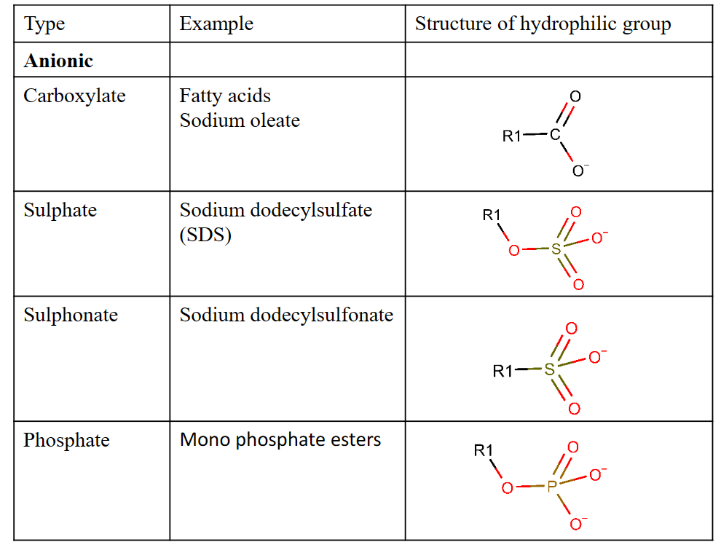
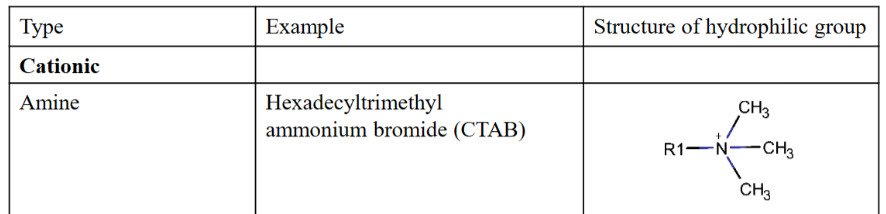
Cationic polar head group
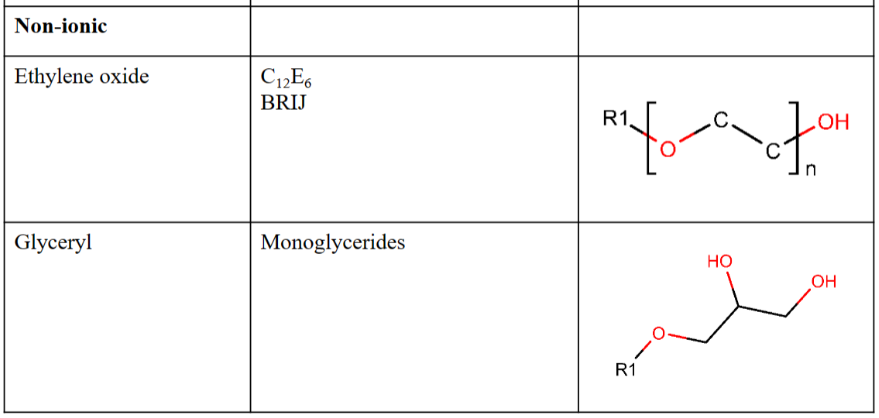
Non-ionic polar head group
Surfactants in aqueous solution
The polar head groups are hydrated and take part in the H-bonding structure of water
Hydrocarbon tails do not interact with water molecules.
– “Hydrophobic effect” (the segregation of water and nonpolar substances)
– Tail in solution → free energy increase
– Aggregation → minimize contact between hydrocarbon tails and water molecules
Formation of micelles
Micelles are self-assembled equilibrium structures
Equilibrium - Thermodynamically stable
Constant rapid exchange of individual molecules between solution and surfactants particles
Micellar solutions are not dispersions – they are one-phase solutions!
Critical micelle concentration (CMC)
Micelles form at the critical micelle concentration (CMC)
Below CMC, only dissolved particles, no micelles
What happens with free energy at formation of micelles?
The standard free energy (ΔG= ΔH-TΔS) is affected by:
– Decrease
• Removal of non-polar chains from the aqueous phase.
– Increase
• Interface creation
• Repulsion between hydrophilic head groups.
Which force tries to couteract micelle formation?
Repulsion between head groups counteracts micelle formation
– Steric (e.g large head groups → problem with packing)
– Electrostatic
How does micelle formation affect entropy?
It gives an increase in entropy.
What gives a high vs low CMC?
A large hydrophilic group gives a high CMC
A large hydrophobic group (how long carbon chain is) gives a low CMC
Mixed micelles
• Micelles can consist of different types of surfactants
• Non-surfactant molecules can be accommodated in micelles
– Example: fatty alcohol in fatty acid micelle (breaks up repulsion between acid groups)
• Can influence the CMC
– Example: Less repulsion between polar head groups
Which properties of surfactants are determined by the CMC?
Washing – detergency
Foaming
Emulsification
Solubilization of hydrophobic compounds
Describe different steps for detergency
Micellar solution- Above CMC
Surfactant adsorb to the dirt
Roll-up of dirt
Can either occur:
Spontaneously
Mechanical force (rubing etc) - most common
Dispersion (Dirt inside micelle)
Krafft point
The Krafft point is the temperature surfactant solubility increases drastically.
Below Krafft temperature is the solubility of the surfactant is low and micelles can not be formed.
It is a typical property for ionic surfactants.
Wetting
The ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface. Adsorption of surfactants changes the properties of the surface
Clean glass: High energy surface – often slightly anionic
Water on a surfactant monolayer of hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (cationic):
Low energy surface
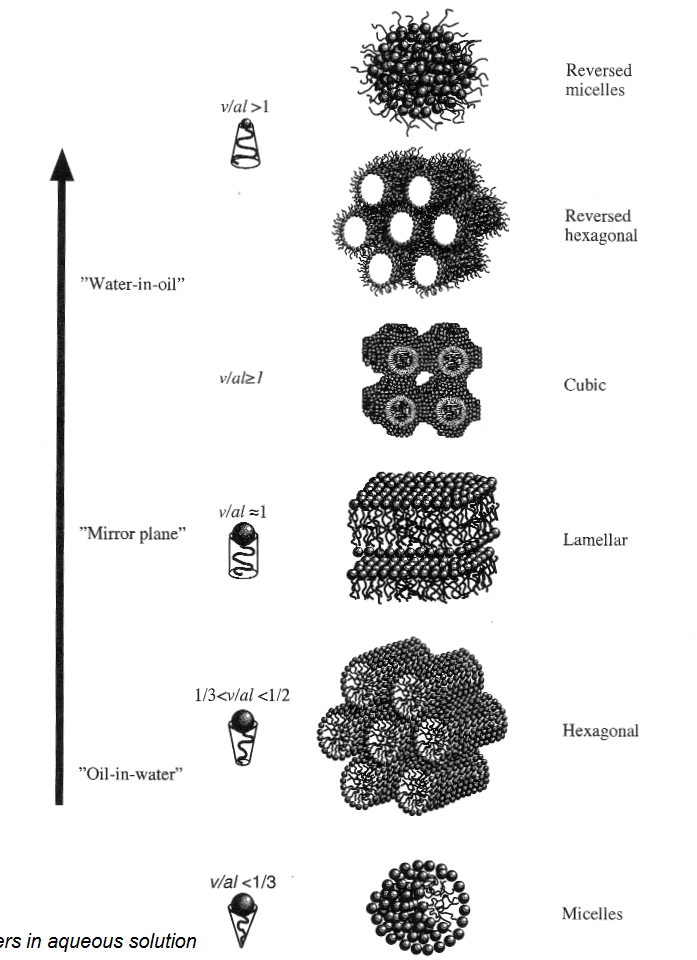
Surfactant self-assembly
Concentration above CMC additional self-assembled structures start to form (affects viscosity)
Different micelle structures
Liposome
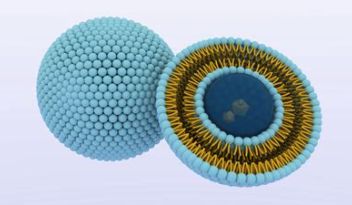
Self-assembled surfactant (polar lipid) structures for drug delivery
Ternary phase diagram
Three component system.
Every corner represents a pure condition
Each side of the triangle represents all possible binary combinations of the three components. On any of those sides, the fraction of the third component is zero (0%).
By drawing parallel lines at regular intervals between the zero line and the corner, fine divisions can be established for easy estimation.
Cloud point
Cloud point temperature at which a surfactant solution leads to a two phase transition, typically from a clear solution to a cloudy state due to phase separation (the point where precipitation starts).
Functionality lost above cloud point (solubility is lost)
Balancing of hydrophobic effects and head-group hydration (temperture might influence orientation of hydrophobic chain → making it less hydrophobic)
What happens with non-ionic ethoxylated surfactants when temperature increases?
Increasing temperature leads to two phases. This is an exception.
Very low Krafft point (not relevant for applications) - we consider it not be have a Krafft point
Applications of anionic surfactants
Used in soaps, detergents and as stabilizers.
Form stable films (good foaming agents)
Sensitive to high ionic strengths (since they are charged)
Sulphate/Sulphonate surfactants are less sensitive to Ca2+ than the fatty acids are. If we have hard water it will be less sufficient, forming an insoluble salt of calcium ions and two surfactants
However, irritant to the skin.
”Bath tub ring”
Applications of nonionic surfactants
As stabilizers in many applications
Less sensitive to high ionic strength and pH
Less efficient at high T
Often efficient at lower T (compared to anionic surfactants)
Form less rigid films than ionic surfactants (lack of electrostatic repulsion)
Useful for low foaming applications.
Applications of cationic surfactants
Cationic surfactants interact strongly with biological membranes → toxic.
– Pesticides and bactericides
Mineral ore flotation
Asphalt – (positive charged bitumen emulsions and negative gravel)
Hair conditioners – reducing static electricity and frizziness (hair is negatively charged → frizzy)
Anti-caking agents – preventing liquid bridges in powders through water-wetting prevention (make cationic → hydrophobic)
Anti-corrosion agents – preventing water wetting of steel surfaces
Drug delivery/gene therapy – form complexes with anionic macromolecules