International Finance - International Debt Markets
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what is Centralized debt denomination
borrow in headquarters' currency
ex.: US company in Belgium debt is issued in USD
what is Decentralized debt denomination
borrow in different currencies of subsidiaries
Ex.: US company in Belgium issue debt in Euro
what are domestic bonds
Bonds that are issued and traded in the domestic market (and denominated in the domestic currency)
what are International bonds
Bonds traded outside the country of the issuer
what are Foreign Bonds
Issued in a domestic market by a foreign borrower (Ex. US company issuing JPY bond in Japan)
Denominated in domestic currency
Marketed to domestic residents
Regulated by domestic authorities
what are Eurobond
Issued simultaneously in various markets, outside the specific jurisdiction of any country
Denominated in one or more currencies
This label, set before the euro creation, does not mean that they are issued in EUR
They mature in less than 10 years (usually 5)
Straight fixed-rate
Zero coupon bonds or coupon
Floating-rate notes
Coupon based on base rate such as LIBOR or Euribor
Equity-related bonds
Convertible bond: Convertible into a number of shares of equity
Warrant: Grants the bondholder the right to purchase a certain amount of common stock at a specified price
what is Dual-currency bond
Issued and paying coupons in one currency but paying back principal in another
how to calculate the annual yield
annual yield = (1+semiannual yield)² - 1
what are Eurobonds
Issued by corporations/institutions/sovereigns to the public
Fixed or floating interest
Listed and traded on exchanges
Long maturities
Issuance process is relatively long and time consuming
what are Eurocredits
Borrowed from banks Banks are lenders
Generally floating interest
Not listed, not traded
Any maturity
Relatively easy issuing process
what is a credit line
allows borrower to withdraw as a loan any amount of money up to a fixed limit
what is a term loan
loan with a fixed maturity for a fixed amount
what are syndicating loans
involves multiple lenders (banks) joining together to provide a large loan to a borrower.
what is the formula of the All-in-cost (AIC)
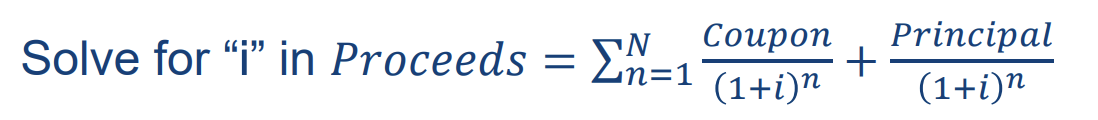
Why source debt internationally
Lower the AIC
Access more liquid debt markets
Diversify funding sources
Hedge foreign currency revenues