Mathematics: Notable Mathematicians (& their Most Famous Works and Contributions and Notable Biographical Information)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Thales of Miletus (Fact 1)
Ancient Greek (Ionian) Mathematician

Thales of Miletus (Fact 2)
Considered the first Greek Mathematician, he was the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery is attributed and who applied Deductive Reasoning to Geometry

Thales of Miletus (Fact 3)
Used geometry to calculate the heights of the Pyramids and the distances of ships from shore

Thales of Miletus (Fact 4)
Discovered that a circle is bisected by its diameter, and learned geometry mainly from the Egyptians

Thales of Miletus: Thales' Theorem (Contribution 1) [Fact 1]
Discovered that right triangles are always formed when connecting the dots out of any set of 3 points along a circle, 2 of which are the ends of a diameter line of the circle (for Proof, See Picture)
Thales of Miletus: Thales' Theorem (Contribution 1) [Fact 2]
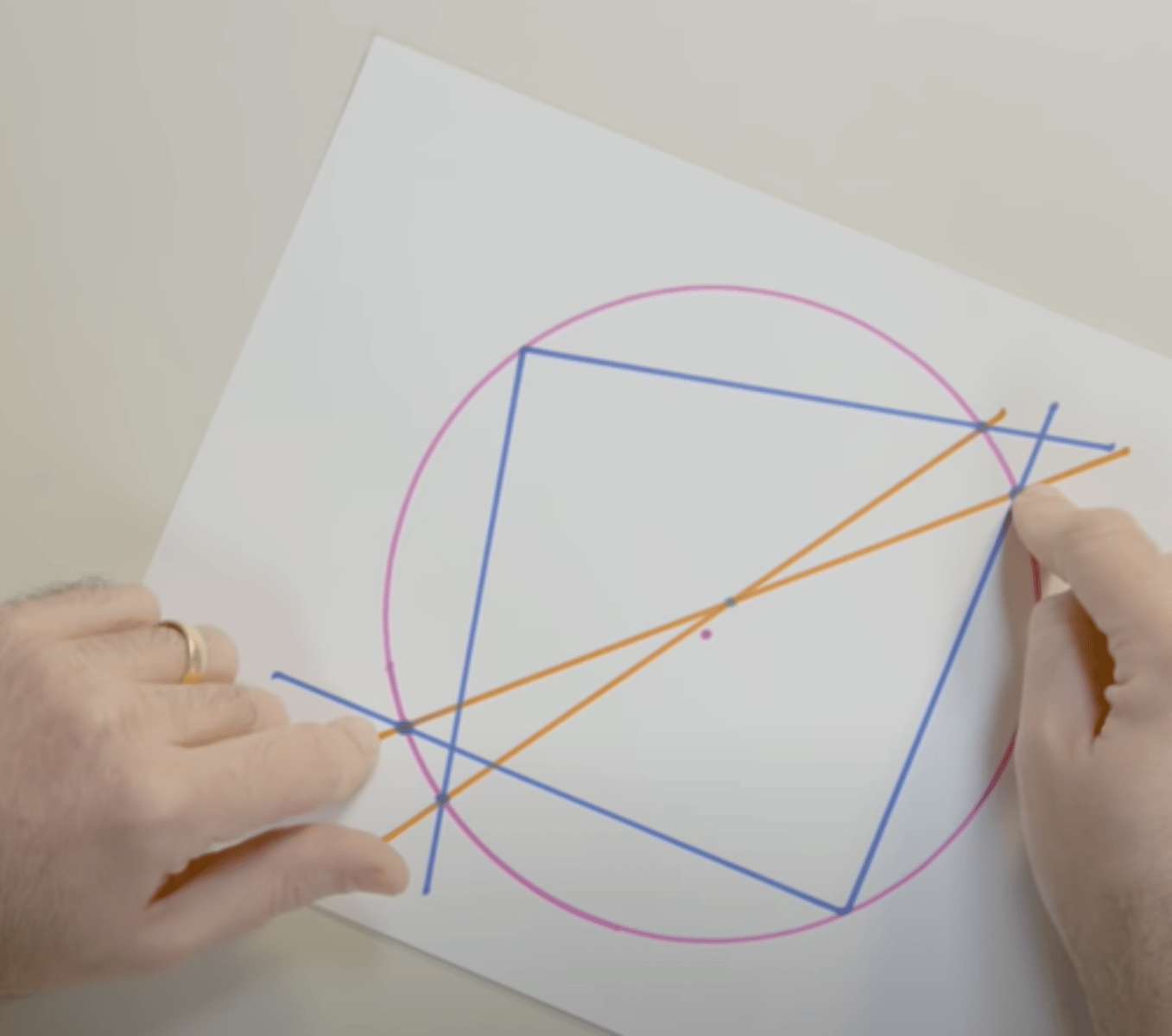
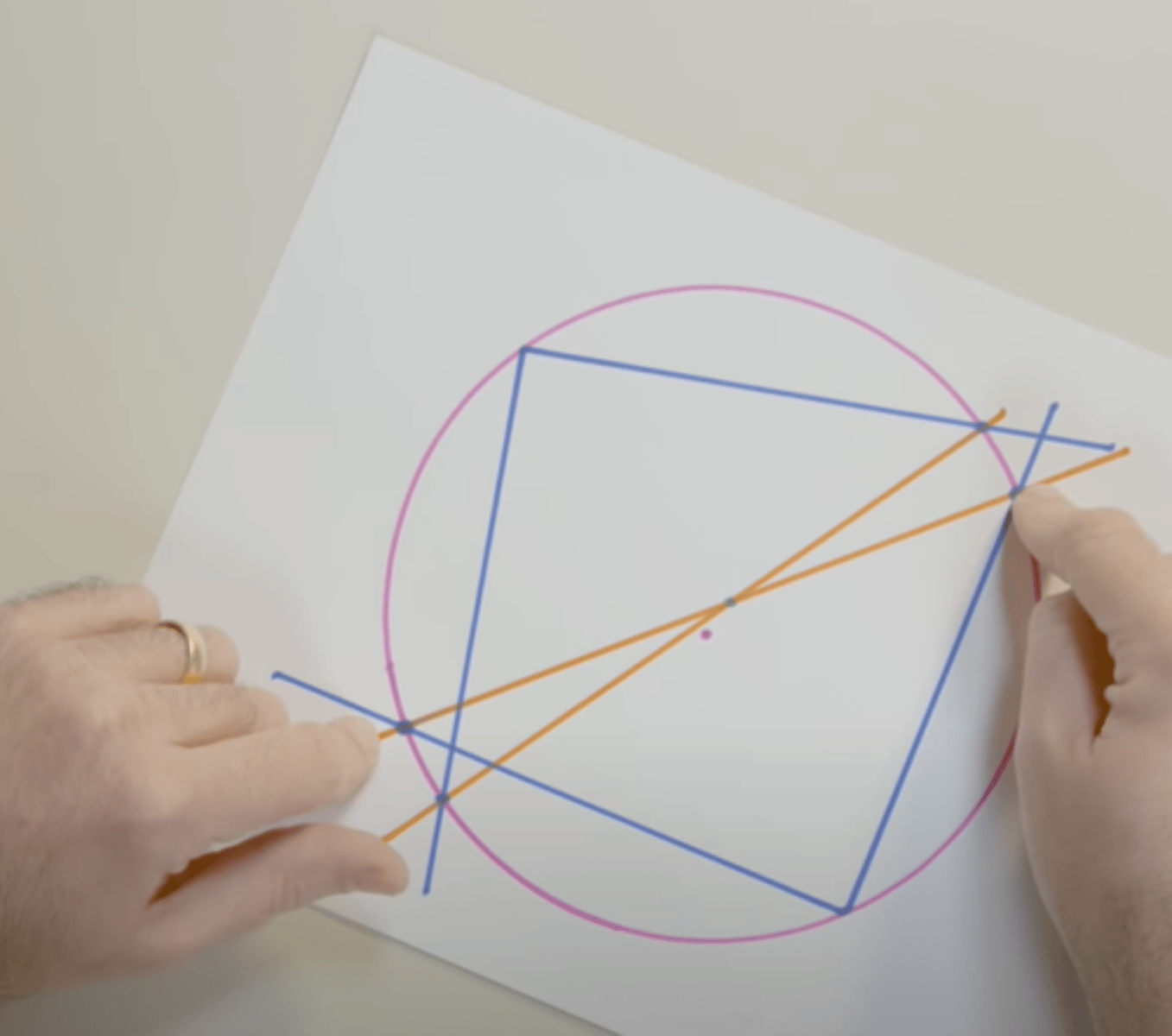
Discovered that the center of a circle (blue dot in picture) can be found by making 2 lines that run through the center of a circle and finding the point where they intersect each other which are made from first connecting 2 sets of diametrically opposed points which are made from first determining the points at which rays (of lines) come into contact with the circle which are made from first making 2 right angles anywhere on the circle
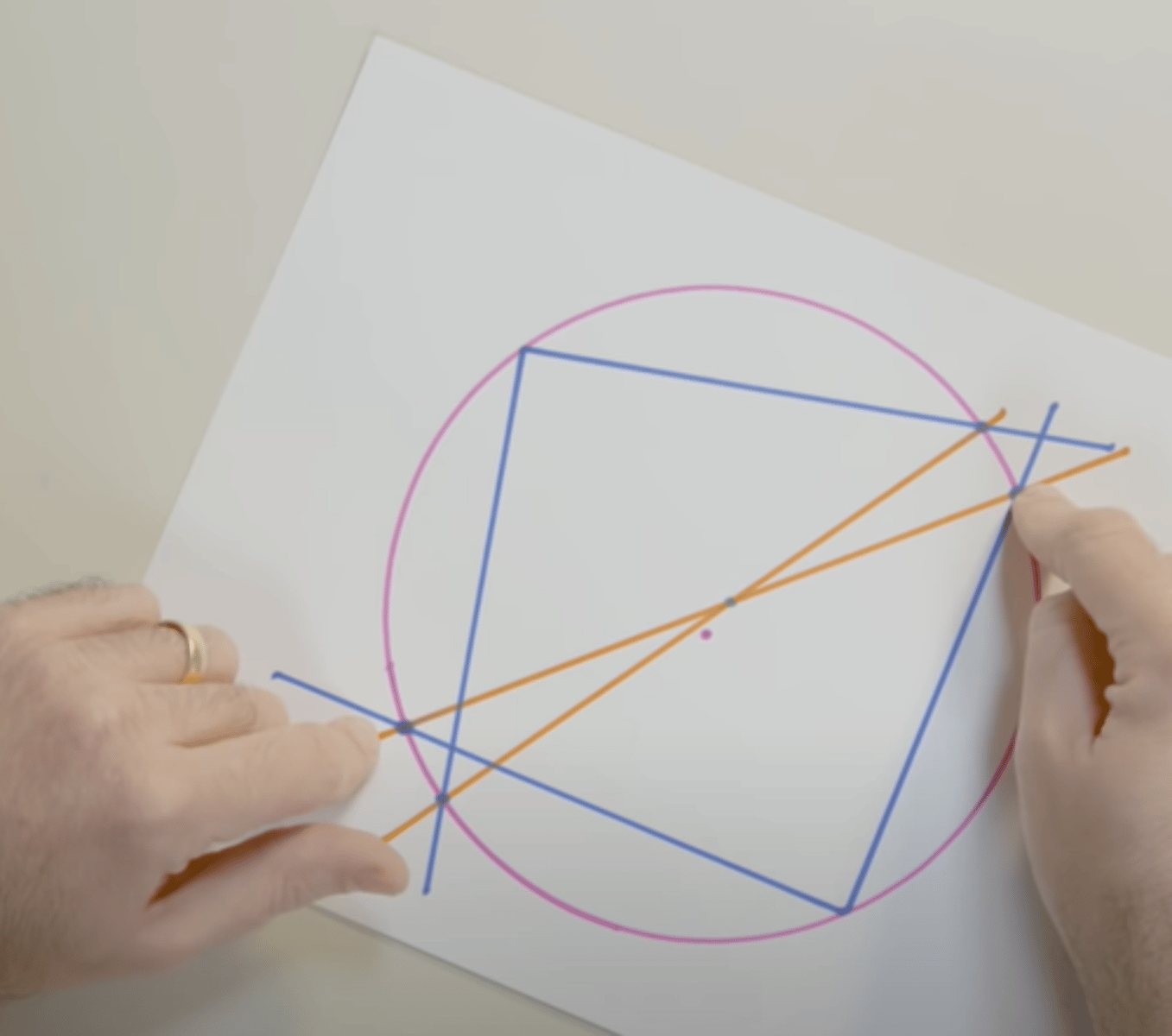
Thales of Miletus: Thales' Theorem (Contribution 1) [Fact 3]
In other words, if a triangle is drawn within a circle with the long side as a diameter of the circle then the opposite angle will always be a right angle
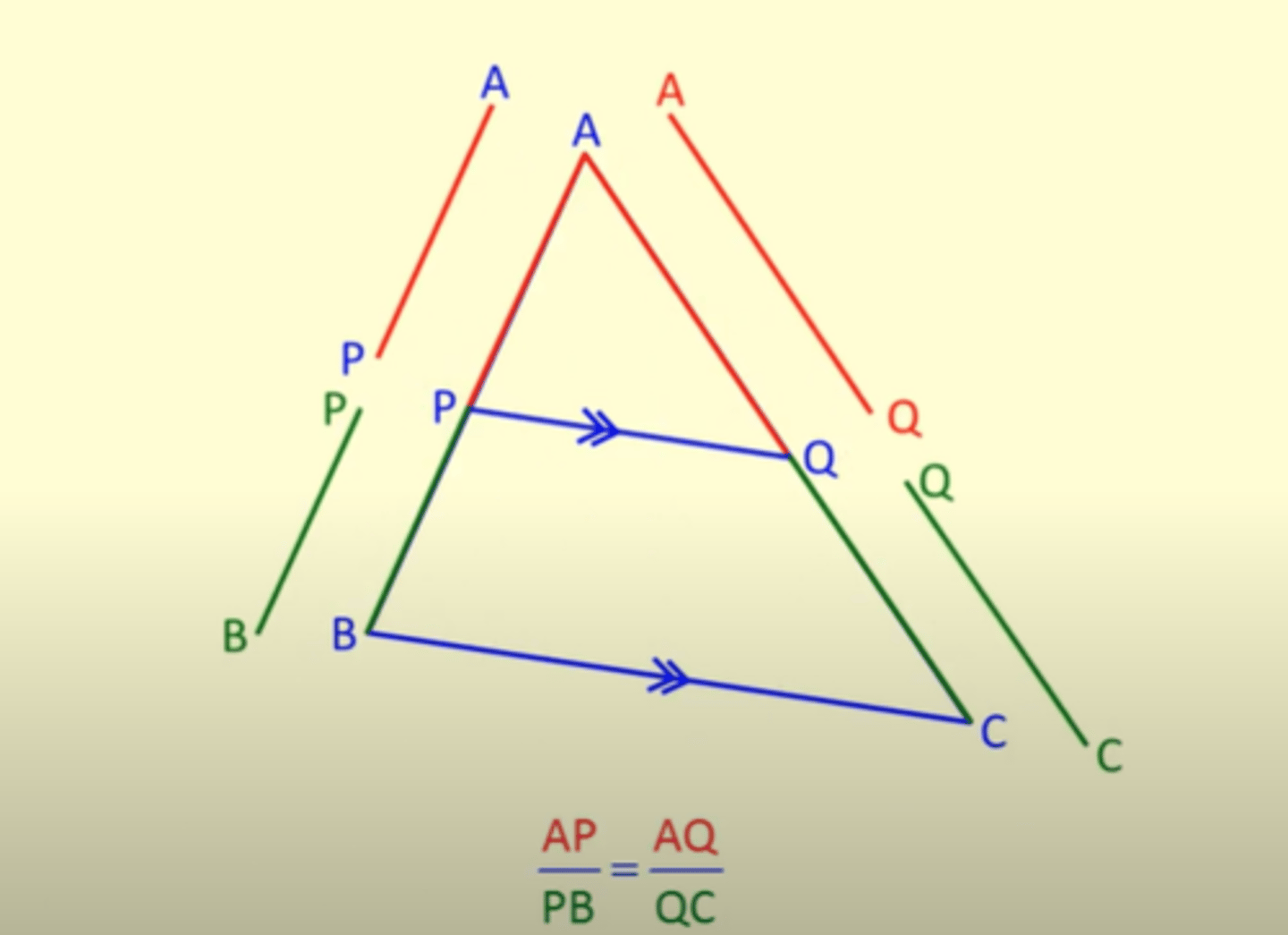
Thales of Miletus: Intercept Theorem (Contribution 2)
Discovered that if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle through the triangle, then it divides the other two sides proportionally; likewise if two sides of a triangle are proportional to each other, then that means that the line running through the triangle making them proportional must be parallel
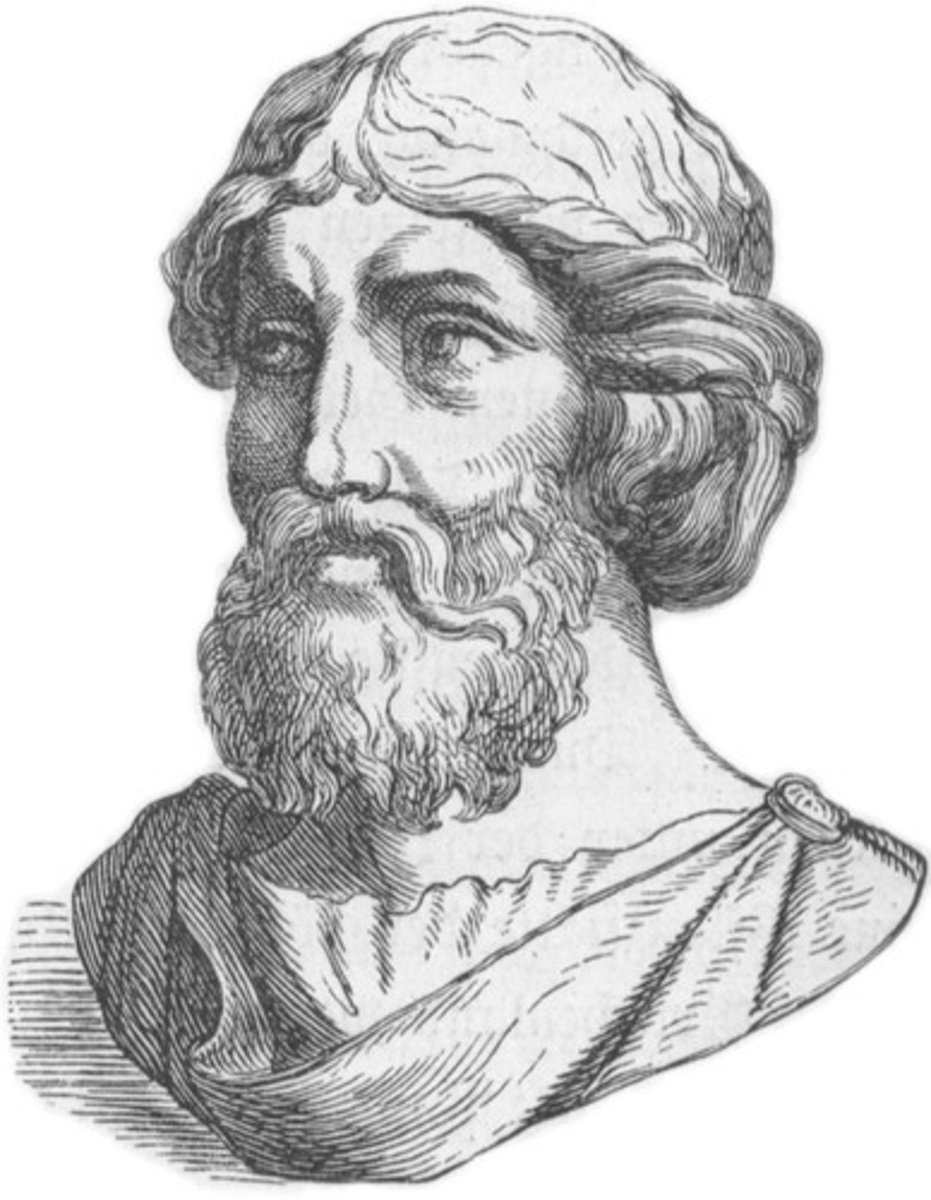
Pythagoras of Samos (Fact 1)
Considered the "Father of Numbers" and/or the first "pure" mathematician, also the first to come up with a mathematical proof for a mathematical concept

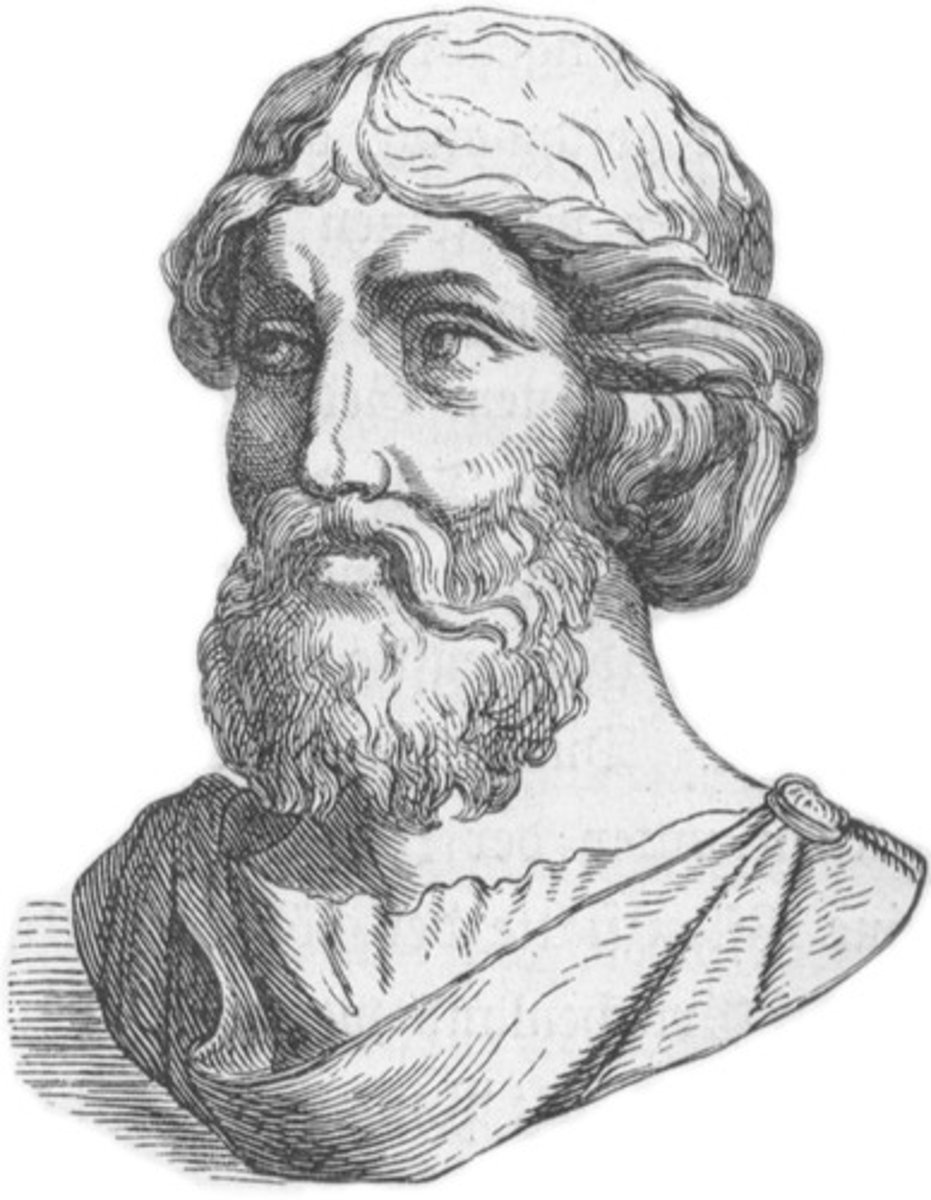
Pythagoras of Samos (Fact 2)
Assigned numbers to various things having seen them through numbers such as the number 2 representing a female (and even numbers being feminine) and the number 3 representing a male (and odd numbers being masculine), thus the number 5 representing marriage (the first odd and first even number coming together)

Pythagoras of Samos (Fact 3)
Assigned numbers to various things having seen them through numbers such as (the number 1 representing the "Hearth of the Universe" - this is only likely), the number 4 (5 in some interpretations for "balancing out" the 4) representing justice, and the number 6 representing "animation"

Pythagoras of Samos (Fact 4)
Assigned numbers to various things having seen them through numbers such as the number 7 representing opportunity (because children can come out of the mother's womb fully developed by 7 months, adults are developed at age 14, a multiple of 7; number of Athena, the virgin goddess, is not generated by or itself generates anything, etc.)
Pythagoras of Samos (Fact 5)
Assigned numbers to dimensions in order to argue that everything is made of numbers in that the number 1 represents a dot, the number 2 represents a line, the number 3 represents a surface, and the number 4 thus represents a solid

Pythagoras of Samos (Fact 6)
According to legend, he discovered "octaves" in music after focusing his hearing on the sound of two blacksmiths hitting their anvils and the "clang" sound being an "octave" higher via the bigger hammer hitting the anvil, and it was an "octave" higher because the bigger hammer was twice as big, essentially discovering the fact that one can express harmony in numbers

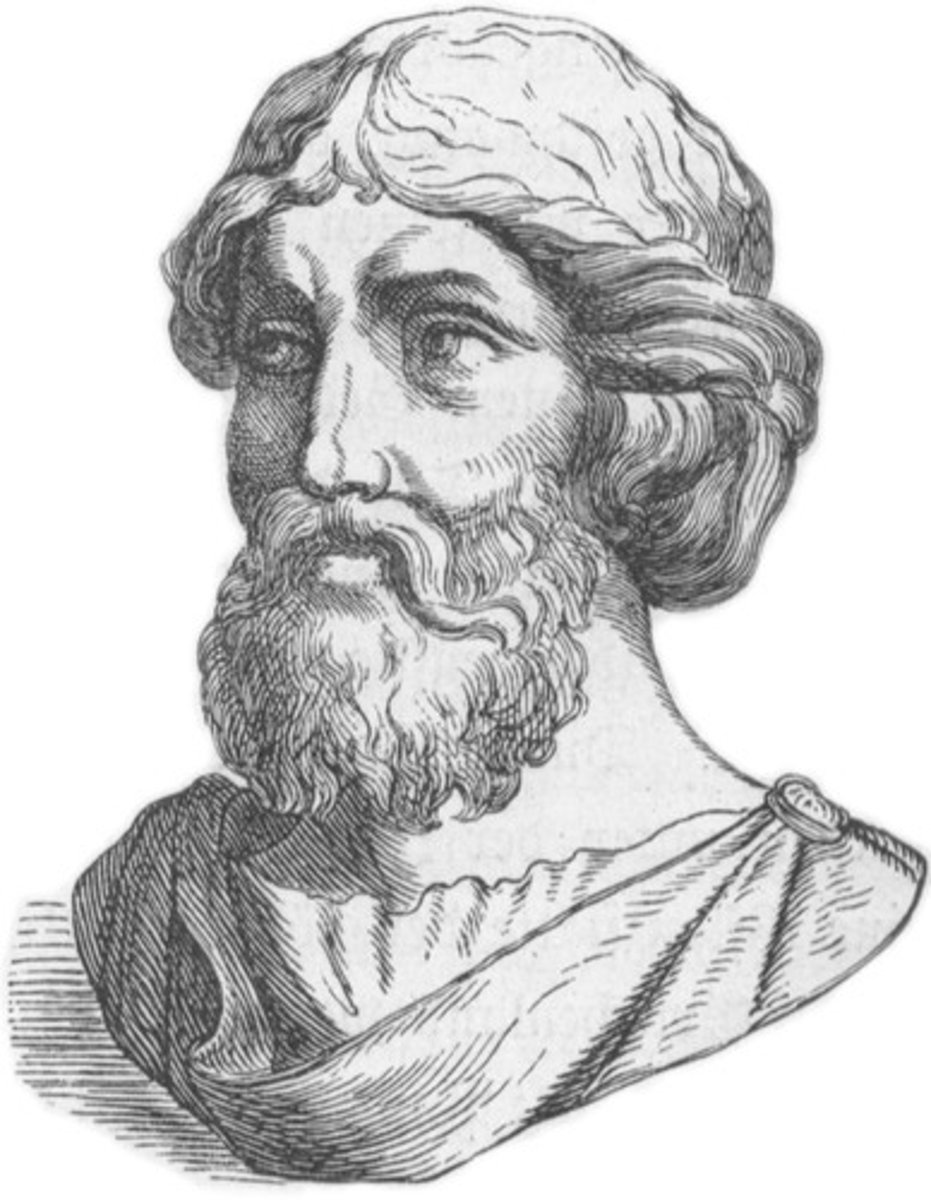
Pythagoras of Samos (Fact 7)
Argued that the entire number system is based on the first four numbers 1-4 and their sum of 10 which, in the form of 10 dots arranged in the form of a triangle form a "Tetractys" which, along with the number 10, represents God

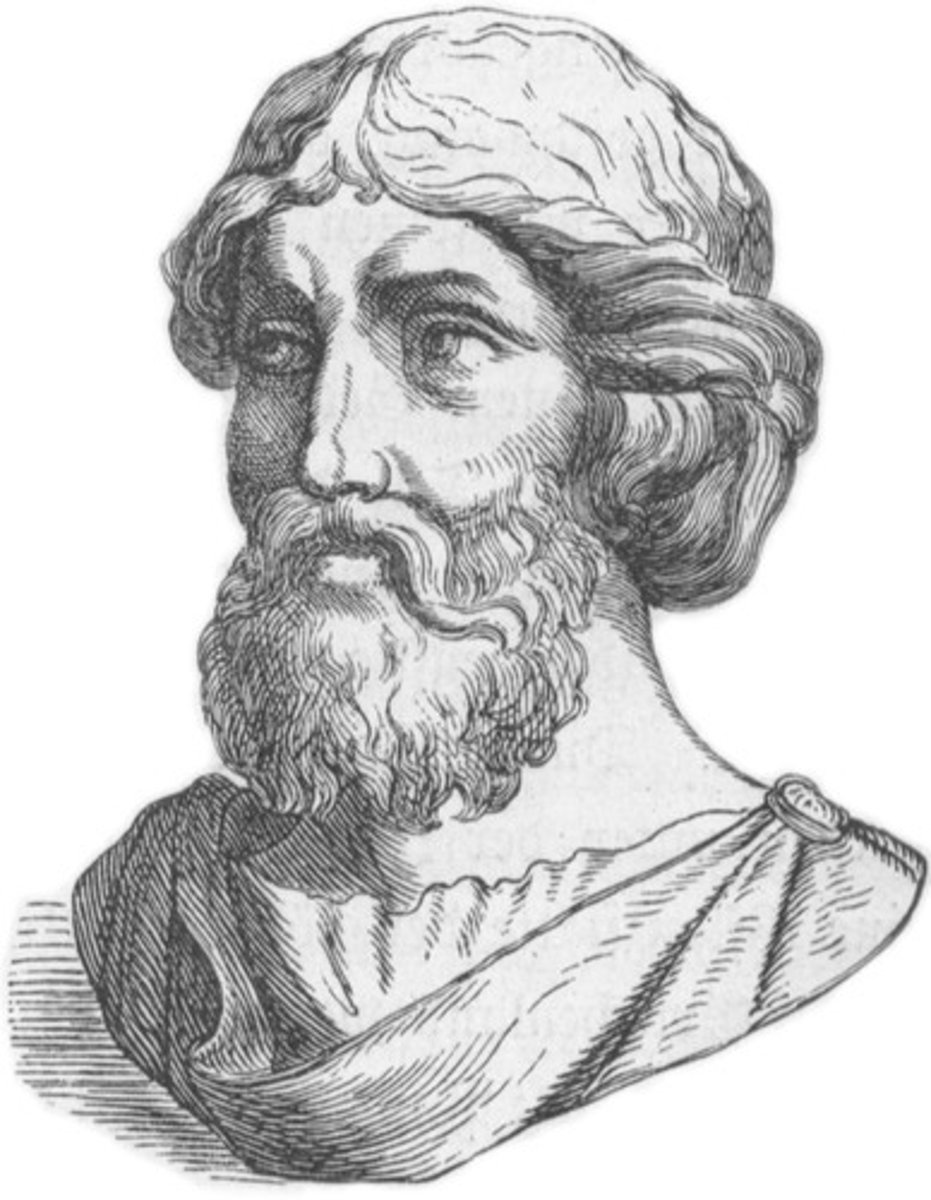
Pythagoras of Samos (Fact 8)
According to legend, he tried to murder one of his students, Hippasus for his discovery of irrational numbers, which the namesake mathematician believed to be an insult to mathematics, a rule of which was already established in his "Mathematikoi" cult by which if one violated would be killed in the name of mathematics

Pythagoras of Samos: Pythagorean Theorem (Contribution 1)
Constructed the first proof for the namesake theorem, despite it having been discovered earlier, despite not yet proven

Hippasus of Metapontum (Fact 1)
"Discovered" the Dodecahedron and the Square Root of 2, which he "discovered" by solving for the diagonal in the already established Pythagorean Theorem for a triangle with a side length(s) of 1
Archytas of Tarentum (Fact 1)
Discovered the cube root of 2 or "Delian Problem" or "Problem of doubling the size of an altar" and was able to make a three-dimensional construction to demonstrate how one could construct this number which could not be constructed using the previously established "ruler and compass" method
Pythagoras of Samos (Contribution 2)
"Discovered" that the sum of the angles of a triangle always equals 180 degrees

Pythagoras of Samos (Contribution 3)
"Discovered" Mathematical Proportions/Ratios

Pythagoras of Samos (Contribution 4)
"Discovered" Squares and Square Roots

Pythagoras of Samos (Contribution 5)
"Discovered" the Golden Ratio

Pythagoras of Samos (Contribution 6)
Discovered his namesake tuning system, a system of musical tuning by which frequency relationships of any and all intervals on the keyboard are based on the ratio 3:2 (a stack of perfect fifths)

Pythagoras of Samos (Contribution 7)
Discovered that the musical intervals between the notes on a lyre can be expressed numerically and that pitch is dependent on number since it depends on the lengths and intervals of a scale, which can be expressed as ratios or proportions

Pythagoras of Samos (Contribution 8)
Discovered that musical notes could be translated into mathematical equations which could be used to make music sound more "harmonious", believing the music of his day wasn't harmonious

Pythagoras of Samos (Contribution 9)
(Probably) founded the idea that numbers are just ratios and ways to think about numbers are as ratios with 1 under them, to prove numbers is to view, say 5 of something as 5 of one thing compared to just one of that thing and that numbers are really abstract, rather than particular quantities
Aristotle (Quote 1)
"Since they (the Pythagoreans) saw that the attributes and ratios of the musical scales were expressible in numbers; since then all other things seemed in their whole nature to be modeled after numbers, and numbers seemed to be the first things in the whole of nature, and the whole heaven to be a musical scale and a number"