Sy Ends
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
Projectile Motion
The motion experienced by a projectile influenced by gravity
2
New cards
Projectile Motion
Follows a parabolic flight path
3
New cards
Velocity
Rate Of Change In Position
4
New cards
Velocity
Shown with v
5
New cards
Velocity
Measured in m/s (meters per second)
6
New cards
Time
Flight duration of an object
7
New cards
Time
Shown with t
8
New cards
Time
Measured in s (seconds)
9
New cards
Distance
The horizontal or vertical distance traveled
10
New cards
Distance
Total Ground Covered
11
New cards
Distance
Shown with d
12
New cards
Distance
Measured in m (meters)
13
New cards
Triangle Formula
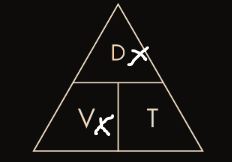
14
New cards
Acceleration
Change in velocity with respect to time
15
New cards
Acceleration
Shown with a
16
New cards
Acceleration
Measured in m/s^2 (meters per second per second)
17
New cards
Acceleration
\-9.8m/s^2
18
New cards
Projectile
Any object projected of its own inertia
19
New cards
Projectile
Influenced by acceleration of gravity
20
New cards
Trajectory
Path the projectile follow through space
21
New cards
Scolar
Magnitude
22
New cards
Vector
Magnitude + Direction
23
New cards
Dy
Height
24
New cards
Dx
Range
25
New cards
Dy
Vertical Distance
26
New cards
Dx
Horizontal Distance
27
New cards
Displacement
Overall Change In Position
28
New cards
Horizontally Launched Projectiles
Projectiles launched above the ground
29
New cards
Horizontally Launched Projectiles
\
* Velocity horizontally is constant
* Velocity vertically goes downward
* Velocity horizontally is constant
* Velocity vertically goes downward
30
New cards
Non-Horizontally Launched Projectiles
Projectiles launched at an angle
31
New cards
Non-Horizontally Launched Projectiles
* \
* vox is the initial velocity horizontally
* voy is the initial velocity vertically
* dymax means the maximum height reached by the projectile
* vox is the initial velocity horizontally
* voy is the initial velocity vertically
* dymax means the maximum height reached by the projectile
32
New cards
Find Time(NHP)
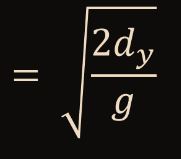
33
New cards
Find Vx(NHP)
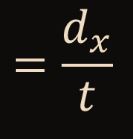
34
New cards
Find Dx(NHP)
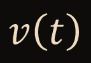
35
New cards
Find Vx(HP)

36
New cards
Find Vy(HP)
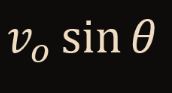
37
New cards
Find Dx(HP)
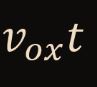
38
New cards
Find DyMax
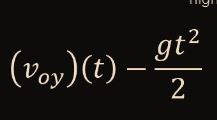
39
New cards
DyMax
the maximum height reached by the projectile