1 • Reflection of Light
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Define Reflection
When light strikes a smooth surface, it bounces back from that surface
Define the laws of reflection
Incident ray, reflected ray and normal all lie on the same plane
Angel of incidence = Angle of reflection
What is the conclusion from the laws of reflection?
Plane mirror image is a far behind as the object
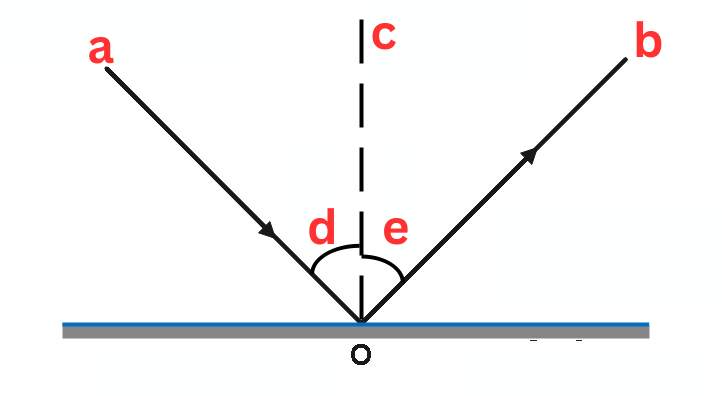
Label This Diagram
Ray Diagrams
a - incident ray
b - reflected ray
c - normal
d - angle of incidence - r
e - angle of reflection - i
Name the types of images in a plane mirror
Real
Virtual
Define Real Image
The actual intersection of light rays
Define Virtual Image
The apparent intersection of light rays
Name the types of curved mirrors
Concave
Convex
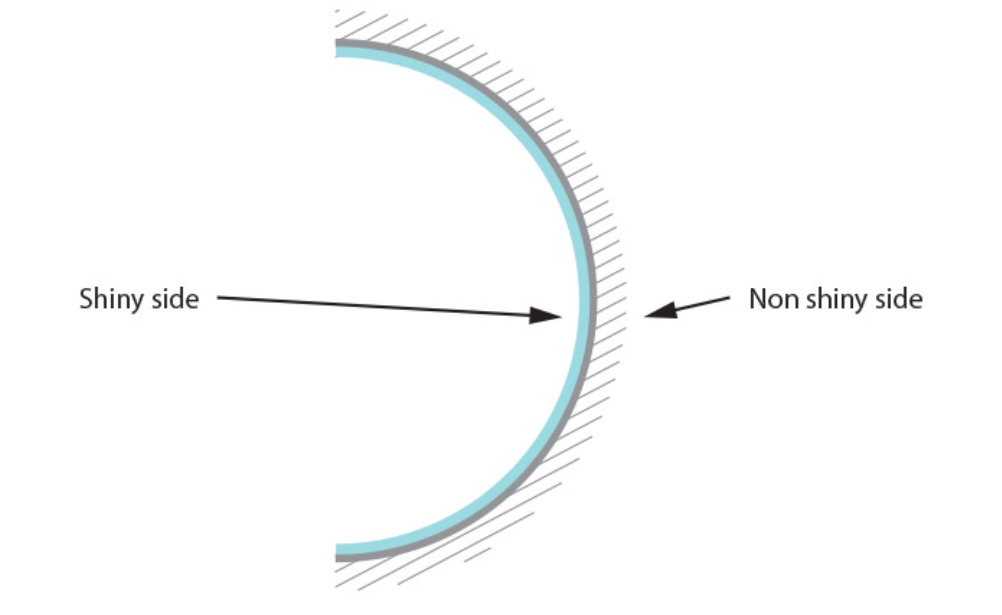
Name the type of curved mirror in this image
Concave
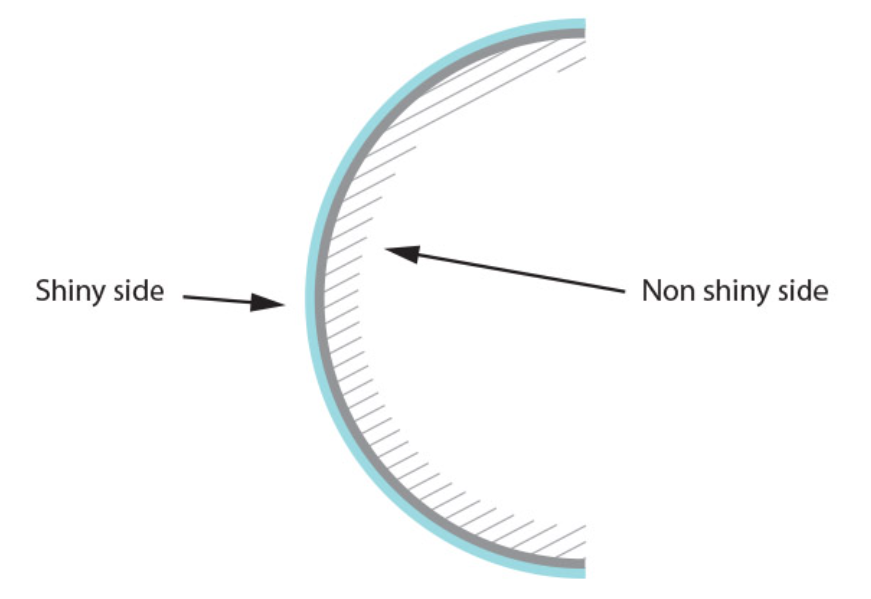
Name the type of curved mirror in this image
Convex
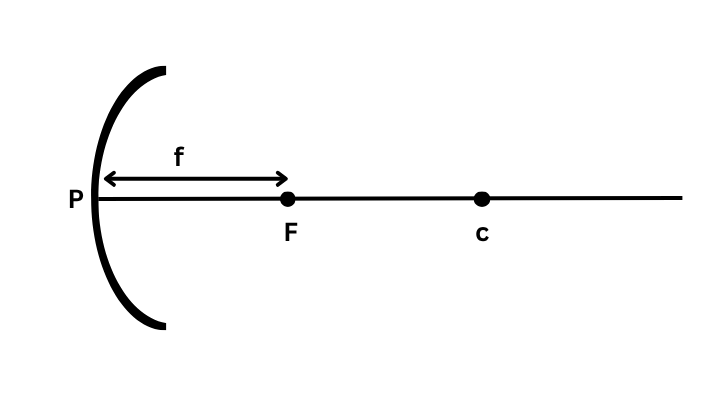
Label This Diagram
Curved Mirror
P - Pole
F - Focus
c - Centre of curvature
f - Focal length
Differentiate between Concave & Convex mirrors
Concave has a real focus
Convex has a virtual focus
What happens to a light ray parallel to the axis?
Reflects through the focus
What happens to a light ray striking the pole?
Reflects at the same angle
What happens to a light ray reflecting through the focus?
Reflected parallel to axis
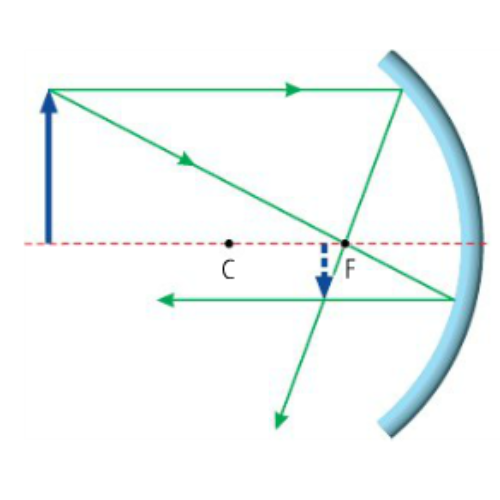
What type of image is formed in this diagram?
Concave Mirror - Object outside C
Real
Inverted
Diminished
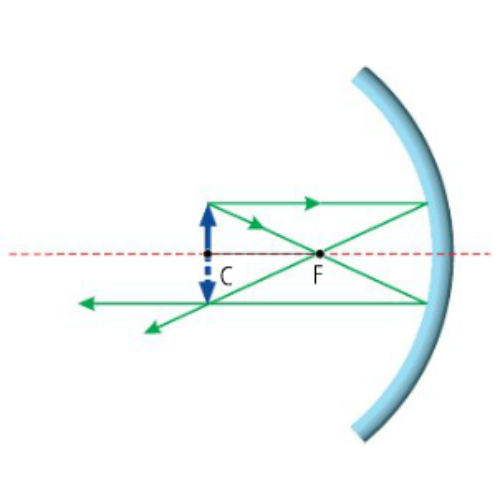
What type of image is formed in this diagram?
Concave Mirror - Object at C
Real
Inverted
Same Size
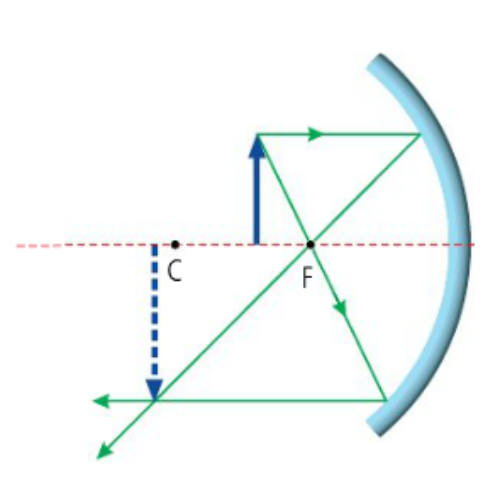
What type of image is formed in this diagram?
Concave Mirror - Object between C & F
Real
Inverted
Magnified
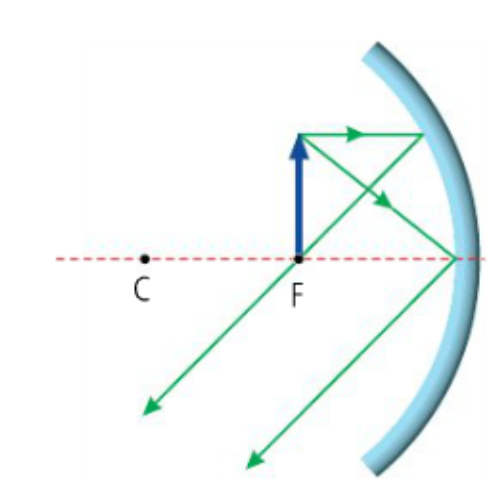
What type of image is formed in this diagram?
Concave Mirror - Object at F
Real
Inverted
At Infinity
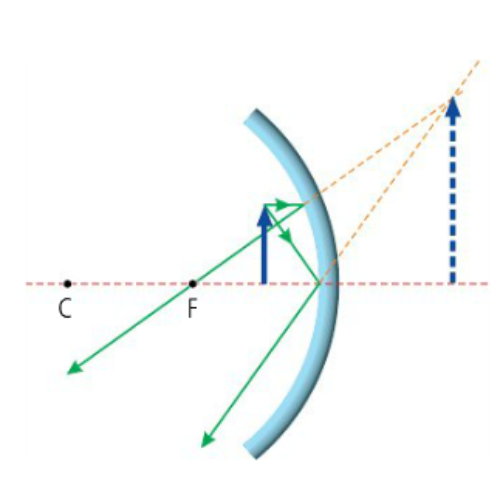
What type of image is formed in this diagram?
Concave Mirror - Object inside F
Virtual
Upright
Magnified
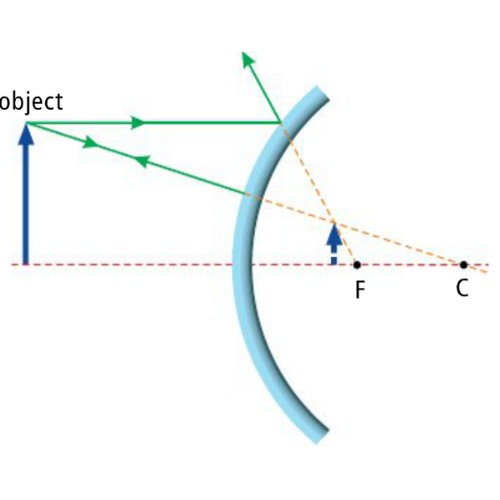
What type of image is formed in this diagram?
Convex Mirror
Virtual
Upright
Diminished
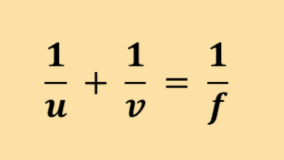
Label This Formula
The Distance Formula
v - image distance
u - object distance
f - focal length
When is u positive and negative?
U is always positive
Never negative
When is v positive and negative?
Positive - Real Images
Negative - Virtual Images
When is f positive and negative?
Positive - Concave Mirrors
Negative - Convex Mirrors
What page of the log tables can you find the Distance formula?
60
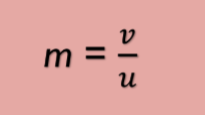
Label This Formula
Magnification Formula
m - magnification
v - image distance / height
u - object distance/ height
When is magnification positive and negative?
Positive - Upright
Negative - Inverted
What page of the log tables can you find the Magnification formula?
60
Name 2 uses of concave mirrors
Shaving Mirrors
Dentist Mirrors
Name 2 uses of convex mirrors
Car wing mirrors
Supermarket mirrors