B5: Communicable diseases
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Health
A state of physical + mental well-being
Disease
Conditions that can cause ill health
How are diseases classed?
Communicable (infectious)
Non-communicable
Communicable disease
Can spread from 1 organism to another
Spread by pathogens
What are communicable diseases spread by?
Pathogens
Non-communicable disease
Can’t spread from 1 organism to another
What can ill health be caused by?
Communicable + non-communicable disease
Poor diet
High stress levels
Life situations
Eg working w harmful chemicals
How can diseases interact?
Defects in IS → individual more likely to suffer from infectious diseases
Viruses living in cells trigger cancers
Immune reactions initially caused by a pathogen can trigger allergies (skin rashes + asthma)
Severe physical ill health can lead to depression + other mental illness
Tuberculosis (TB)
Communicable lung disease
Can be fatal
How does having HIV increase the risk of contracting TB?
People with defective immune system (eg w HIV), more likely to suffer from infectious disease (TB)
Human papilloma virus (HPV)
V common
Harmless in most people
What disease can HPV cause in some people?
Cervical cancer
As HPV infects cells of the cervix
How can a disease be triggered by the immune system (eg allergies)?
Body infected w pathogen
IS fights off pathogen
Person left with allergy
Viruses living in cells can trigger…
Changes that lead to cancers
How can a mental illness be triggered by a physical illness?
Person w arthritis- hard to move
Makes them feel isolated + depresed
Pathogen
Microorganisms that cause infectious disease
Pathogen examples
Bacteria
Virus
Protist
Fungi
How do bacteria make us ill?
Once inside human body, B reproduce v quickly
B then release toxins
Toxins- damage tissues + make us feel ill
Under ideal conditions how often can bacteria divide?
Every 20 mins
Toxins
Harmful chemicals
What do bacteria release that make us feel ill?
Toxins
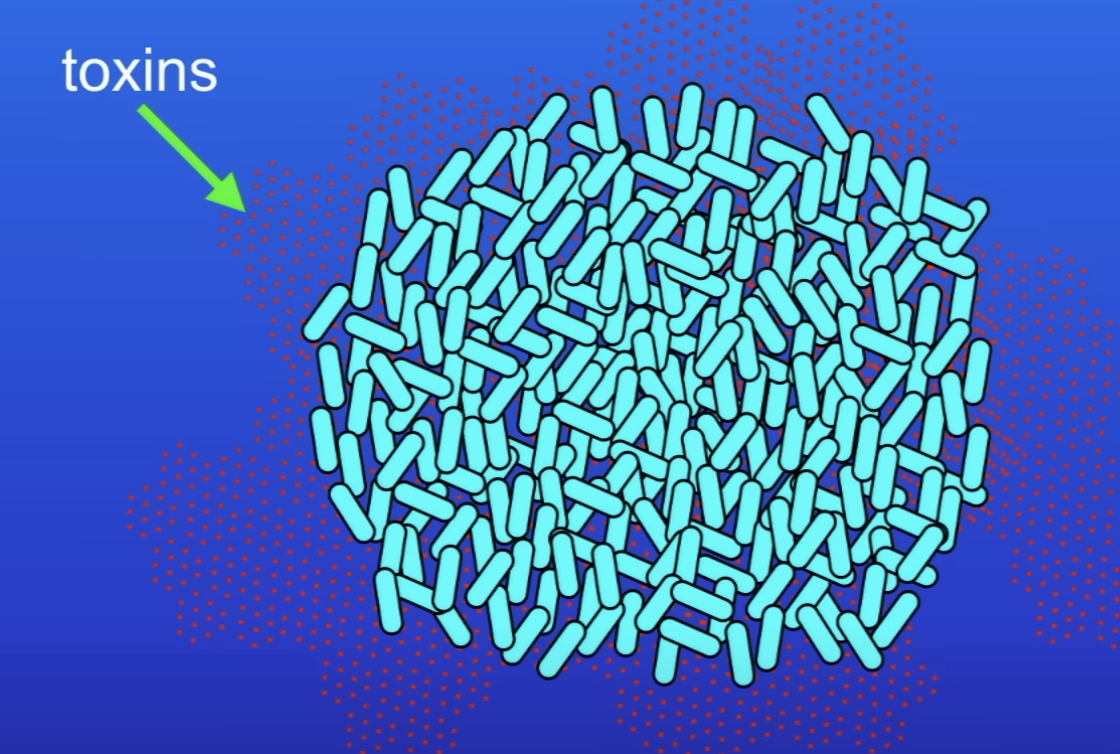
What do toxins do?
Damage tissues + make us feel ill
What do viruses need to reproduce?
Inside host cell
Can’t reproduce by themselves
How do viruses make us feel ill?
Virus invades + reproduces host cell (v damging for HC)
When virus leaves cell → causes cell to burst open + die
What happens when a virus leaves a cell?
Causes cell to burst open + die

How are pathogens spread?
Air, eg in water droplets
Water
Direct contact betw individuals
Factors affecting physical + mental health
Diet
Stress
Life situations
How can diseases interact? general
1 disease can increase the risk of contracting another
1 disease can be the cause of another
Disease can be triggered by the immune system
Mental illness can be triggered by a physical illness
What can bacteria + viruses both do inside the body?
Reproduce rapidly
What do viruses do?
Live + reproduce inside cells, causing cell damage
How to reduce the spread of pathogens?
5
Wash hands before eating (basic hygiene)
Provide people w clean drinking water
Reduce direct contact betw individuals
Isolate patients w highly infectious diseases
Vaccination
What does drinking water normally contain to reduce the spread of pathogens?
Chlorine to kill microbes
How do bacteria divide?
Binary fission
Splitting in 2
Can viruses be killed by antibiotics?
No
Droplet infection
Inhalation of droplets containing pathogens from sneezes + coughs.
How are pathogens spread by droplet infection?
Infected person coughs / sneezes → expels droplets
Virus passes into diff person when droplets inhaled
What can measles cause if complications develop?
Damage to breathing system + brain
Why are most children vaccinated against measles when they are very young?
Can be fatal in sevre cases
What does HIV initially cause?
Flu-like illness
How does the immune system become damaged in HIV + what does this lead to?
Virus attacks cells of patients IS
Overtime, IS becomes severely damaged
IS can’t fight of other infections + cancer cells (that other people could easily deal w)
In HIV when the immune system becomes severely damaged, what can the patient not fight off?
Cancer cells
Other infections
If the patient’s IS can’t fight off other infections, what does this lead to?
Patient can:
Easily contract other infections
Develop cancer
When is the HIV disease fatal?
When patient has:
Late stage HIV / AIDS
When does late stage HIV / AIDS occur?
When the body’s IS becomes so badly damaged it can no longer deal with other infections / cancers
What do antiretroviral drugs do?
Stop the virus from multiplying inside the patient → so virus doesn’t damage patients IS
Why should a patient with HIV take antiretroviral drugs?
Don’t go on to develop AIDS
Can lead a normal life expectancy
Are antiretroviral drugs a cure for HIV / AIDS?
No
Patient must take the drugs for the rest of their life
How does HIV spread when drug users share infected needles?
Blood passes in the needle from 1 person to another
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
Widespread plant pathogen affecting many species of plants, incl tomatoes
How does TMV causing a mosaic pattern of discoloration of the leaves affect plants?
Rate of PS reduced
So plant growth reduced
How can bacteria be killed?
Antibiotics
How is the spread of salmonella controlled in the UK?
Poultry are vaccinated against Salmonella
What causes the symptoms of salmonella?
Salmonella bacteria secrete toxins
Where can salmonella bacteria be found?
Poultry, eg chicken
What is gonorrhoea caused by?
Bacteria
Gonorrhoea
Sexually transmitted disease (STD)
How was gonorrhoea easily treated in the past?
Antibiotic penicillin
Why is it hard to treat gonorrhoea with penicillin antibiotics now?
Antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria are now common
Diff antibiotics used to treat it
Why should people use barrier methods of contraception (condom) during SI to reduce spread of gonorrhoea?
Prevents bacteria from passing from person to person
Why should people who have unprotected sex be tested for gonorrhoea to reduce spread of gonorrhoea?
Then they are treated with antibiotics to kill the bacteria before they pass it to another person
What is rose black spot caused by?
Fungus
How does RBS affect the plant?
Rate of PS falls
Reduced growth of plant
Fungicides
Chemicals that kill fungi
What causes malaria?
Protist
Can a protist pass directly from 1 person to another?
No
Vector
Living organisms that carries pathogens from an infected organism to a healthy one
What vector is part of the malarial protist life cycle?
Mosquito
Malarial protist life cycle
Malaria infected person bitten by mosquito
Malaria pathogen passes into mosquito
Mosquito bites a diff person + passes malaria pathogen to them
How to prevent the spread of malaria
Prevent the vectors (mosquitos) from breeding
Use mosquito nets when sleeping to avoid being bitten
Where do mosquitos breed?
Still water
How to prevent mosquitoes from breeding?
Drain areas of still water
Spray areas of still water w insecticide (kills mosquitos)
Viral diseases
Measles
HIV
TMV
Bacterial diseases
Salmonella
Gonorrhoea
2 main defence systems against pathogens
Non-specific defence system
Immune system
Role of non-specific defence system
Prevent pathogens from entering the human body
4 parts of the non-specific defence system
Skin
Nose
Trachea + bronchi
Stomach
Cilia
Tiny hairs covered with mucus that can trap pathogens
What pathogens would HCl in the stomach help kill
Microorganisms in the:
Mucus swallowed
In food
Example of when the non-specific defence system doesn’t work
Skin damaged → pathogens can invade body + enter BS
What can pathogens do once they are inside the body?
Multiply + damage healthy tissue
2 roles of the immune system
Destroy pathogens + toxins they produce
Protect us incase the same type of pathogen invades us in the future
What does the immune system involve?
WBC
What does the IS try to do if a pathogen enters the body?
Destroy the pathogen
How do WBC defend against pathogens?
Phagocytosis
Antibody production
Antitoxin production
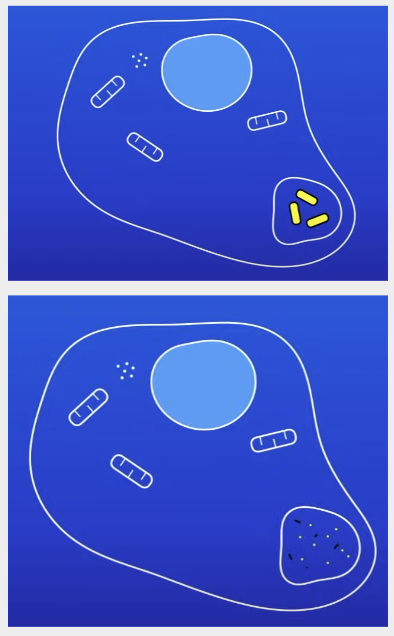
Phagocytosis
WBC ingest + destroy pathogens
How does phagocytosis work?
WBC detects chemicals released from pathogen + moves towards it
WBC ingests the pathogen
WBC uses enzymes to destroy the pathogen
How do WBC destroy pathogens by making antibodies?
WBC produces antibodies
Antibodies stick to pathogen → triggers pathogen to be destroyed
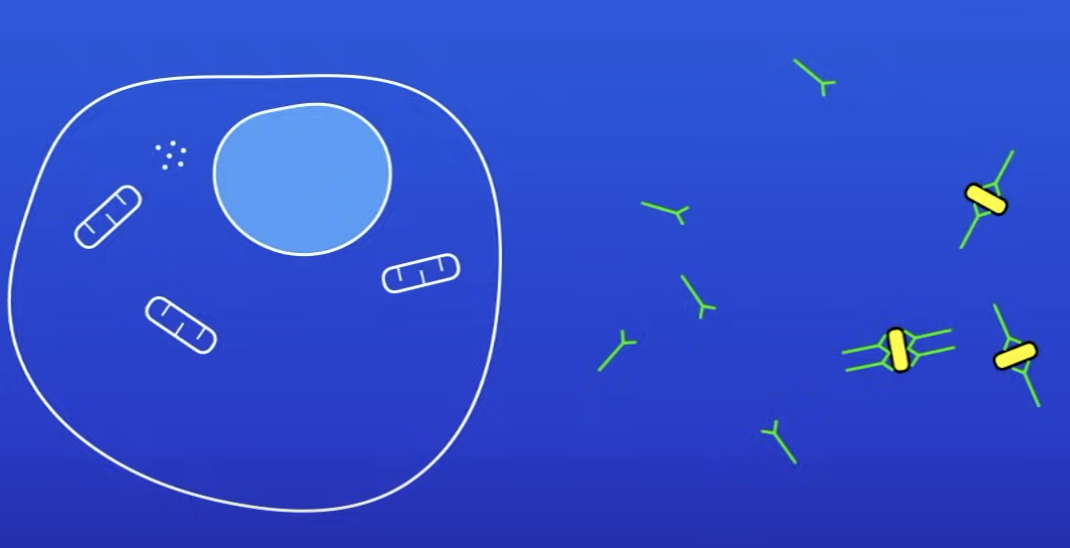

Antibodies
Protein molecules produced by WBC
Are antibodies general or specific?
Specific
What is meant by antibodies are specific?
WBC produces antibodies against a specific pathogen
Those antibodies only protect against that certain pathogen (nothing else)
Do antibodies stay in the blood for a long or short time?
Long
Why is it good that antibodies remain in the blood for a long time?
They can protect us if we ever get infected again with the same pathogen
How do WBC destroy pathogens by making antitoxins?
WBC produce antitoxins
Antitoxins stick to toxin molecules + prevent them from damaging cells
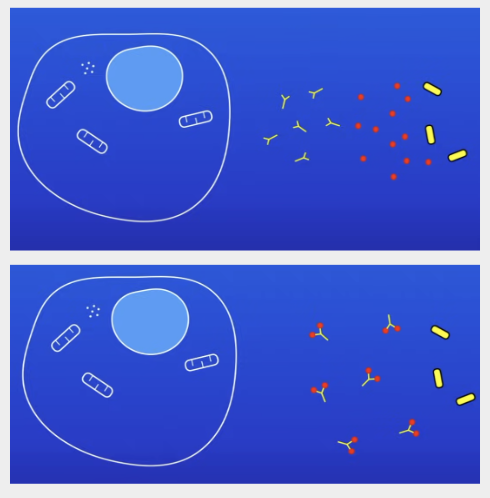
What do antitoxin stick to?
Toxin molecules
What can plants be infected by?
Pathogens
Insects
What insects can plants be infected by?
Aphids
How do aphids affect plants?
Extract nutrients (eg sugars) from plants → stunting its growth
Are insects a pathogen?
No- can’t cause infectious disease
But can be a vector
How to detect plant diseases?
7
Stunted growth
Spots on leaves
Areas of decay (rot)
Growths
Malformed stems or leaves
Discolouration
Presence of pests
How to identify plant diseases?
Reference a gardening manual or website
Take infected plant to a lab to identify the pathogen
Use testing kits containing monoclonal antibodies