Ch. 6 Emotion and Affect
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts, theories, and definitions related to emotions in the context of social psychology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Emotion
Conscious evaluative rection to some event
A feeling
Conscious emotion
Powerful and clearly unifies feeling state
realizing we are feeling a certain way
Mood
Feeling state that is not clearly linked to some event
For no reason
Affect
Automatic response that something is good or bad
Outward expression of an emotional state, such as facial expressions or body language.
James-Lange theory of emotion
physiological arousal to a stimulus cause the experience of an emotion, rather than the emotion causing the physiological arousal
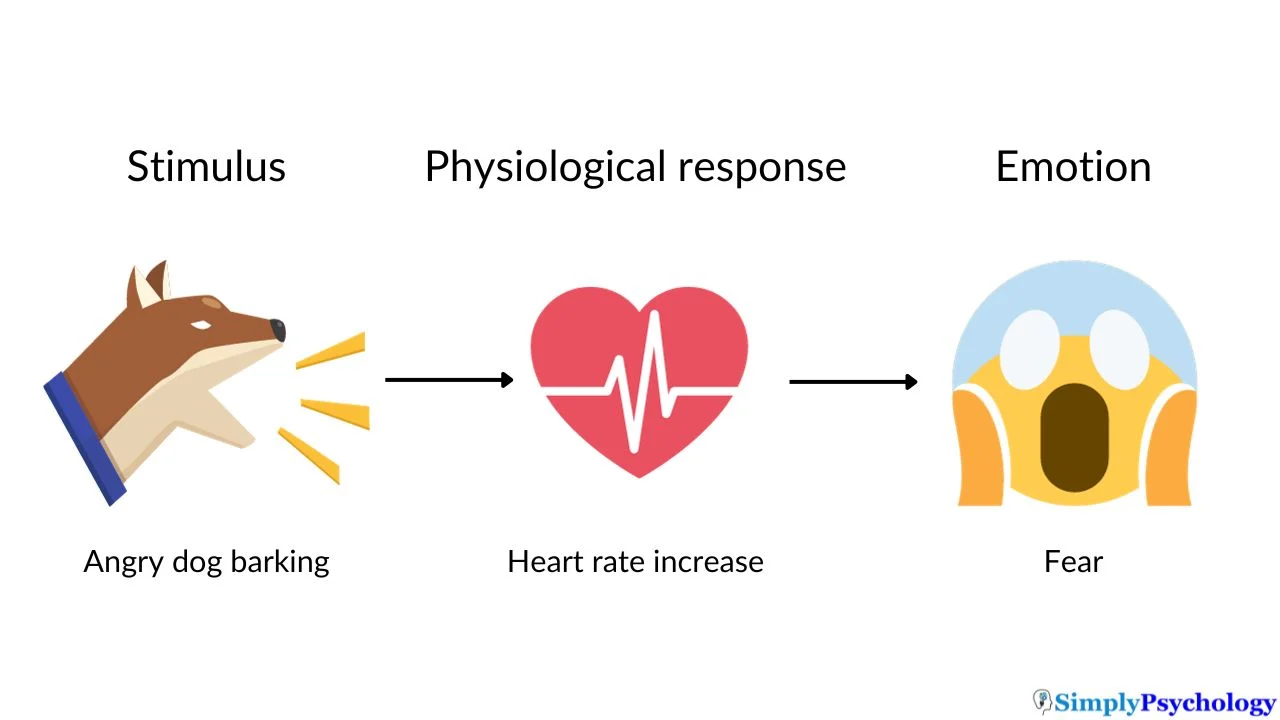
Physiological Arousal
The bodily state that accompanies emotions, influencing how they are experienced.
Facial Feedback Hypothesis
The theory that facial expressions can influence emotional experiences.
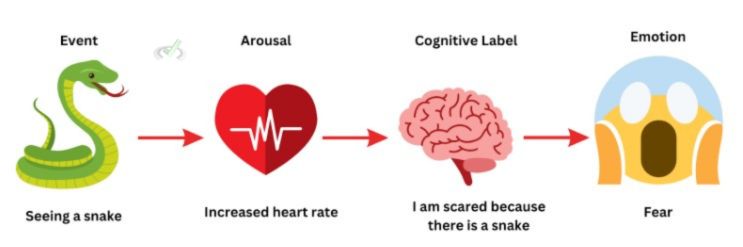
Schachter-Singer theory of emotion
Our emotions are the product of both physical arousal and our thoughts
adding a cognitive label of the arousal.
Duplex Mind
The concept that describes two different modes of processing information: conscious emotion and automatic affect.
Emotional Intelligence
The ability to perceive, access and generate, understand, and reflectively regulate emotions.
Hedonic Treadmill
The tendency for people to maintain a stable level of happiness despite major positive or negative events.
Risk-as-Feelings Hypothesis
The idea that individuals rely on emotional processes to evaluate risk, which can bias judgment.
Affect-as-Information Hypothesis
The notion that people use their feelings as information when making judgments or decisions.
Guilt
An unpleasant moral emotion associated with feeling bad about specific actions.
specific actions
Shame
Involves feeling bag but spreads to the whole person
yourself
Disgust
A strong negative feeling of repugnance or revulsion, often associated with a desire to avoid something.
Yerkes-Dodson Law
The principle that performance is best at moderate levels of arousal, with performance suffering at extremely high or low arousal levels.