BIOL2141 Lab Practical 2
1/452
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
453 Terms
joint
Arthro (prefix)
with or together
Syn (prefix)
Sym (prefix)
variation of Syn prefix; a growing together
two or double
Di (prefix)
two or both
Amphi (prefix)
articulation
Arthroses (suffix)
cartilage
Chondro (suffix)
Articulations
hold bones together, allow body movements
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
3 structural types of joints
synarthroses, amphiarthroses, diarthroses
3 functional types of articulations
Synarthroses
immovable (axial skeleton-cartilaginous and fibrous joints)
Amphiarthroses
slightly movable (axial skeleton-cartilaginous)
Diarthroses
freely movable (limbs-synovial)
Suture
Fibrous joint-Joint held together with very short, interconnecting fibers, and bone edges interlock. Found only in the skull
Syndesmosis
Fibrous joint-Joint held together by a ligament. Fibrous tissue can vary in length, but is longer than in sutures
Gomphosis
fibrous joint-short periodontal ligament
Synchondroses
cartilaginous joint-bones united by hyaline cartilage
Symphyses
cartilaginous joint-bones united by fibrocartilage
Plane
synovial joint-allows sliding (nonaxial) movements in 1 or 2 planes (ex: intercarpal
Hinge
synovial joint-allows movement in 1 plane (uniaxial)-flexion and extension (ex: elbow)
Pivot
synovial joint-allows rotational movement in 1 axis (ex: radioulnar joint)
Condyloid
synovial joint-allows biaxial movements in 2 planes (ex: radiocarpal)
Saddle
synovial joint-allows movement in 2 planes (biaxial)
Ball and Socket
synovial joint-allows multiaxial movement (ex: shoulder and hip joints)
Flexion
Movement of synovial joint-decreases the angle of joint. Reduces distance between 2 bones
Extension
movement of synovial joint-increases angle of a joint. Increases distance between 2 bones
Hyperextension
movement of synovial joint-increasing angle greater than 180 degrees
Dorsiflexion
movement specific to foot-foot moves upwards
Plantar flexion
movement specific to foot-foot flexes downwards
Abduction
limb moves away from the midline
Adduction
limb moves towards midline
Rotation
move bone around its longitudinal axis
Circumduction
a combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
Supination
radius and ulna parallel
Pronation
radius moves across ulna
Inversion
turn foot medially
Eversion
Turn foot laterally
Protraction
anterior movement in a transverse plane
Retraction
posterior movement in a transverse plane
Elevation
moving a body part superiorly
Depression
moving a body part inferiorly
Opposition
touch thumb to finger tips-made possible by thumb saddle joint
cranial and facial bones
Articulating Bones of Skull
temporal bone of skull and mandible
articulating bones of temporomandibular joint
atlas (c1) and axis (c2)
articulating bones of atlantoaxial joint
between adjacent vertebral bodies
articulating bones of intervertebral joint
sternum and clavicle
articulating bones of sternoclavicular joint
acromion of scapula and clavicle
articulating bones of acromio-clavicular joint
scapula and humerus
articulating bones of shoulder (glenohumeral) joint
ulna (and radius) with humerus
articulating bones of elbow
radius and ulna
articulating bones of radioulnar (proximal) joint
adjacent carpals
articulating bones of intercarpal joint
carpal (trapezium) and metacarpal 1
articulating bones of carpometacarpal of digit 1 (thumb)
metacarpal and proximal phalanx
articulating bones of knuckle (metacarpophalangeal) joint
pubic bones
articulating bones of pubic symphysis
hip bone and femur
articulating bones of hip (coxal)
femur and tibia
articulating bones of knee (tibiofemoral) joint
tibia and fibula (distally)
articulating bones of tibiofibular joint
Knee joint
largest and most complex joint in the body-only
Shoulder joint
most freely moving joint in the body
Articular Capsule
fibrous capsule + synovial membrane
articular cartilage
All synovial joints have ___________ _________ covering the bone surface
reinforcing ligaments
All synovial joints have _______ _________
fibrocartilage
Synovial joints may have _____________ pads within a capsule
Synovial Joint
freely movable joint with a cavity containing fluid
Cartilaginous Joints
slightly movable joints with no joint cavity
synchondrosis
name the specific type of cartilaginous joint
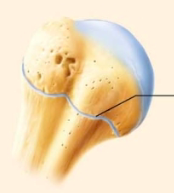
symphysis
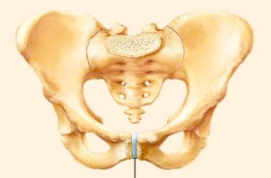
name the specific type of cartilaginous joint
Plane joint
name the specific type of synovial joint

Hinge joint
name the specific type of synovial joint

Pivot joint
name the specific type of synovial joint
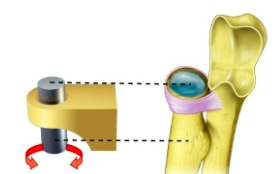
condyloid joint
name the specific type of synovial joint

saddle joint
name the specific type of synovial joint
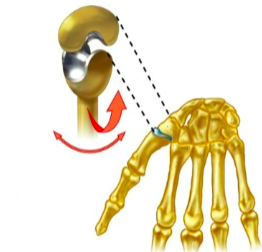
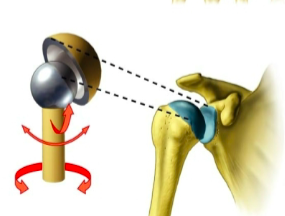
Ball and socket joint
name the specific type of synovial joint
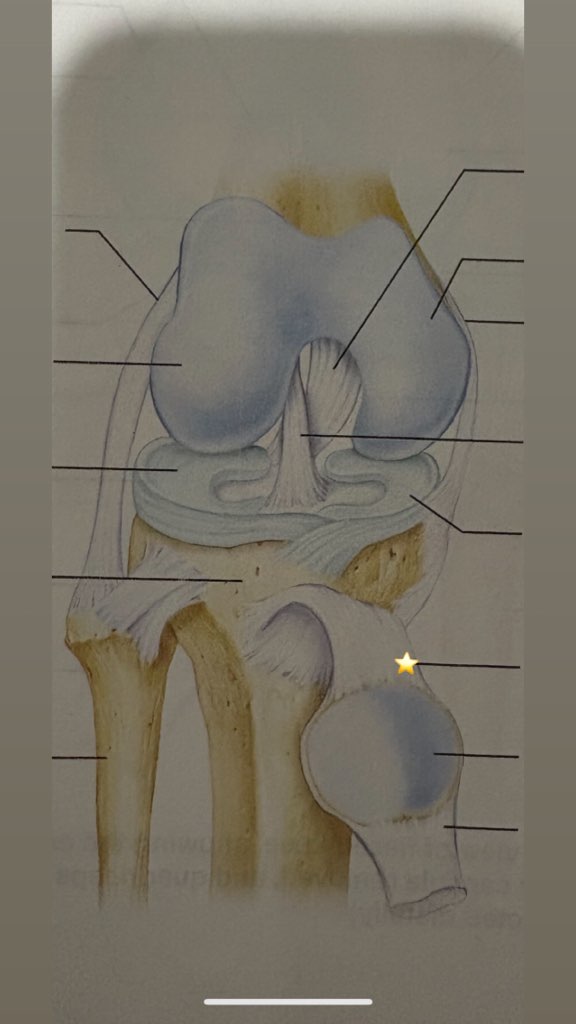
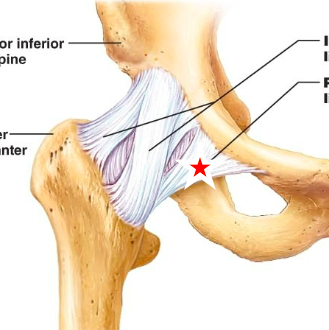
Iliofemoral ligament
name the starred ligament
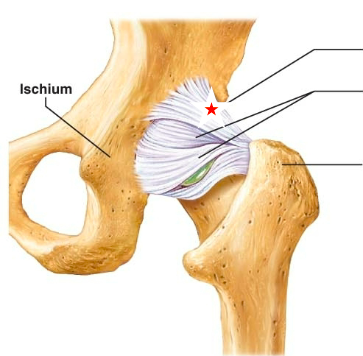
Ischiofemoral ligament
name the starred ligament
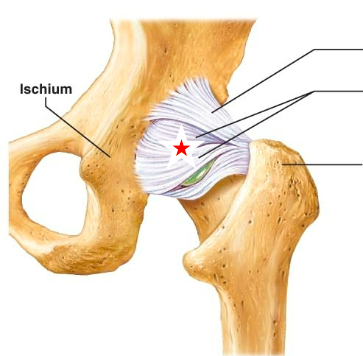
Pubofemoral ligament
name the starred ligament
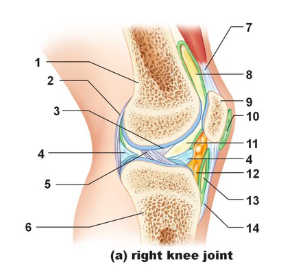
Tendon of quadriceps femoris
Name the structure indicated by #7
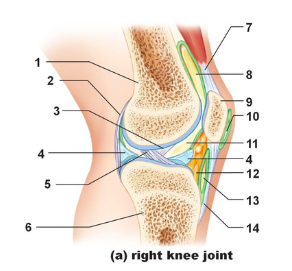
suprapatellar bursa
Name the structure indicated by #8

patella
name the structure indicated by #9
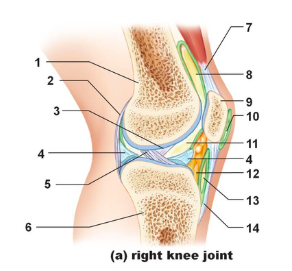
subcutaneous prepatellar bursa
Name the structure indicated by #10
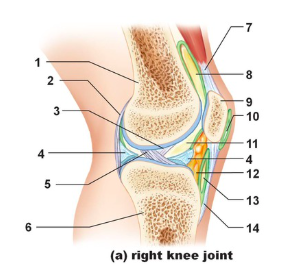
synovial cavity
Name the structure indicated by #11
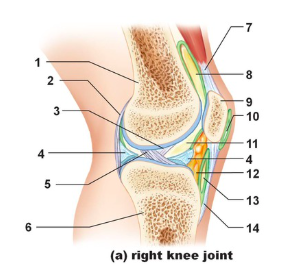
Lateral meniscus
Name the structure indicated by #4
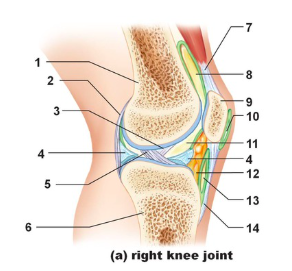
Deep infrapatellar bursa
Name the structure indicated by #13
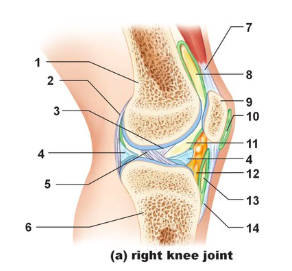
Infrapatellar fat pad
Name the structure indicated by #12
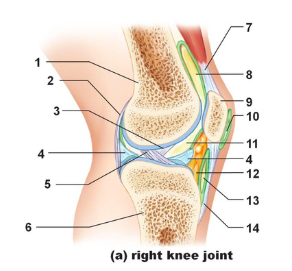
Patellar ligament
Name the structure indicated by #14
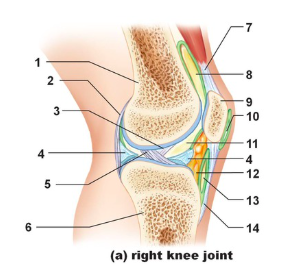
Tibia
Name the structure indicated by #6
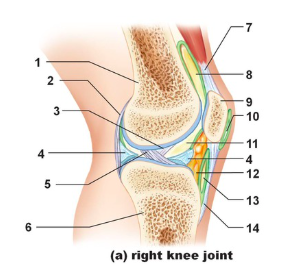
Anterior cruciate ligament
Name the structure indicated by #5
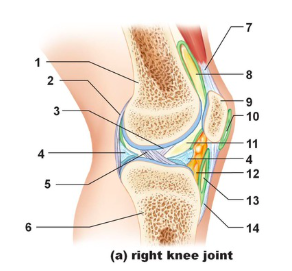
Posterior cruciate ligament
Name the structure indicated by #3
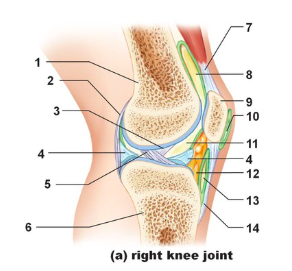
Articular capsule
Name the structure indicated by #2
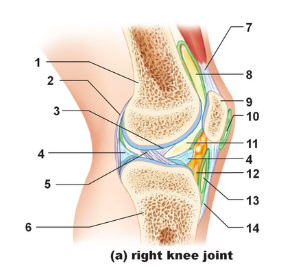
Femur
Name the structure indicated by #1
Tibial collateral ligament
name the starred structure
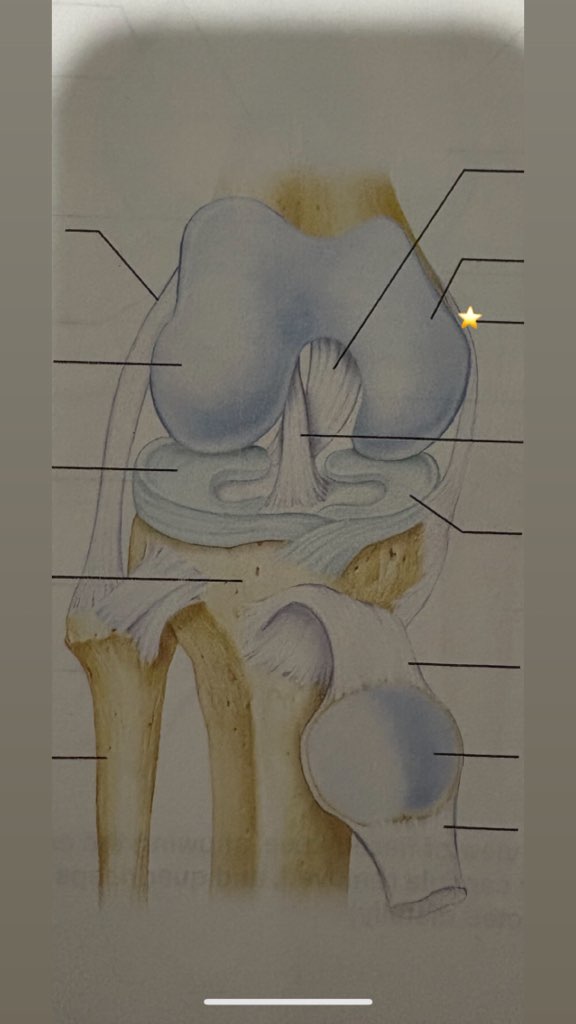
Fibular collateral ligament
Name the starred structure
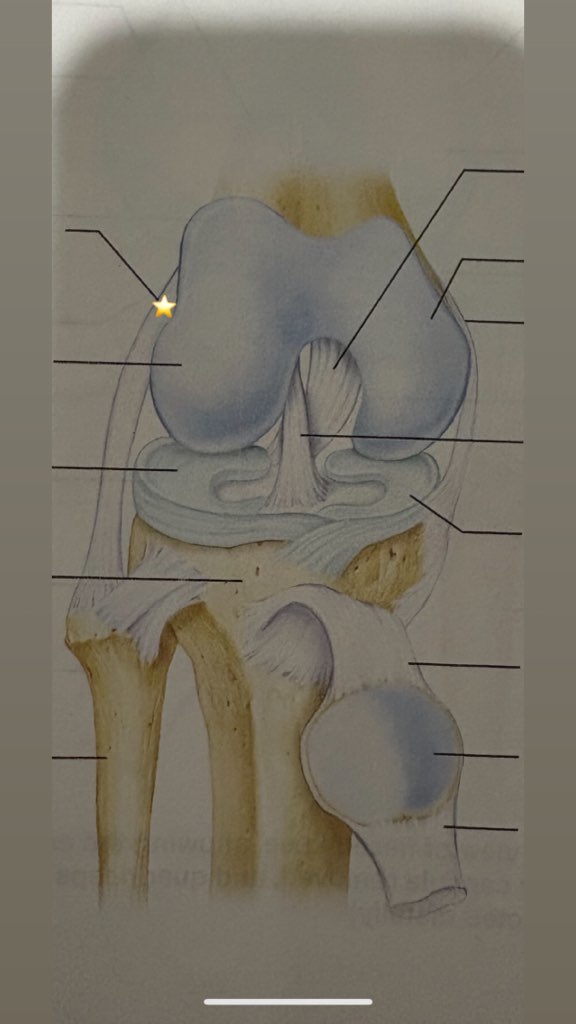
Lateral condyle of femur
Name the starred structure
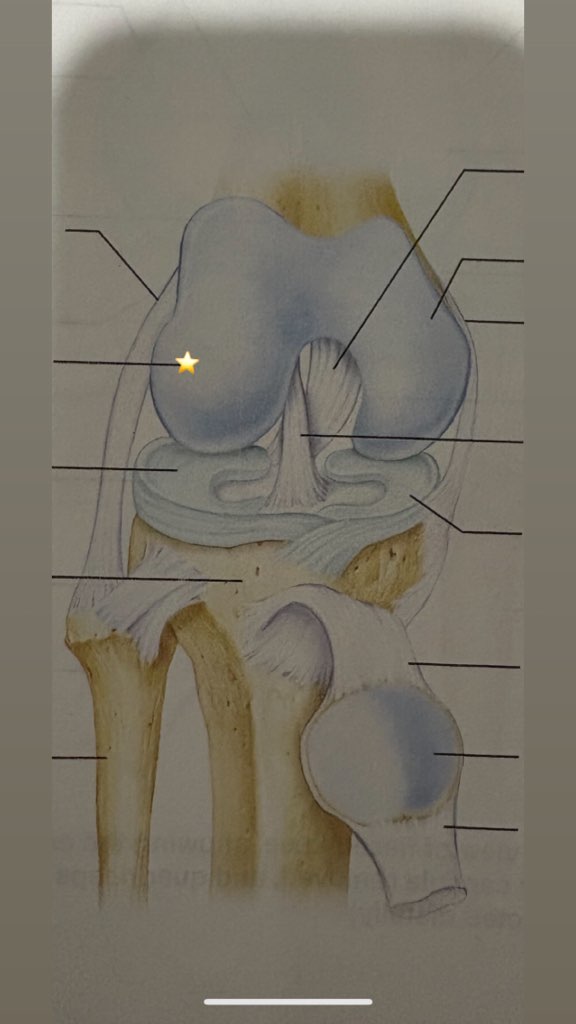
Lateral meniscus
name the starred structure
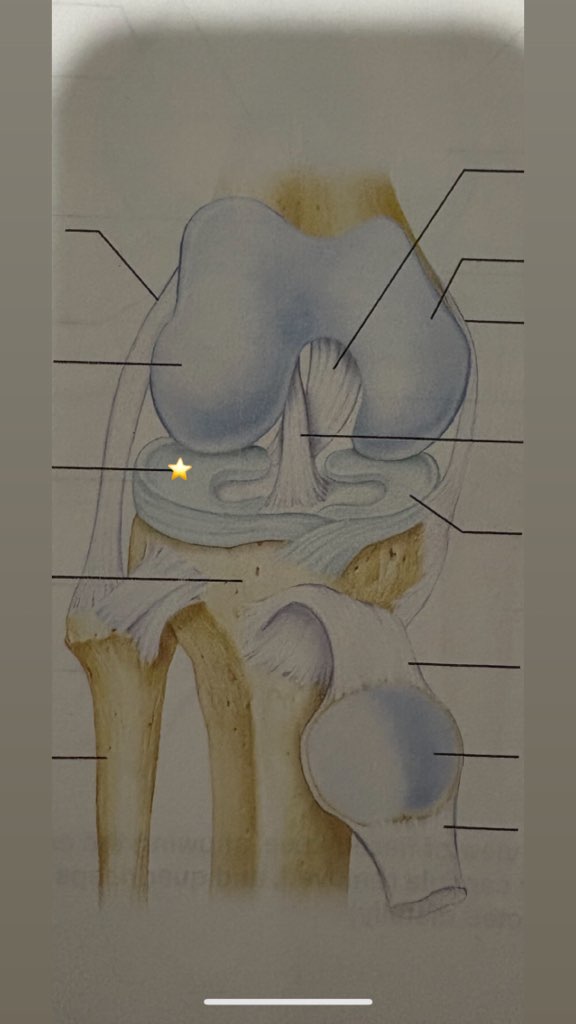
Tibia
Name the starred structure

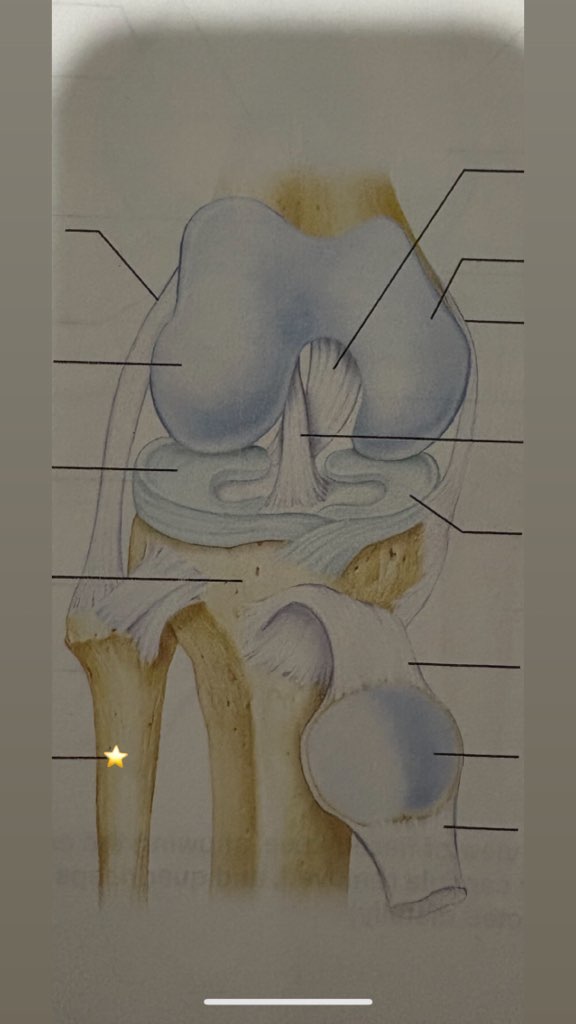
fibula
name the starred structure
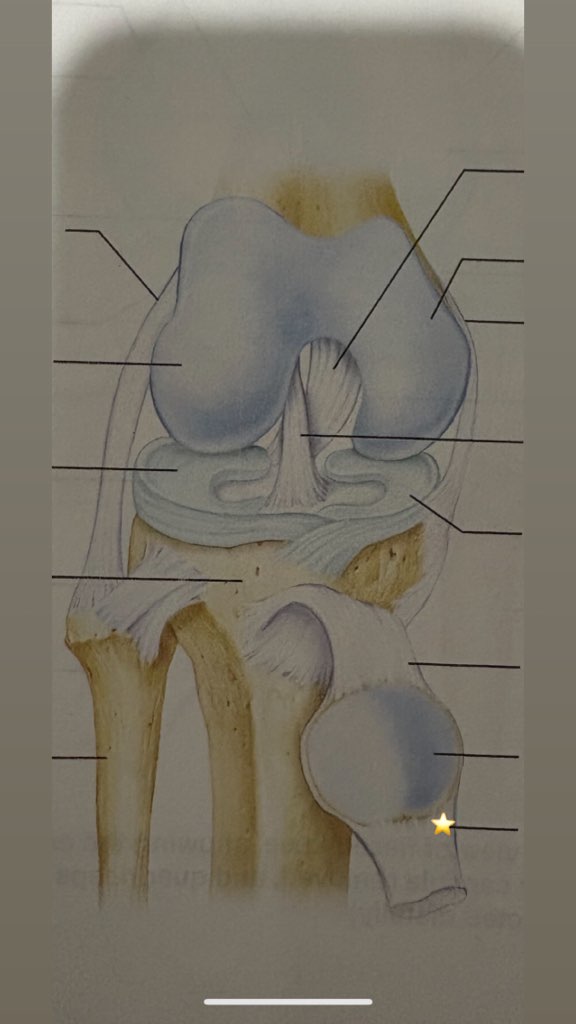
quadriceps tendon
name the starred structure
patella
name the starred structure
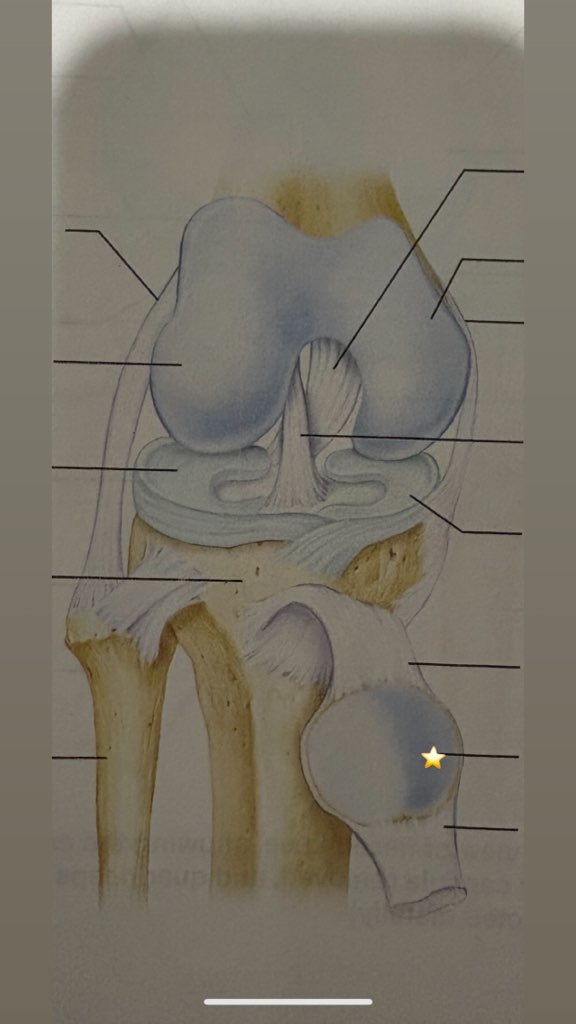
patellar ligament
name the starred structure