Human Anatomy & Physiology Exam #4
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
what does the central nervous system consist of?
brain and spinal cord
is white matter myelinated or unmyelinated?
myelinated
does gray or white matter have faster communication?
white matter
do tracts belong to white or gray matter?
white matter
is gray matter myelinated or unmyelinated?
unmyelinated
does gray or white matter have slower communication?
gray matter
nuclei belongs to gray or white matter?
gray matter
what protects the brain?
bones, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood-brain barrier
what bones protect the brain?
cranial and facial bones
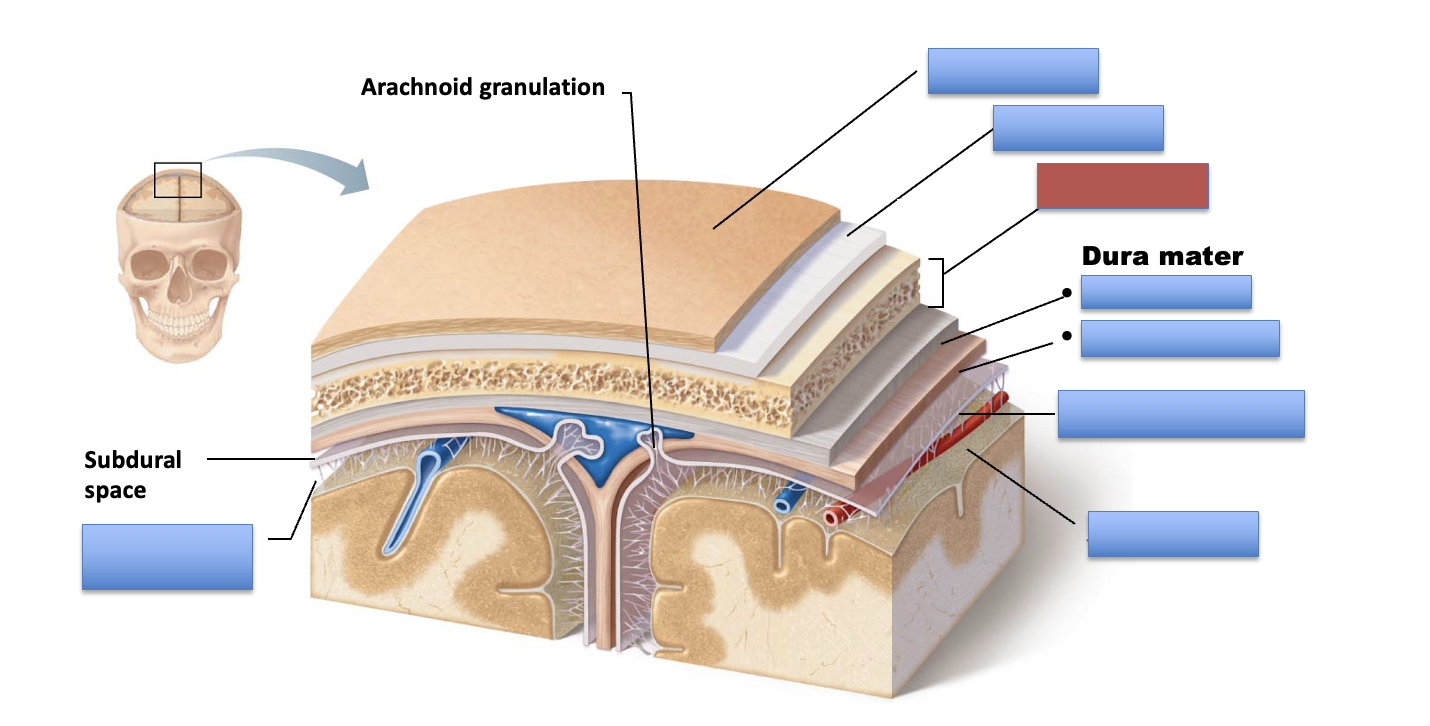
what are the parts of the meninges that protects the brain?
the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
the dura mater is the ____ _____ layer of the meninges?
outer most
what are the layers of the dura mater?
periosteal and meningeal layer
what layer of the dura mater is the most superficial?
periosteal layer
what layer of the dura mater is the most deep?
meningeal layer
where is the arachnoid mater located?
deep to the dura mater
what is the subarachnoid space?
the area between the arachnoid mater and pia mater
what is the role of subarachnoid space in protecting the brain?
it contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
where is the pia mater located?
deep to the arachnoid mater
what are the functions of the cerebrospinal fluid?
shock absorber, optimal chemical environment for neurons, and circulation
what is the function shock absorber in the cerebrospinal fluid mean?
acts as a cushion for the brain to float in cranial cavity and prevents crashing against bones
what is the function optimal chemical environment for neurons in the cerebrospinal fluid mean?
selective entry of substances from blood into cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
what is the function circulation in the cerebrospinal fluid mean?
nutrients are filtered from blood, waste removal, and circulation within cavities and subarachnoid space occurs
what does the blood-brain barrier consist of?
capillaries, thick basement membrane, and astrocytes
what are the substances that can easily pass through the blood-brain barrier?
oxygen, water, carbon dioxide, and nonpolar and lipid based molecules (alcohol)
what is the protective safeguard of the blood-brain barrier?
separates CSF and brain ECF from chemicals and diseases causing organisms
what substance is prevented from crossing the blood-brain barrier?
most large polar molecules
what is meningitis?
a potentially life threatening infection of meninges in the subarachnoid space
inflammation causes what signs of meningitis?
headache, lethargy, stiff neck, and fever
how can you get diagnosed with meningitis?
examination of CSF for infectious agents and white blood cells
what are the most common causes of meningitis?
bacteria and viruses
if meningitis is caused by viral its?
generally mild and resolves in 1-2 weeks
if meningitis is caused by bacteria is can?
rapidly progress to brain involvement and death
aggressive antibiotic treatment is necessary is meningitis is caused by?
bacteria
most common forms of meningitis caused by bacteria are preventable with?
vaccines
where in the brain is cerebrospinal fluid located?
ventricles and subarachnoid space
where in the spinal cord is cerebrospinal fluid located?
central canal and subarachnoid space
what are capillaries?
tight junctions with no gaps in lining
what is hydrocephalus?
an imbalanced amount of CSF made and filtered out into the bloodstream
buildup of CSF puts pressure on the?
brain
what is the treatment for hydrocephalus?
shunt excess fluid from brain to abdomen
the brain has a ____ blood flow?
high
what is required in the blood flow of the brain?
oxygen and glucose
how does the brain use oxygen and glucose?
to make ATP via oxidative phosphorylation
what happens if theres no glucose in the brain?
mental confusion, dizziness, convulsions, and loss of consciousness
what happens if theres no oxygen in the brain?
you briefly lose consciousness
if the brain does not have oxygen for more than four minutes, what happens?
permanent cell damage
the brain has billions of?
neurons and neuroglia
what are the different parts of the brain?
cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, brainstem, ——————————————
what happens in the cerebrum?
conscious thought processes and origin of intellectual functions
what percent of the brains mass is the cerebrum?
83%
the cerebrum has __ hemispheres?
2
the cerebrum has __ lobes?
5
what are the layers of the cerebrum?
outer gray, middle white matter, and inner gray
the outer gray layer is?
the cerebral cortex
the middle white matter is?
the myelinated axon tracts
the inner gray layer is?
the basal nuclei
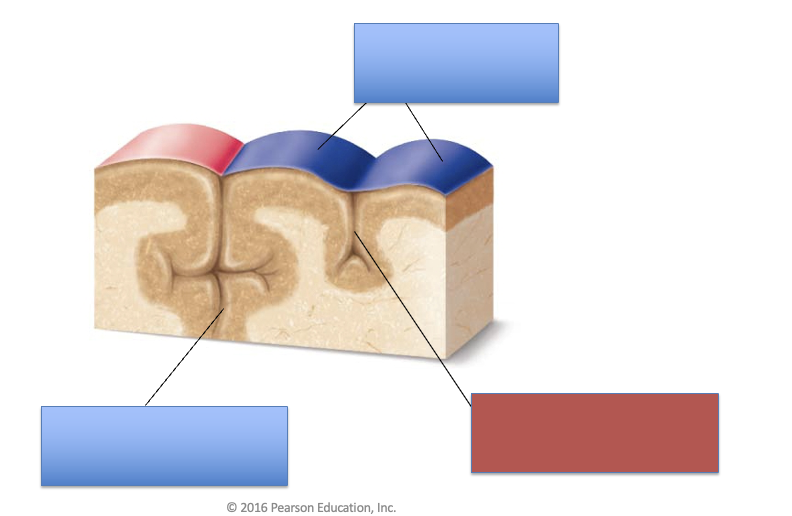
what is the gyrus?
the elevation of the cerebrum
what is the sulcus?
the grooves of the cerebrum
what is the fissure?
the deep grooves of the cerebrum
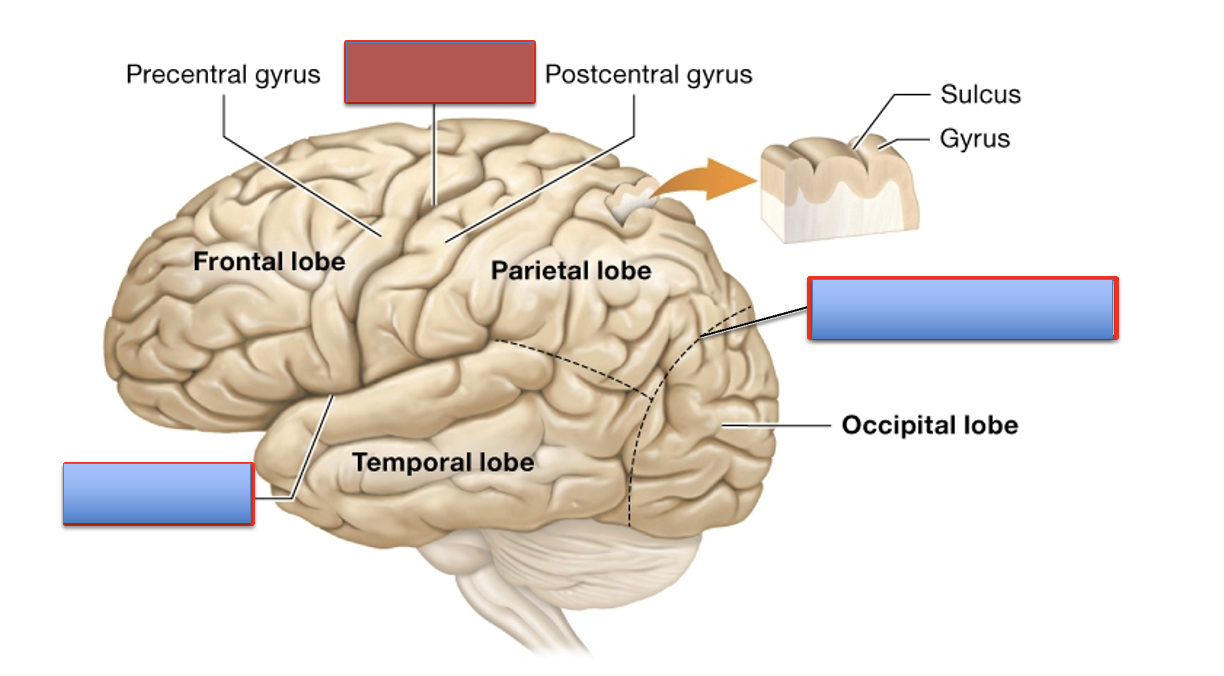
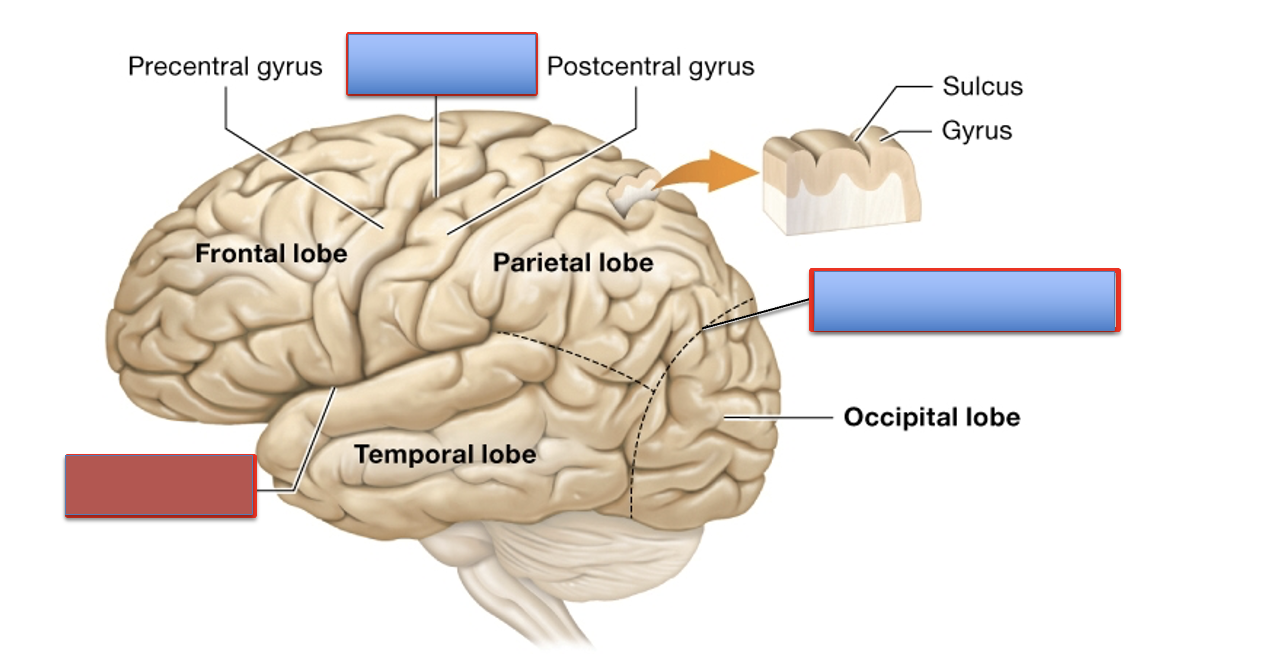
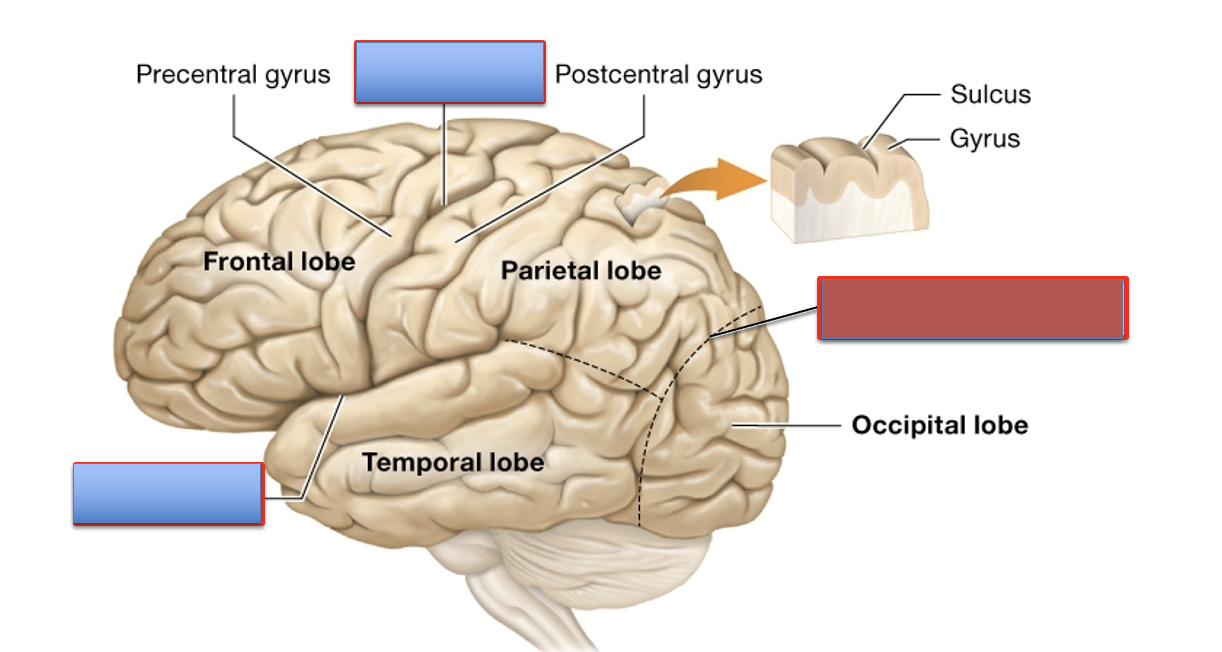
what is the central sulcus?
it separates the frontal and parietal lobe
what is the lateral fissure?
it separates the frontal and temporal bone
what is the parieto-occipital sulcus?
it separates the parietal and occipital lobe
what are the lobes of the cerebrum?
parietal, frontal, temporal, occipital, and insula
where is the insula located?
its buried deep under the temporal lobe
what is the function of the frontal lobe?
motor control
what is the function of the parietal lobe?
sensory processes
ventricles contain?
choroid plexuses
what is the choroid plexuses?
clusters of capillaries surrounded by ependymal cells
what does the choroid plexuses produce?
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
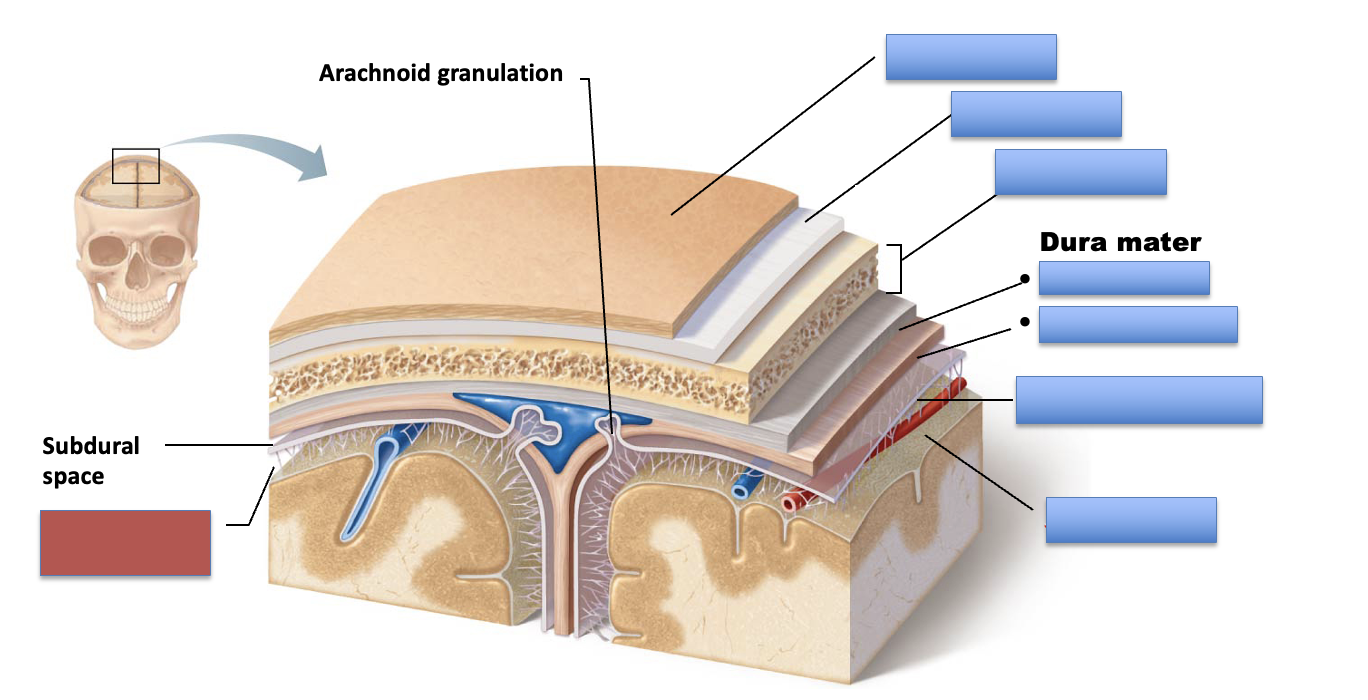
what is the red area?
subarachnoid space
what is the red area?
skin of scalp
what is the red area?
periosteum
what is the red area?
bone of skull
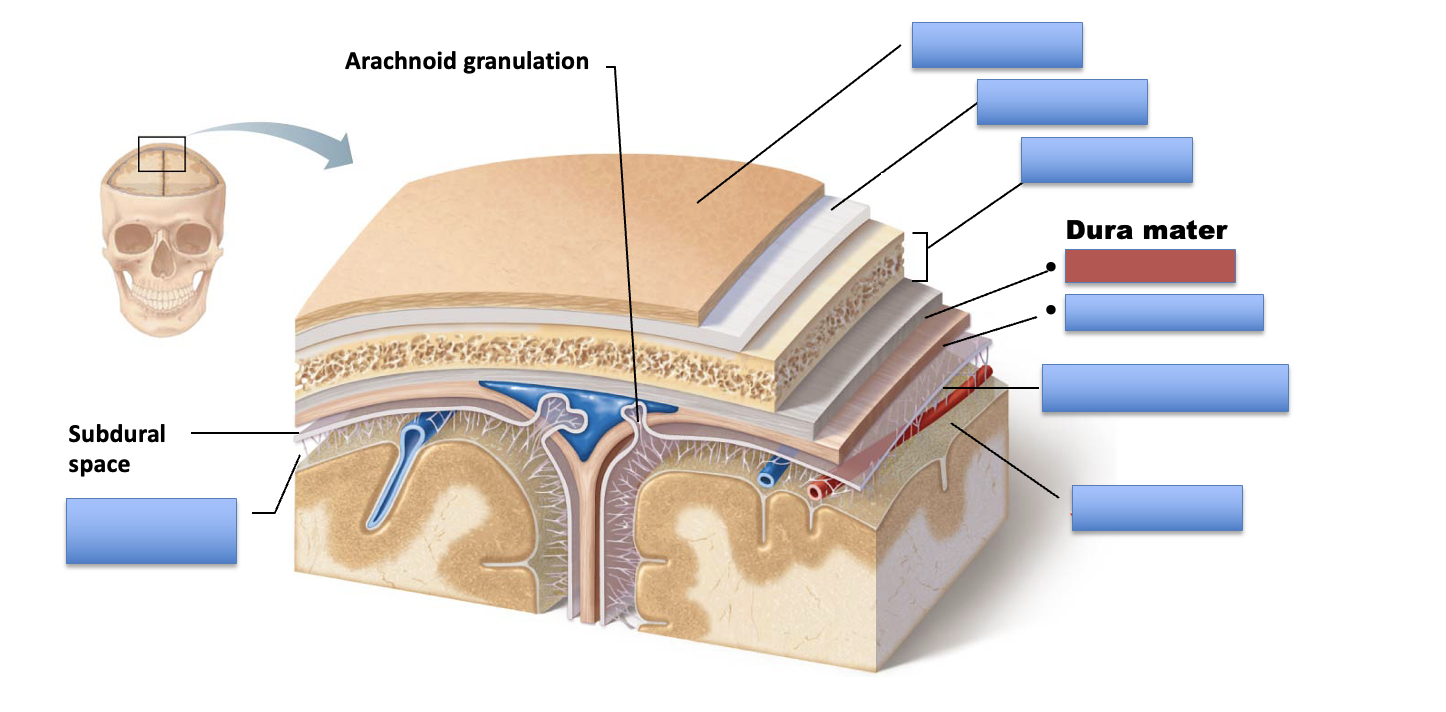
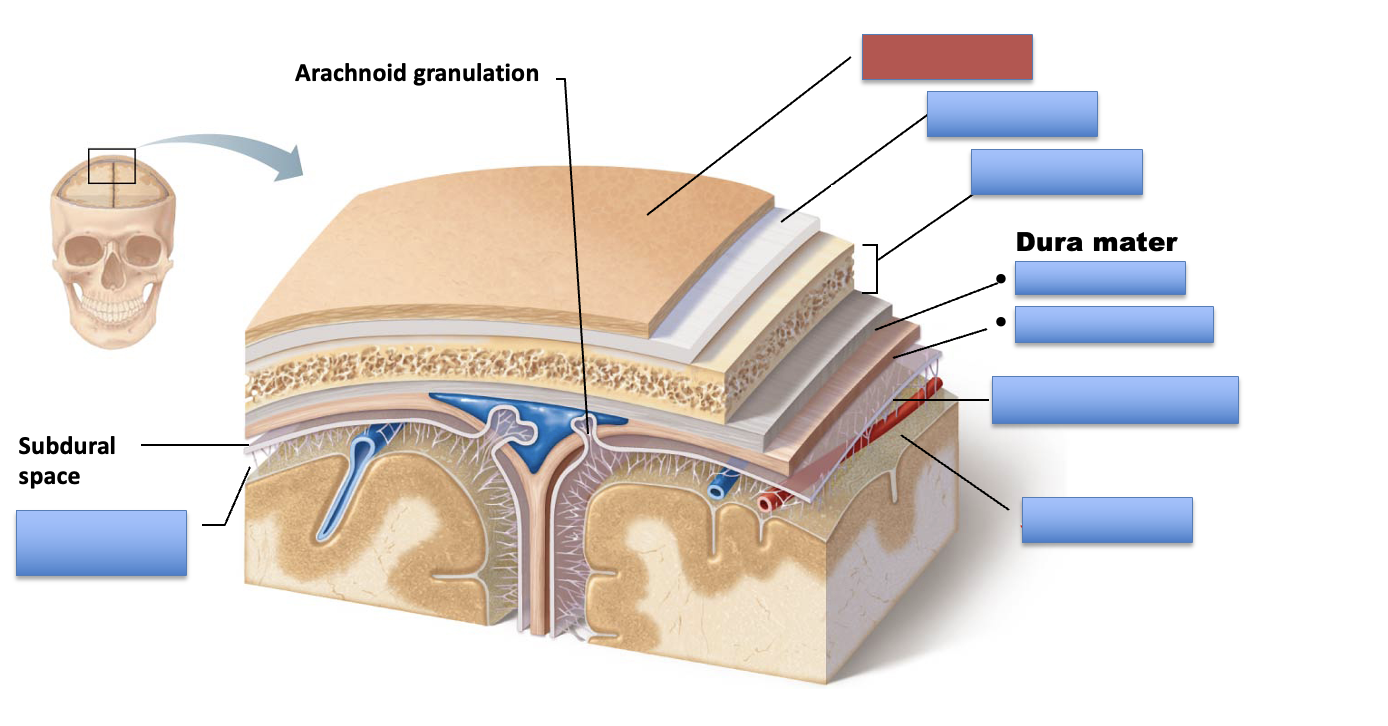
what is the red area?
periosteal layer
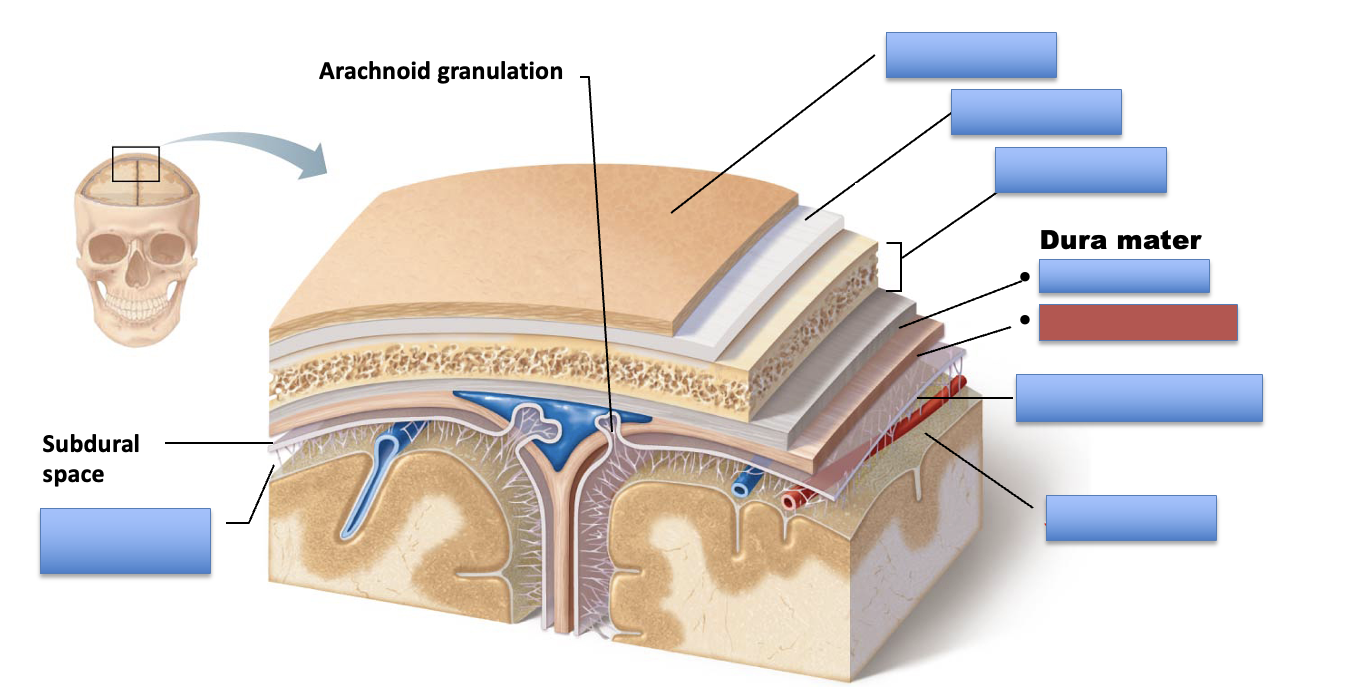
what is the red area?
meningeal layer
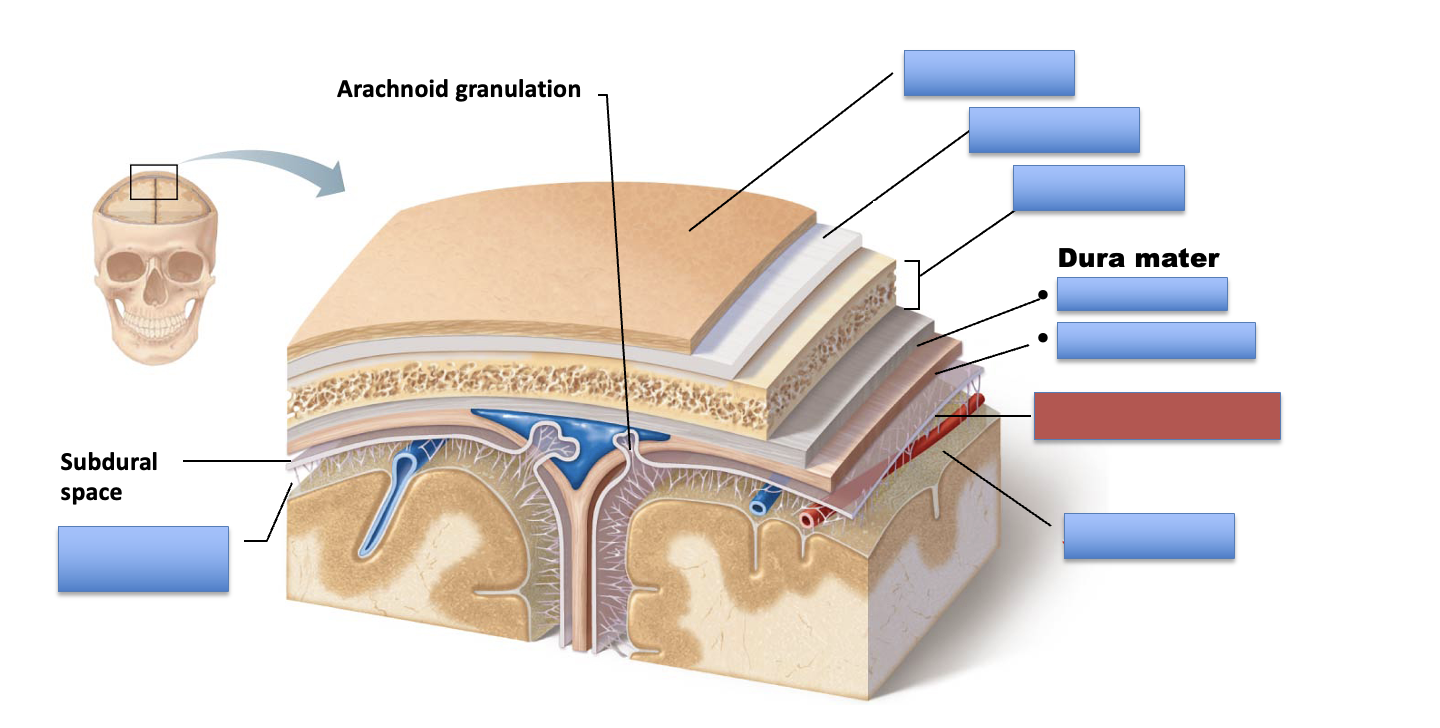
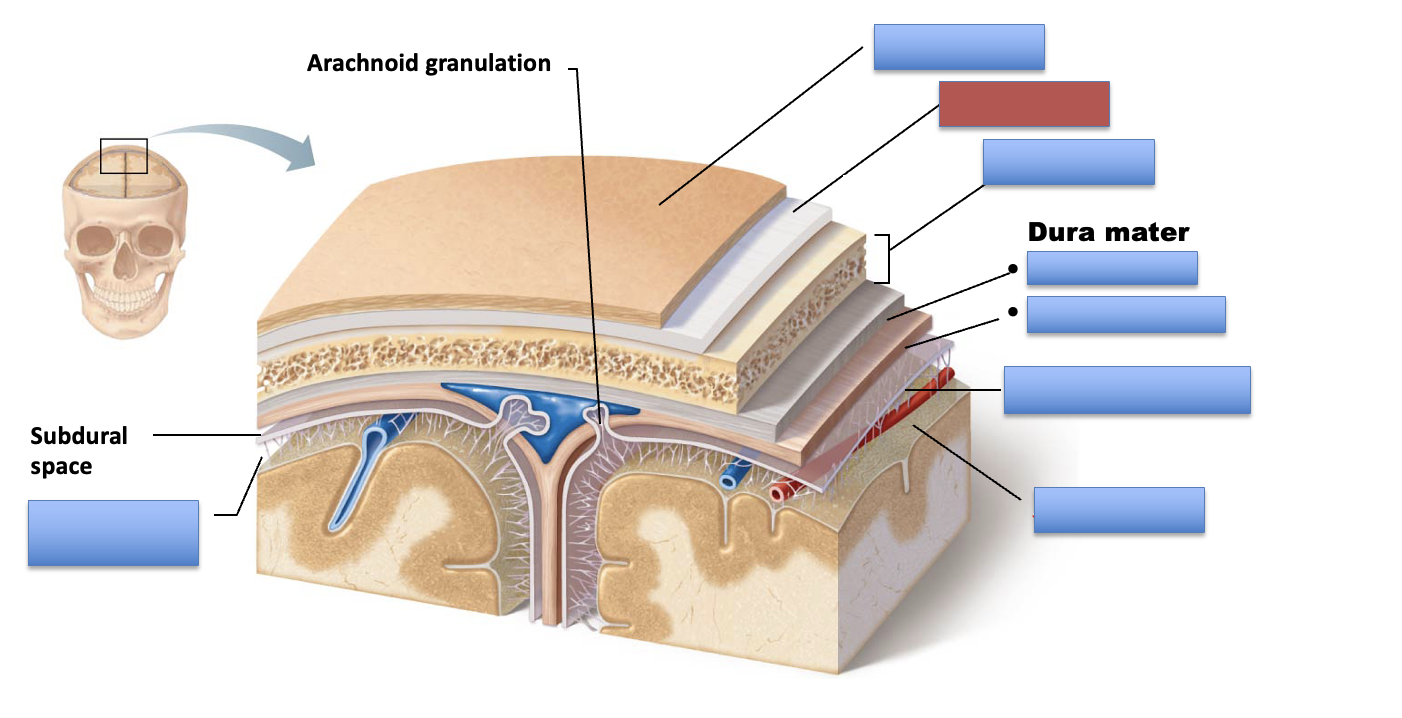
what is the red area?
arachnoid mater
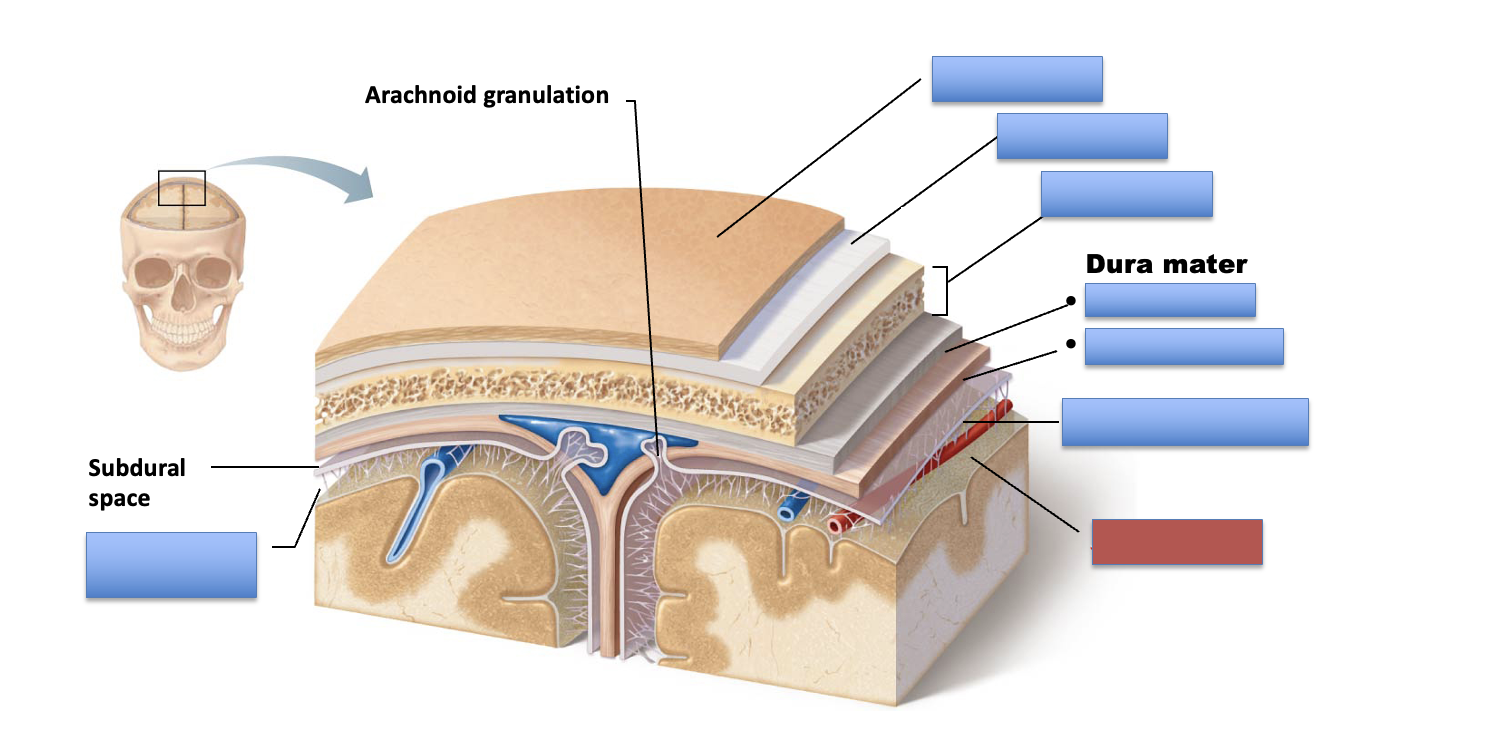
what is the red area?
pia mater
what is included in the brain stem?
midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
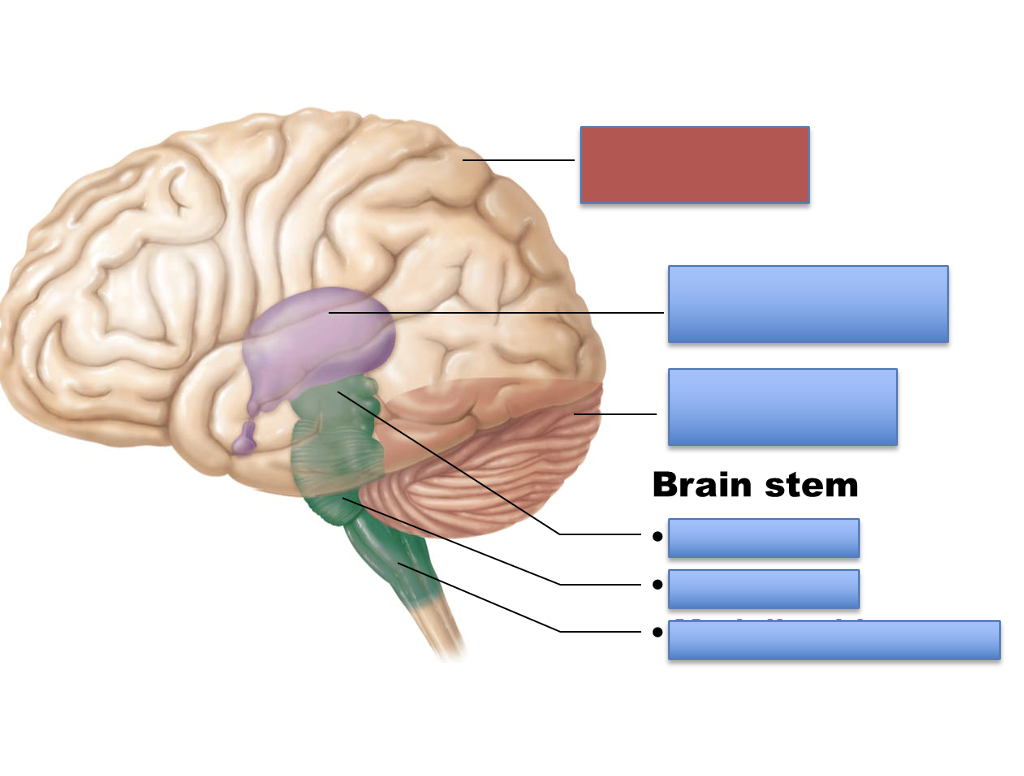
what is the red area?
cerebrum
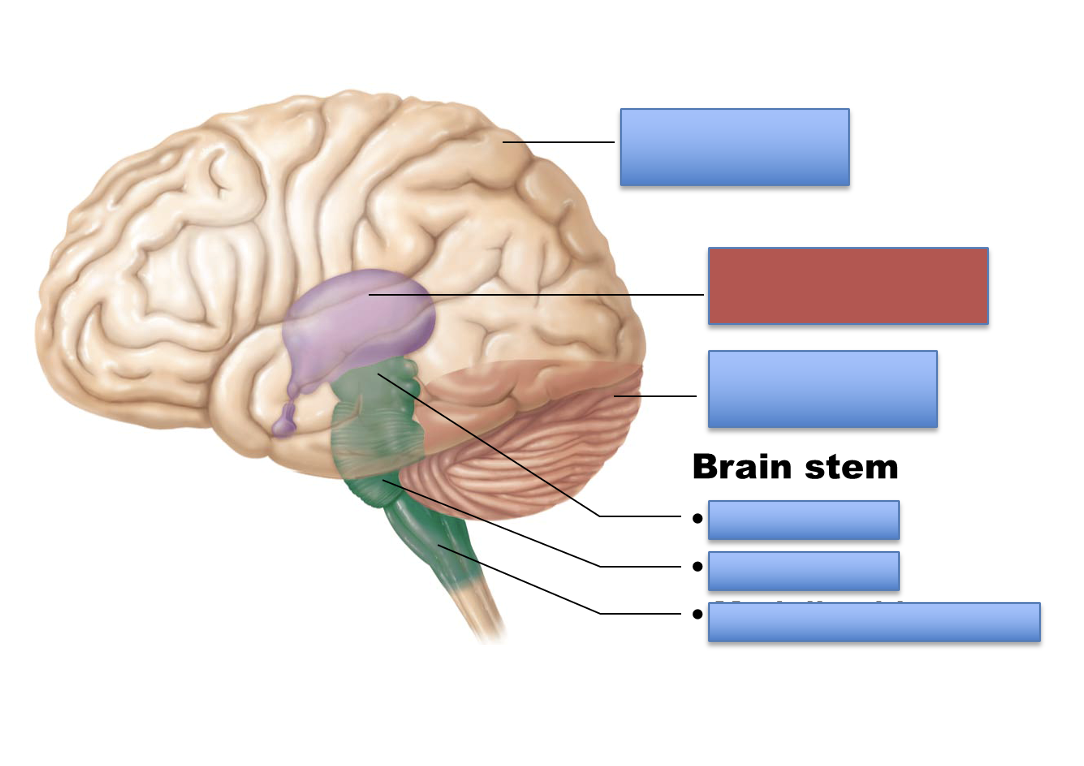
what is the red area?
diencephalon
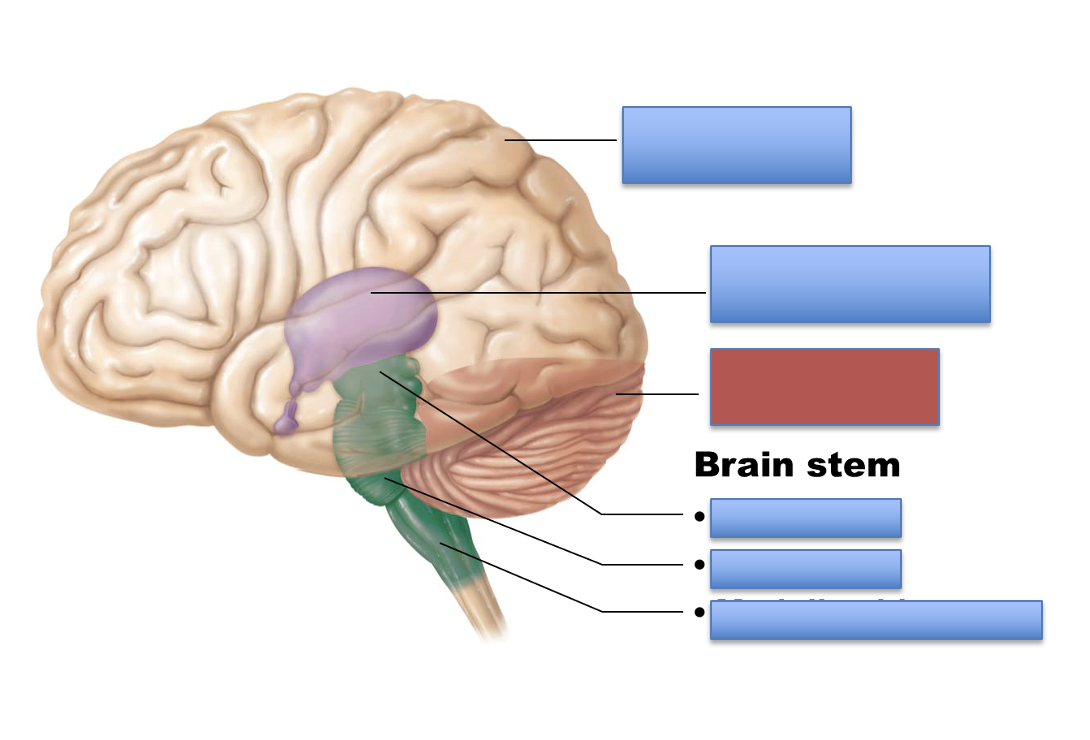
what is the red area?
cerebellum
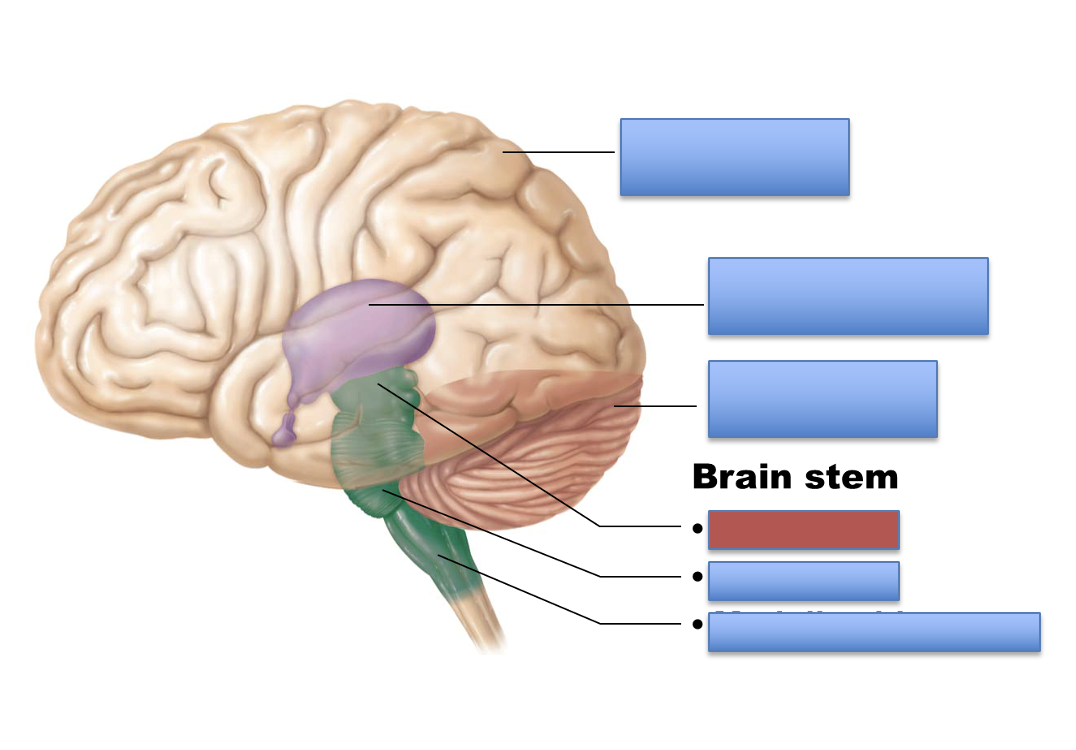
what is the red area?
midbrain
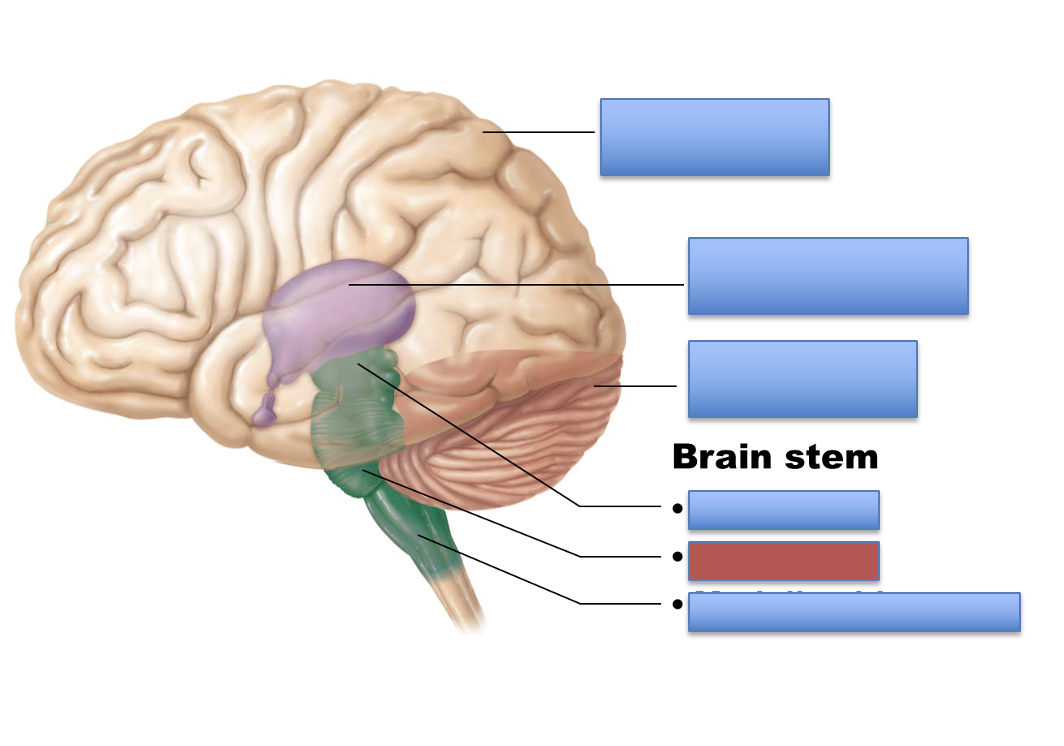
what is the red area?
pons
what is the red area?
medulla oblongata
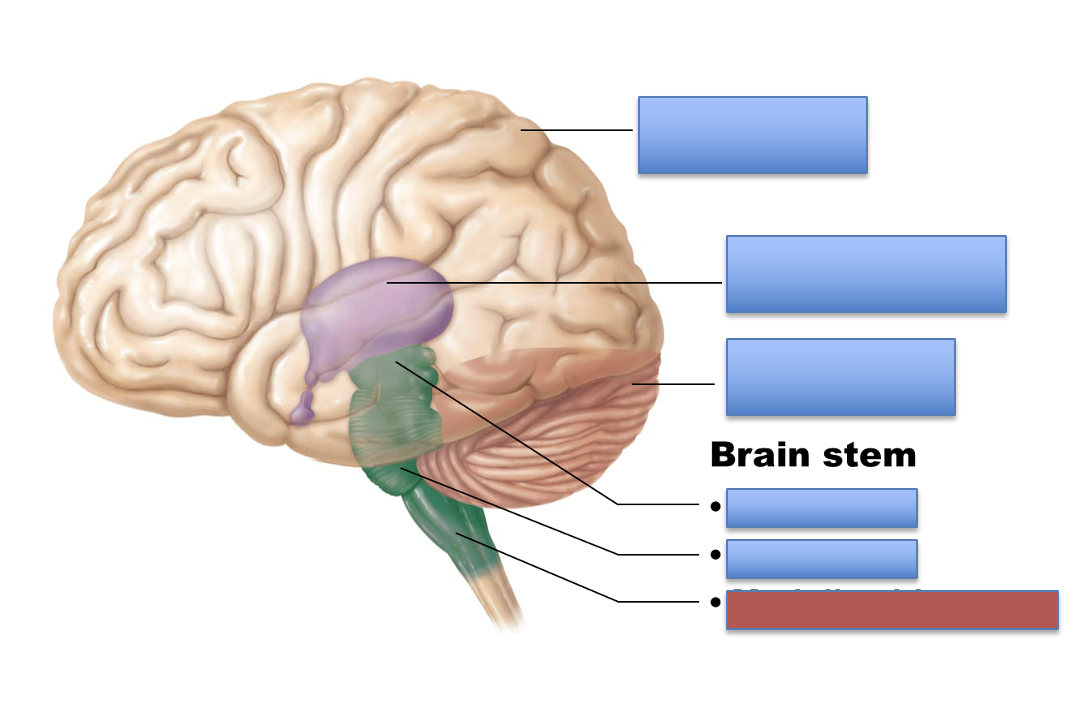
what is the red area?
gyrus
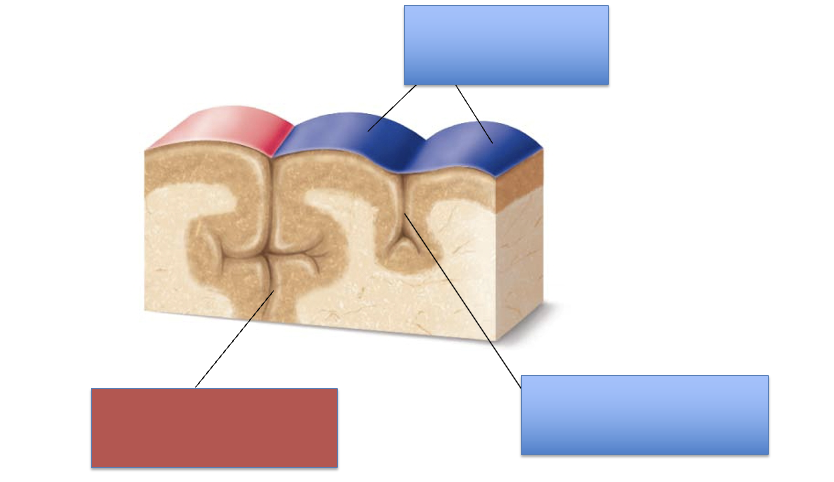
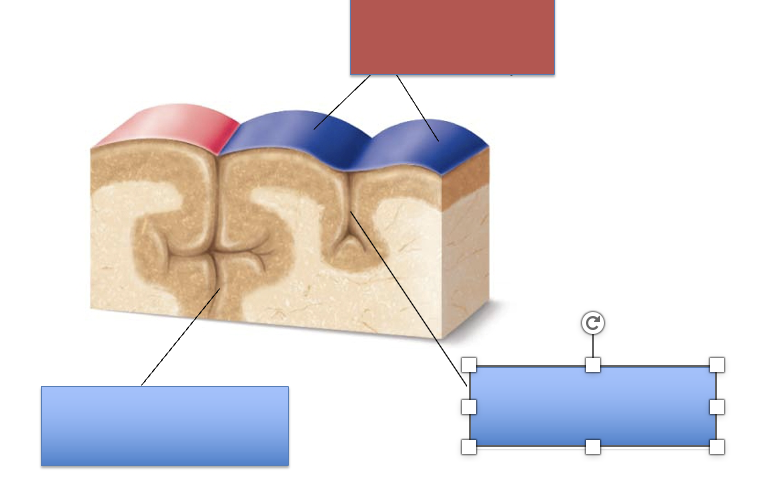
what is the red area?
fissure
what is the red area?
sulcus
what is the red area?
central sulcus
what is the red area?
lateral fissure
what is the red area?
parieto-occipital sulcus
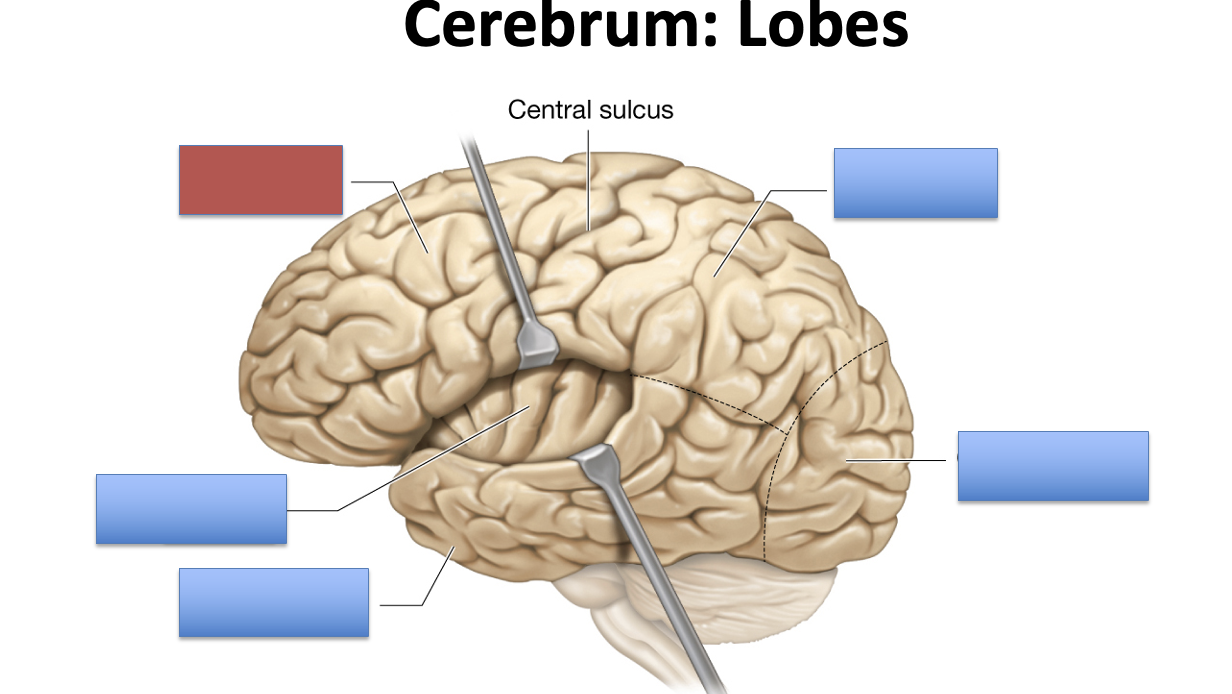
what is the red area?
frontal lobe
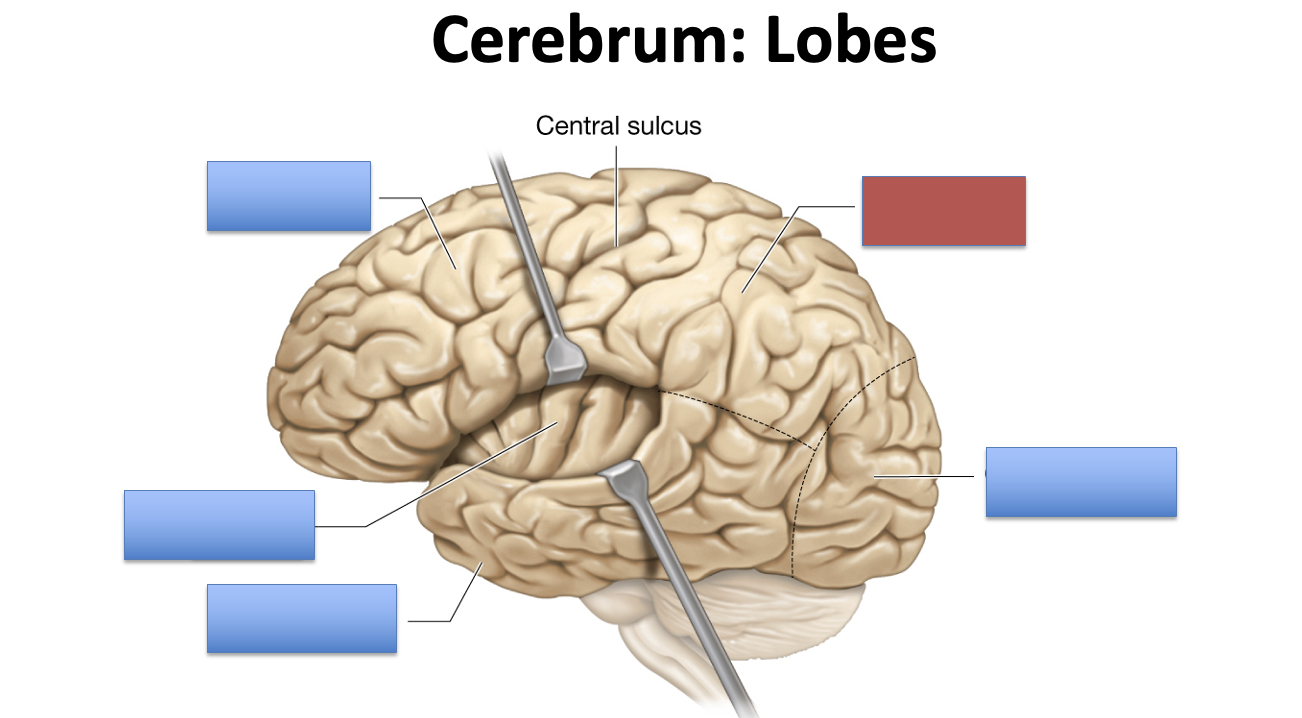
what is the red area?
parietal lobe
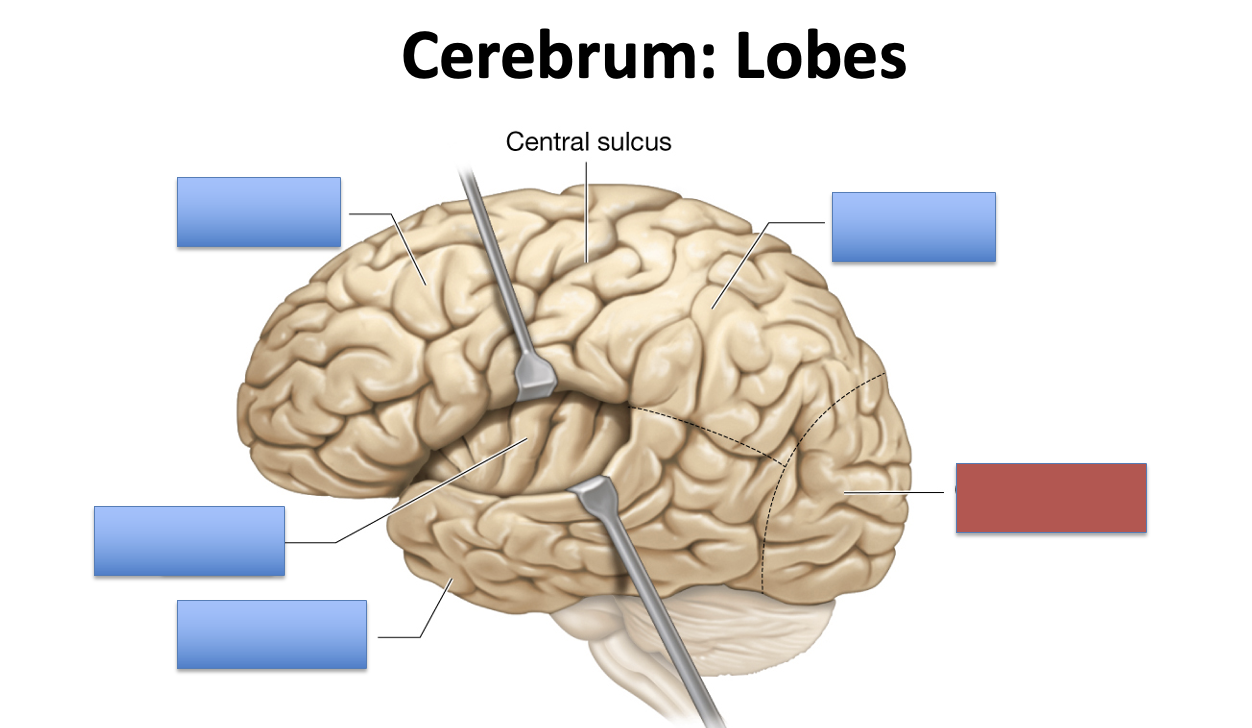
what is the red area?
occipital lobe
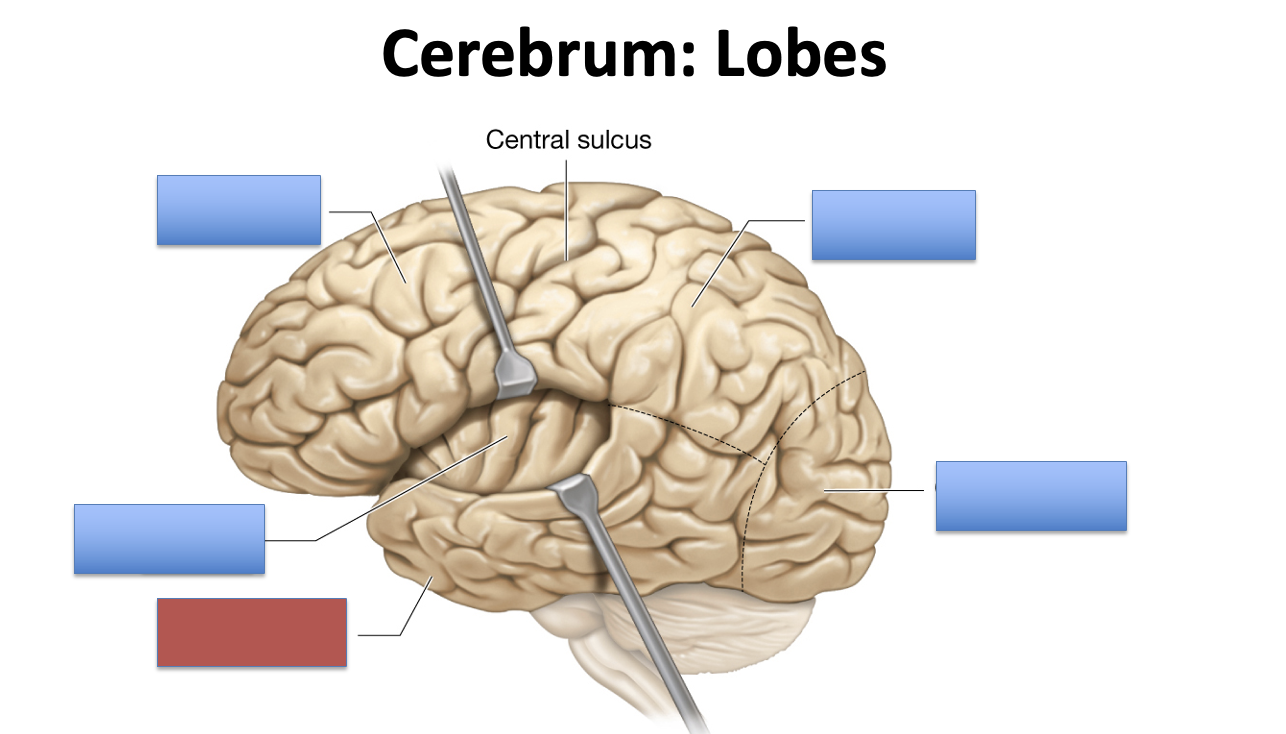
what is the red area?
temporal lobe
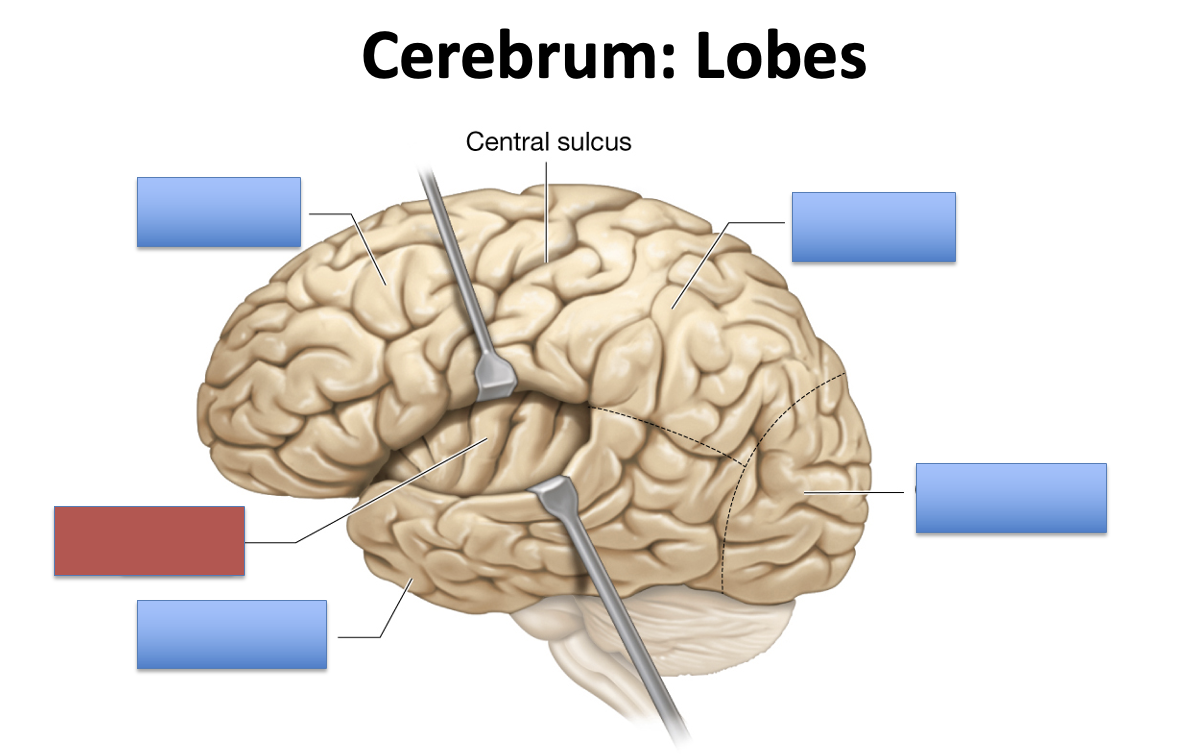
what is the red area?
insula
the cerebral cortex is part of which brain area?
the cerebrum
what is the cerebral cortex?
the outermost layer of gray matter
what are the functional areas in the cerebral cortex?
motor, sensory, and accessory
what is the motor functional area in the cerebral cortex?
it controls voluntary movement
what is the sensory functional area in the cerebral cortex?
it has conscious awareness of sensation