Heart and Blood Vessels Lecture Notes
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on lecture notes about blood flow, heart function, and blood pressure regulation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Describe the sequence of blood flow through the heart.
Deoxygenated blood from the systemic circuit enters the right atrium through the IVC, SVC, and coronary sinus.
Then, it travels through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle, through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary trunk, splitting into right and left pulmonary arteries to the lungs for oxygenation.
Oxygenated blood returns via pulmonary veins to the left atrium, passes through the mitral valve to the left ventricle, and is pumped through the aortic valve into the aorta for systemic circulation.
What is the main goal of the left side of the heart?
To pump oxygenated blood received from the lungs to the rest of the body to perfuse tissues and organs.
What is the main goal of the right side of the heart?
To pump deoxygenated blood received from the rest of the body to the lungs to become oxygenated.
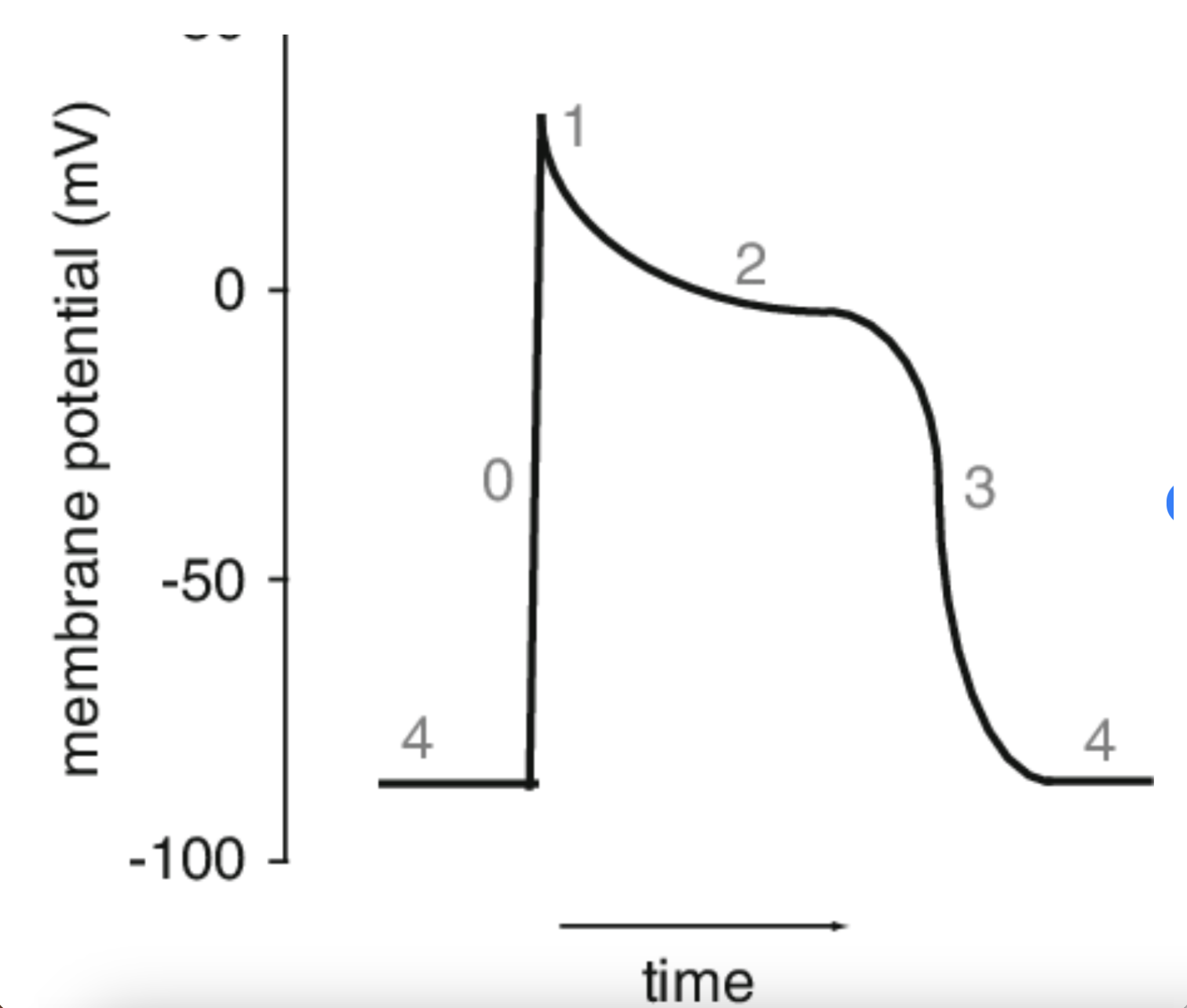
Match the description with the appropriate phase of the action potential in a cardiac myocyte.
0 - resting membrane potential,
2 - plateau phase due to delay in repolarization,
3 - repolarization: slow Ca++ channels are open, K+ channels are open (Ca++ influx, K+ efflux),
4 - rapid depolarization
What is the direct effect of increased heart rate?
Both cardiac output (CO) and blood pressure (BP) increase.
What is the direct effect of sleep?
Both cardiac output (CO) and blood pressure (BP) decrease.
What is the direct effect of increased blood vessel diameter?
Only blood pressure (BP) decreases.
What is the direct effect of increased blood volume?
Both cardiac output (CO) and blood pressure (BP) increase.
What is the direct effect of increased preload?
Only cardiac output (CO) increases.
What is the direct effect of increased stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Only cardiac output (CO) decreases.
What is the direct effect of decreased ADH?
Both cardiac output (CO) and blood pressure (BP) decrease.
What is the direct effect of excessive blood loss?
Both cardiac output (CO) and blood pressure (BP) decrease.
What is the direct effect of decreased contractility?
Only cardiac output (CO) decreases.
What is the direct effect of systemic vasoconstriction?
Only blood pressure (BP) increases.
Which of the following correctly matches the heart chambers and valves?
Tricuspid valve - between the right atrium and right ventricle.
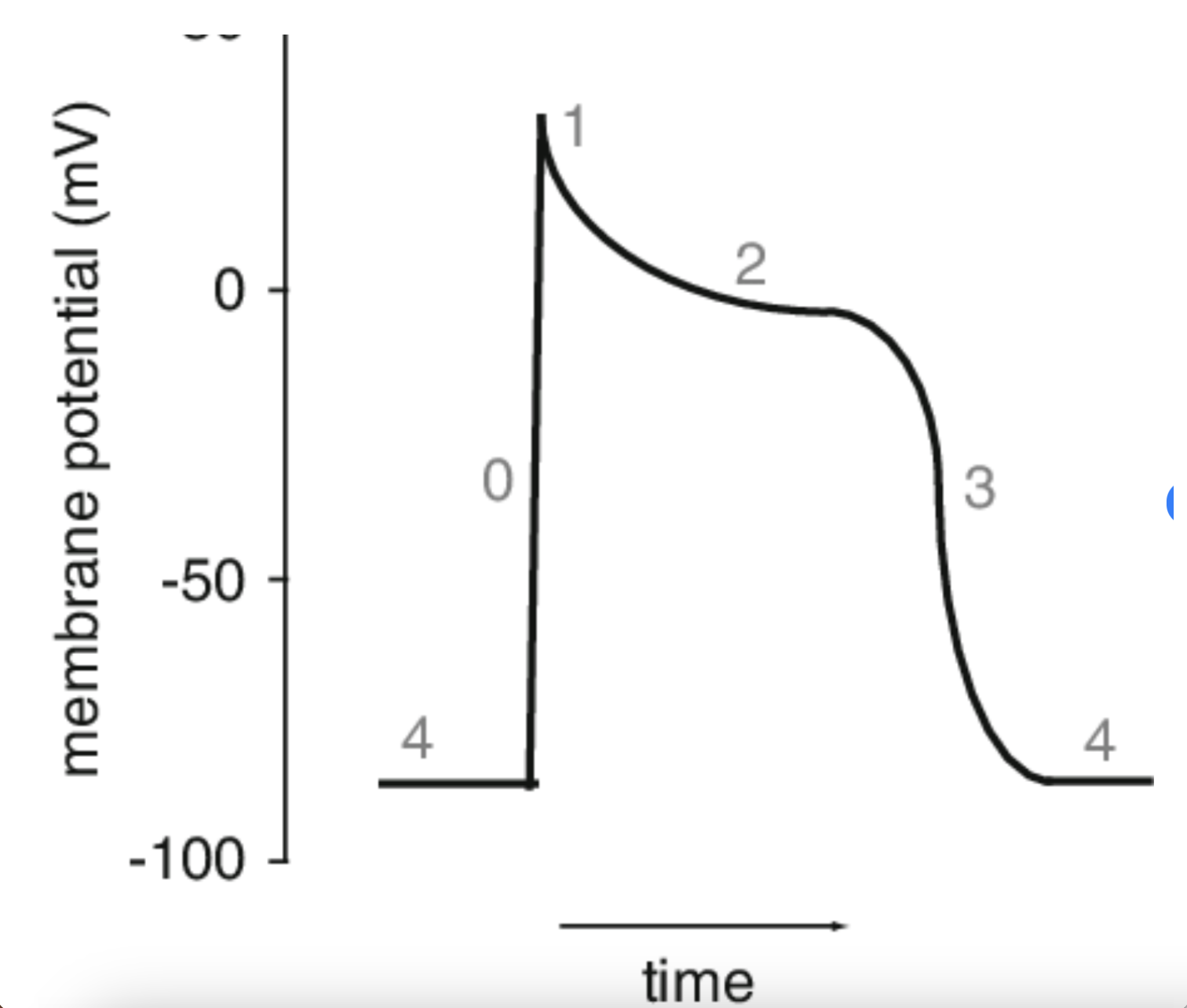
At point 3, what is occurring?
Repolarization due to Ca2+ channels inactivating and K+ channels remaining open.
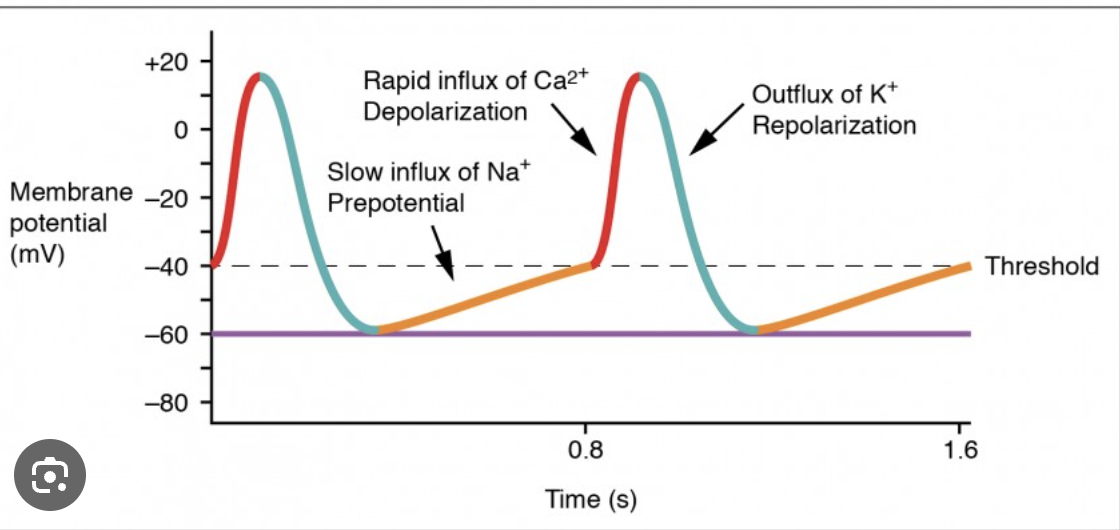
Which of the following statements are true of cardiac muscle vs skeletal muscle?
Cardiac muscle contains gap junctions between cells while skeletal muscle does not. Cardiac muscle has more mitochondria than skeletal muscle.
Match the heart wall layers:
1 - Endocardium (inner lining of the heart chambers),
2 - Myocardium (muscular tissue of the heart),
3 - Epicardium (visceral serous layer covering the heart muscle),
4 - Parietal layer (outermost layer of the serous pericardium, lines fibrous pericardium)
Which valve action results from pressure in the ventricle being lower than that of the atria?
AV valves open
Why is the left ventricular wall thicker than the right?
The left ventricle pumps blood to all parts of the body, while the right ventricle only pumps blood to the lungs against lower pressure.
The heart sounds heard when listening with a stethoscope are due to:
Closure of the heart valves
Define the term end systolic volume (ESV):
The volume of blood remaining in a ventricle after it has contracted
What is transported by the pulmonary circuit?
Deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
Which of the following is transported by the pulmonary circuit?
Deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
What could happen to the heart if damage occurred to the vagus nerves?
Heart rate would increase by about 25 beats per minute
Choose all that are correct regarding the isovolumetric relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle:
Aortic valves are closed, Pulmonary valves are closed, Atrioventricular valves (bicuspid/tricuspid) are closed
Which of the following functions as the normal pacemaker of the heart?
Sinoatrial node
Which of the following directly receives blood during ventricular systole?
Both the aorta and pulmonary trunk
Which wave represents atrial depolarization?
P wave
What occurs in the heart during ventricular filling?
Blood flows mostly passively from the atria into the ventricles
If Matt has a resting heart rate of 60 bpm and a stroke volume of 70 ml, what is his cardiac output?
CO = HR * SV = 60 bpm * 70 ml = 4200 ml/min = 4.2 L/min
An athletes resting CO is 6,000 ml/min and her stroke volume is 100 ml/beat. What is her pulse?
CO = HR * SV 6000 ml = HR * 100 ml HR = 6000 / 100 = 60 bpm
During exercise, pulse is 120 bpm and stroke volume is 100 ml. What is the CO?
CO = HR * SV = 120 bpm * 100 ml = 12,000 ml/min = 12 L/min
Patients BP is 80/56. What is the MAP and how do you interpret this?
MAP = Diastolic + 1/3(Systolic - Diastolic) = 56 + 1/3(24) = 56 + 8 = 64 mmHg Low
How do you determine pulse pressure?
Pulse Pressure = Systolic - Diastolic
A 56-year-old male has BP 156/96 and pulse 85 bpm. What are his values?
Systolic: 156 mmHg, Diastolic: 96 mmHg, Pulse Pressure: 60 mmHg, MAP = 96 + 1/3(60) = 116 mmHg, BP Classification: Hypertension, Pulse Classification: Normal (60-100 bpm)
Systolic: 156 mmHg
Diastolic: 96 mmHg
Pulse Pressure: 60 mmHg (156 − 96)
MAP: 116 mmHg (96 + ⅓ × 60)
BP category: Hypertension
Pulse category: Normal
A blood cell is returning from the foot back to the lungs. Which structures will it pass through?
Inferior vena cava -> Right atrium -> Tricuspid valve -> Right ventricle -> Pulmonary valve -> Pulmonary trunk -> Pulmonary arteries
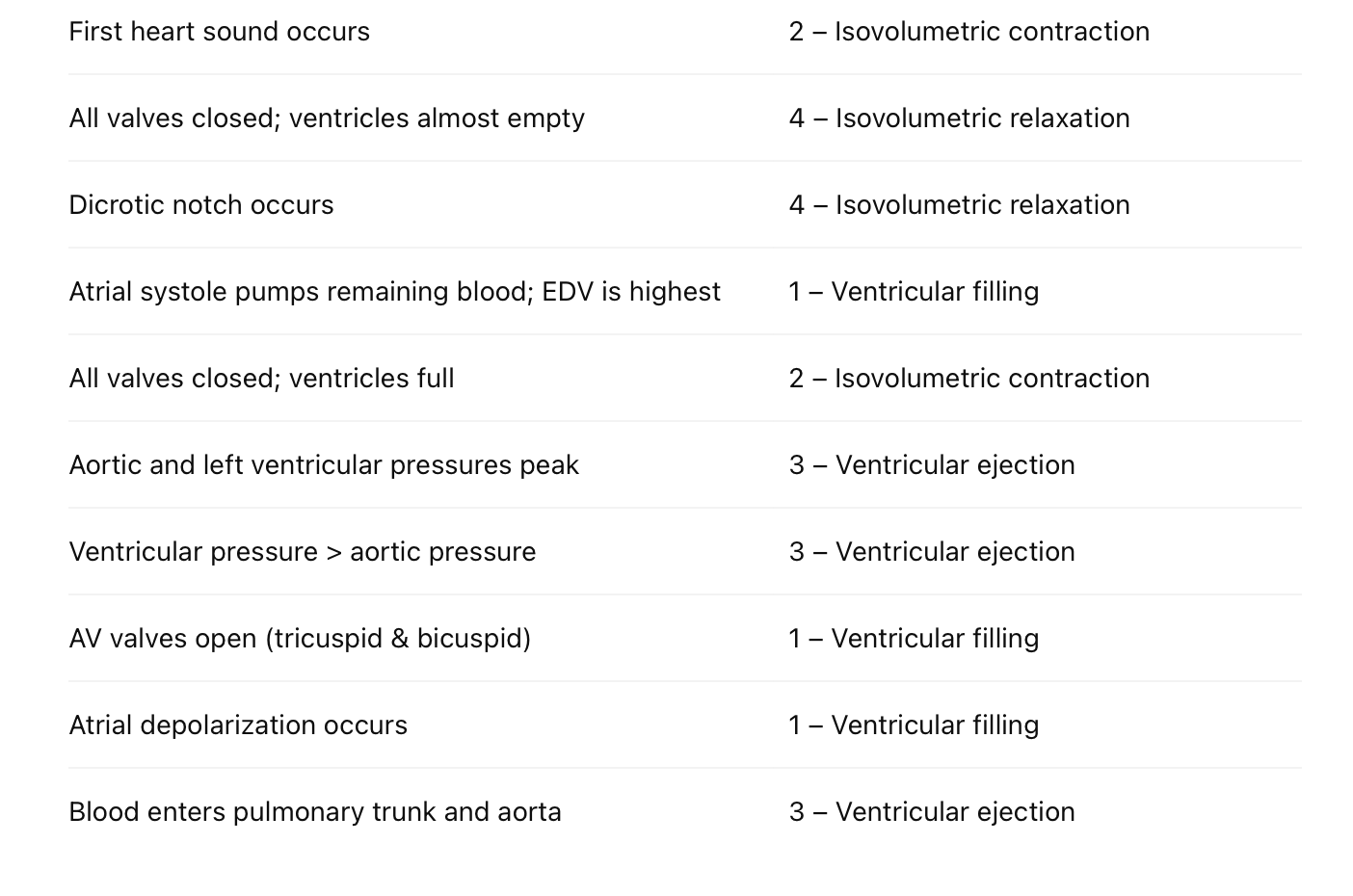
Put the following events of the cardiac cycle in order:
- P wave, 2. Atrial systole, 3. QRS complex begins, 4. AV valves close, 5. Ventricular systole begins, 6. SL valves close, 7. T wave, 8. Ventricular diastole begins
Increased afterload causes decreases to all of the following except:
Aortic pressure
If the concentration of albumin in blood plasma was reduced, what effect would this have on capillary exchange?
Decreasing colloid osmotic pressure and edema will occur
How can the aorta receive the full force of blood exiting the heart during ventricular systole and not be damaged?
Elastic fibers are extensive in the tunica media of the aorta and dampen the pulse pressure generated by the heart
Which of the following would NOT be a benefit of slow, low-pressure blood flow in capillaries?
Lower pressure in the capillary bed would greatly increase pressure in the venous circulation
Which pressure would indicate hypertension?
150/96
Which of the following would not be a means of short-term control of blood pressure?
Altering blood volume
Oxygen and nutrients leave the arteriole end of a capillary due to and wastes and water enter the venule end due to
Hydrostatic pressure; Osmotic pressure
Distributing arteries that deliver blood to body organs are called:
Muscular Arteries
Which description correctly describes blood flow in vessels? Blood flow is
directly related to the pressure gradient but inversely related to the resistance.
A blood cell is returning from the foot back to the lungs. Which structures will it pass through? (Select 7)
Inferior vena cava
Right atrium
Tricuspid valve
Right ventricle
Pulmonary valve
Pulmonary trunk
Pulmonary arteries
Put the following events of the cardiac cycle in order:
P wave
Atrial systole
QRS complex begins
AV valves close
Ventricular systole begins
T wave
SL valves close
Ventricular diastole begins
Match descriptions to cardiac cycle phases:
Effect on cardiac output (CO) and blood pressure (BP):
In which blood vessel is blood pressure the lowest?
Veins, specifically vena cavae.
If a patient was found to have very low levels of protein in their blood net filtration pressure would be
higher than normal
In BP reading, yhe systolic blood pressure is the one that is recorded
in arteries and is the maximal pressure that is recorded during ventricular contraction.
Blood colloid osmotic pressure is caused by
the proteins in the blood and it promotes reabsorption
Which of the following is the proper description of peripheral resistance?
directly related to vessel length and inversely related to vessel radius.
If someone's blood pressure were listed as 130/85 mmHg, then their mean arterial pressure (MAP) would be
100 mmHg
Which of the following is the best description of a portal system?
A vascular system that connects two capillary beds before draining into the heart, allowing for specialized blood flow.
Which layer found in blood vessels is made up of an endothelium and a thin subendothelial layer consisting of areolar connective tissue.
tunica intima
Some large molecules (fatty acids for example), are transported between capillaries and tissues by vesicular transport because they are too large to pass directly through.
True
The cardiac center located in the brainstem includes the
vasomotor center, from which parasympathetic pathways exits.
All of the choices are correct.
cardioacceleratory center, where the sympathetic pathway exits from
cardioinhibitory center, from which sympathetic pathways exits.
cardioacceleratory center, where the parasympathetic pathways exits from
When observing an artery, what layer is the thickest layer.
tunica media
Large arteries like the aorta are called:
elastic arteries
If your cardiac output increases, then your blood pressure
increases
What happens to net filtration pressure as blood moves from the arterial end to the venous end of a capillary?
NFP decreases, as blood colloid osmotic pressure decreases
Net filtration pressure (NFP)
net hydrostatic pressure minus the net colloid osmotic pressure
What is the purpose of valves found in veins?
They cause venous blood flow to go in only one direction
Generally, when looking at the different types of arteries, as an artery's diameter decreases, the artery walls show
an increase in the relative amount of smooth muscle and a decrease in the relative amount of elastic fibers
What vessel carries oxygen-rich blood from lungs to heart?
Pulmonary veins
Which hormone increases BP by vasoconstriction and aldosterone release?
Angiotensin II
Which part of the brain regulates heart rate and BP reflexively?
Medulla oblongata
What vessel type has only a tunica intima?
Capillaries
Which layer of the blood vessel contains smooth muscle and controls vasoconstriction?
Tunica media
Which is NOT a short-term BP control mechanism?
Altering blood volume (Long-term mechanism)
How to determine pulse pressure?
Systolic − Diastolic pressure
Which is NOT a benefit of slower capillary blood flow?
Lower pressure in capillary beds would greatly increase venous pressure (False statement)
Why doesn't aorta rupture during systole?
Elastic fibers in tunica media dampen the pulse pressure
Distributing arteries =
Muscular arteries
Effect of reduced albumin in plasma?
Decreasing colloid osmotic pressure and edema will occur
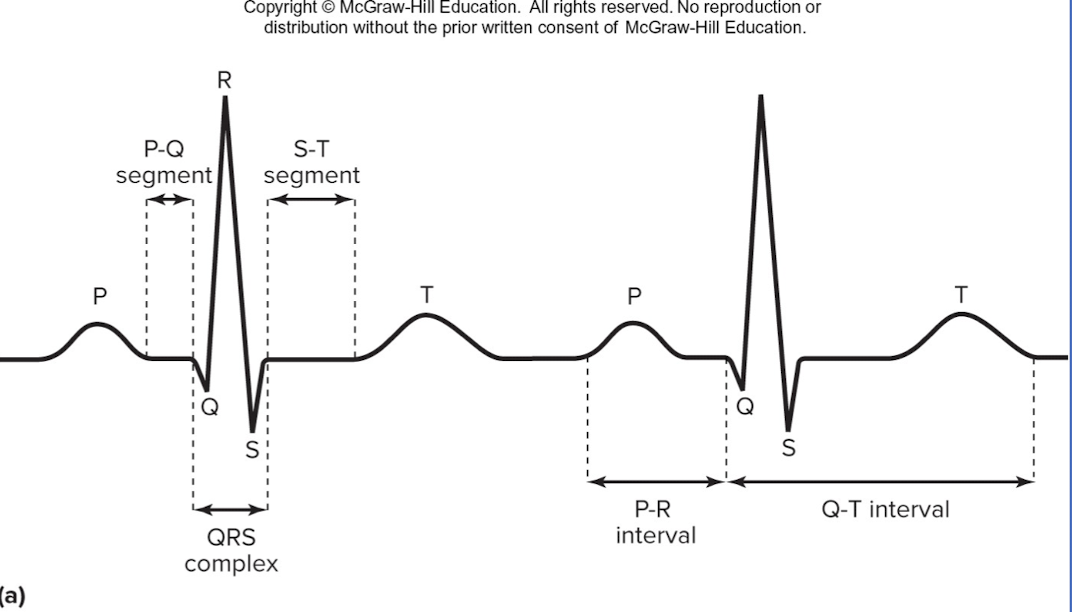
P wave
depolarization of SA node and atria
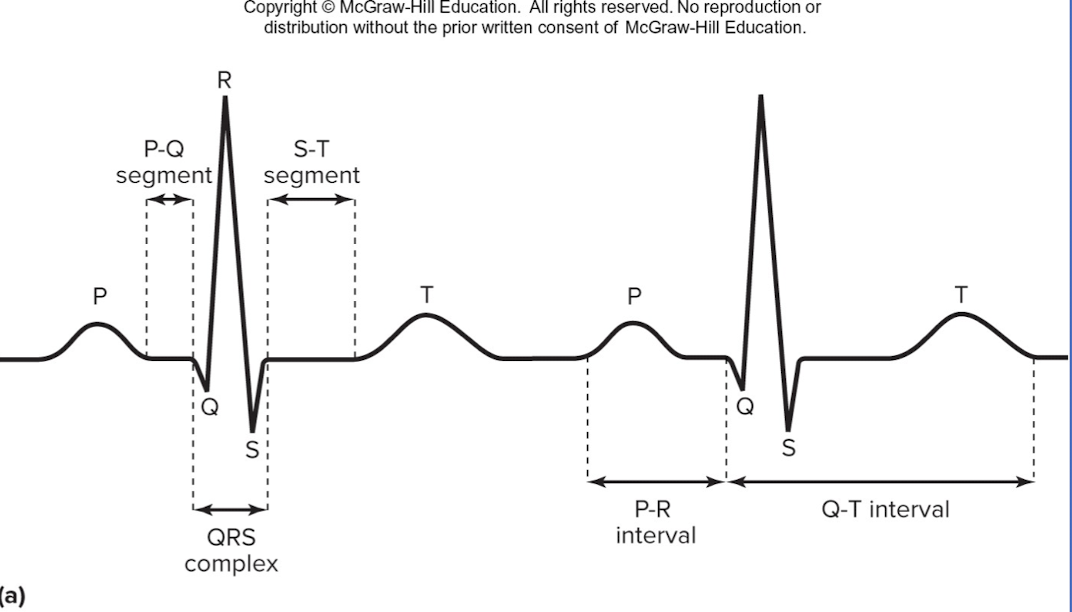
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
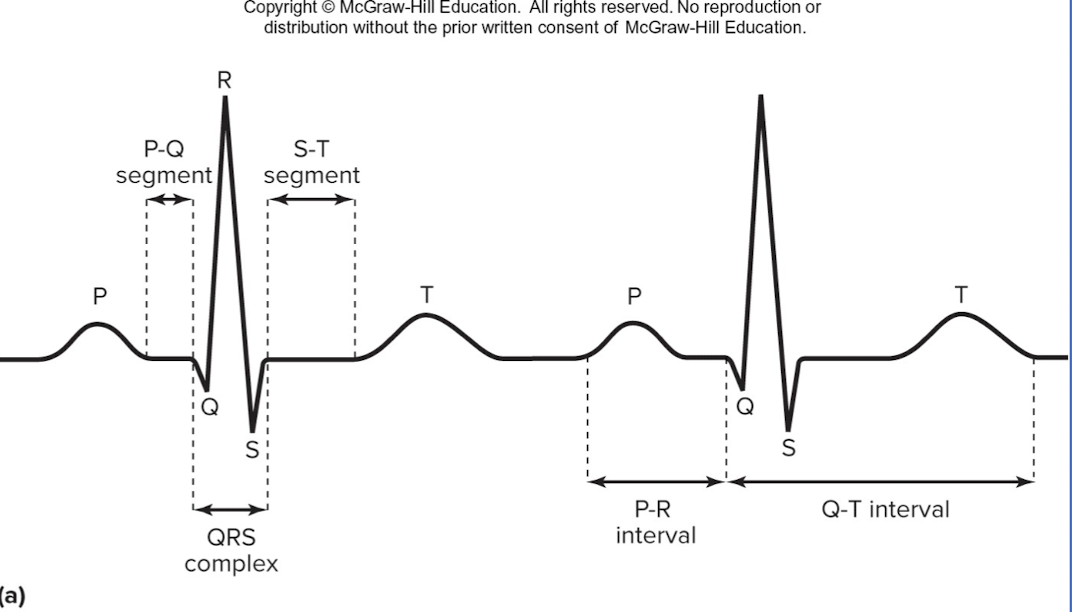
T wave
ventricular repolarization
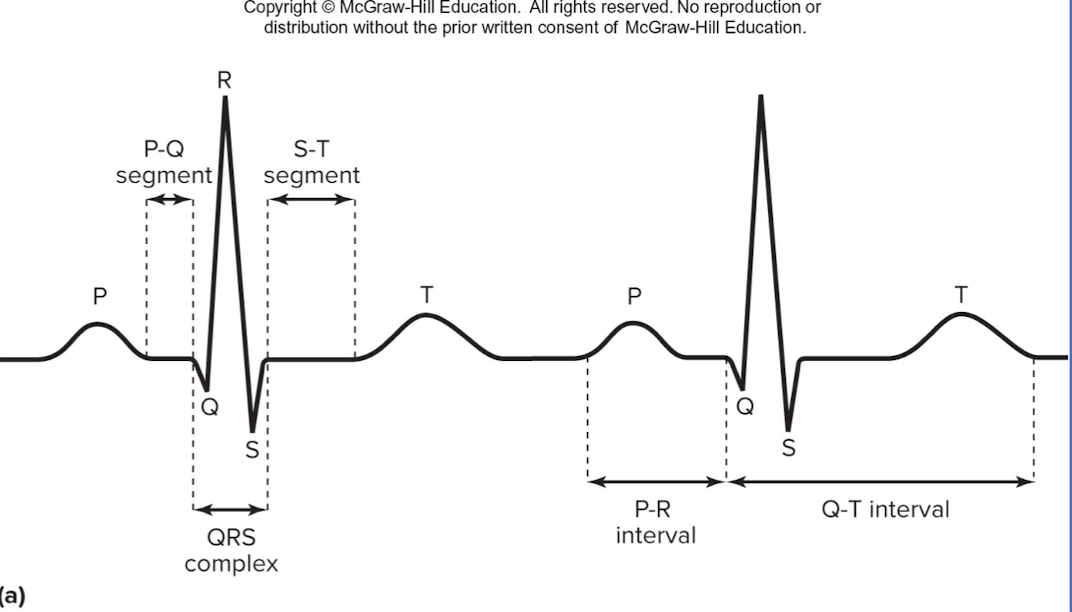
P-R interval:
beginning of atrial excitation to beginning of ventricular excitation
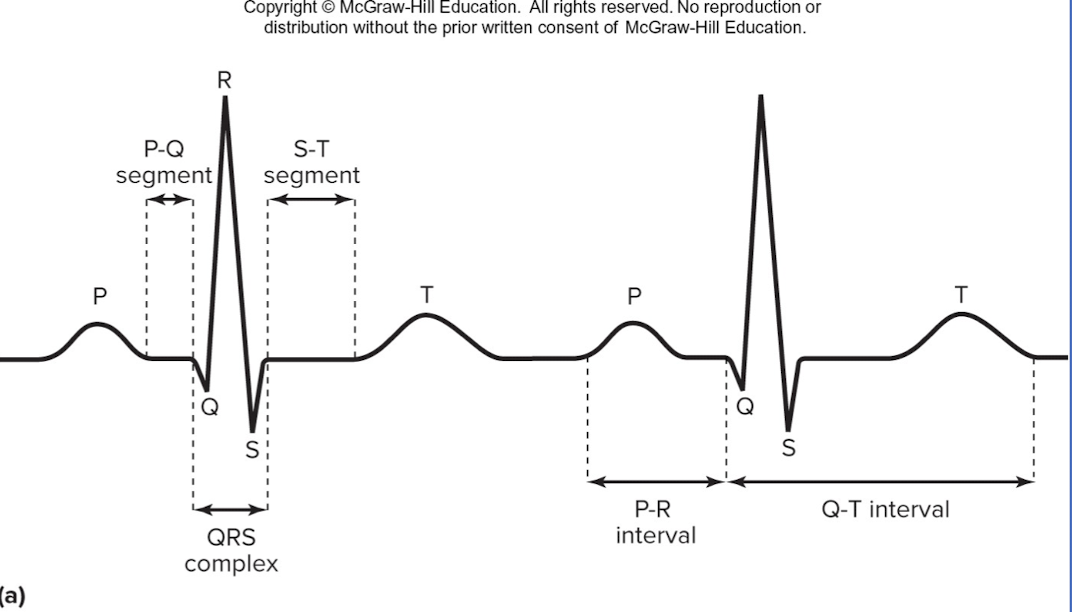
Q-T interval
beginning of ventricular depolarization through ventricular repolarization