micro hw questions
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
Pasteur’s Experiments with Swan Neck Flasks disproved which of the following theories on the origin of microorganisms:
Spontaneous Generation
Clay Theory
Creationism
Evolution
Spontaneous generation
Compared to Eukaryotes, Bacteria and Archaea have ________ surface-area-to-volume ratios, causing ________ nutrient exchange and growth rates.
higher, slower
higher, faster
lower, slower
lower, faster
higher, faster
You have discovered a new ovoid (oval-shaped) microorganism that is 1um in diameter. The organism's genome is a single circular chromosome. The new microorganism is:
a virus
a fungus
a bacteria
a plant
A bacteria
The germ theory of disease refers to:
The theory that some human disease is transferred from person to person via microorganisms.
The theory that some human diseases are caused by microorganisms that have gained access to the human body.
The theory that all human disease is the result of microorganisms already living inside or on a human body.
The theory that all human diseases are caused by microorganisms that have gained access to the human body.
The theory that some human diseases are caused by microorganisms that have gained access to the human body.
When examining the evolution of life on Earth, scientist find the eukaryotes are more similar to the kingdom _____________ at the genetic level.
Fungi
Bacteria
Archaea
Algae
Archaea
Dr. Strummer is examining a new microorganism isolated from the permafrost of Siberia. Transmission electron micrographs show a unicellular organism 100um in diameter. The organism appears to have a nucleus, membrane bound organelles, and a cell wall. What would you predict is the main chemical component of this organism's cell wall?
Protein
Lipopolysaccharide and Lipotechoic acid
Cellulose or Chitin
N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid
Cellulose or Chitin
Which of the following is the correct way of writing the genus and species name of a bacteria:
Escherichia Coli
escherichia coli
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli
Uncle Billy Bob is nervous. Three of his prize winning roosters, Huey, Dewey, and Louie, at Billy Bob’s Ranch for Interesting Chickens have developed sores on their beaks consistent with a condition called beak rot. Dr. Strummer visits the ranch, takes samples from the sores of the three diseased chickens, and brings the samples back to his research lab. He isolates bacteria from the each sample (Huey, Dewey, and Louie) and grows them in three SEPARATE culture tubes. He then injects aliquots (small portions) of each diluted culture into the backs of 5 healthy laboratory chickens that are sterile and lack any disease immunity. After 3 days the laboratory chickens injected with bacteria cultured from the samples of Huey and Dewey have sores on their beaks similar to those observed in Huey and Dewey. Chickens injected with bacteria cultured from the samples of Louie are perfectly healthy. Is the cause of Huey’s beak rot an infectious disease?
Yes, because bacteria were isolated from the sore sample of all three chickens, consistent with Koch’s 2nd postulate.
No, because bacteria don’t cause beak rot, it is a fungal infection
Yes, because bacteria isolated from Huey’s sore sample were able to cause sores in laboratory chickens consistent with Koch’s 3rd postulate.
No, because bacteria isolated from the Louie’s sore sample were unable to cause sores in laboratory chickens, inconsistent Koch’s 3rd postulate.
Yes, because bacteria isolated from Huey’s sore sample were able to cause sores in laboratory chickens consistent with Koch’s 3rd postulate.
_____________ refers to the evolutionary relationships between organisms deduced through the comparison of their genetic material.
Relatedness
Phylogeny
Ecology
Geneology
Phylogeny
Which of the following activities is NOT an activity observed in living cells?
All cells metabolize.
All cells communicate with other cells.
All cells evolve.
All cells grow.
All cells communicate with other cells.
True or False: All cellular microorganisms are prokaryotic cells.
True
False
False
A ________ is smaller than a _______ which, in turn, is smaller than a ________.
bacteria, virus, human cell
human cell, bacteria, virus
virus, bacteria, human cell
bacteria, human cell, virus
virus, bacteria, human cell
____________ is defined as the smallest distance by which two objects can be separated and still be distinguished.
Contrast
Magnification
Refraction Index
Resolution
Resolution
Rod shaped bacteria arranged in chains are referred to as:
Staphylococci
Streptococci
Streptobacilli
Staphylobacilli
Streptobacilli
True or False: Cell morphology can be used to predict the physiology, ecology, and phylogeny of a prokaryotic cell.
False
Which of the following statement is NOT true about the use of staining in microscopy?
Staining is used to to increase the resolving power of a microscope.
Staining is used to increase contrast.
Staining can be used to colorize a cell OR colorize the background surrounding a cell.
Staining almost always kills the cells being stained.
Staining is used to to increase the resolving power of a microscope.
True or False: Prokaryotes contain membrane bound organelles like a nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, or mitochondria.
False
Which type of microscopy is best used to view living cells?
Transmission electron microscopy.
Light microscopy of a simple stained specimen.
Light microscopy of an unstained specimen.
Scanning electron microscopy.
Light microscopy of an unstained specimen.
Which of the following types of cellular organisms is classified as a prokaryote?
Fungi
Virus
Protists
Bacteria
Bacteria
True or False: Cell morphology can be used to predict the physiology, ecology, and phylogeny of a prokaryotic cell.
False
The Cell Wall of bacteria is made up of:
Chains of N-Acetylglucosamine and N-Acetylmuramic acid linked by peptide crosslinks.
Chains of N-Acetylglucosamine and N-Acetylmuramic acid.
Chains of N-Acetylglucosamine and N-Acetylmuramic acid linked by lipid crosslinks.
Chains of N-Acetylglucosamine and N-Acetylmuramic acid linked by carbohydrate crosslinks.
Chains of N-Acetylglucosamine and N-Acetylmuramic acid linked by peptide crosslinks.
Which of the following is TRUE about gram-positive bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan cell wall that includes Lipotechoic acids (LTA).
Gram-positive bacteria have an inner membrane and an outer membrane.
Gram-positive bacteria stain pink when Gram stained.
The inner membrane of gram-positive bacteria contains lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan cell wall that includes Lipotechoic acids (LTA).
The NCX protein is integral membrane used by many eukaryotic cells to remove cytoplasmic calcium. It uses the power of an electrochemical gradient of sodium ions to move of one calcium ion out of the cytoplasm and three sodium ions into the cytoplasm. NCX is an example of a:
Antiporter
Uniporter
Symporter
Cotransporter
Antiporter
Which of the following components is NOT found in bacterial cell membranes?
cholesterol
lipids
proteins
hopanoids
Cholesterol
Bacterial membrane proteins function as:
carrier proteins
receptor proteins
channel proteins
all of the answers are correct.
all of the answers are correct.
Lipopolysaccharide is found in the:
outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria.
inner membrane of gram-negative bacteria.
outer membrane of the gram-positive bacteria.
inner membrane of gram-positive bacteria.
outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane contracts to allow cell movement.
The cell membrane acts as a permeability barrier.
The cell membrane acts as anchor for proteins involved in cellular processes.
The cell membrane allows for the production of a proton (H+) gradient.
The cell membrane contracts to allow cell movement.
Lactose permease is a membrane protein which uses a proton (H+) gradient to import both a lactose molecule and a proton (H+) into the cell. Lactose permease is an example of:
a Simple Transport Protein
a Group Translocation Protein
an ABC Transport Protein
an Antiport protein
a Simple Transport Protein
Flagella are:
protein filaments that rotate allowing bacteria to move.
proteins that help compact the nucleoid of bacteria.
pentacyclic chemicals that stabilize the membranes of bacteria.
protein filaments that allow for attachment of bacteria to a surface.
protein filaments that rotate allowing bacteria to move.
Which of the following is TRUE about endospores:
Endospores are metabolically dormant forms of bacteria.
All bacteria can make endospores.
Endospores are easily destroyed by washing surfaces with ethanol.
The process of forming an endospore is faster than the normal process of cell growth and division.
Endospores are metabolically dormant forms of bacteria.
Using phase contrast microscopy on a wet mount of live cells, you observe motile bacilli moving rapidly through the field of view, changing directions after a brief tumble and taking off in a different direction. These cells are exhibiting:
swimming/flagellar motility, due to the action of flagella.
twitching motility, due to the action of pili.
gliding motility, due to the action of fimbrae
creeping motility, due to the presence of water.
swimming/flagellar motility, due to the action of flagella.
Bacterial pili function:
to allow for twitching motility
in the attachment of bacteria to a surface.
allow for the exchange of genetic material.
All of the answers are possibly functions of pili.
All of the answers are possibly functions of pili.
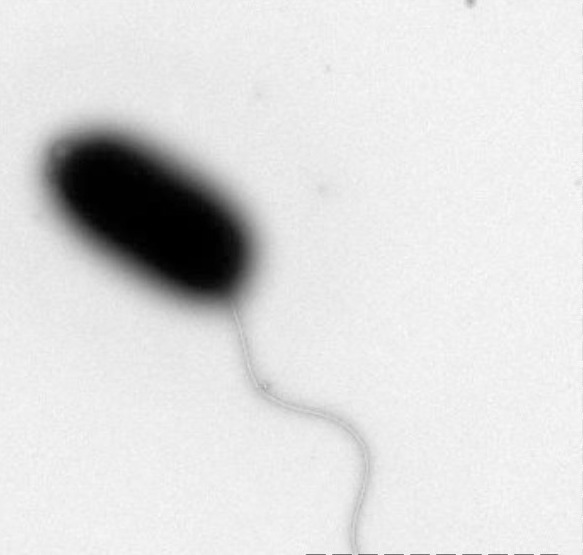
The micrograph below depicts a bacterium with a/an _______________ arrangement of flagella.
monotrichous
peritrichous
lophotrichous
amphitrichous
monotrichous
______________ are structures found on the surface of some bacteria that assist the bacteria in attachment to surfaces, protect the bacteria from desiccation, and inhibit phagocytosis of the bacteria by immune cells.
Capsules
Pili
Flagella
Endospores
Capsules
True or False: the bacterial genome must be compacted via supercoiling in order to fit inside the bacterial cell.
True
CHROMagar MRSA is a culture media that is designed to only grow Staphylococcus. It contains a chromogenic substrate that will turn colonies Methicillin-Resistant-Staphylococcus aureus pink. All other Staphylococcus species grow as colorless colonies on this media. CHROMagar MRSA is an example of:
selective and differential media
selective media
differential media
synthetic media
selective and differential media
Autotrophs:
utilize Carbon from CO2.
utilize Carbon from organic compounds.
generate ATP from harnessing light energy
are the sworn enemy of the Decepticon
utilize Carbon from CO2.
A cell membrane is _______ , allowing ______ molecules to move across while tending to keep _______ in (or out).
semipermeable, water, solute
semipermeable, solute, water
permeable, water, solute
impermeable, solute, water
semipermeable, water, solute
_____________ is all of the biochemical reactions taking place in an organism.
Metabolism
Catabolism
Anabolism
Catalysis
Metabolism
Competitive inhibition occurs when:
an inhibitor binds to the enzyme’s active site preventing it from binding substrate.
an inhibitor binds to substrate and preventing it from binding the enzyme’s active site.
an inhibitor binds to the substrate-enzyme complex preventing enzyme activity.
an inhibitor binds to an alternate site in the enzyme changing the confirmation of the active site and preventing it from binding substrate.
an inhibitor binds to the enzyme’s active site preventing it from binding substrate.
____________ act as catalysts, __________ the activation energy of a specific reaction.
Enzymes, increasing
Enzymes, lowering
Proteins, lowering
Proteins, increasing
Enzymes, lowering
Feedback inhibition hinders a metabolic pathway by:
having the product of the metabolic pathway destroy the initial substrate of the metabolic pathway.
having the product of the metabolic pathway inhibit the activity of an enzyme required for an earlier reaction.
having the product of the metabolic pathway exported out of the cell.
having the product of the metabolic pathway destroy an enzyme required for an earlier reaction.
having the product of the metabolic pathway inhibit the activity of an enzyme required for an earlier reaction.
A holoenzyme is:
a non-functional enzyme that lacks it co-factor.
a functional enzyme-co-factor complex.
a non-functional enzyme that does not require a co-factor.
a non-functional enzyme bound to an inhibitor.
a functional enzyme-co-factor complex.
Lithotrophs ______________ to generate ATP.
oxidize organic chemicals (glucose, amino acids, fats, etc)
harvest light energy
oxidize inorganic chemicals (H2, Fe2+, H2S, etc)
reduce inorganic chemicals (H2, Fe2+, H2S, etc)
oxidize inorganic chemicals (H2, Fe2+, H2S, etc)
True or False: Twitching motility requires the rotation of pili in a clockwise fashion.
False
Which of the following is NOT true about enzymes?
Enzymes are reusable.
Enzymes are highly specific and generally catalyze a specific reaction.
All enzymes are proteins
Enzymes are catalysts that reduce the activation energy of biochemical reactions.
All enzymes are proteins
By dry weight, bacterial cells are mostly composed of:
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Carbon
Carbon
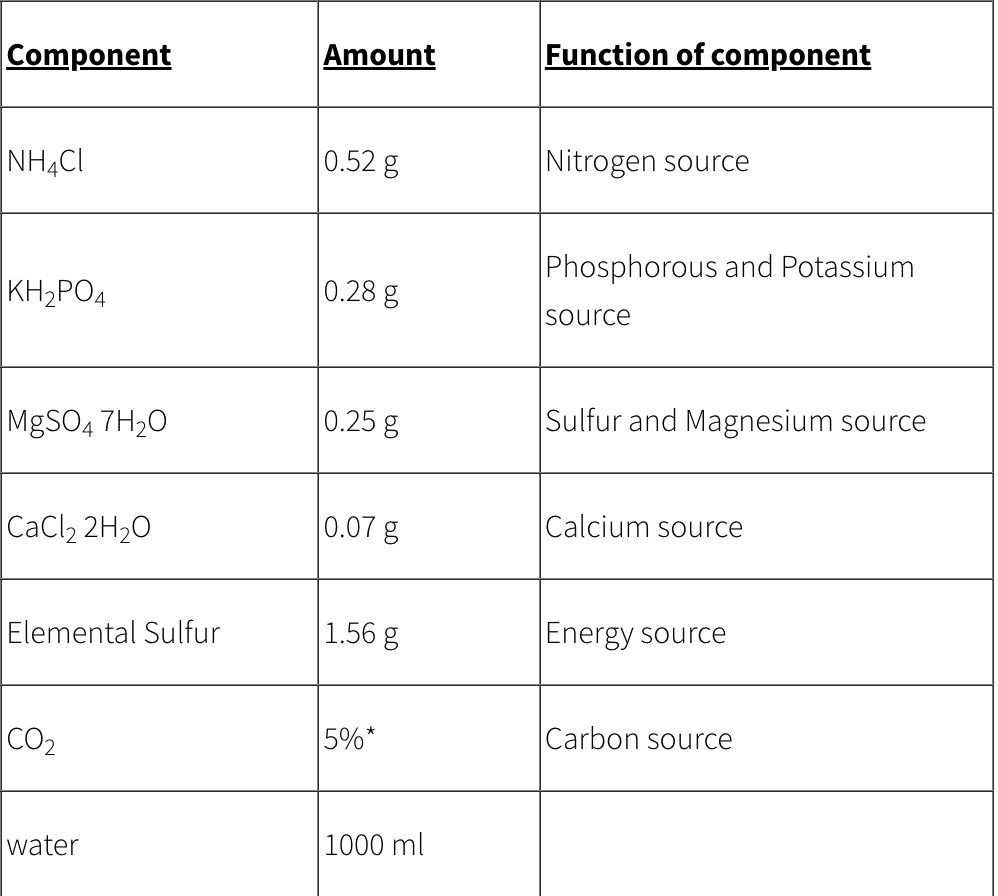
Dr. Strummer is studying Thiobacillus thiooxidans, a lithoautotrophic bacterium. He asks you, his faithful laboratory technician to use the recipe below and make the media required to grow his bacterium. This media is best described as:
a complex media.
a starvation media.
a synthetic/defined media.
a differential media.
a synthetic/defined media.
________________ media allows for differentiation of bacteria via colony morphology and pure culture.
Liquid
Solid
Semi-solid
Vapor
Solid
In a continuous culture, the amount of biomass/bacteria produced in the culture is dependent on the ________
concentration of the limiting nutrient.
concentration of glucose.
dilution rate.
none of the answers are correct.
concentration of the limiting nutrient.
Dr. Strummer decides to measure the growth of his liquid culture of bacteria using two different methods: reading the optical density of liquid culture at 600nm and plating dilutions of the liquid culture and counting the colony forming units. The cell count obtained by the optical density measurement and the colony forming unit assay will be the LEAST proportional to each other during:
death phase
exponential/log phase
stationary phase
lag phase
death phase
Genetically modified bacteria are commonly used to manufacture consumer health goods like insulin and antibiotics. Which of the following terms best describes the culture method used in biomanufacturing?
Batch Culture
Synthetic Culture
Continuous Culture
Defined Culture
Continuous Culture
Bacteria increase in mass during which stage of the cell cycle?
B period
C period
A period
D period
B period
The time between inoculation of bacteria into liquid media and the beginning of growth is usually called the:
growth phase.
lag phase.
death phase.
exponential/log phase.
lag phase.
Dr. Strummer is growing a culture of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Nutrient broth. He begins by inoculating the nutrient broth with 50 bacteria. He allows the bacteria to grow for 2 hours. The generation time for S. pneumoniae in nutrient broth is 60 minutes. How many bacteria will Dr. Strummer have in his culture at the end of the experiment?
Nt = N0 x 2n ; log10 (Nt/N0) / 0.301 = n ; k = n/t; g = 1/k; g = t
400
100
800
200
200
Dr. Strummer is growing a laboratory strain of Escherichia coli in MacConkey Broth. He inoculated the culture broth with 50 bacteria. After 4 hours of growth, Dr. Strummer uses a plate Colony Unit Assay and determines his culture now has 15,000 bacteria what is the approximate generation time of the bacteria?
Nt = N0 x 2n ; log10 (Nt/N0) / 0.301 = n ; k = n/t; g = 1/k; g = t
30 minutes
60 minutes
90 minutes
100 minutes
30 minutes
Which of the following best describes synthetic media:
A media that contains chemicals to indicate bacterial species that possess or lack a biochemical process.
A media whose exact chemical composition is unknown.
A media that contains ingredients to inhibit growth of certain bacterial species, but allow the growth of others
A media whose exact chemical composition is known.
A media whose exact chemical composition is known.
The tendency of a biological system to maintain internal stability, owing to the coordinated response of its parts to any situation or stimulus that would tend to disturb its normal condition or function is referred to as:
heterostasis
homeostasis
equilibrium
balance
homeostasis
After testifying against his criminal conspirators, Tekashi69, real name Daniel Hernandez, has just entered the FBI witness protection program. While working at his new day job in construction, Tekashi69 "falls" from a two story window, leaving him unable to walk and in incredible pain. His handler, Jack Webb, takes Tekashi69 to his local area hospital hoping that his prominent facial tattoos will not blow his cover. Physician's diagnose Tekashi69 with a shattered hip and say he is in need of an immediate hip joint replacement. Dr. Octagon, the consulting orthopedic surgeon, prepares for surgery but notices the packaging of the hip prosthetic he needs to use has been compromised and is no longer sterile. The prosthetic is composed of metal and plastic, stable at temperatures under 100oC, sensitive to ionizing radiation, and chemically non-reactive. Which sterilization technique would you recommend Dr. Octagon use to sterilize the hip prosthetic?
Autoclave
Formaldehyde Gas Vapor
Dry Heat Oven
X-ray Sterilization
Formaldehyde Gas Vapor
An antiseptic is distinguished from other chemical disinfectants by:
its ability to inhibit growth of microorganisms but not necessarily kill all of them.
its ability to protect from subsequent microbial infections—not just initial sterilization.
its ability to be used on living tissues without harm.
its ability to kill all bacteria and microscopic fungi but not being effective against viruses.
its ability to be used on living tissues without harm.
Dr. Strummer is comparing three chemical disinfectants, Lysol, tincture of iodine, and chloramine, for their ability to kill Staphylococcus aureus. Lysol has a phenol coefficient of 3.5. Tincture of iodine has a phenol coefficient of 6.3. Chloramine has a phenol coefficient of 133. Which chemical agent is the least effective at killing Staphylococcus aureus?
tincture of iodine
chloramine
Lysol
It is impossible for me to tell with the information provided.
Lysol
Sterilization indicates
the elimination of pathogenic microbes.
a form of radiation used to prevent microbial growth.
the elimination of all microbes.
using chemicals to disinfect tissues.
the elimination of all microbes.
Soap combined with hot water is considered":
a low level disinfectant.
a mid level disinfectant.
a high level disinfectant
not effective at reducing microbial content.
a low level disinfectant.
In an oxidation reduction reaction, the substance reduced _____ electrons and the substance oxidized _____ electrons.
gains, loses
loses, gains
gains. gains
loses, loses
gains, loses
True or false: Cellular energy can be stored in the form of ATP
False
Which of the following is TRUE about the Citric Acid Cycle?
The Citric Acid Cycle requires 2 NADH and generates 2 ATP, for each glucose molecule catabolized.
The Citric Acid Cycle is utilized during fermentation, aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
The Citric Acid Cycle catabolizes glucose generating 4 ATP and 2 acetyl-CoA.
FAD+ is required for the Citric Acid Cycle.
FAD+ is required for the Citric Acid Cycle.
Which of the following metabolic pathways generates ATP through oxidative phosphorylation?
Glycolysis
Electron Transport System
Citric Acid Cycle
Fermentation
Electron Transport System
Glycolysis converts glucose into two _____ carbon molecules of pyruvate, generating a net _____ ATP and _____ NADH.
3, 2, 2
4, 3, 2
2, 2, 2
2, 3, 4
3, 2, 2
Glycolysis and the Citric Acid cycle generate ATP via:
oxidative phosphorylation
substrate-level phosphorylation
substrate-level phosphorylation AND oxidative phosphorylation
None of the answers are correct. Glycolysis and the Citric Acid Cycle do not generate ATP.
substrate-level phosphorylation
The Proton Motive Force or Δp, generated by the pumping of protons from the cytoplasm to the periplasmic space creates:
an electrical potential (Δψ) based on the charge difference between the cytoplasm and periplasm.
a pH difference (ΔpH) based on the difference in chemical concentration of H+ between the cytoplasm and periplasm.
both an electrical potential (Δψ) and pH difference (ΔpH).
None of the above are correct.
both an electrical potential (Δψ) and pH difference (ΔpH).
Electrons are transferred between proteins in the electron transport chain using:
Shuttle Proteins
Retinal
Quinones
Fatty Acids
Quinones
In aerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor is:
H2O
ATP
NO3-
O2
O2
UV irradiation works as a disinfectant procedure because:
it damages bacteria cell walls.
it denatures bacterial proteins
it damages bacterial DNA by causing the formation of Thymine dimers.
it damages bacterial membranes.
it damages bacterial DNA by causing the formation of Thymine dimers.
A bacterium that uses glucose as an energy source has been isolated from an anaerobic environment. After growth of the bacterium in an anaerobic culture, Dr. Strummer observes the bacterium producing methane gas (CH4). The pH of the media does not change. Which of the following processes is the bacteria utilizing?
Anaerobic Respiration
Aerobic Respiration
Fermentation
Sporulation
Anaerobic Respiration
Which one of the following is NOT utilized in both aerobic respiration and fermentation?
NAD+
Glucose
ATP
FADH2
FADH2
The unique tart flavor of Swiss cheese is a result of the bacteria Propionibacterium freudenreichii being added to milk. This bacteria produces propionic acid as result of which metabolic process?
Aerobic Respiration
Fermentation
Anaerobic Respiration
The Electron Transport System
Fermentation
The Proton Motive Force or Δp, generated by the pumping of protons from the cytoplasm to the extracellular space creates:
an electrical potential (Δψ) based on the charge difference between the cytoplasm and periplasm.
a pH difference (ΔpH) based on the difference in chemical concentration of H+ between the cytoplasm and periplasm.
both an electrical potential (Δψ) and pH difference (ΔpH).
None of the above are correct.
both an electrical potential (Δψ) and pH difference (ΔpH).
Fermentation converts ______ allowing for organisms to continue to use _______.
NADH to NAD+, the Electron Transport System
FADH2 to FAD+, Glycolysis
NADH to NAD+, Glycolysis
FADH2 to FAD+, the Citric Acid Cycle
NADH to NAD+, Glycolysis
_________ makes more ATP than ________ which makes more ATP than __________.
Anaerobic Respiration, Aerobic Respiration, Fermentation
Fermentation, Aerobic Respiration, Anaerobic Respiration,
Aerobic Respiration, Anaerobic Respiration, Fermentation
Aerobic Respiration, Fermentation, Anaerobic Respiration
Aerobic Respiration, Anaerobic Respiration, Fermentation
Glycolysis and the Citric Acid cycle generate ATP via:
substrate-level phosphorylation
oxidative phosphorylation
substrate-level phosphorylation AND oxidative phosphorylation
None of the answers are correct. Glycolysis and the Citric Acid Cycle do not generate ATP.
substrate-level phosphorylation
Dr. Strummer is conducting a series of experiments to examine the aerobic respiration of Escherichia coli grown in three different chemically defined media each with a single carbon source: either glucose (a sugar), glycine (an amino acid), or phosphotidyl inositol (a lipid). Which of the following statements correctly describes the results of his experiments?
Bacteria will not grow in the phosphotidyl inositol media because lipid cannot be used to generate ATP
Bacteria grown in glycine media will generate more ATP than bacteria grown in glucose media.
Bacteria grown in phosphotidyl inositol media will generate the same amount of ATP as bacteria grown in glucose media.
Bacteria grown in glucose media will generate more ATP than bacteria grown in glycine media.
Bacteria grown in glucose media will generate more ATP than bacteria grown in glycine media.
A bacterium that uses glucose as an energy source has been isolated from an anaerobic environment. After growth of the bacterium in an anaerobic culture, Dr. Strummer observes the bacterium producing methane gas (CH4). The pH of the media does not change. Which of the following processes is the bacteria utilizing?
Aerobic Respiration
Fermentation
Sporulation
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic Respiration
Lithotrophs ______________ to generate ATP.
oxidize inorganic chemicals (H2, Fe2+, H2S, etc)
oxidize organic chemicals (glucose, amino acids, fats, etc)
harvest light energy
reduce inorganic chemicals (H2, Fe2+, H2S, etc)
oxidize inorganic chemicals (H2, Fe2+, H2S, etc)
Fermentation converts ______ allowing for organisms to continue to use _______.
NADH to NAD+, the Electron Transport System
NADH to NAD+, Glycolysis
FADH2 to FAD+, Glycolysis
FADH2 to FAD+, the Citric Acid Cycle
NADH to NAD+, Glycolysis
In Bacteriorhodopsin
a photon of light is absorbed by retinal, which shifts its configuration from trans to cis pumping out 1 H+
a photon of light is harvested to photolyse an electron donor molecule like H2S, Fe2+, or succinate.
a photon of light is harvested to photolyse H2O.
a photon of light is harvested to transfer an electron from chlorophyll to photosystem I.
a photon of light is absorbed by retinal, which shifts its configuration from trans to cis pumping out 1 H+
Which of the following Photosystems does NOT generate NADH or NADPH?
Anaerobic Photosystem I
Anaerobic Photosystem II
Oxygenic Photosystem (Z- Pathway)
All of the above pathways generate NADH or NADPH.
Anaerobic Photosystem II
The Calvin Cycle utilizes ______ to generate glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate which can be used as a precursor for biosynthesis of glucose, amino acids and co-enzymes.
CO2, ATP, and NADH
Glucose, ATP, and NAD+
CO2, H2O, ATP, and NADPH
Pyruvate, Acetyl-CoA, and NAD+
CO2, H2O, ATP, and NADPH
Intermediates from ______ can be utilized to produce amino acids.
Glycolysis
the Citric Acid Cycle
Glycolysis and the Citric Acid Cycle
Glycolysis, the Citric Acid Cycle, and the Electron Transport System
Glycolysis and the Citric Acid Cycle
Photolysis refers to:
the excitation of a light-absorbing pigment.
the light-driven breakdown of glucose to generate ATP
the light-driven separation of an electron from a donor molecule
the light-driven production of ATP by ATP Synthase
the light-driven separation of an electron from a donor molecule.
How are plasmids different than chromosomes?
Plasmids carry unimportant genes that are of little significance for the ecology and metabolism of an organism.
Plasmids are composed of single-stranded DNA.
Plasmids are always small, linear pieces of DNA.
Plasmids contain genes that are NOT essential for cellular growth and replication in all conditions.
Plasmids contain genes that are NOT essential for cellular growth and replication in all conditions.
The two strands of the DNA double helix are held together by:
5' to 3' attraction.
codons.
hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases.
peptide bonds between nucleotide bases.
hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases.
Binding and polymerization of _____ allows for DNA strand separation at _____ initiating DNA replication.
DnaA, oriC
Primase, oriR
DnaB, dnaC
ribosome, Shine Dalgarno sequence
DnaA, oriC
During DNA replication, how are Okazaki fragments of the lagging strand are processed?
DnaA removes RNA primers, DNA Polymerase III synthesizes DNA to fill the gaps and connect the DNA fragments.
RNAse H removes RNA primers, DNA Polymerase I synthesizes DNA to fill the gaps and connect the DNA fragments.
RNAse H removes RNA primers, DNA Polymerase I synthesizes DNA to fill the gaps and DNA ligase connects the DNA fragments.
RNAse H removes RNA primers, DNA Polymerase III synthesizes DNA to fill the gaps and connect the DNA fragments.
RNAse H removes RNA primers, DNA Polymerase I synthesizes DNA to fill the gaps and DNA ligase connects the DNA fragments.
Double stranded DNA is replicated semi-conservatively in the mother cell to create two sister chromosomes, one for each daughter cell. Semi-conservative replication means that:
one sister chromosome is composed of two template strands of DNA and the other sister chromosome is composed two newly replicated strands of DNA.
each strand of DNA of in the new sister chromosomes contains both template DNA and new DNA fragments.
each strand of DNA of in the new sister chromosomes contains both template DNA and new RNA fragments.
each sister chromosome is composed of one template strand of DNA and one newly replicated strand of DNA.
each sister chromosome is composed of one template strand of DNA and one newly replicated strand of DNA.
True or False: DNA replication in prokaryotes is unidirectional, with one replisome complex replicating the entire chromosome.
False
Tus and ter sites are involved in which portion of the DNA Replication process:
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Initiation, Elongation, and Termination
Termination
In Photosystem II the electron donor utilized during photolysis is:
H2O
chlorophyll
H2S
NADH
chlorophyll
During DNA replication _______ lays down a _______ primer that is utilized by DNA polymerase.
PriA, RNA
PriA, DNA
DnaA, RNA
DnaA, DNA
PriA, RNA
In Oxygenic Photosynthesis the electron donor utilized during photolysis is:
O2
Fe3+
H2O
succinate
H2O
The energy for photosynthesis derives from the _________ of a light-absorbing pigment called _________.
photolysis, chlorophyl
photoexcitation, chlorophyl
photoexcitation, succinate
photolysis, succinate
photoexcitation, chlorophyl