W1L1: Introduction
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
neurons, synapses, receptors, neurotransmitters, drug addictions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
number of neurons in brain
100 billion
number of neurons in cortex
0.15 quadrillion
cell membrane of neuron
acts as wall to prevent things from entering and leaving neuron
cell membrane of neuron: layers
two fatty layers with fatty inside of each layer sticking together like a sandwich
cell membrane of neuron: fatty layer
because of the layer, fluids and other chemicals like neurotransmitters can’t pass through
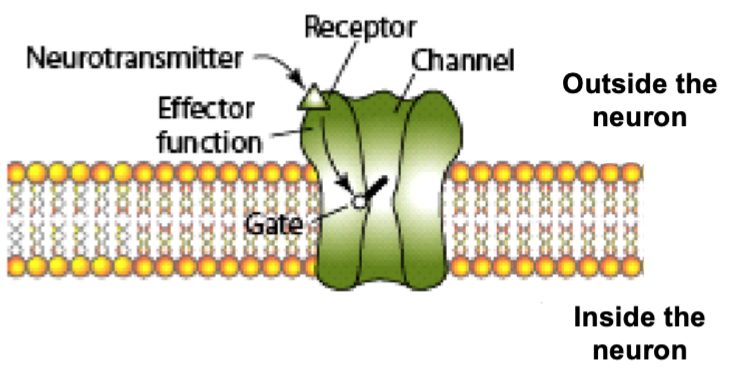
receptors
located on outside of cell membrane and allow released neurotransmitters to influence post-synaptic neuron
types of receptors
Ion channels
G-Protein coupled
receptor: specificity
have very specific function - when a neurotransmitter binds to the receptor this will trigger the same event every time
receptor: structure
not open-shut gates but have complex structures and often a small change in shape will open a channel
receptor: ion channels
act as gates for ions - when neurotransmitter binds to receptor outside neuron, gate opens and ions (either + or - charged molecules) flow through
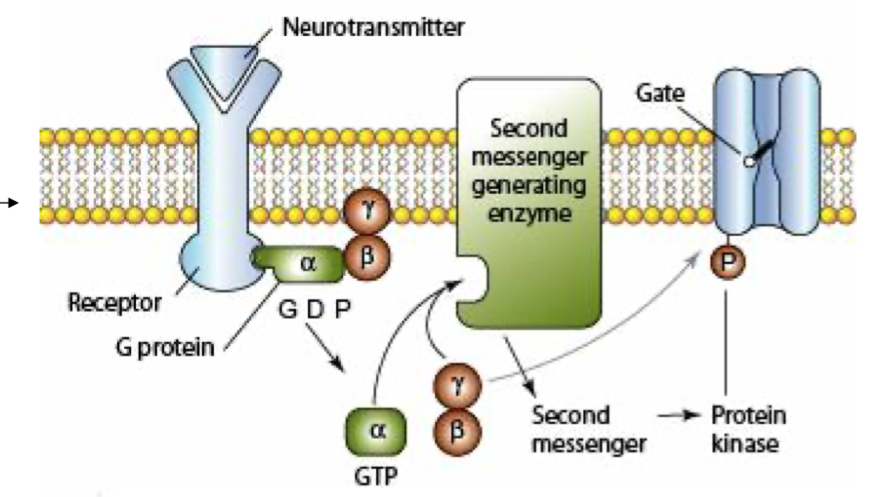
receptor: g-protein coupled receptor
work through second messengers - when neurotransmitter binds to receptor it activates a second messenger system that can either open a channel or cause other things to change in the cell (DNA being transcribed and new proteins being made)
neurotransmission
1:1 info processing relationship: chemical substance from a neuron at an anatomically specialised junction (synapse), which diffuses across a narrow cleft to affect one of sometimes two postsynaptic neuron’s, a muscle cell or other effector cell
neuromodulation
acting on multiple neutrons with long lasting effects: chemical substance released from a neuron in the CNS or PNS that affects groups of neuron’s, or effector cells that have appropriate receptors - may not be released at synaptic sites, often acts through second messengers
neurotransmission: time
excitatory or inhibitory effect - rapid (millisecond), precise, point to point communication
neuromodulation: time
slower (milliseconds to seconds) processes that alter subsequent responsiveness of neurons, diffusion of communication to a number of neurons
neurotransmitters: currency
excitatory (glutamate) /inhibitory (GABA)
neuromodulators: government
modulatory (serotonin, dopamine, noradrenaline)
neuromodulation: presynaptic
alters neurotransmitter release
neuromodulation: postsynaptic
alters neurotransmitter action (e.g alters excitability, firing pattern)
neuromodulation: changes
can cause changes in neural function or structure (e.g number of receptors/enzymes/synaptic plasticity)
nuclei
bundle of cell bodies
neuromodulators: location
originate in small clusters of neurons (nuclei) deep within brain (mostly brain stem)
noradrenaline (NE) system: location
main nucleus is ‘locus coeruleus’ in the pons
histamine (HA) system: location
‘forgotten one’ - neurons localised to posterior hypothalamus (affects sleep and arousal)
cholinergic (ACh) system: location
pontine and basal forebrain groups (smoking affects)
dopamine (DA) system: location
ventral tegmental area and substantial nigra area (midbrain)
serotonin (5-HT) system: location
several ‘raphe’ nuclei distributed in brainstem (across medulla, pons and midbrain of brainstem)
neurotransmitter: synthesis and transport to synapse
slow
neurotransmitter: action
extremely fast because it sits ready for release
psychopharmacology
study of drug induced changes in mood, sensation, thinking and behaviour
drugs: action at recepetor
mimic natural neurotransmitters/neuromodulators
drugs: agonists
activate receptor like natural compound
drugs: antagonists
block receptor and prevent natural compound from activating it
cycle of neurotransmitters
synthesis
release from synaptic vesicles
binds to receptors
± influence on post synaptic neuron
broken down into enzymes
reuptake of transmitter
formation and storage in synaptic vesicles
synthesis interruption
neurotransmitter function can be altered by increasing or decreasing synthesis of the neurotransmitter - adding or subtracting molecules is how neurotransmitters are synthesised
MDMA: transport in neurotransmitter interruption
MDMA mimics serotonin (5-HT) and enters neurons
MDMA prevents serotonin storage in vesicles
serotonin accumulates in cytosol because packaging is inhibited
MDMA switches direction of explore, instead of import
serotonin concentrations increase in synaptic cleft
Post-synaptic serotonergic neurons fire continuously
hormones
signalling molecules produced by glands and transported through blood to regulate physiology (muscles, neurons) and behaviour
pharmacology affects psychology
natural neurotransmitters and natural/artificial drugs can affect mood, cognition and behaviour
psychology affecting pharmacology
emotional or stressful events, thoughts and behaviour affect humans because they influence neurotransmitters